40e5a40ca5d453803777a2f1348c21f6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Chapter 4 Identifying Market Segments and Selecting Target Markets
Chapter 4 Identifying Market Segments and Selecting Target Markets
 The Learning Objectives l l l Levels and Patterns of Marketing Segmentation Marketing Target Positioning Strategy
The Learning Objectives l l l Levels and Patterns of Marketing Segmentation Marketing Target Positioning Strategy
 Market Segmentation Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers on the basis of needs, characteristics, or behavior who might require separate products or marketing mixes.
Market Segmentation Dividing a market into distinct groups of buyers on the basis of needs, characteristics, or behavior who might require separate products or marketing mixes.
 Segment Market A group of consumers who respond in a similar way to a given set of marketing effort.
Segment Market A group of consumers who respond in a similar way to a given set of marketing effort.
 Market targeting The process of evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segment to enter.
Market targeting The process of evaluating each market segment’s attractiveness and selecting one or more segment to enter.
 Marketing positioning l Arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target consumers.
Marketing positioning l Arranging for a product to occupy a clear, distinctive, and desirable place relative to competing products in the minds of target consumers.
 Levels of market segmentation l l l Mass marketing Segment marketing Niche marketing
Levels of market segmentation l l l Mass marketing Segment marketing Niche marketing
 micromarketing l l Local marketing Individual Marketing
micromarketing l l Local marketing Individual Marketing
 Discussion l l 1. How do you think the relationship between local marketing and international marketing? 2. How to interpret One –one marketing? (eg. Del: smart marketing)
Discussion l l 1. How do you think the relationship between local marketing and international marketing? 2. How to interpret One –one marketing? (eg. Del: smart marketing)
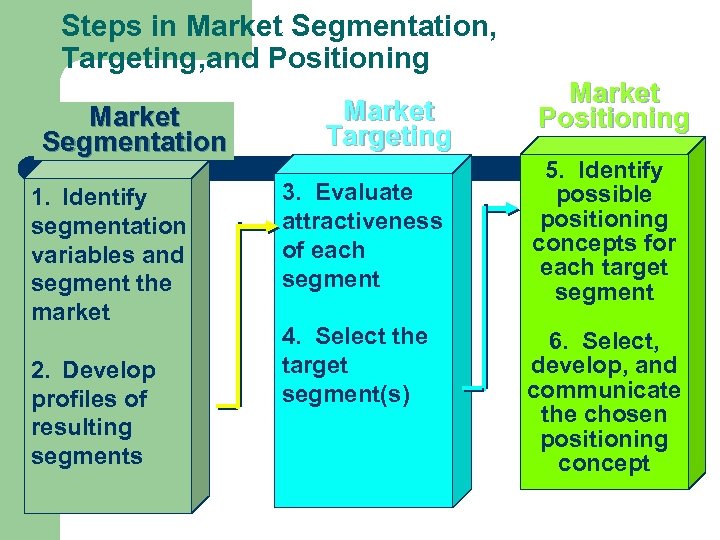 Steps in Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Market Segmentation 1. Identify segmentation variables and segment the market 2. Develop profiles of resulting segments Market Targeting 3. Evaluate attractiveness of each segment 4. Select the target segment(s) Market Positioning 5. Identify possible positioning concepts for each target segment 6. Select, develop, and communicate the chosen positioning concept
Steps in Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning Market Segmentation 1. Identify segmentation variables and segment the market 2. Develop profiles of resulting segments Market Targeting 3. Evaluate attractiveness of each segment 4. Select the target segment(s) Market Positioning 5. Identify possible positioning concepts for each target segment 6. Select, develop, and communicate the chosen positioning concept
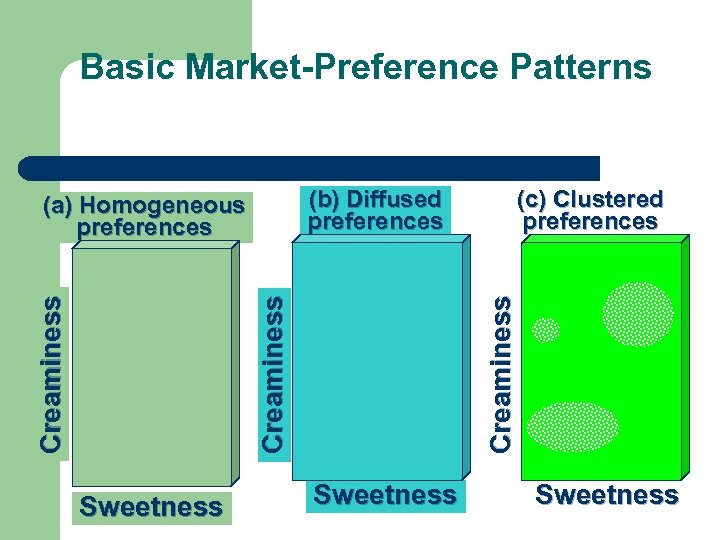 Basic Market-Preference Patterns Creaminess Sweetness (c) Clustered preferences Creaminess (b) Diffused preferences (a) Homogeneous preferences Sweetness
Basic Market-Preference Patterns Creaminess Sweetness (c) Clustered preferences Creaminess (b) Diffused preferences (a) Homogeneous preferences Sweetness
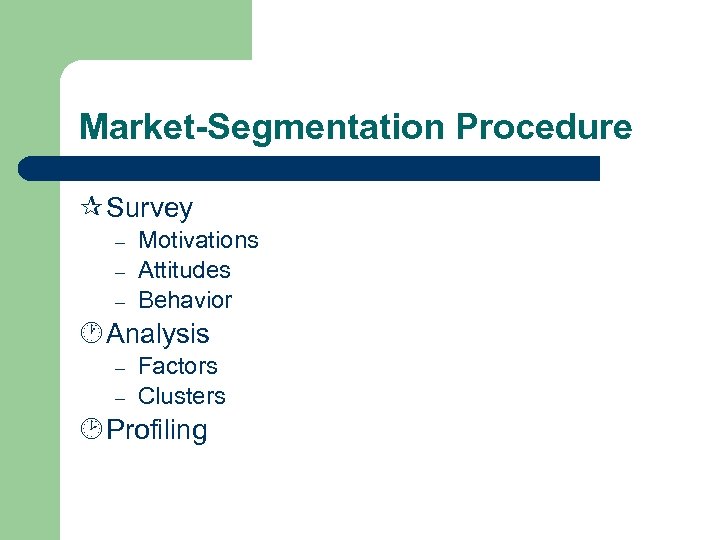 Market-Segmentation Procedure ¶ Survey – – – Motivations Attitudes Behavior · Analysis – – Factors Clusters ¸ Profiling
Market-Segmentation Procedure ¶ Survey – – – Motivations Attitudes Behavior · Analysis – – Factors Clusters ¸ Profiling
 Segmenting consumer markets(p 252) l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Psychographic Behavioral
Segmenting consumer markets(p 252) l l Geographic Segmentation Demographic Psychographic Behavioral
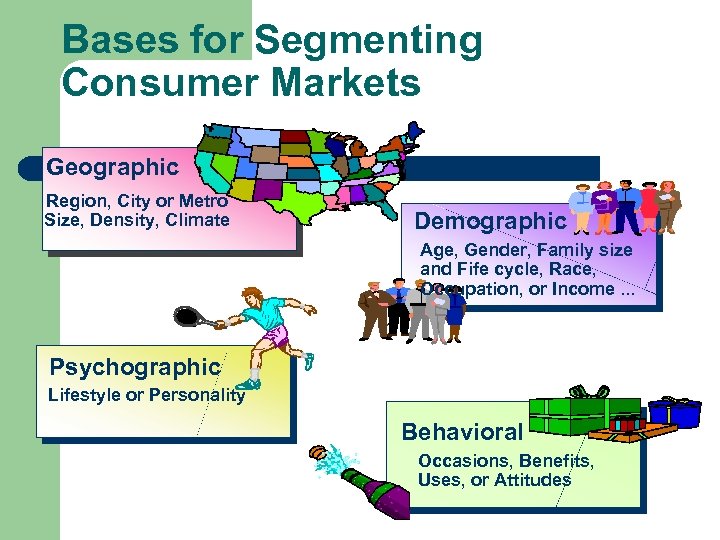 Bases for Segmenting Consumer Markets Geographic Region, City or Metro Size, Density, Climate Demographic Age, Gender, Family size and Fife cycle, Race, Occupation, or Income. . . Psychographic Lifestyle or Personality Behavioral Occasions, Benefits, Uses, or Attitudes
Bases for Segmenting Consumer Markets Geographic Region, City or Metro Size, Density, Climate Demographic Age, Gender, Family size and Fife cycle, Race, Occupation, or Income. . . Psychographic Lifestyle or Personality Behavioral Occasions, Benefits, Uses, or Attitudes
 Discussion How to choose the segmenting variables? l Consider the following products, please list the segmenting standard for each product and explain the reasons for them. 1. computer; 2. shampoo; 3. Life insurance; 4. book l
Discussion How to choose the segmenting variables? l Consider the following products, please list the segmenting standard for each product and explain the reasons for them. 1. computer; 2. shampoo; 3. Life insurance; 4. book l
 Bases for Segmenting Business Markets l l l Demographic Operating Variables Purchasing Approaches Situational Factors Personal Characteristics
Bases for Segmenting Business Markets l l l Demographic Operating Variables Purchasing Approaches Situational Factors Personal Characteristics
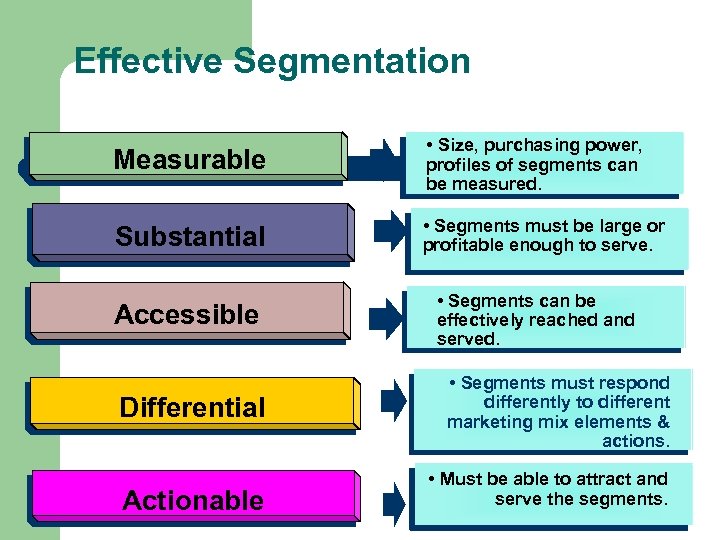 Effective Segmentation Measurable • Size, purchasing power, profiles of segments can be measured. Substantial • Segments must be large or profitable enough to serve. Accessible Differential Actionable • Segments can be effectively reached and served. • Segments must respond differently to different marketing mix elements & actions. • Must be able to attract and serve the segments.
Effective Segmentation Measurable • Size, purchasing power, profiles of segments can be measured. Substantial • Segments must be large or profitable enough to serve. Accessible Differential Actionable • Segments can be effectively reached and served. • Segments must respond differently to different marketing mix elements & actions. • Must be able to attract and serve the segments.
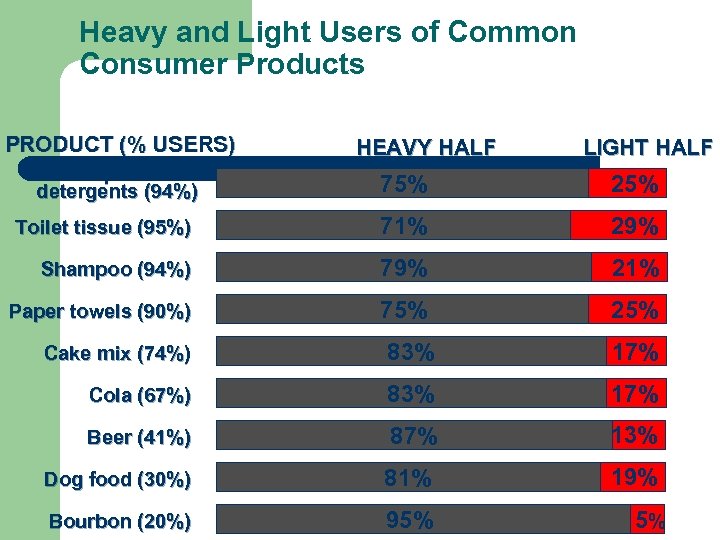 Heavy and Light Users of Common Consumer Products PRODUCT (% USERS) Soups and detergents (94%) HEAVY HALF LIGHT HALF 75% 25% Toilet tissue (95%) 71% 29% Shampoo (94%) 79% 21% Paper towels (90%) 75% 25% Cake mix (74%) 83% 17% Cola (67%) 83% 17% Beer (41%) 87% 13% Dog food (30%) 81% 19% Bourbon (20%) 95% 5%
Heavy and Light Users of Common Consumer Products PRODUCT (% USERS) Soups and detergents (94%) HEAVY HALF LIGHT HALF 75% 25% Toilet tissue (95%) 71% 29% Shampoo (94%) 79% 21% Paper towels (90%) 75% 25% Cake mix (74%) 83% 17% Cola (67%) 83% 17% Beer (41%) 87% 13% Dog food (30%) 81% 19% Bourbon (20%) 95% 5%
 Additional Segmentation Criteria l l Ethical Choice of Market Targets Segment Interrelationships & Supersegments Segment-by-Segment Invasion Plans Intersegment Cooperation
Additional Segmentation Criteria l l Ethical Choice of Market Targets Segment Interrelationships & Supersegments Segment-by-Segment Invasion Plans Intersegment Cooperation
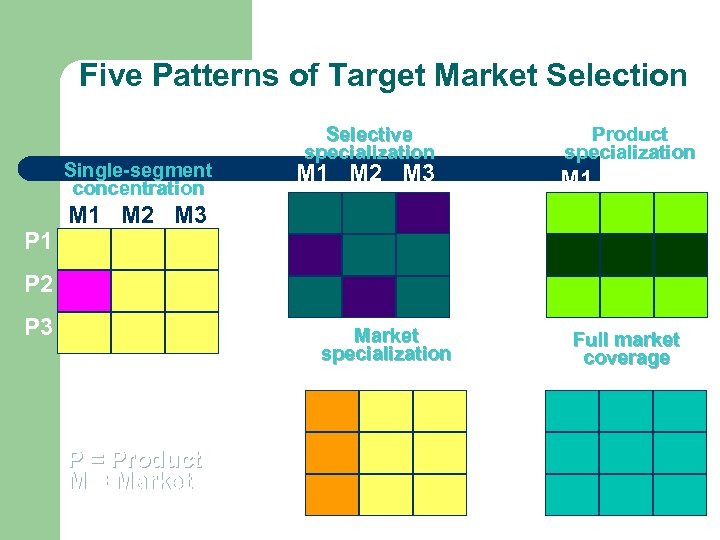 Five Patterns of Target Market Selection Single-segment concentration P 1 Product specialization Selective specialization M 1 M 2 M 3 P 1 P 2 P 3 P 2 P 1 P 2 M 1 M 2 M 3 P 3 Market specialization Full market coverage M 1 M 2 M 3 P 1 P = Product M = Market M 1 M 2 M 3 P 1 P 2 P 3
Five Patterns of Target Market Selection Single-segment concentration P 1 Product specialization Selective specialization M 1 M 2 M 3 P 1 P 2 P 3 P 2 P 1 P 2 M 1 M 2 M 3 P 3 Market specialization Full market coverage M 1 M 2 M 3 P 1 P = Product M = Market M 1 M 2 M 3 P 1 P 2 P 3
 2. Market Targeting l l Target market Undifferentiated marketing Differentiated marketing Concentrated Marketing
2. Market Targeting l l Target market Undifferentiated marketing Differentiated marketing Concentrated Marketing
 Undifferentiated Marketing l A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer.
Undifferentiated Marketing l A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer.
 Differentiated marketing l A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs separate offers for each.
Differentiated marketing l A market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs separate offers for each.
 Concentrated marketing l A market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large share of one or a few submarkets.
Concentrated marketing l A market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large share of one or a few submarkets.
 Discussion l How to choose the Target market?
Discussion l How to choose the Target market?
 3. Positioning l l l Product position Competitive advantage Value propositioning
3. Positioning l l l Product position Competitive advantage Value propositioning
 Product Position l The way the product is defined by consumers on important attributes----the place the product occupies in consumers’ minds relative to competing product.
Product Position l The way the product is defined by consumers on important attributes----the place the product occupies in consumers’ minds relative to competing product.
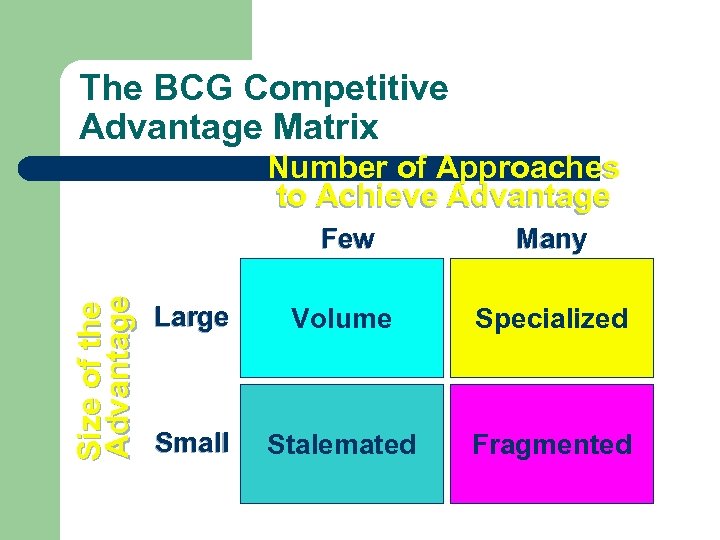 The BCG Competitive Advantage Matrix Number of Approaches to Achieve Advantage Size of the Advantage Few Many Large Volume Specialized Small Stalemated Fragmented
The BCG Competitive Advantage Matrix Number of Approaches to Achieve Advantage Size of the Advantage Few Many Large Volume Specialized Small Stalemated Fragmented
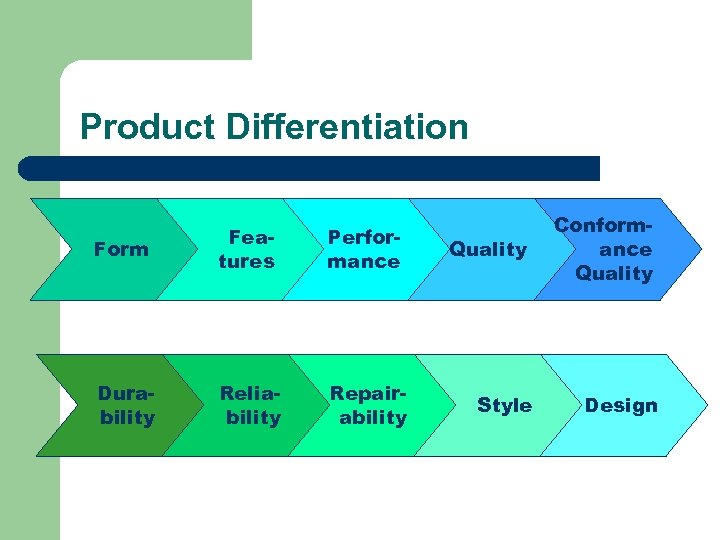 Product Differentiation Form Features Performance Durability Reliability Repairability Quality Style Conformance Quality Design
Product Differentiation Form Features Performance Durability Reliability Repairability Quality Style Conformance Quality Design
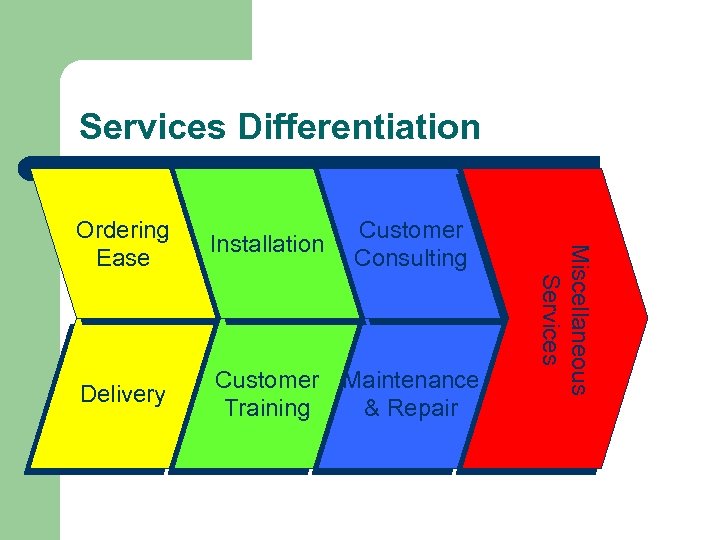 Services Differentiation Installation Customer Consulting Delivery Customer Maintenance Training & Repair Miscellaneous Services Ordering Ease
Services Differentiation Installation Customer Consulting Delivery Customer Maintenance Training & Repair Miscellaneous Services Ordering Ease
 Differentiation l l Personnel Channel
Differentiation l l Personnel Channel
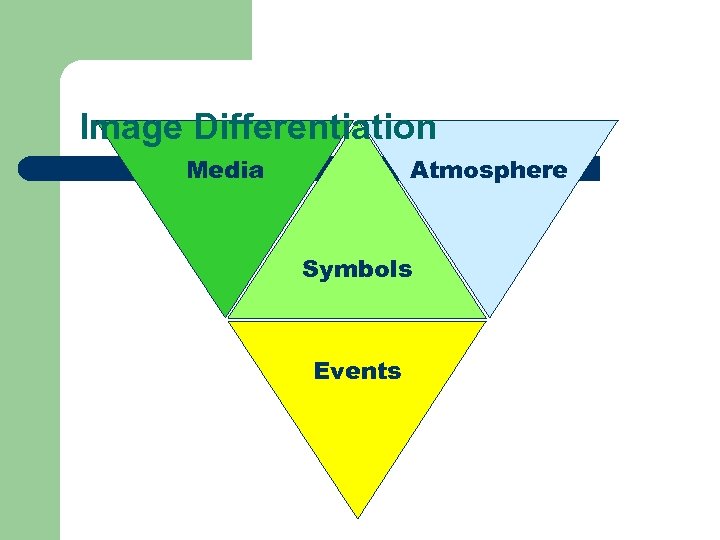 Image Differentiation Media Atmosphere Symbols Events
Image Differentiation Media Atmosphere Symbols Events
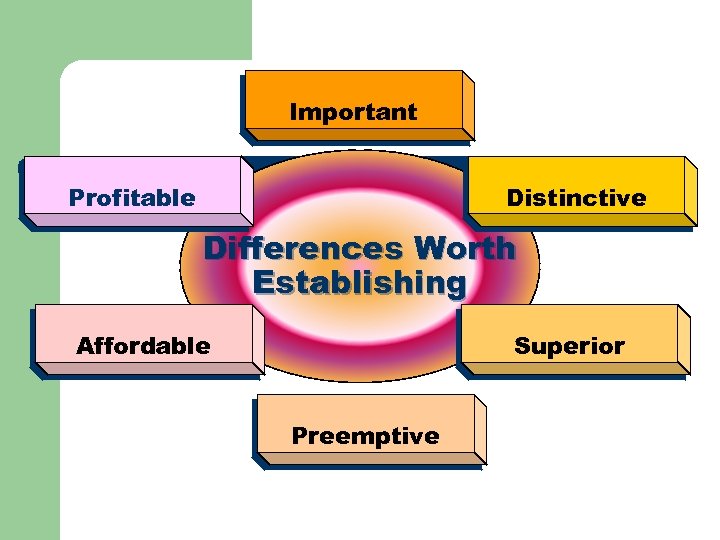 Important Distinctive Profitable Differences Worth Establishing Affordable Superior Preemptive
Important Distinctive Profitable Differences Worth Establishing Affordable Superior Preemptive
 Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the target market’s mind. P 298
Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in the target market’s mind. P 298
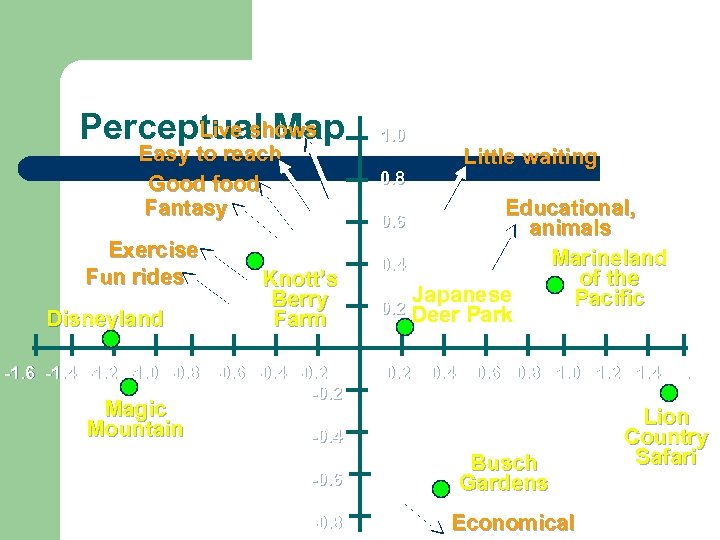 Live shows Perceptual Map Easy to reach Good food Fantasy Exercise Fun rides Disneyland Little waiting 0. 8 Educational, animals Marineland 0. 4 of the Japanese Pacific 0. 2 Deer Park 0. 6 Knott’s Berry Farm -1. 6 -1. 4 -1. 2 -1. 0 -0. 8 -0. 6 -0. 4 -0. 2 Magic Mountain 1. 0 0. 2 0. 4 0. 6 0. 8 1. 0 1. 2 1. 4 1. 6 -0. 4 -0. 6 -0. 8 Busch Gardens Economical Lion Country Safari
Live shows Perceptual Map Easy to reach Good food Fantasy Exercise Fun rides Disneyland Little waiting 0. 8 Educational, animals Marineland 0. 4 of the Japanese Pacific 0. 2 Deer Park 0. 6 Knott’s Berry Farm -1. 6 -1. 4 -1. 2 -1. 0 -0. 8 -0. 6 -0. 4 -0. 2 Magic Mountain 1. 0 0. 2 0. 4 0. 6 0. 8 1. 0 1. 2 1. 4 1. 6 -0. 4 -0. 6 -0. 8 Busch Gardens Economical Lion Country Safari
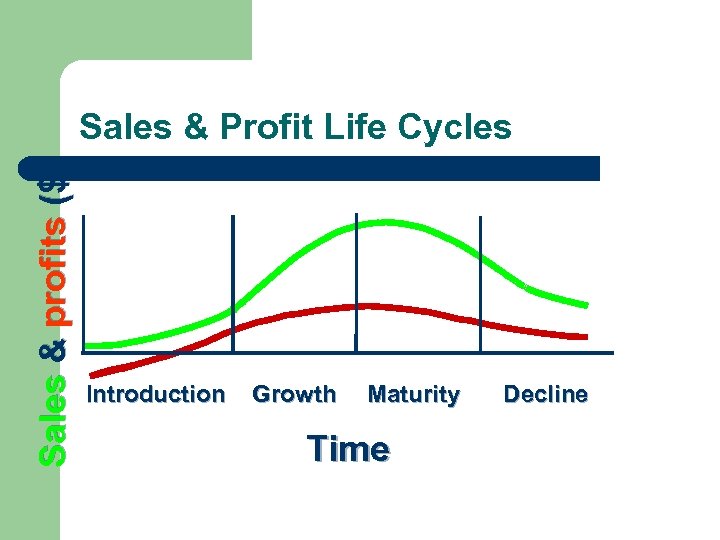 Sales & profits ($) Sales & Profit Life Cycles Introduction Growth Maturity Time Decline
Sales & profits ($) Sales & Profit Life Cycles Introduction Growth Maturity Time Decline
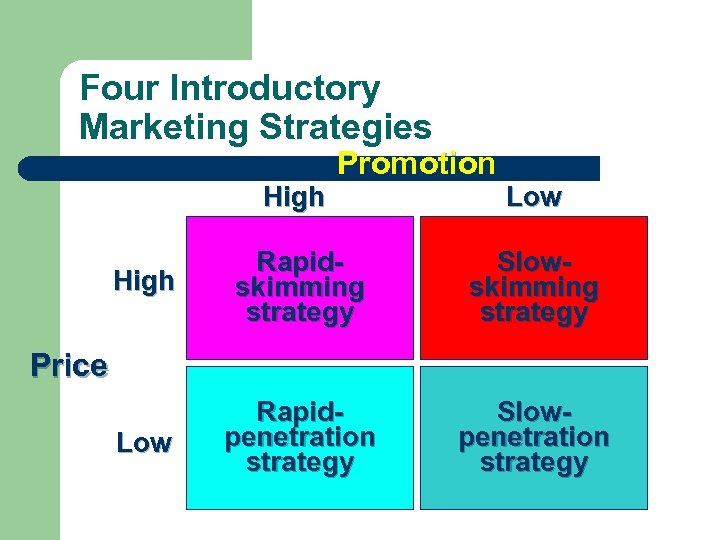 Four Introductory Marketing Strategies High Promotion Low High Rapidskimming strategy Slowskimming strategy Low Rapidpenetration strategy Slowpenetration strategy Price
Four Introductory Marketing Strategies High Promotion Low High Rapidskimming strategy Slowskimming strategy Low Rapidpenetration strategy Slowpenetration strategy Price
 Case study l l 香港大班月饼 Background
Case study l l 香港大班月饼 Background


