ffe605a9d0758e35adcf36be6da65b5b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Chapter 4 Exchange Rate Determination Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Chapter 4 Exchange Rate Determination Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Chapter Objectives • • • To explain how exchange rate movements are measured. To explain how the equilibrium exchange rate is determined. To examine the factors that affect the equilibrium exchange rate. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Chapter Objectives • • • To explain how exchange rate movements are measured. To explain how the equilibrium exchange rate is determined. To examine the factors that affect the equilibrium exchange rate. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Measuring Exchange Rate Movements (1) • An exchange rate measures the value of one currency in units of another currency. • When a currency declines in value, it is said to depreciate. When it increases in value, it is said to appreciate. • On the days when some currencies appreciate while others depreciate against a particular currency, that currency is said to be “mixed in trading. ” Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Measuring Exchange Rate Movements (1) • An exchange rate measures the value of one currency in units of another currency. • When a currency declines in value, it is said to depreciate. When it increases in value, it is said to appreciate. • On the days when some currencies appreciate while others depreciate against a particular currency, that currency is said to be “mixed in trading. ” Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Foreign Exchange Rate Determination • Exchange rate determination is complex. • Some argue that there are three major schools of thought (parity conditions, balance of payments approach, asset market approach) • These are not competing theories but rather complementary theories. Without the depth and breadth of the various approaches combined, our ability to capture the complexity of the global market for currencies is lost. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Foreign Exchange Rate Determination • Exchange rate determination is complex. • Some argue that there are three major schools of thought (parity conditions, balance of payments approach, asset market approach) • These are not competing theories but rather complementary theories. Without the depth and breadth of the various approaches combined, our ability to capture the complexity of the global market for currencies is lost. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
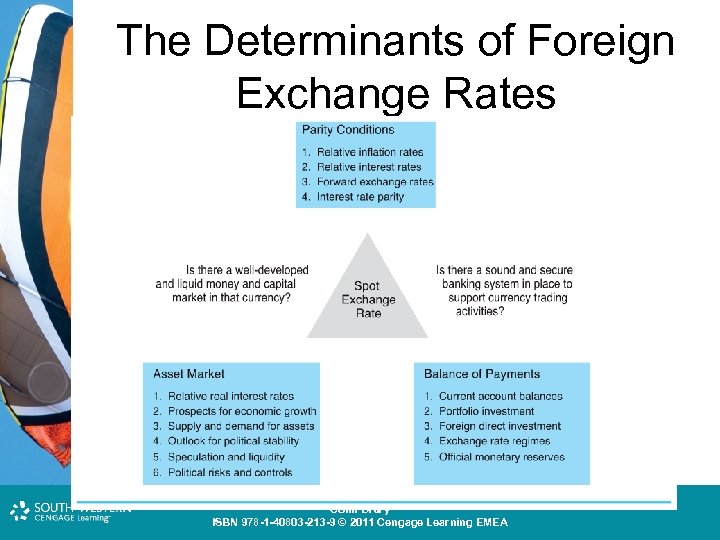 The Determinants of Foreign Exchange Rates Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
The Determinants of Foreign Exchange Rates Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
 Exchange Rate Determination: Theoretical Thread • The theory of purchasing power parity is a widely accepted theory of exchange rate determination: – PPP is the oldest and most widely followed of the exchange rate theories, and deals with exchange rates and inflation. Countries who suffer from high inflation, will se a deterioration in the value of their currency – Most exchange rate determination theories have PPP elements embedded within their frameworks. – We will look at PPP in more detail in chapter 8 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Exchange Rate Determination: Theoretical Thread • The theory of purchasing power parity is a widely accepted theory of exchange rate determination: – PPP is the oldest and most widely followed of the exchange rate theories, and deals with exchange rates and inflation. Countries who suffer from high inflation, will se a deterioration in the value of their currency – Most exchange rate determination theories have PPP elements embedded within their frameworks. – We will look at PPP in more detail in chapter 8 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
 Exchange Rate Determination: Theoretical Thread • The balance of payments approach is also a widely utilized theoretical approach in exchange rate determination: – The basic approach argues that the equilibrium exchange rate is found currency flows match up vis a vis current and financial account activities. – If a country suffers from prolonged BOP deficits, the value of its currency will fall Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Exchange Rate Determination: Theoretical Thread • The balance of payments approach is also a widely utilized theoretical approach in exchange rate determination: – The basic approach argues that the equilibrium exchange rate is found currency flows match up vis a vis current and financial account activities. – If a country suffers from prolonged BOP deficits, the value of its currency will fall Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
 Exchange Rate Determination: Theoretical Thread • The asset market approach argues that exchange rates are determined by the supply and demand for a wide variety of financial assets: – Shifts in the supply and demand for financial assets alter exchange rates. – Changes in monetary and fiscal policy alter expected returns and perceived relative risks of financial assets, which in turn alter exchange rates. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Exchange Rate Determination: Theoretical Thread • The asset market approach argues that exchange rates are determined by the supply and demand for a wide variety of financial assets: – Shifts in the supply and demand for financial assets alter exchange rates. – Changes in monetary and fiscal policy alter expected returns and perceived relative risks of financial assets, which in turn alter exchange rates. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
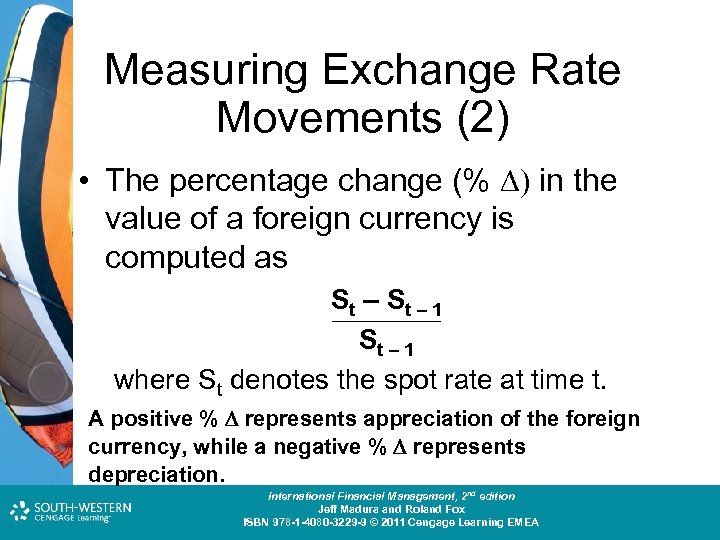 Measuring Exchange Rate Movements (2) • The percentage change (% ) in the value of a foreign currency is computed as St – S t – 1 St – 1 where St denotes the spot rate at time t. • A positive % D represents appreciation of the foreign currency, while a negative % D represents depreciation. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Measuring Exchange Rate Movements (2) • The percentage change (% ) in the value of a foreign currency is computed as St – S t – 1 St – 1 where St denotes the spot rate at time t. • A positive % D represents appreciation of the foreign currency, while a negative % D represents depreciation. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
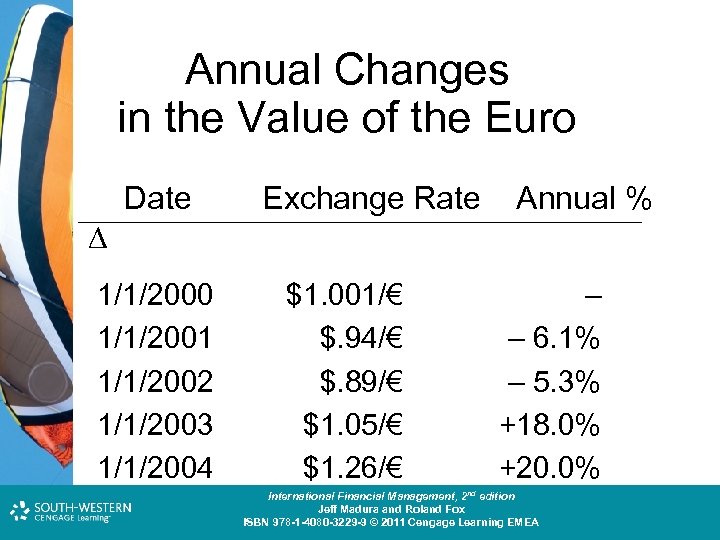 Annual Changes in the Value of the Euro Date Exchange Rate 1/1/2000 1/1/2001 1/1/2002 1/1/2003 1/1/2004 $1. 001/€ $. 94/€ $. 89/€ $1. 05/€ $1. 26/€ Annual % – – 6. 1% – 5. 3% +18. 0% +20. 0% Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Annual Changes in the Value of the Euro Date Exchange Rate 1/1/2000 1/1/2001 1/1/2002 1/1/2003 1/1/2004 $1. 001/€ $. 94/€ $. 89/€ $1. 05/€ $1. 26/€ Annual % – – 6. 1% – 5. 3% +18. 0% +20. 0% Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Exchange Rate Equilibrium (1) • An exchange rate represents the price of a currency, which is determined by the demand for that currency relative to the supply for that currency. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Exchange Rate Equilibrium (1) • An exchange rate represents the price of a currency, which is determined by the demand for that currency relative to the supply for that currency. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
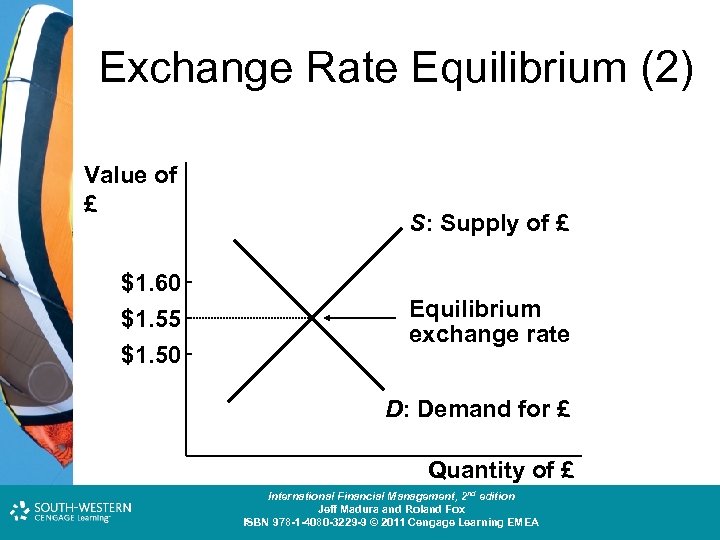 Exchange Rate Equilibrium (2) Value of £ $1. 60 $1. 55 $1. 50 S: Supply of £ Equilibrium exchange rate D: Demand for £ Quantity of £ Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Exchange Rate Equilibrium (2) Value of £ $1. 60 $1. 55 $1. 50 S: Supply of £ Equilibrium exchange rate D: Demand for £ Quantity of £ Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Exchange Rate Equilibrium (3) • The liquidity of a currency affects the sensitivity of the exchange rate to specific transactions. • With many willing buyers and sellers, even large transactions can be easily accommodated. • Conversely, illiquid currencies tend to exhibit more volatile exchange rate movements. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Exchange Rate Equilibrium (3) • The liquidity of a currency affects the sensitivity of the exchange rate to specific transactions. • With many willing buyers and sellers, even large transactions can be easily accommodated. • Conversely, illiquid currencies tend to exhibit more volatile exchange rate movements. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
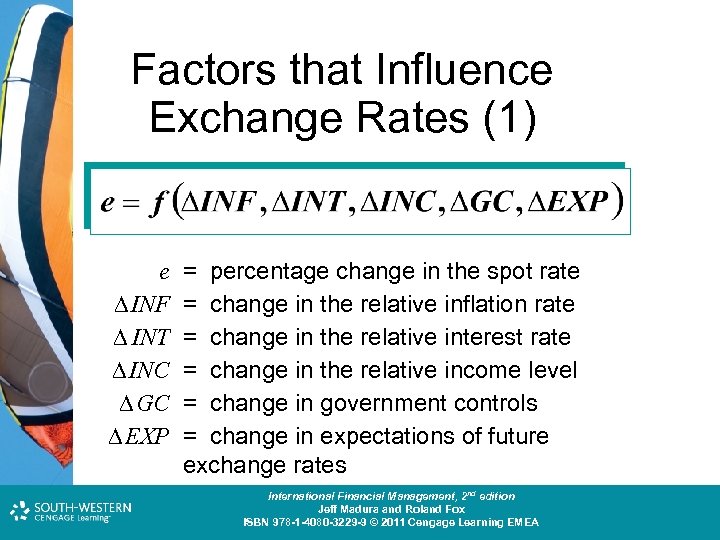 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (1) e INF INT INC GC EXP = percentage change in the spot rate = change in the relative inflation rate = change in the relative interest rate = change in the relative income level = change in government controls = change in expectations of future exchange rates Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (1) e INF INT INC GC EXP = percentage change in the spot rate = change in the relative inflation rate = change in the relative interest rate = change in the relative income level = change in government controls = change in expectations of future exchange rates Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
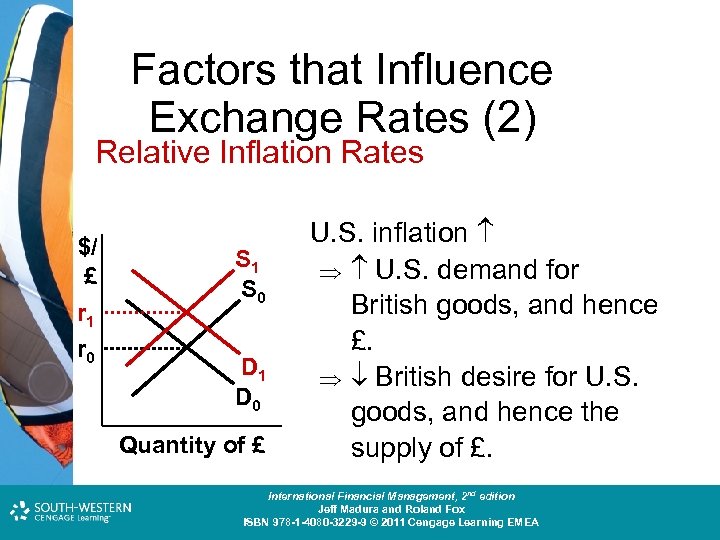 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (2) Relative Inflation Rates $/ £ r 1 r 0 S 1 S 0 D 1 D 0 Quantity of £ U. S. inflation U. S. demand for British goods, and hence £. British desire for U. S. goods, and hence the supply of £. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (2) Relative Inflation Rates $/ £ r 1 r 0 S 1 S 0 D 1 D 0 Quantity of £ U. S. inflation U. S. demand for British goods, and hence £. British desire for U. S. goods, and hence the supply of £. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
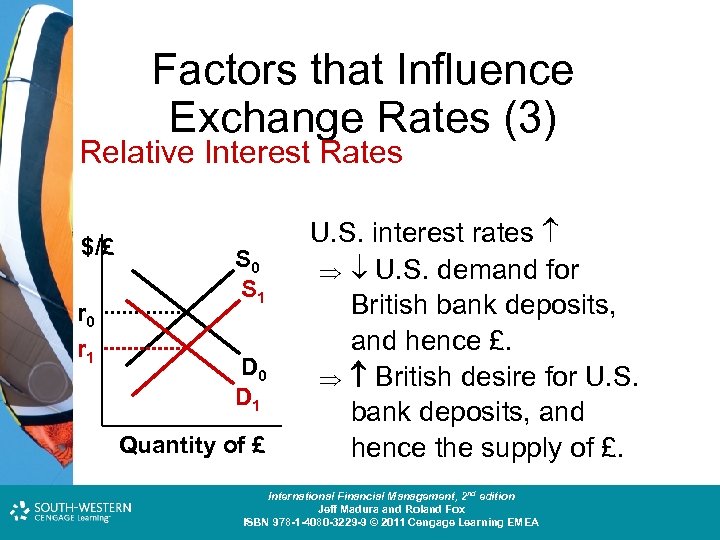 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (3) Relative Interest Rates $/£ r 0 r 1 S 0 S 1 D 0 D 1 Quantity of £ U. S. interest rates U. S. demand for British bank deposits, and hence £. British desire for U. S. bank deposits, and hence the supply of £. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (3) Relative Interest Rates $/£ r 0 r 1 S 0 S 1 D 0 D 1 Quantity of £ U. S. interest rates U. S. demand for British bank deposits, and hence £. British desire for U. S. bank deposits, and hence the supply of £. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (4) Relative Interest Rates • A relatively high interest rate may actually reflect expectations of relatively high inflation, which may discourage foreign investment. • It is thus useful to consider the real interest rate, which adjusts the nominal interest rate for inflation. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (4) Relative Interest Rates • A relatively high interest rate may actually reflect expectations of relatively high inflation, which may discourage foreign investment. • It is thus useful to consider the real interest rate, which adjusts the nominal interest rate for inflation. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (5) Relative Interest Rates • real nominal interest – inflation rate • This relationship is sometimes called the Fisher effect. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (5) Relative Interest Rates • real nominal interest – inflation rate • This relationship is sometimes called the Fisher effect. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
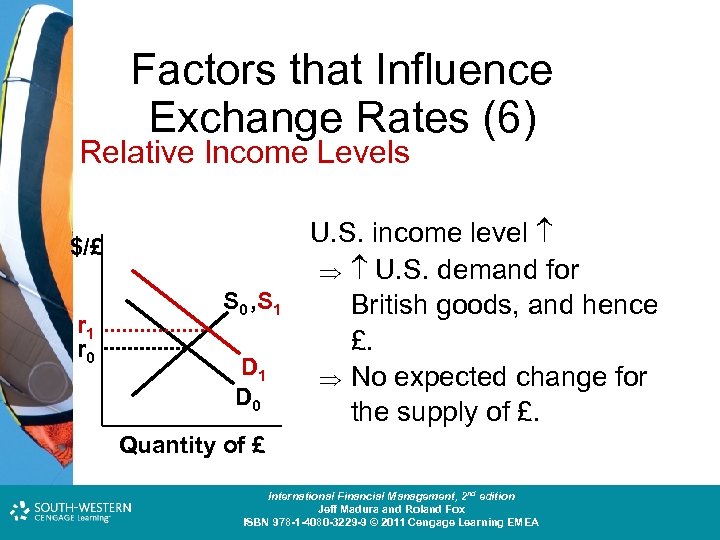 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (6) Relative Income Levels $/£ r 1 r 0 S 0 , S 1 D 0 U. S. income level U. S. demand for British goods, and hence £. No expected change for the supply of £. Quantity of £ Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (6) Relative Income Levels $/£ r 1 r 0 S 0 , S 1 D 0 U. S. income level U. S. demand for British goods, and hence £. No expected change for the supply of £. Quantity of £ Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (7) Government Controls • Governments may influence the equilibrium exchange rate by: – – imposing foreign exchange barriers, imposing foreign trade barriers, intervening in the foreign exchange market, and affecting macro variables such as inflation, interest rates, and income levels. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (7) Government Controls • Governments may influence the equilibrium exchange rate by: – – imposing foreign exchange barriers, imposing foreign trade barriers, intervening in the foreign exchange market, and affecting macro variables such as inflation, interest rates, and income levels. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (8) Expectations • Foreign exchange markets react to any news that may have a future effect. – News of a potential surge in U. S. inflation may cause currency traders to sell dollars. • Many institutional investors take currency positions based on anticipated interest rate movements in various countries. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (8) Expectations • Foreign exchange markets react to any news that may have a future effect. – News of a potential surge in U. S. inflation may cause currency traders to sell dollars. • Many institutional investors take currency positions based on anticipated interest rate movements in various countries. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (9) Expectations • Economic signals that affect exchange rates can change quickly, such that speculators may overreact initially and then find that they have to make a correction. • Speculation on the currencies of emerging markets can have a substantial impact on their exchange rates. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (9) Expectations • Economic signals that affect exchange rates can change quickly, such that speculators may overreact initially and then find that they have to make a correction. • Speculation on the currencies of emerging markets can have a substantial impact on their exchange rates. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (10) Interaction of Factors • The various factors sometimes interact and simultaneously affect exchange rate movements. • For example, an increase in income levels sometimes causes expectations of higher interest rates, thus placing opposing pressures on foreign currency values. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (10) Interaction of Factors • The various factors sometimes interact and simultaneously affect exchange rate movements. • For example, an increase in income levels sometimes causes expectations of higher interest rates, thus placing opposing pressures on foreign currency values. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
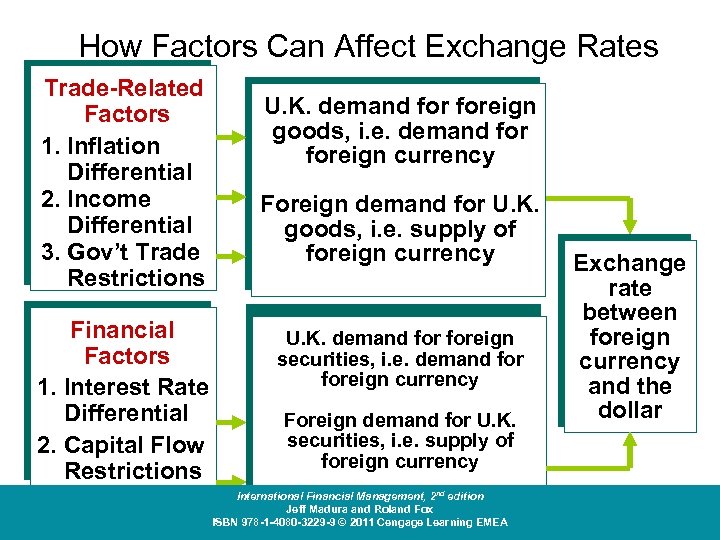 How Factors Can Affect Exchange Rates Trade-Related Factors 1. Inflation Differential 2. Income Differential 3. Gov’t Trade Restrictions Financial Factors 1. Interest Rate Differential 2. Capital Flow Restrictions U. K. demand foreign goods, i. e. demand foreign currency Foreign demand for U. K. goods, i. e. supply of foreign currency U. K. demand foreign securities, i. e. demand foreign currency Foreign demand for U. K. securities, i. e. supply of foreign currency International Financial Management, 2 nd edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Exchange rate between foreign currency and the dollar
How Factors Can Affect Exchange Rates Trade-Related Factors 1. Inflation Differential 2. Income Differential 3. Gov’t Trade Restrictions Financial Factors 1. Interest Rate Differential 2. Capital Flow Restrictions U. K. demand foreign goods, i. e. demand foreign currency Foreign demand for U. K. goods, i. e. supply of foreign currency U. K. demand foreign securities, i. e. demand foreign currency Foreign demand for U. K. securities, i. e. supply of foreign currency International Financial Management, 2 nd edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Exchange rate between foreign currency and the dollar
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (11) Interaction of Factors • The sensitivity of an exchange rate to the factors is dependent on the volume of international transactions between the two countries. Large volume of international trade relative inflation rates may be more influential Large volume of capital flows interest rate fluctuations may be more influential Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (11) Interaction of Factors • The sensitivity of an exchange rate to the factors is dependent on the volume of international transactions between the two countries. Large volume of international trade relative inflation rates may be more influential Large volume of capital flows interest rate fluctuations may be more influential Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (12) Interaction of Factors • An understanding of exchange rate equilibrium does not guarantee accurate forecasts of future exchange rates because that will depend in part on how the factors that affect exchange rates will change in the future. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Factors that Influence Exchange Rates (12) Interaction of Factors • An understanding of exchange rate equilibrium does not guarantee accurate forecasts of future exchange rates because that will depend in part on how the factors that affect exchange rates will change in the future. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Speculating on Anticipated Exchange Rates • Many commercial banks attempt to capitalize on their forecasts of anticipated exchange rate movements in the foreign exchange market. • The potential returns from foreign currency speculation are high for banks that have large borrowing capacity. • The simple strategy is to get out of the currency about to depreciate and into the currency that is going to appreciate against it. Then reverse the positions after the event to end up with more than you started with. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Speculating on Anticipated Exchange Rates • Many commercial banks attempt to capitalize on their forecasts of anticipated exchange rate movements in the foreign exchange market. • The potential returns from foreign currency speculation are high for banks that have large borrowing capacity. • The simple strategy is to get out of the currency about to depreciate and into the currency that is going to appreciate against it. Then reverse the positions after the event to end up with more than you started with. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
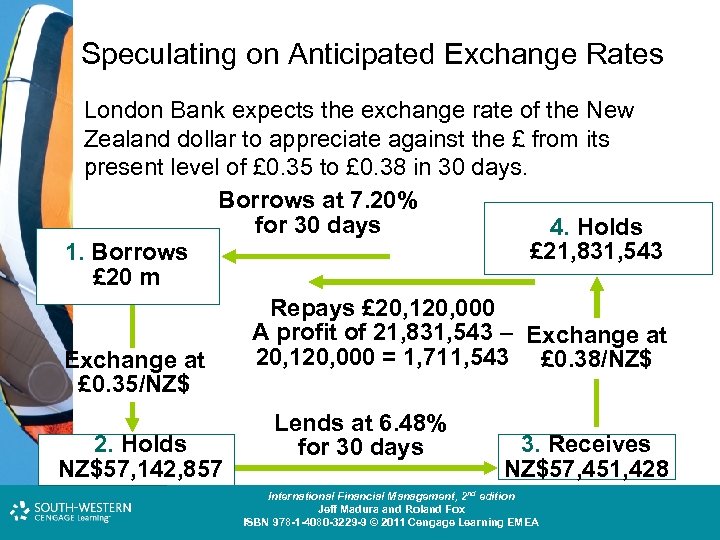 Speculating on Anticipated Exchange Rates London Bank expects the exchange rate of the New Zealand dollar to appreciate against the £ from its present level of £ 0. 35 to £ 0. 38 in 30 days. Borrows at 7. 20% for 30 days 4. Holds £ 21, 831, 543 1. Borrows £ 20 m Repays £ 20, 120, 000 A profit of 21, 831, 543 – Exchange at 20, 120, 000 = 1, 711, 543 £ 0. 38/NZ$ Exchange at £ 0. 35/NZ$ 2. Holds NZ$57, 142, 857 Lends at 6. 48% for 30 days 3. Receives NZ$57, 451, 428 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Speculating on Anticipated Exchange Rates London Bank expects the exchange rate of the New Zealand dollar to appreciate against the £ from its present level of £ 0. 35 to £ 0. 38 in 30 days. Borrows at 7. 20% for 30 days 4. Holds £ 21, 831, 543 1. Borrows £ 20 m Repays £ 20, 120, 000 A profit of 21, 831, 543 – Exchange at 20, 120, 000 = 1, 711, 543 £ 0. 38/NZ$ Exchange at £ 0. 35/NZ$ 2. Holds NZ$57, 142, 857 Lends at 6. 48% for 30 days 3. Receives NZ$57, 451, 428 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
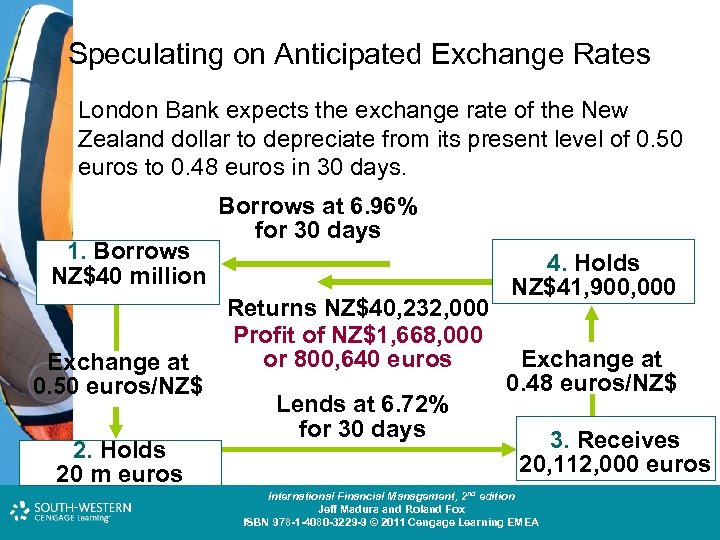 Speculating on Anticipated Exchange Rates London Bank expects the exchange rate of the New Zealand dollar to depreciate from its present level of 0. 50 euros to 0. 48 euros in 30 days. 1. Borrows NZ$40 million Exchange at 0. 50 euros/NZ$ 2. Holds 20 m euros Borrows at 6. 96% for 30 days Returns NZ$40, 232, 000 Profit of NZ$1, 668, 000 or 800, 640 euros Lends at 6. 72% for 30 days 4. Holds NZ$41, 900, 000 Exchange at 0. 48 euros/NZ$ 3. Receives 20, 112, 000 euros Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
Speculating on Anticipated Exchange Rates London Bank expects the exchange rate of the New Zealand dollar to depreciate from its present level of 0. 50 euros to 0. 48 euros in 30 days. 1. Borrows NZ$40 million Exchange at 0. 50 euros/NZ$ 2. Holds 20 m euros Borrows at 6. 96% for 30 days Returns NZ$40, 232, 000 Profit of NZ$1, 668, 000 or 800, 640 euros Lends at 6. 72% for 30 days 4. Holds NZ$41, 900, 000 Exchange at 0. 48 euros/NZ$ 3. Receives 20, 112, 000 euros Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, nd th edition International Financial Management, 2 7 edition Jeff Madura and Roland Fox Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA ISBN 978 -1 -4080 -3229 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning
 Norwegian Kroner (NOK) • Until a few years ago, the operational objective behind monetary policy in Norway was to stabilise the exchange rate • Now, most Central Banks have price stability as their number one priority. • The Norwegian Central Bank sets interest rates so as to reach an inflation rate of 2. 5%. The exchange rate will then have to become more unstable Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Norwegian Kroner (NOK) • Until a few years ago, the operational objective behind monetary policy in Norway was to stabilise the exchange rate • Now, most Central Banks have price stability as their number one priority. • The Norwegian Central Bank sets interest rates so as to reach an inflation rate of 2. 5%. The exchange rate will then have to become more unstable Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
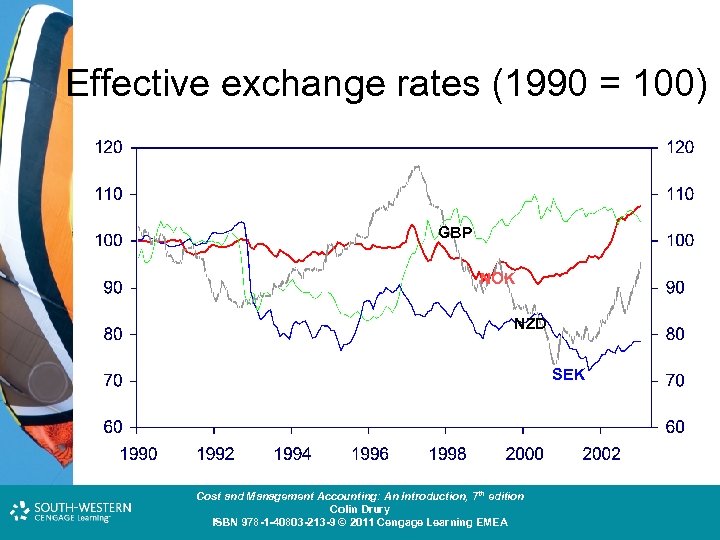 Effective exchange rates (1990 = 100) GBP NOK NZD SEK Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Effective exchange rates (1990 = 100) GBP NOK NZD SEK Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
 What made the NOK appreciate? • The NOK appreciated a lot from 2000 until January 2003. • Market players have suggested several explanations as to why this happened: – The exchange rate was particularly driven by the interest rate differential. Foreign interest rates fell while Norwegian remained high Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
What made the NOK appreciate? • The NOK appreciated a lot from 2000 until January 2003. • Market players have suggested several explanations as to why this happened: – The exchange rate was particularly driven by the interest rate differential. Foreign interest rates fell while Norwegian remained high Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
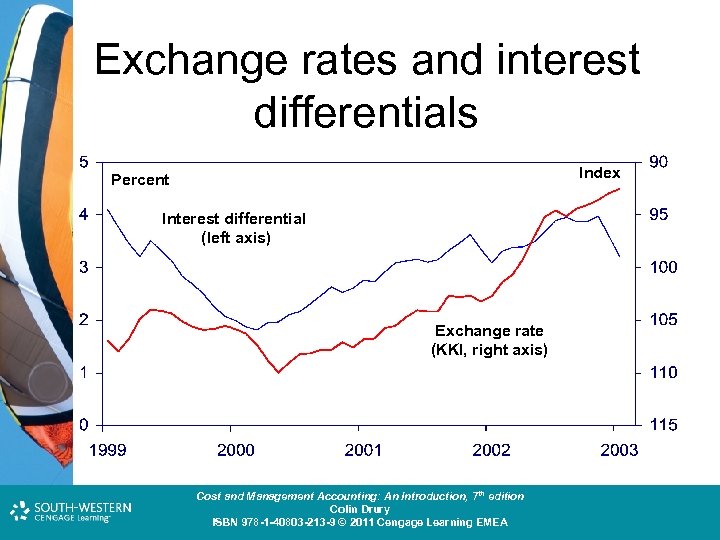 Exchange rates and interest differentials Index Percent Interest differential (left axis) Exchange rate (KKI, right axis) Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Exchange rates and interest differentials Index Percent Interest differential (left axis) Exchange rate (KKI, right axis) Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
 Falling stock markets • The adverse developments in many major international stock markets made investors more risk averse • Many investors wanted to put their money into interest paying papers, and NOK was considered a very good asset due to high interest rates and sound economic situation • The NOK exchange rate has been highly correlated with the US stock market Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Falling stock markets • The adverse developments in many major international stock markets made investors more risk averse • Many investors wanted to put their money into interest paying papers, and NOK was considered a very good asset due to high interest rates and sound economic situation • The NOK exchange rate has been highly correlated with the US stock market Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
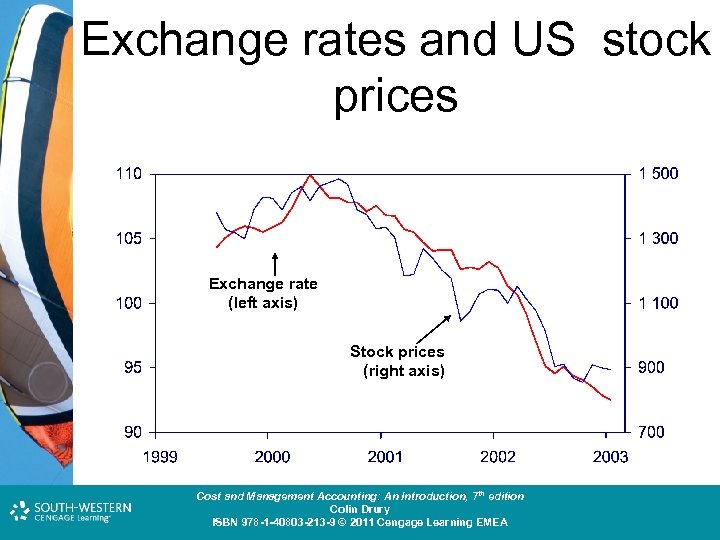 Exchange rates and US stock prices Exchange rate (left axis) Stock prices (right axis) Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Exchange rates and US stock prices Exchange rate (left axis) Stock prices (right axis) Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
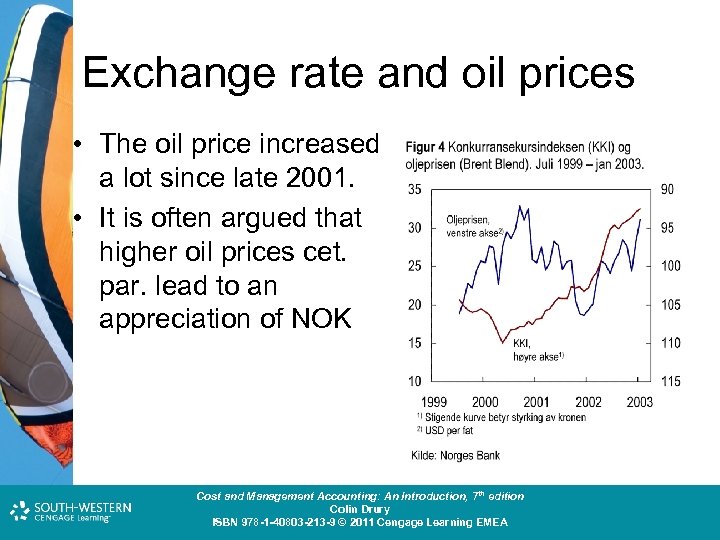 Exchange rate and oil prices • The oil price increased a lot since late 2001. • It is often argued that higher oil prices cet. par. lead to an appreciation of NOK Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
Exchange rate and oil prices • The oil price increased a lot since late 2001. • It is often argued that higher oil prices cet. par. lead to an appreciation of NOK Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
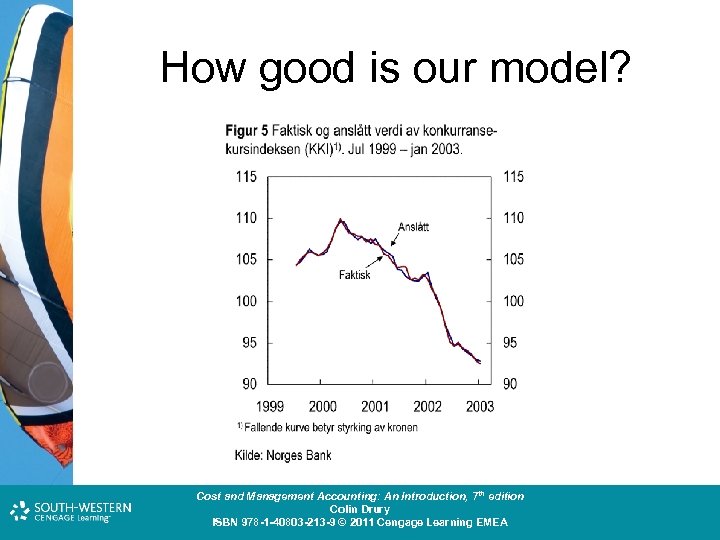 How good is our model? Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA
How good is our model? Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7 th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978 -1 -40803 -213 -9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA


