fc061c6e104cd61dc1c06270daafbac2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34
 CHAPTER 4 Environmental Scanning and Industry Analysis Continuation of last session’s lecture THOMAS L. WHEELEN J. DAVID HUNGER 4 -1
CHAPTER 4 Environmental Scanning and Industry Analysis Continuation of last session’s lecture THOMAS L. WHEELEN J. DAVID HUNGER 4 -1
 Porter’s Approach to Industry Analysis Rivalry Among Existing Firms – –Number of competitors –Rate of industry growth –Product or service characteristics –Amount of fixed costs –Capacity –Height of exit barriers –Diversity of rivals Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -2
Porter’s Approach to Industry Analysis Rivalry Among Existing Firms – –Number of competitors –Rate of industry growth –Product or service characteristics –Amount of fixed costs –Capacity –Height of exit barriers –Diversity of rivals Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -2
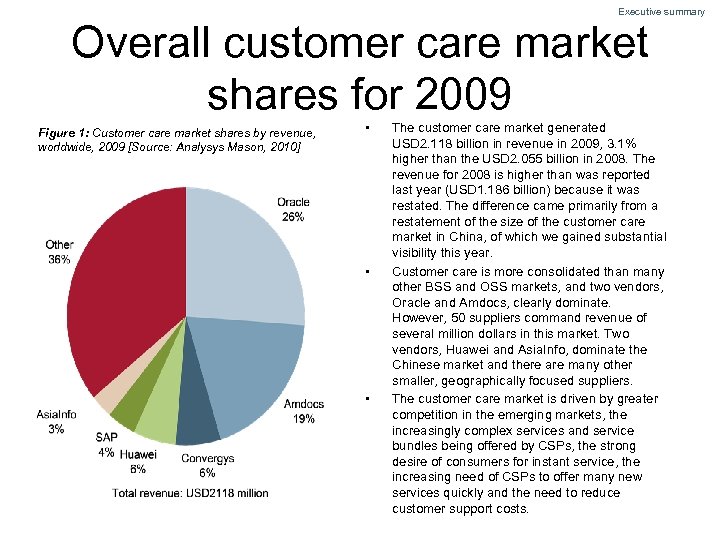 Executive summary Overall customer care market shares for 2009 Figure 1: Customer care market shares by revenue, worldwide, 2009 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2010] • • • The customer care market generated USD 2. 118 billion in revenue in 2009, 3. 1% higher than the USD 2. 055 billion in 2008. The revenue for 2008 is higher than was reported last year (USD 1. 186 billion) because it was restated. The difference came primarily from a restatement of the size of the customer care market in China, of which we gained substantial visibility this year. Customer care is more consolidated than many other BSS and OSS markets, and two vendors, Oracle and Amdocs, clearly dominate. However, 50 suppliers command revenue of several million dollars in this market. Two vendors, Huawei and Asia. Info, dominate the Chinese market and there are many other smaller, geographically focused suppliers. The customer care market is driven by greater competition in the emerging markets, the increasingly complex services and service bundles being offered by CSPs, the strong desire of consumers for instant service, the increasing need of CSPs to offer many new services quickly and the need to reduce customer support costs.
Executive summary Overall customer care market shares for 2009 Figure 1: Customer care market shares by revenue, worldwide, 2009 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2010] • • • The customer care market generated USD 2. 118 billion in revenue in 2009, 3. 1% higher than the USD 2. 055 billion in 2008. The revenue for 2008 is higher than was reported last year (USD 1. 186 billion) because it was restated. The difference came primarily from a restatement of the size of the customer care market in China, of which we gained substantial visibility this year. Customer care is more consolidated than many other BSS and OSS markets, and two vendors, Oracle and Amdocs, clearly dominate. However, 50 suppliers command revenue of several million dollars in this market. Two vendors, Huawei and Asia. Info, dominate the Chinese market and there are many other smaller, geographically focused suppliers. The customer care market is driven by greater competition in the emerging markets, the increasingly complex services and service bundles being offered by CSPs, the strong desire of consumers for instant service, the increasing need of CSPs to offer many new services quickly and the need to reduce customer support costs.
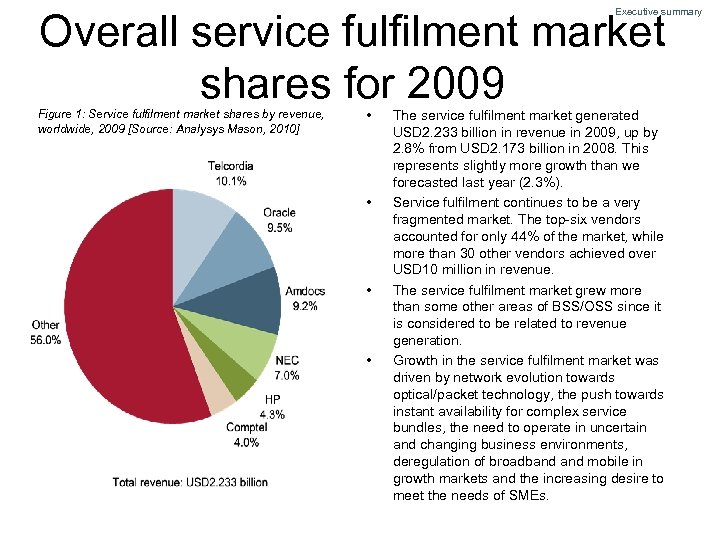 Overall service fulfilment market shares for 2009 Executive summary Figure 1: Service fulfilment market shares by revenue, worldwide, 2009 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2010] • • The service fulfilment market generated USD 2. 233 billion in revenue in 2009, up by 2. 8% from USD 2. 173 billion in 2008. This represents slightly more growth than we forecasted last year (2. 3%). Service fulfilment continues to be a very fragmented market. The top-six vendors accounted for only 44% of the market, while more than 30 other vendors achieved over USD 10 million in revenue. The service fulfilment market grew more than some other areas of BSS/OSS since it is considered to be related to revenue generation. Growth in the service fulfilment market was driven by network evolution towards optical/packet technology, the push towards instant availability for complex service bundles, the need to operate in uncertain and changing business environments, deregulation of broadband mobile in growth markets and the increasing desire to meet the needs of SMEs.
Overall service fulfilment market shares for 2009 Executive summary Figure 1: Service fulfilment market shares by revenue, worldwide, 2009 [Source: Analysys Mason, 2010] • • The service fulfilment market generated USD 2. 233 billion in revenue in 2009, up by 2. 8% from USD 2. 173 billion in 2008. This represents slightly more growth than we forecasted last year (2. 3%). Service fulfilment continues to be a very fragmented market. The top-six vendors accounted for only 44% of the market, while more than 30 other vendors achieved over USD 10 million in revenue. The service fulfilment market grew more than some other areas of BSS/OSS since it is considered to be related to revenue generation. Growth in the service fulfilment market was driven by network evolution towards optical/packet technology, the push towards instant availability for complex service bundles, the need to operate in uncertain and changing business environments, deregulation of broadband mobile in growth markets and the increasing desire to meet the needs of SMEs.
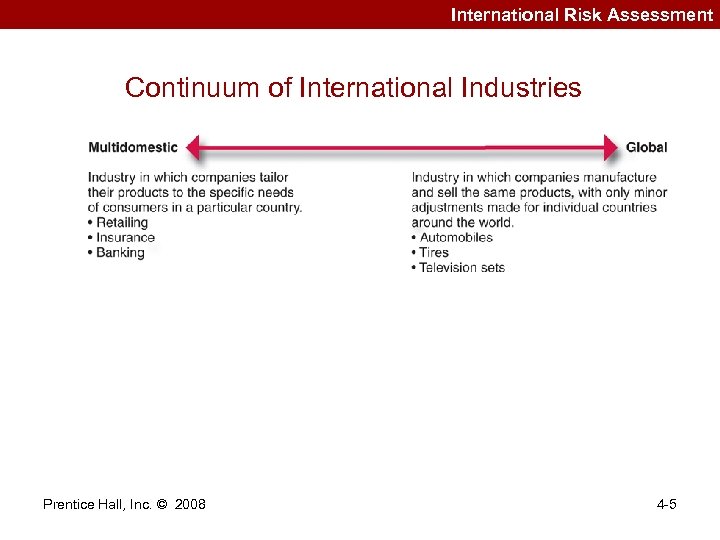 International Risk Assessment Continuum of International Industries Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -5
International Risk Assessment Continuum of International Industries Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -5
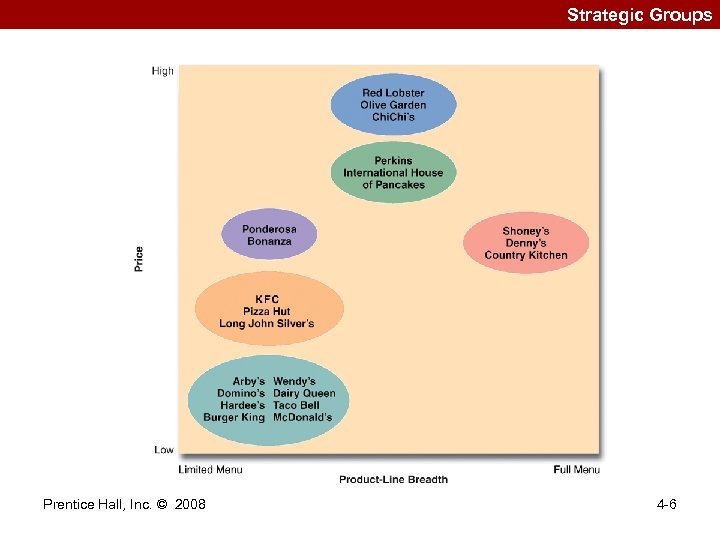 Strategic Groups Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -6
Strategic Groups Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -6
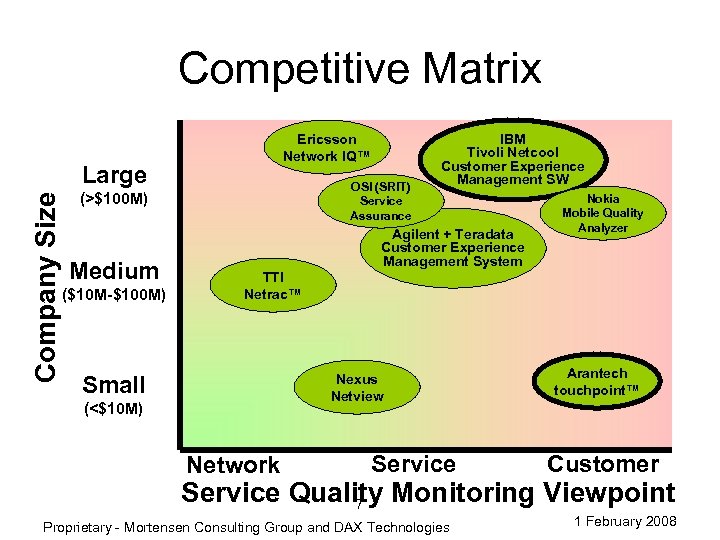 Competitive Matrix Ericsson Network IQ™ Company Size Large OSI (SRIT) Service Assurance (>$100 M) Medium ($10 M-$100 M) IBM Tivoli Netcool Customer Experience Management SW Agilent + Teradata Customer Experience Management System Nokia Mobile Quality Analyzer TTI Netrac™ Nexus Netview Small (<$10 M) Network Service Arantech touchpoint™ Customer Service Quality Monitoring Viewpoint 7 Proprietary - Mortensen Consulting Group and DAX Technologies 1 February 2008
Competitive Matrix Ericsson Network IQ™ Company Size Large OSI (SRIT) Service Assurance (>$100 M) Medium ($10 M-$100 M) IBM Tivoli Netcool Customer Experience Management SW Agilent + Teradata Customer Experience Management System Nokia Mobile Quality Analyzer TTI Netrac™ Nexus Netview Small (<$10 M) Network Service Arantech touchpoint™ Customer Service Quality Monitoring Viewpoint 7 Proprietary - Mortensen Consulting Group and DAX Technologies 1 February 2008
 Example of Strategic Positioning Chart: Gartner Magic Quadrant 8
Example of Strategic Positioning Chart: Gartner Magic Quadrant 8
 Strategic Types General Types of Strategies – • Defenders – hold on; cost & market share • Prospectors – create; innovation • Analyzers – portfolio; large companies • Reactors – watch what happens, try to react quickly and effectively 4 -9
Strategic Types General Types of Strategies – • Defenders – hold on; cost & market share • Prospectors – create; innovation • Analyzers – portfolio; large companies • Reactors – watch what happens, try to react quickly and effectively 4 -9
 Competitive Intelligence is often called business intelligence Gathering information on a company’s competitors • Product/offering – features, functionality, pricing, targets, etc. • Company – size, profitability, margins, target markets, apparent strategy, etc. Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -10
Competitive Intelligence is often called business intelligence Gathering information on a company’s competitors • Product/offering – features, functionality, pricing, targets, etc. • Company – size, profitability, margins, target markets, apparent strategy, etc. Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -10
 Forecasting Techniques - • Extrapolation – from the past to the future • Brainstorming – informed people mapping out possibilities • Expert opinion – buy reports or commission a study • Delphi technique – structured polling technique; ‘The Wisdom of Crowds” • Statistical modeling – projecting past patterns into the future • Scenario planning – a formal technique for mapping out futures, of various probabilities 4 -11
Forecasting Techniques - • Extrapolation – from the past to the future • Brainstorming – informed people mapping out possibilities • Expert opinion – buy reports or commission a study • Delphi technique – structured polling technique; ‘The Wisdom of Crowds” • Statistical modeling – projecting past patterns into the future • Scenario planning – a formal technique for mapping out futures, of various probabilities 4 -11
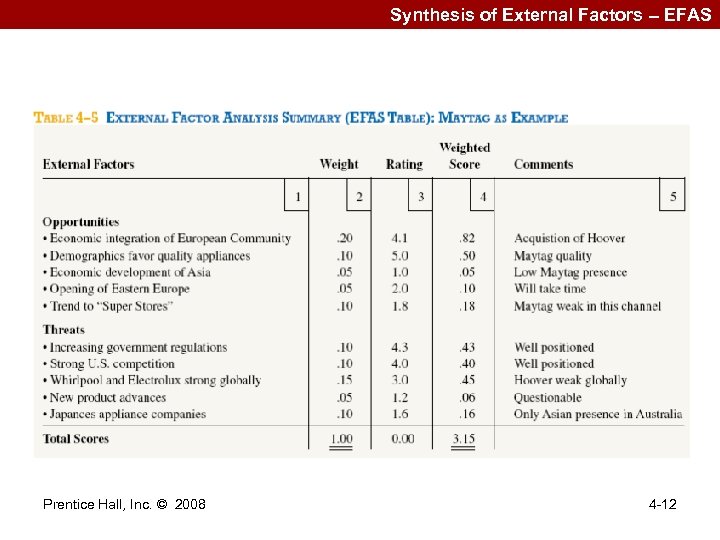 Synthesis of External Factors -- EFAS Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -12
Synthesis of External Factors -- EFAS Prentice Hall, Inc. © 2008 4 -12
 CHAPTER 5 Internal Scanning: Organizational Analysis STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT & BUSINESS POLICY 13 TH EDITION THOMAS L. WHEELEN J. DAVID HUNGER 5 -13
CHAPTER 5 Internal Scanning: Organizational Analysis STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT & BUSINESS POLICY 13 TH EDITION THOMAS L. WHEELEN J. DAVID HUNGER 5 -13
 Resource-Based Approach to Organizational Analysis Internal strategic factors -–Critical strengths and weaknesses that are likely to determine if the firm will be able to take advantage of opportunities while avoiding threats • Resources • Capabilities • Competency • Core competency • Distinctive competency 5 -14
Resource-Based Approach to Organizational Analysis Internal strategic factors -–Critical strengths and weaknesses that are likely to determine if the firm will be able to take advantage of opportunities while avoiding threats • Resources • Capabilities • Competency • Core competency • Distinctive competency 5 -14
 Core and Distinctive Competencies VRIO Framework -–Value –Rareness –Imitability –Organization 5 -15
Core and Distinctive Competencies VRIO Framework -–Value –Rareness –Imitability –Organization 5 -15
 Resource-Based Approach to Organizational Analysis 5 -Step Approach Strategy Analysis -1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify and classify resources Combine strengths into capabilities Appraise profit potential of capabilities Select strategy that best exploits Identify resource gaps invest in weaknesses 5 -16
Resource-Based Approach to Organizational Analysis 5 -Step Approach Strategy Analysis -1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Identify and classify resources Combine strengths into capabilities Appraise profit potential of capabilities Select strategy that best exploits Identify resource gaps invest in weaknesses 5 -16
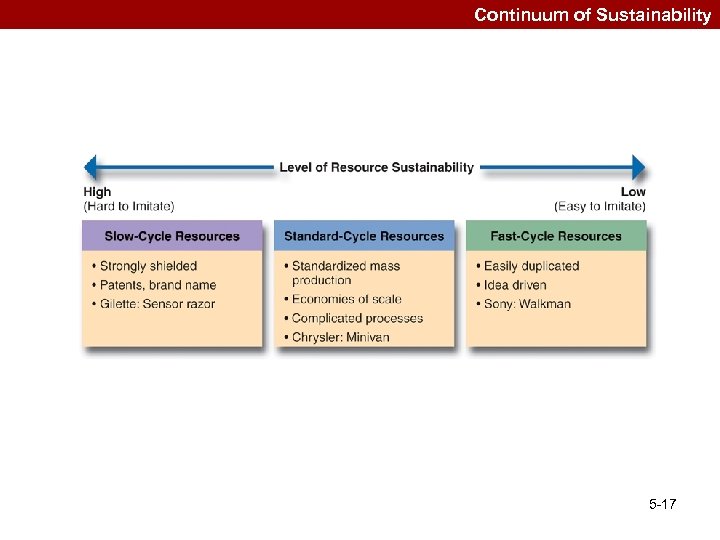 Continuum of Sustainability 5 -17
Continuum of Sustainability 5 -17
 Sustainability of Advantage Imitability -–Rate at which a firm’s underlying resources and capabilities can be duplicated by others Durability -–Rate at which a firm’s underlying resources and capabilities depreciate or become obsolete 5 -18
Sustainability of Advantage Imitability -–Rate at which a firm’s underlying resources and capabilities can be duplicated by others Durability -–Rate at which a firm’s underlying resources and capabilities depreciate or become obsolete 5 -18
 Sustainability of Advantage Core Competency can be imitated -–Transparency –Transferability –Replicability 5 -19
Sustainability of Advantage Core Competency can be imitated -–Transparency –Transferability –Replicability 5 -19
 Business Models BUSINESS MODEL: Company’s method for making money in the current business environment. 5 -20
Business Models BUSINESS MODEL: Company’s method for making money in the current business environment. 5 -20
 Business Models Types of Business Models -–Customer Solutions Model –Profit Pyramid Model –Multi-Component System/Installed Base Model –Advertising Model –Switchboard Model 5 -21
Business Models Types of Business Models -–Customer Solutions Model –Profit Pyramid Model –Multi-Component System/Installed Base Model –Advertising Model –Switchboard Model 5 -21
 Business Models Types of Models -–Time Model –Efficiency Model –Blockbuster Model –Profit Multiplier Model –Entrepreneurial Model –De Facto Standard Model 5 -22
Business Models Types of Models -–Time Model –Efficiency Model –Blockbuster Model –Profit Multiplier Model –Entrepreneurial Model –De Facto Standard Model 5 -22
 Value-Chain Analysis Linked set of value-creating activities beginning with basic raw material and ending with distributors getting final goods into hands of customers Typical Value Chain for a Manufactured Product 5 -23
Value-Chain Analysis Linked set of value-creating activities beginning with basic raw material and ending with distributors getting final goods into hands of customers Typical Value Chain for a Manufactured Product 5 -23
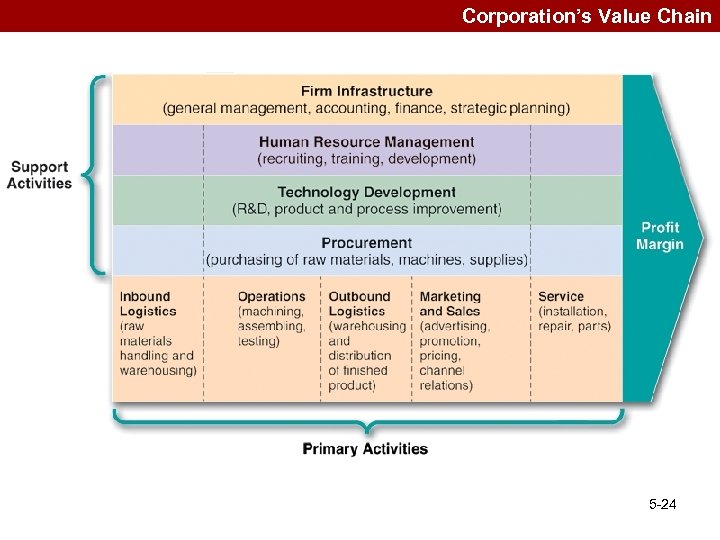 Corporation’s Value Chain 5 -24
Corporation’s Value Chain 5 -24
 Scanning Functional Resources & Capabilities Basic Organizational Structures -–Simple structure –Functional structure –Divisional structure –Strategic business units (SBU’s) –Conglomerate structure 5 -25
Scanning Functional Resources & Capabilities Basic Organizational Structures -–Simple structure –Functional structure –Divisional structure –Strategic business units (SBU’s) –Conglomerate structure 5 -25
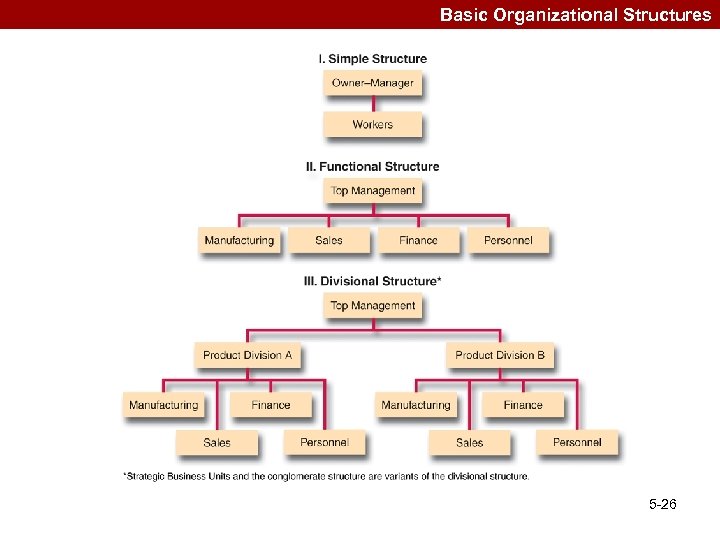 Basic Organizational Structures 5 -26
Basic Organizational Structures 5 -26
 Corporate Culture Collection of beliefs, expectations, and values learned and shared by a corporation’s members and transmitted from one generation of employees to another 5 -27
Corporate Culture Collection of beliefs, expectations, and values learned and shared by a corporation’s members and transmitted from one generation of employees to another 5 -27
 Strategic Marketing Issues –Market Position & Segmentation –Marketing Mix –Product Life Cycle –Brand & Corporate Reputation 5 -28
Strategic Marketing Issues –Market Position & Segmentation –Marketing Mix –Product Life Cycle –Brand & Corporate Reputation 5 -28
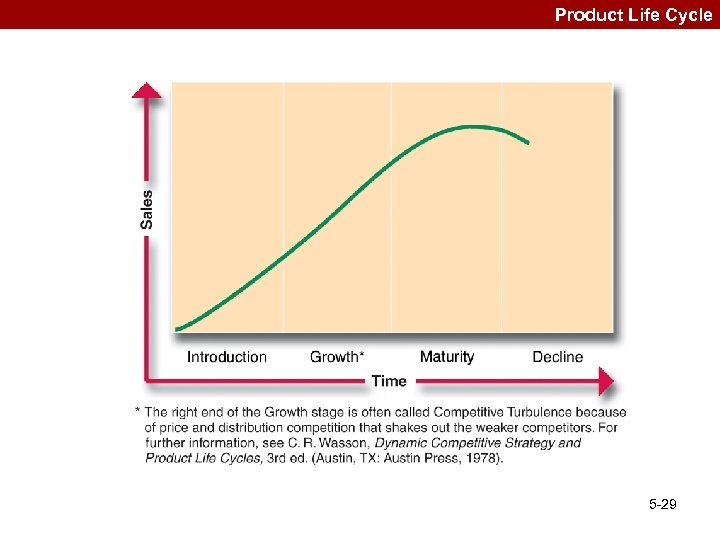 Product Life Cycle 5 -29
Product Life Cycle 5 -29
 Strategic Financial Issues –Financial leverage –Capital budgeting 5 -30
Strategic Financial Issues –Financial leverage –Capital budgeting 5 -30
 Strategic Research & Development Issues –R&D Intensity –Technological Competence –Technology Transfer 5 -31
Strategic Research & Development Issues –R&D Intensity –Technological Competence –Technology Transfer 5 -31
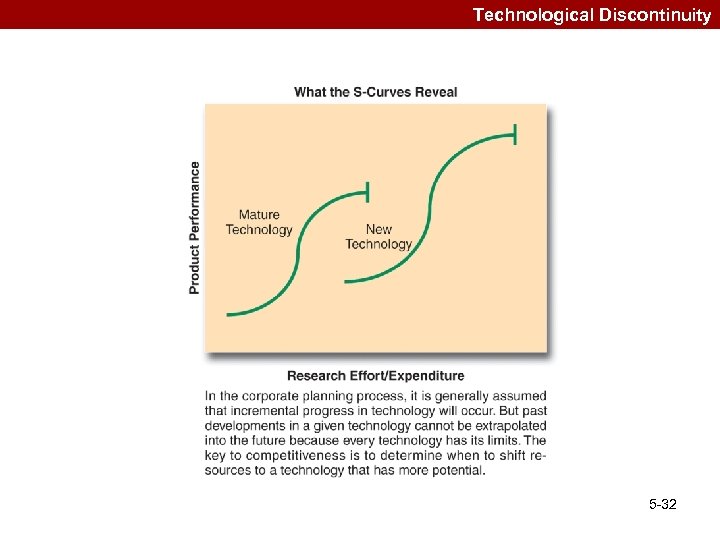 Technological Discontinuity 5 -32
Technological Discontinuity 5 -32
 Strategic Human Resource Management Issues Human Resources Management –Increasing use of teams –Union relations –Temporary workers –Quality of work life –Human diversity 5 -33
Strategic Human Resource Management Issues Human Resources Management –Increasing use of teams –Union relations –Temporary workers –Quality of work life –Human diversity 5 -33
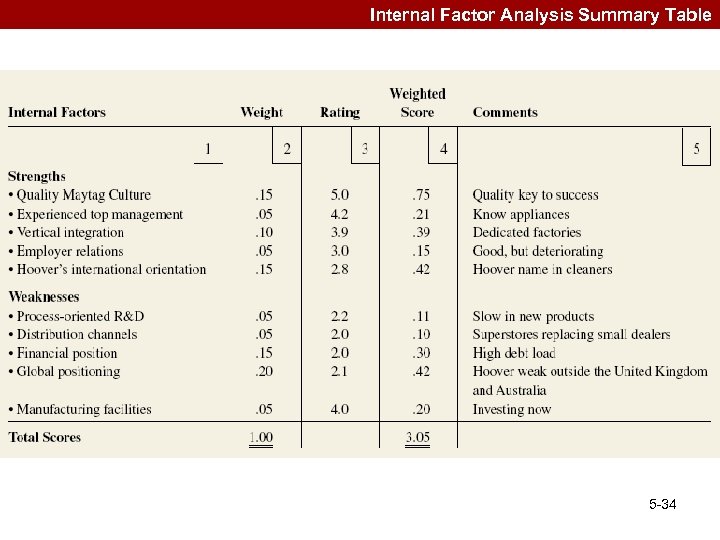 Internal Factor Analysis Summary Table 5 -34
Internal Factor Analysis Summary Table 5 -34


