a6cd3342e434bbac756c5d81a432f24e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 CHAPTER 4 Demand Management, Order Management, and Customer Service
CHAPTER 4 Demand Management, Order Management, and Customer Service
 Learning Objectives F To understand how a firm processes incoming orders F To understand the importance of customer service to a firm’s marketing activities F To relate the role of logistics in the customer service area © 2008 Prentice Hall 2
Learning Objectives F To understand how a firm processes incoming orders F To understand the importance of customer service to a firm’s marketing activities F To relate the role of logistics in the customer service area © 2008 Prentice Hall 2
 Learning Objectives F To examine why customer service standards should be specific and measurable F To describe how a customer service program is established and maintained © 2008 Prentice Hall 3
Learning Objectives F To examine why customer service standards should be specific and measurable F To describe how a customer service program is established and maintained © 2008 Prentice Hall 3
 Order Management and Customer Service F Key Terms F Key – Customer service – Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) – Load planning – Order cycle Terms – Order delivery – Order entry – Order handling – Order management © 2008 Prentice Hall 4
Order Management and Customer Service F Key Terms F Key – Customer service – Efficient Consumer Response (ECR) – Load planning – Order cycle Terms – Order delivery – Order entry – Order handling – Order management © 2008 Prentice Hall 4
 Order Management and Customer Service F Key Terms – Order picking and assembly – Order processing – Order transmittal Terms – Quick Response (QR) – Replenishment cycle © 2008 Prentice Hall 5
Order Management and Customer Service F Key Terms – Order picking and assembly – Order processing – Order transmittal Terms – Quick Response (QR) – Replenishment cycle © 2008 Prentice Hall 5
 Order Management F Order management is the activities that take place in the period between the time a firm receives an order and the time a warehouse is notified to ship the goods to fill that order – – – Order planning-connected to sales forecasting Order transmittal Order processing Order picking and assembly Order delivery © 2008 Prentice Hall 6
Order Management F Order management is the activities that take place in the period between the time a firm receives an order and the time a warehouse is notified to ship the goods to fill that order – – – Order planning-connected to sales forecasting Order transmittal Order processing Order picking and assembly Order delivery © 2008 Prentice Hall 6
 Order Management F Order cycle defined by the seller: time from when an order is received to when the goods arrive at the customer’s dock F Order cycle defined by the buyer: time from when an order is placed to when the goods are received. Also called replenishment cycle – – Getting shorter More precise delivery times Customer can track orders Quality is important and is benchmarked © 2008 Prentice Hall 7
Order Management F Order cycle defined by the seller: time from when an order is received to when the goods arrive at the customer’s dock F Order cycle defined by the buyer: time from when an order is placed to when the goods are received. Also called replenishment cycle – – Getting shorter More precise delivery times Customer can track orders Quality is important and is benchmarked © 2008 Prentice Hall 7
 Order Management F Order planning – Needs an efficient order handling system to prevent bunching u Methods to reduce bunching – Use of field salespeople – Use of phone salespeople – Price discounts to customers placing regular orders © 2008 Prentice Hall 8
Order Management F Order planning – Needs an efficient order handling system to prevent bunching u Methods to reduce bunching – Use of field salespeople – Use of phone salespeople – Price discounts to customers placing regular orders © 2008 Prentice Hall 8
 Order Management F Order transmittal is the series of events that occur between the time a customer places or sends an order and the time the seller receives the order – Methods of order transmittal u Phone u FAX u Mail u Scanning bar codes-electronic submission u POS registers u Internet © 2008 Prentice Hall 9
Order Management F Order transmittal is the series of events that occur between the time a customer places or sends an order and the time the seller receives the order – Methods of order transmittal u Phone u FAX u Mail u Scanning bar codes-electronic submission u POS registers u Internet © 2008 Prentice Hall 9
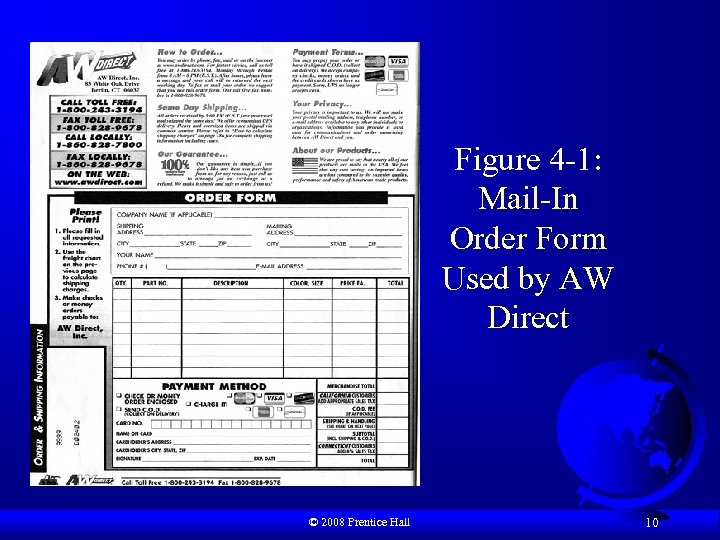 Figure 4 -1: Mail-In Order Form Used by AW Direct © 2008 Prentice Hall 10
Figure 4 -1: Mail-In Order Form Used by AW Direct © 2008 Prentice Hall 10
 Order Management F Order processing includes: – Checking for completeness and accuracy – A customer credit check – Order entry into the computer system – Marketing department credits salesperson – Accounting department records transaction – Inventory department locates nearest warehouse to customer and advises them to pick the order – Transportation department arranges for shipment © 2008 Prentice Hall 11
Order Management F Order processing includes: – Checking for completeness and accuracy – A customer credit check – Order entry into the computer system – Marketing department credits salesperson – Accounting department records transaction – Inventory department locates nearest warehouse to customer and advises them to pick the order – Transportation department arranges for shipment © 2008 Prentice Hall 11
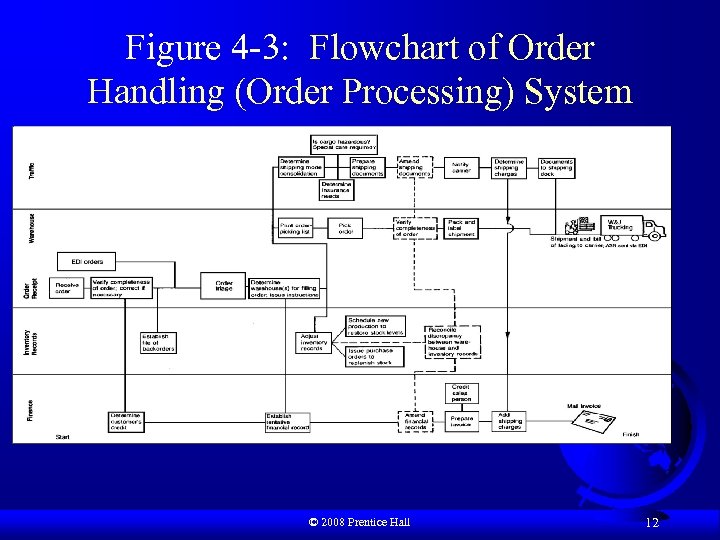 Figure 4 -3: Flowchart of Order Handling (Order Processing) System © 2008 Prentice Hall 12
Figure 4 -3: Flowchart of Order Handling (Order Processing) System © 2008 Prentice Hall 12
 Order Management F Order processing – If there is a stockout u Notify the customer as soon as possible of stockout u Notify when shipment will occur u Give the customer the option of accepting in-stock, similar products – Export orders u Need a letter of credit u International freight forwarders prepare documents and arrange shipment © 2008 Prentice Hall 13
Order Management F Order processing – If there is a stockout u Notify the customer as soon as possible of stockout u Notify when shipment will occur u Give the customer the option of accepting in-stock, similar products – Export orders u Need a letter of credit u International freight forwarders prepare documents and arrange shipment © 2008 Prentice Hall 13
 Order Management F Order picking and assembly includes – Notifying the warehouse to assemble a given order – Providing an order picking list, indicating items and order of pick to a warehouse employee – Checking picked orders for accuracy – Stockout information sent to order handling department so that documents can be adjusted – Packing list enclosed with order including employee initials of person who packed order © 2008 Prentice Hall 14
Order Management F Order picking and assembly includes – Notifying the warehouse to assemble a given order – Providing an order picking list, indicating items and order of pick to a warehouse employee – Checking picked orders for accuracy – Stockout information sent to order handling department so that documents can be adjusted – Packing list enclosed with order including employee initials of person who packed order © 2008 Prentice Hall 14
 Order Management F Order delivery is the time from when a carrier picks up the shipment until it is delivered to the customer’s receiving dock – Load planning is the arrangement of goods within the trailer or container – Carriers establish their own service standards – Some customers pick up their orders © 2008 Prentice Hall 15
Order Management F Order delivery is the time from when a carrier picks up the shipment until it is delivered to the customer’s receiving dock – Load planning is the arrangement of goods within the trailer or container – Carriers establish their own service standards – Some customers pick up their orders © 2008 Prentice Hall 15
 Order Management F Importance of the order cycle – Short cycle time used as a marketing and sales tool – Monitoring the order cycle can increase firm efficiency – Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)/Quick Response (QR) u Used in grocery industry and by mass merchandisers u POS data used to trigger order u Keyed to more orderly, regular flow of product, smaller inventory © 2008 Prentice Hall 16
Order Management F Importance of the order cycle – Short cycle time used as a marketing and sales tool – Monitoring the order cycle can increase firm efficiency – Efficient Consumer Response (ECR)/Quick Response (QR) u Used in grocery industry and by mass merchandisers u POS data used to trigger order u Keyed to more orderly, regular flow of product, smaller inventory © 2008 Prentice Hall 16
 Customer Service F Customer service is a collection of activities performed in a way that keeps customers happy and creates in the customer’s mind the perception of an organization that is easy to do business with F Customer service is much more difficult for competitors to imitate than price cuts or other competitive strategies © 2008 Prentice Hall 17
Customer Service F Customer service is a collection of activities performed in a way that keeps customers happy and creates in the customer’s mind the perception of an organization that is easy to do business with F Customer service is much more difficult for competitors to imitate than price cuts or other competitive strategies © 2008 Prentice Hall 17
 Customer Service F Value-added activities provided by customer service include: – Placing bar code labels on cartons – Arranging a carton, pallet, or truck in the sequence the customer would like to unload it – Shrink-wrapping – Inserting documents into cartons – Blending products – Adding price tags – Adding graphics for export goods – Assembling kits © 2008 Prentice Hall 18
Customer Service F Value-added activities provided by customer service include: – Placing bar code labels on cartons – Arranging a carton, pallet, or truck in the sequence the customer would like to unload it – Shrink-wrapping – Inserting documents into cartons – Blending products – Adding price tags – Adding graphics for export goods – Assembling kits © 2008 Prentice Hall 18
 Customer Service F Establishing Objectives – Specific – Measurable – Achievable – Consistent with broader firm goals – Must consider competitor’s objectives – Provide guidance to operating personnel © 2008 Prentice Hall 19
Customer Service F Establishing Objectives – Specific – Measurable – Achievable – Consistent with broader firm goals – Must consider competitor’s objectives – Provide guidance to operating personnel © 2008 Prentice Hall 19
 Customer Service F Returned Products – New flow of products are set up – New infrastructure is required – Goods and materials are returned for various reasons – Grocery industry uses reclamation centers for returns © 2008 Prentice Hall 20
Customer Service F Returned Products – New flow of products are set up – New infrastructure is required – Goods and materials are returned for various reasons – Grocery industry uses reclamation centers for returns © 2008 Prentice Hall 20
 Role of Logistics in Establishing Customer Service Levels F Advisor to marketing F Establishing a customer service program – Ask the customer what is important to them – Investigate the service offered by competitors – Consider the cost of alternative service programs – Analyze the information and write the objectives F Using the Internet to improve customer service © 2008 Prentice Hall 21
Role of Logistics in Establishing Customer Service Levels F Advisor to marketing F Establishing a customer service program – Ask the customer what is important to them – Investigate the service offered by competitors – Consider the cost of alternative service programs – Analyze the information and write the objectives F Using the Internet to improve customer service © 2008 Prentice Hall 21
 Measuring and Controlling Customer Service F Performance F Audit model credit memos © 2008 Prentice Hall 22
Measuring and Controlling Customer Service F Performance F Audit model credit memos © 2008 Prentice Hall 22
 Meeting Customer Demands F Control the process – Firms demanding higher levels of customer service u With reliable service, the firm can maintain lower inventory levels u Resellers monitor vendor quality looking for those with unacceptable quality levels u Process is often dehumanized; service can make it more personal © 2008 Prentice Hall 23
Meeting Customer Demands F Control the process – Firms demanding higher levels of customer service u With reliable service, the firm can maintain lower inventory levels u Resellers monitor vendor quality looking for those with unacceptable quality levels u Process is often dehumanized; service can make it more personal © 2008 Prentice Hall 23


