8cabd79e4c9bb724cd0ba1be66ce5f4d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Chapter 38 Energy Prices Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter 38 Energy Prices Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2012 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Outline • • • Historical View OPEC Why Prices Change So Fast? What Will The Future Hold? Kick It Up A Notch Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -2 1 -2
Chapter Outline • • • Historical View OPEC Why Prices Change So Fast? What Will The Future Hold? Kick It Up A Notch Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -2 1 -2
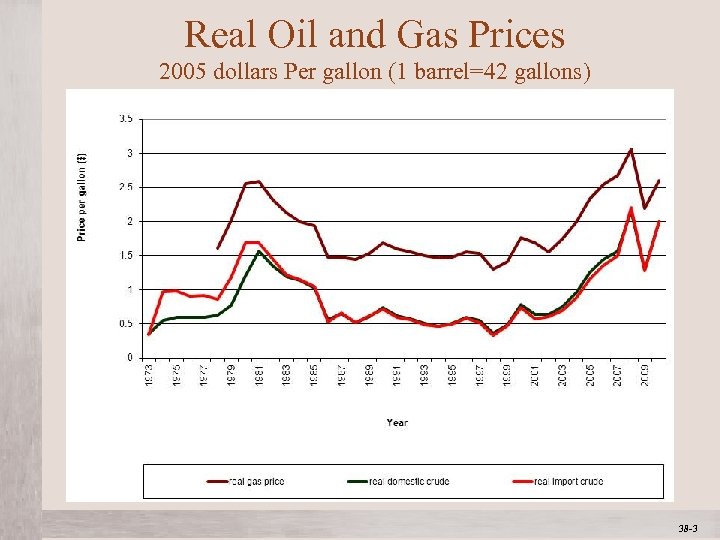 Real Oil and Gas Prices 2005 dollars Per gallon (1 barrel=42 gallons) Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -3 1 -3
Real Oil and Gas Prices 2005 dollars Per gallon (1 barrel=42 gallons) Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -3 1 -3
 Historical Events Relating to Oil and Gas Prices • 1972 Arab-Israeli War • US support for Israel prompted an embargo by Arab oil producers against the US and Europe. This led to a significant increase in crude oil prices. • 1979 Iranian Revolution • Iran’s Islamic revolution led to instability in the Persian Gulf. This led to a significant increase in crude oil prices. • 1980’s • Rapid increases in profits led to significant discoveries of oil in Mexico and the North Sea • 1980 -1988 Iran-Iraq War • The war led to increased production by both parties as each needed to fund their war effort. This caused a precipitous fall in crude oil prices. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -4 1 -4
Historical Events Relating to Oil and Gas Prices • 1972 Arab-Israeli War • US support for Israel prompted an embargo by Arab oil producers against the US and Europe. This led to a significant increase in crude oil prices. • 1979 Iranian Revolution • Iran’s Islamic revolution led to instability in the Persian Gulf. This led to a significant increase in crude oil prices. • 1980’s • Rapid increases in profits led to significant discoveries of oil in Mexico and the North Sea • 1980 -1988 Iran-Iraq War • The war led to increased production by both parties as each needed to fund their war effort. This caused a precipitous fall in crude oil prices. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -4 1 -4
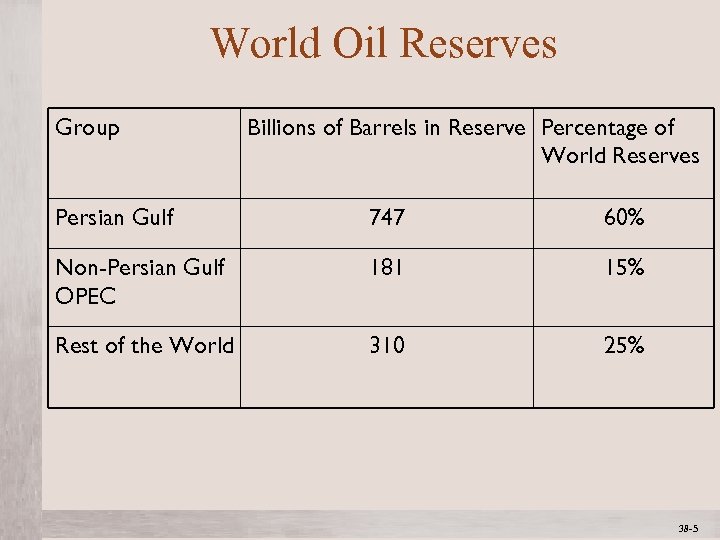 World Oil Reserves Group Billions of Barrels in Reserve Percentage of World Reserves Persian Gulf 747 60% Non-Persian Gulf OPEC 181 15% Rest of the World 310 25% Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -5 1 -5
World Oil Reserves Group Billions of Barrels in Reserve Percentage of World Reserves Persian Gulf 747 60% Non-Persian Gulf OPEC 181 15% Rest of the World 310 25% Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -5 1 -5
 OPEC • The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) • Algeria, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela • OPEC began as a cartel. • A cartel is an organization of individual competitors that join to form as a single monopolist. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -6 1 -6
OPEC • The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) • Algeria, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Venezuela • OPEC began as a cartel. • A cartel is an organization of individual competitors that join to form as a single monopolist. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -6 1 -6
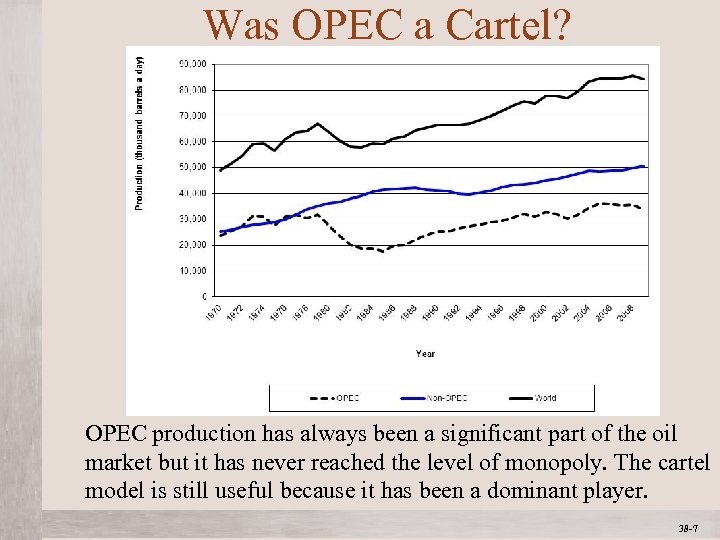 Was OPEC a Cartel? OPEC production has always been a significant part of the oil market but it has never reached the level of monopoly. The cartel model is still useful because it has been a dominant player. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -7 1 -7
Was OPEC a Cartel? OPEC production has always been a significant part of the oil market but it has never reached the level of monopoly. The cartel model is still useful because it has been a dominant player. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -7 1 -7
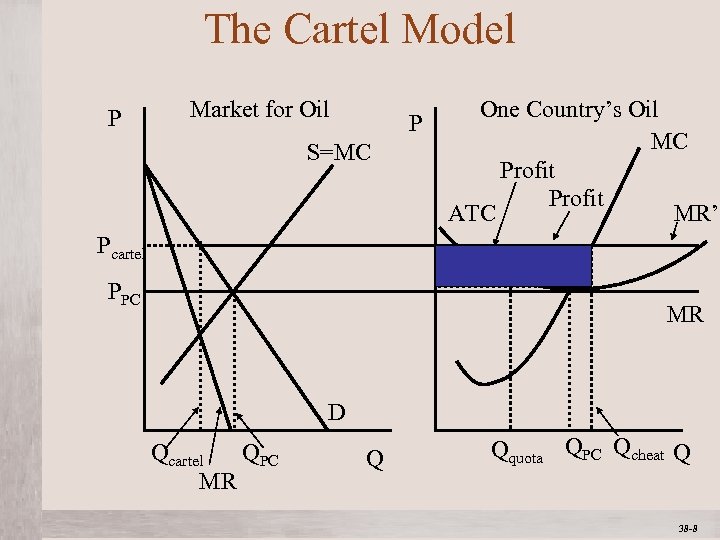 The Cartel Model Market for Oil P P S=MC One Country’s Oil MC Profit ATC MR’ Pcartel PPC MR D Qcartel QPC MR Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Q Qquota QPC Qcheat Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -8 1 -8
The Cartel Model Market for Oil P P S=MC One Country’s Oil MC Profit ATC MR’ Pcartel PPC MR D Qcartel QPC MR Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Q Qquota QPC Qcheat Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -8 1 -8
 Why Oil and Gas Prices Change So Fast • Because expected price is a determinant of supply and demand a world event that causes people to expect a price increase will • Increase current demand (as middlemen and consumers try to buy as much as possible) • Decrease current supply (as middlemen and gas stations try to hold onto their current stocks) • This causes an immediate increase in prices. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -9 1 -9
Why Oil and Gas Prices Change So Fast • Because expected price is a determinant of supply and demand a world event that causes people to expect a price increase will • Increase current demand (as middlemen and consumers try to buy as much as possible) • Decrease current supply (as middlemen and gas stations try to hold onto their current stocks) • This causes an immediate increase in prices. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -9 1 -9
 Historical Events Relating to Oil and Gas Prices • 1990 Iraq Invasion of Kuwait • 1992 -1998 OPEC massive overproduction • 1999 OPEC discipline • 2003 US invasion of Iraq • 2004 -2005 Hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico • 2007 Iran-US tensions; Commodity Speculation • 2008 Global Financial Crisis Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -10 1 -10
Historical Events Relating to Oil and Gas Prices • 1990 Iraq Invasion of Kuwait • 1992 -1998 OPEC massive overproduction • 1999 OPEC discipline • 2003 US invasion of Iraq • 2004 -2005 Hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico • 2007 Iran-US tensions; Commodity Speculation • 2008 Global Financial Crisis Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -10 1 -10
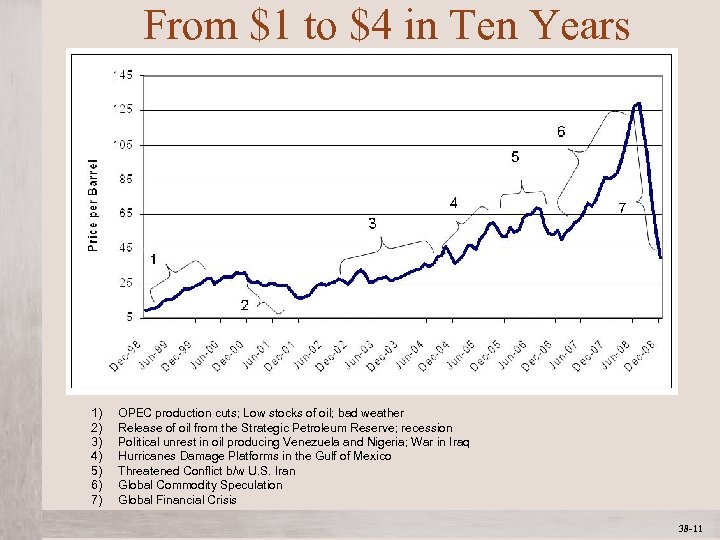 From $1 to $4 in Ten Years 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) OPEC production cuts; Low stocks of oil; bad weather Release of oil from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve; recession Political unrest in oil producing Venezuela and Nigeria; War in Iraq Hurricanes Damage Platforms in the Gulf of Mexico Threatened Conflict b/w U. S. Iran Global Commodity Speculation Global Financial Crisis Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -11 1 -11
From $1 to $4 in Ten Years 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) OPEC production cuts; Low stocks of oil; bad weather Release of oil from the Strategic Petroleum Reserve; recession Political unrest in oil producing Venezuela and Nigeria; War in Iraq Hurricanes Damage Platforms in the Gulf of Mexico Threatened Conflict b/w U. S. Iran Global Commodity Speculation Global Financial Crisis Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -11 1 -11
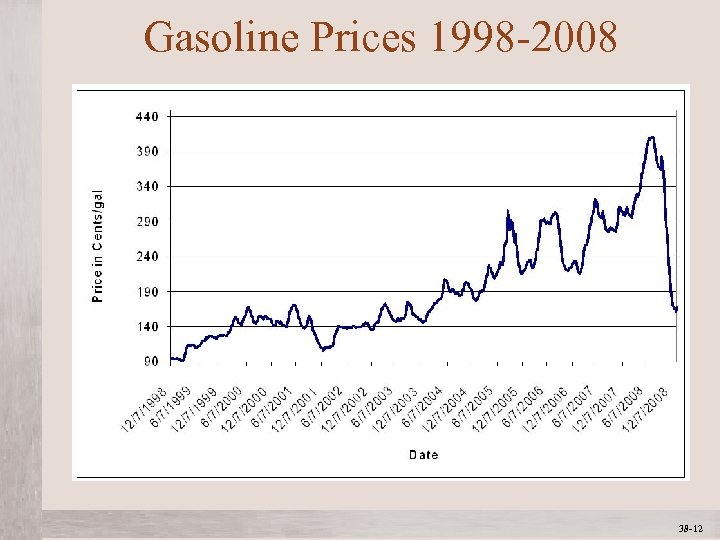 Gasoline Prices 1998 -2008 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -12 1 -12
Gasoline Prices 1998 -2008 Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -12 1 -12
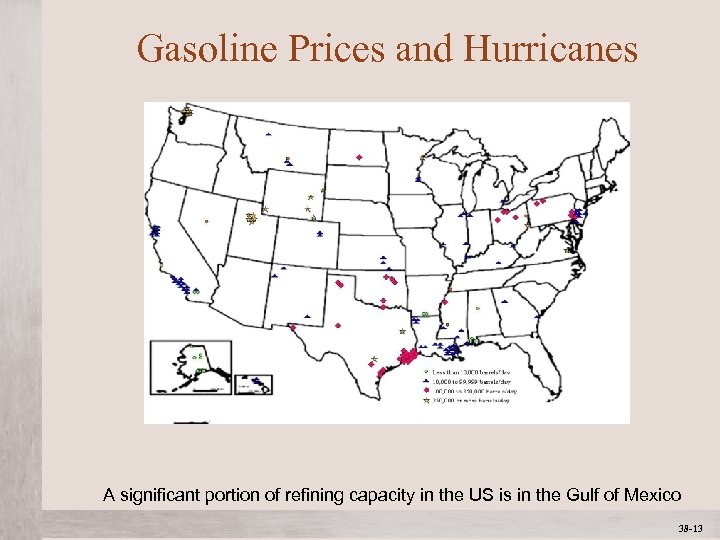 Gasoline Prices and Hurricanes A significant portion of refining capacity in the US is in the Gulf of Mexico Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -13 1 -13
Gasoline Prices and Hurricanes A significant portion of refining capacity in the US is in the Gulf of Mexico Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -13 1 -13
 Electricity • Residential electric power tends to be sold by a regulated monopoly. • It has been a monopoly because of significant barriers to entry. • It has been regulated because prices would be much higher than is socially optimal. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -14 1 -14
Electricity • Residential electric power tends to be sold by a regulated monopoly. • It has been a monopoly because of significant barriers to entry. • It has been regulated because prices would be much higher than is socially optimal. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -14 1 -14
 Types of Monopolies • Simple Monopoly: a monopoly in which marginal costs of production are rising. • Natural Monopoly: a monopoly in which marginal costs of production are falling. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -15 1 -15
Types of Monopolies • Simple Monopoly: a monopoly in which marginal costs of production are rising. • Natural Monopoly: a monopoly in which marginal costs of production are falling. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -15 1 -15
 Monopoly in the Market for Residential Electricity • The market for residential electricity is likely to be a natural monopoly for nuclear power because of the very high fixed costs (transmission lines and the power plant and diminishing marginal costs. ) • The market may be characterized as a simple monopoly or natural monopoly for coal or gas generated electricity. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -16 1 -16
Monopoly in the Market for Residential Electricity • The market for residential electricity is likely to be a natural monopoly for nuclear power because of the very high fixed costs (transmission lines and the power plant and diminishing marginal costs. ) • The market may be characterized as a simple monopoly or natural monopoly for coal or gas generated electricity. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -16 1 -16
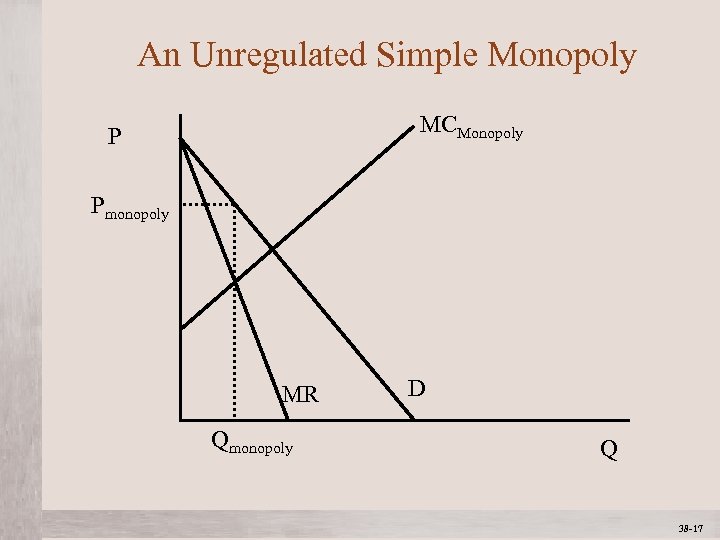 An Unregulated Simple Monopoly MCMonopoly P Pmonopoly MR Qmonopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin D Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -17 1 -17
An Unregulated Simple Monopoly MCMonopoly P Pmonopoly MR Qmonopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin D Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -17 1 -17
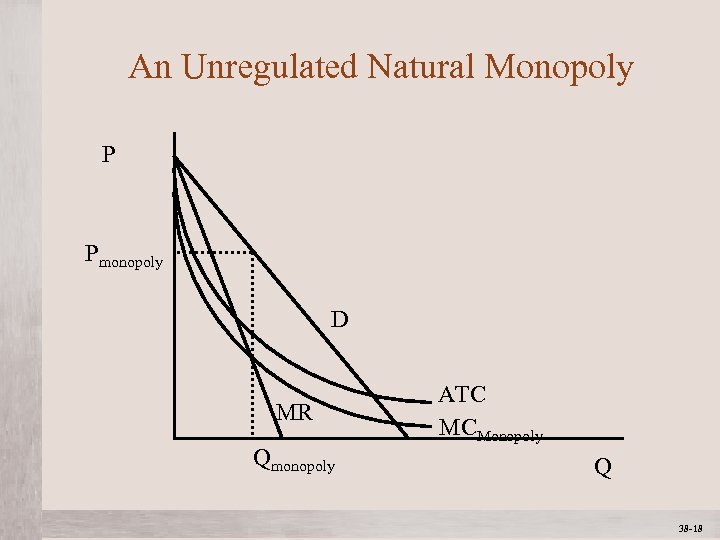 An Unregulated Natural Monopoly P Pmonopoly D MR Qmonopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin ATC MCMonopoly Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -18 1 -18
An Unregulated Natural Monopoly P Pmonopoly D MR Qmonopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin ATC MCMonopoly Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -18 1 -18
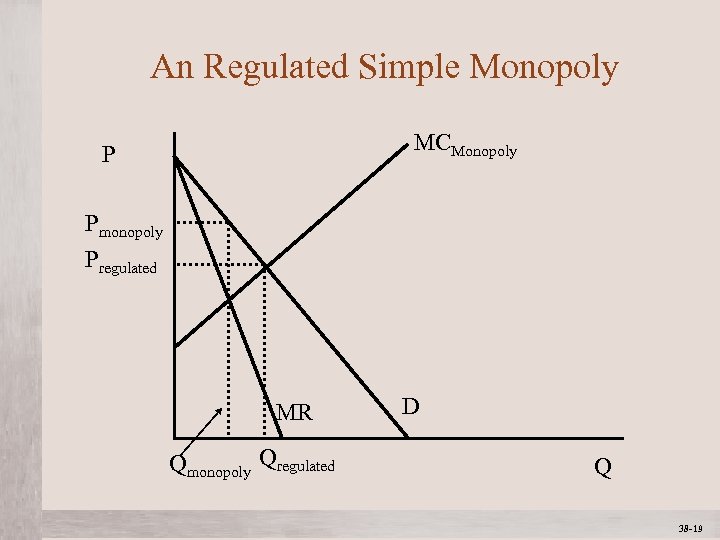 An Regulated Simple Monopoly MCMonopoly P Pmonopoly Pregulated D MR Qmonopoly Qregulated Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -19 1 -19
An Regulated Simple Monopoly MCMonopoly P Pmonopoly Pregulated D MR Qmonopoly Qregulated Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -19 1 -19
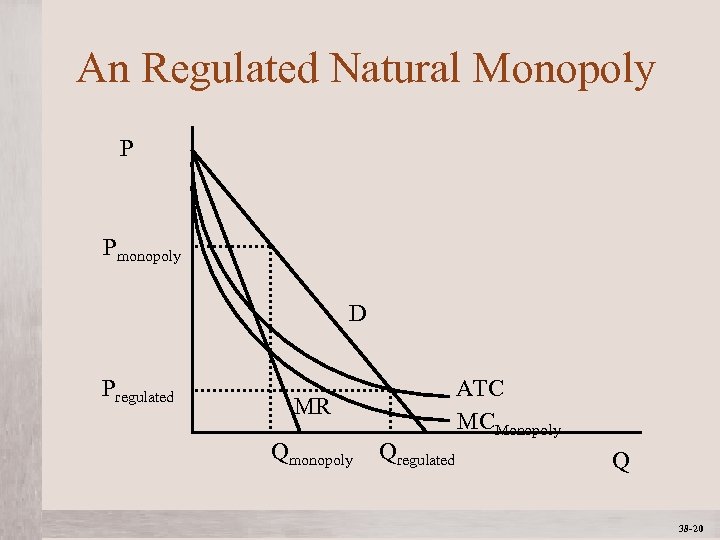 An Regulated Natural Monopoly P Pmonopoly D Pregulated MR Qmonopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Qregulated ATC MCMonopoly Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -20 1 -20
An Regulated Natural Monopoly P Pmonopoly D Pregulated MR Qmonopoly Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Qregulated ATC MCMonopoly Q © 2012 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved 38 -20 1 -20


