3efd19993a44564b0a727b6781b48251.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 CHAPTER 33 INFORMATION AND ADMINISTRATION CAREERS Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
CHAPTER 33 INFORMATION AND ADMINISTRATION CAREERS Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Standards • Standard 4: Self Esteem and Career Exploration: – Plan and demonstrate skills to improve self esteem and make appropriate career choices. • Foundation Standard 11: Information Technology Applications: Health care workers – will use information technology applications required within all career specialties – Will demonstrate use as appropriate to health care applications Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Standards • Standard 4: Self Esteem and Career Exploration: – Plan and demonstrate skills to improve self esteem and make appropriate career choices. • Foundation Standard 11: Information Technology Applications: Health care workers – will use information technology applications required within all career specialties – Will demonstrate use as appropriate to health care applications Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Objectives: 1. Identify terms related to health care information and administration. 2. Specify the role of selected persons within these careers , including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements. 3. Identify 3 personal characteristics needed in an efficient health occupations clerk. 4. Identify at least 5 forms used as part of the medical record. 5. Describe at least 3 methods of payment for health care. Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Objectives: 1. Identify terms related to health care information and administration. 2. Specify the role of selected persons within these careers , including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements. 3. Identify 3 personal characteristics needed in an efficient health occupations clerk. 4. Identify at least 5 forms used as part of the medical record. 5. Describe at least 3 methods of payment for health care. Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Information and Administration Careers • Critical to the quality of care delivered • Health care administration covers a broad spectrum of careers and include: – Health care facility managers – Supervisors – Medical secretaries – Unit coordinators – Medical records personnel http: //www. youtube. com/watch? NR=1&v= B 3 GMy. Z 87 g. MY&feature=endscreen Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Information and Administration Careers • Critical to the quality of care delivered • Health care administration covers a broad spectrum of careers and include: – Health care facility managers – Supervisors – Medical secretaries – Unit coordinators – Medical records personnel http: //www. youtube. com/watch? NR=1&v= B 3 GMy. Z 87 g. MY&feature=endscreen Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Box 33 -1 Information and Administration Careers Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Box 33 -1 Information and Administration Careers Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Heath Service Managers • Manage the facility budget, programs, and personnel • Responsible for relations with other agencies and organizations • Coordinate services, hiring, and training of personnel • Responsible for establishing the policies and procedures of the facility Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Heath Service Managers • Manage the facility budget, programs, and personnel • Responsible for relations with other agencies and organizations • Coordinate services, hiring, and training of personnel • Responsible for establishing the policies and procedures of the facility Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Health Service Managers (Continued) • Education – Health care manager’s with a 4 -year bachelor’s degree usually find positions in small institutions – Master’s or doctoral-level preparation is preferred to work in large facilities – Internship is required by many administrative programs • Licensure is usually required for administrator position in large Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. facilities All rights reserved.
Health Service Managers (Continued) • Education – Health care manager’s with a 4 -year bachelor’s degree usually find positions in small institutions – Master’s or doctoral-level preparation is preferred to work in large facilities – Internship is required by many administrative programs • Licensure is usually required for administrator position in large Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. facilities All rights reserved.
 Support Personnel • Health services clerk or office manager – Has the duties of receptionist, accountant, and assistant • Clerk or manager – Responsible for the smooth operation of the services • Hospital registration staff – Record and manage the admission of clients Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Support Personnel • Health services clerk or office manager – Has the duties of receptionist, accountant, and assistant • Clerk or manager – Responsible for the smooth operation of the services • Hospital registration staff – Record and manage the admission of clients Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Support Personnel (continued) • Medical secretary – Takes dictation, transcribes reports and charts, assists the physician with medical reports, articles, and conference proceedings, and prepares correspondence • Health unit coordinator (HUC) – Performs nonclinical activities such as assembling and maintaining client charts, transcribing physician's orders, and acting as receptionist and secretary on the unit Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Support Personnel (continued) • Medical secretary – Takes dictation, transcribes reports and charts, assists the physician with medical reports, articles, and conference proceedings, and prepares correspondence • Health unit coordinator (HUC) – Performs nonclinical activities such as assembling and maintaining client charts, transcribing physician's orders, and acting as receptionist and secretary on the unit Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 • Medical Records Personnel • Registered records administrator (RRA) – Responsible for management of the information system • Medical transcriptionist – Listens to and types information to provide a permanent record from a variety of audio equipment Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
• Medical Records Personnel • Registered records administrator (RRA) – Responsible for management of the information system • Medical transcriptionist – Listens to and types information to provide a permanent record from a variety of audio equipment Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Medical Records Personnel • Organizes, analyzes, and generates relating to patient records • Most employment is in hospitals • One of the fastest growing occupations http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Kq. WCYY 9 Uu. E Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Medical Records Personnel • Organizes, analyzes, and generates relating to patient records • Most employment is in hospitals • One of the fastest growing occupations http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Kq. WCYY 9 Uu. E Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Medical Records Personnel (continued) • Registered records administrator (RRA) or Health Information Manager (HIM) – Responsible for management of the information system – Education/training • 2 -year college certificate or 4 -year college/university degree • Supervised experience may be required in some programs Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Medical Records Personnel (continued) • Registered records administrator (RRA) or Health Information Manager (HIM) – Responsible for management of the information system – Education/training • 2 -year college certificate or 4 -year college/university degree • Supervised experience may be required in some programs Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Medical Records Personnel (Continued) • Medical transcriptionist (medical stenographer) – Listens to and types information to provide a permanent record from a variety of audio equipment – Training: • Knowledge of medical terminology and computer skills • Some community colleges and vocational schools offer associate degree programs in transcription – Certification is voluntary Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Medical Records Personnel (Continued) • Medical transcriptionist (medical stenographer) – Listens to and types information to provide a permanent record from a variety of audio equipment – Training: • Knowledge of medical terminology and computer skills • Some community colleges and vocational schools offer associate degree programs in transcription – Certification is voluntary Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Health Information and Communication Careers • Health science librarian – Locates and provides information to practicing professionals, researchers, and students – Education • Master’s degree – Certification is available Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Health Information and Communication Careers • Health science librarian – Locates and provides information to practicing professionals, researchers, and students – Education • Master’s degree – Certification is available Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Health Information and Communication Careers (Continued) • Public health educator – Teach new and experienced health personnel • May specialize in fields of practice – Organize and direct health education programs for groups and community needs – Education • Bachelor’s or master’s degree • Standard teacher certificate may be required Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Health Information and Communication Careers (Continued) • Public health educator – Teach new and experienced health personnel • May specialize in fields of practice – Organize and direct health education programs for groups and community needs – Education • Bachelor’s or master’s degree • Standard teacher certificate may be required Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Health Information and Communication Careers (Continued) • Public relations personnel – Plan and conduct programs such as press releases and advertising strategies for the agency – Education • Bachelor’s degree in public relations is preferred • Biomedical photographer – Document life-related health events • Often specialize in one area – Education • 2 to 4 years of college for training in photography and basic sciences • Certification and registration is available Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Health Information and Communication Careers (Continued) • Public relations personnel – Plan and conduct programs such as press releases and advertising strategies for the agency – Education • Bachelor’s degree in public relations is preferred • Biomedical photographer – Document life-related health events • Often specialize in one area – Education • 2 to 4 years of college for training in photography and basic sciences • Certification and registration is available Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Health Information and Communication Careers (Continued) • Medical illustrator – Specialized artist who provides sketches, paintings, drawings, computer images, and three-dimensional models – Education • Completion of program at one of five accredited schools requiring bachelor’s degree for admission Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Health Information and Communication Careers (Continued) • Medical illustrator – Specialized artist who provides sketches, paintings, drawings, computer images, and three-dimensional models – Education • Completion of program at one of five accredited schools requiring bachelor’s degree for admission Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Office Management • Maintaining confidentiality of patient records • Filing • Appointment procedures • Scheduling laboratory tests and other procedures Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Office Management • Maintaining confidentiality of patient records • Filing • Appointment procedures • Scheduling laboratory tests and other procedures Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Records Management • The medical record for a patient is a legal record and contains: – Medical history and physical assessment – Test results – Surgery reports – Notes about patient’s condition and course of treatment – Making sure patients understand forms • Confidential information may not be given to anyone other than those authorized by the patient and health care practitioner Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Records Management • The medical record for a patient is a legal record and contains: – Medical history and physical assessment – Test results – Surgery reports – Notes about patient’s condition and course of treatment – Making sure patients understand forms • Confidential information may not be given to anyone other than those authorized by the patient and health care practitioner Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Records Management (Continued) • Records must be accurate, legible, complete, and organized to provide efficient care – Oral record must be transcribed or written in permanent form Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Records Management (Continued) • Records must be accurate, legible, complete, and organized to provide efficient care – Oral record must be transcribed or written in permanent form Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Box 33 -3 Guidelines for Charting Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Box 33 -3 Guidelines for Charting Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Methods of Payment • Insurance – Payment in advance for services in the event that they are needed – Types of insurance • • Group Private insurance Federal Medicare and Medicaid programs States provide worker’s compensation and disability programs Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Methods of Payment • Insurance – Payment in advance for services in the event that they are needed – Types of insurance • • Group Private insurance Federal Medicare and Medicaid programs States provide worker’s compensation and disability programs Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Methods of Payment • Billing ICD-9 -CM - International Classification of Diseases CPT – Current Procedural Terminology http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=L 6 SDGNL 8 b. OA Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Methods of Payment • Billing ICD-9 -CM - International Classification of Diseases CPT – Current Procedural Terminology http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=L 6 SDGNL 8 b. OA Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Methods of Payment (Continued) • Billing codes – Used to designate the type of treatment and to determine whether coverage is allowed – DRGs (Diagnostic-Related Groups) • Established by the federal government • Determine a usual, reasonable, and customary (URC) fee for services for Medicare recipients Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Methods of Payment (Continued) • Billing codes – Used to designate the type of treatment and to determine whether coverage is allowed – DRGs (Diagnostic-Related Groups) • Established by the federal government • Determine a usual, reasonable, and customary (URC) fee for services for Medicare recipients Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
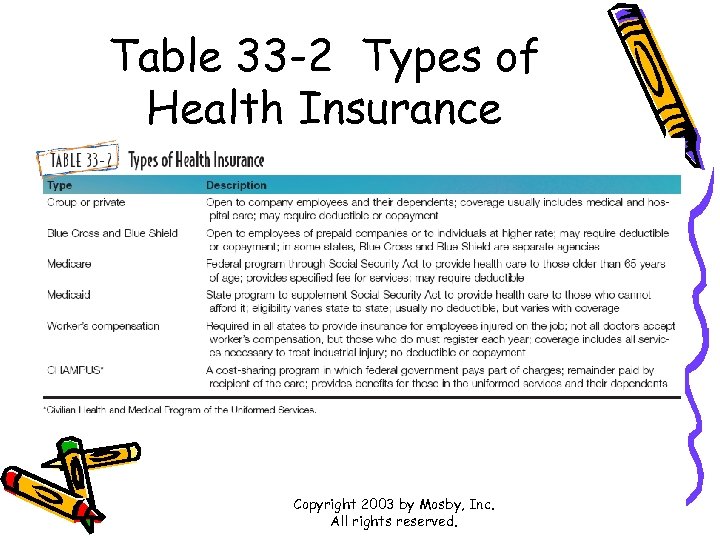 Table 33 -2 Types of Health Insurance Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Table 33 -2 Types of Health Insurance Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Performance Instruction • All patients should be greeted by name and asked to log in their time of arrival – Patient may need help with completion of forms • Use of the telephone – Clerk or receptionist uses the telephone to obtain and give information to patients and other health care professionals • Good communication skills are necessary at all times Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Performance Instruction • All patients should be greeted by name and asked to log in their time of arrival – Patient may need help with completion of forms • Use of the telephone – Clerk or receptionist uses the telephone to obtain and give information to patients and other health care professionals • Good communication skills are necessary at all times Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.


