f67478e735b733de3ad0d1ea18686c05.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply CHAPTER 3 Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Prepared by: Fernando Quijano Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 1 of 46
Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply CHAPTER 3 Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Prepared by: Fernando Quijano Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 1 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Perfectly Competitive Market A market that meets the conditions of (1) many buyers and sellers, (2) all firms selling identical products, and (3) no barriers to new firms entering the market. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 2 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Perfectly Competitive Market A market that meets the conditions of (1) many buyers and sellers, (2) all firms selling identical products, and (3) no barriers to new firms entering the market. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 2 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Demand Schedules and Demand Curves Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Quantity demanded The amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase at a given price. Demand curve A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Market demand The demand by all the consumers of a given good or service. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 3 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Demand Schedules and Demand Curves Demand schedule A table showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Quantity demanded The amount of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to purchase at a given price. Demand curve A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product demanded. Market demand The demand by all the consumers of a given good or service. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 3 of 46
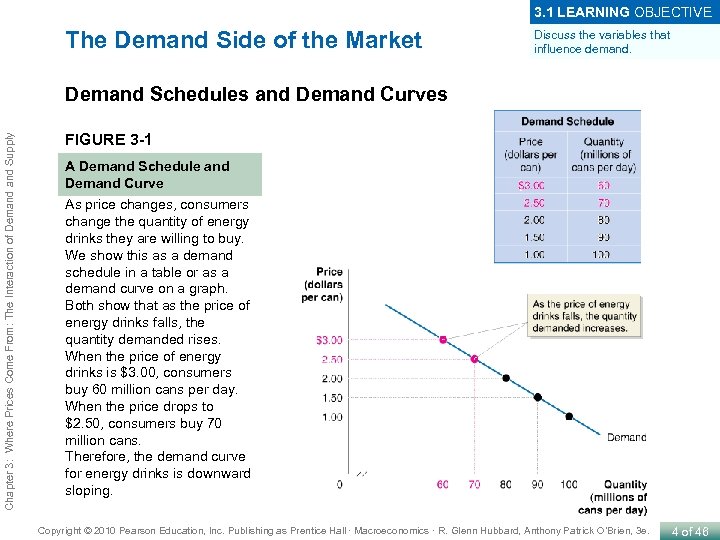 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Demand Schedules and Demand Curves FIGURE 3 -1 A Demand Schedule and Demand Curve As price changes, consumers change the quantity of energy drinks they are willing to buy. We show this as a demand schedule in a table or as a demand curve on a graph. Both show that as the price of energy drinks falls, the quantity demanded rises. When the price of energy drinks is $3. 00, consumers buy 60 million cans per day. When the price drops to $2. 50, consumers buy 70 million cans. Therefore, the demand curve for energy drinks is downward sloping. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 4 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Demand Schedules and Demand Curves FIGURE 3 -1 A Demand Schedule and Demand Curve As price changes, consumers change the quantity of energy drinks they are willing to buy. We show this as a demand schedule in a table or as a demand curve on a graph. Both show that as the price of energy drinks falls, the quantity demanded rises. When the price of energy drinks is $3. 00, consumers buy 60 million cans per day. When the price drops to $2. 50, consumers buy 70 million cans. Therefore, the demand curve for energy drinks is downward sloping. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 4 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Law of Demand Law of demand The rule that, holding everything else constant, when the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded of the product will increase, and when the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded of the product will decrease. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 5 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Law of Demand Law of demand The rule that, holding everything else constant, when the price of a product falls, the quantity demanded of the product will increase, and when the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded of the product will decrease. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 5 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Why does every demand curve slope downward? Substitution effect (S. E. ) The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from a change in price, making the good more or less expensive relative to other goods that are substitutes. Income effect (I. E. ) The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from the effect of a change in the good’s price on consumers’ purchasing power. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 6 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Why does every demand curve slope downward? Substitution effect (S. E. ) The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from a change in price, making the good more or less expensive relative to other goods that are substitutes. Income effect (I. E. ) The change in the quantity demanded of a good that results from the effect of a change in the good’s price on consumers’ purchasing power. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 6 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Holding Everything Else Constant: The Ceteris Paribus Condition Ceteris paribus (“all else equal”) condition The requirement that when analyzing the relationship between two variables—such as price and quantity demanded—other variables must be held constant. A shift of the demand curve is an “increase/decrease in demand”. A movement along the demand curve is an “increase/decrease in the quantity demanded”. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 7 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Holding Everything Else Constant: The Ceteris Paribus Condition Ceteris paribus (“all else equal”) condition The requirement that when analyzing the relationship between two variables—such as price and quantity demanded—other variables must be held constant. A shift of the demand curve is an “increase/decrease in demand”. A movement along the demand curve is an “increase/decrease in the quantity demanded”. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 7 of 46
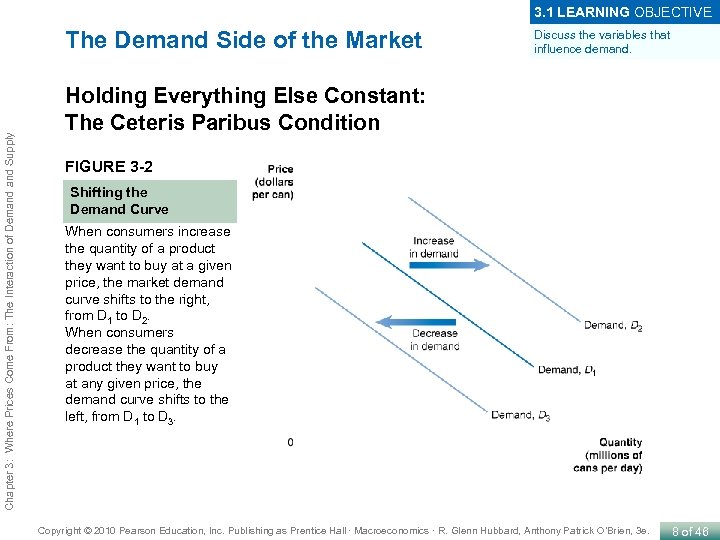 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Holding Everything Else Constant: The Ceteris Paribus Condition FIGURE 3 -2 Shifting the Demand Curve When consumers increase the quantity of a product they want to buy at a given price, the market demand curve shifts to the right, from D 1 to D 2. When consumers decrease the quantity of a product they want to buy at any given price, the demand curve shifts to the left, from D 1 to D 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 8 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Holding Everything Else Constant: The Ceteris Paribus Condition FIGURE 3 -2 Shifting the Demand Curve When consumers increase the quantity of a product they want to buy at a given price, the market demand curve shifts to the right, from D 1 to D 2. When consumers decrease the quantity of a product they want to buy at any given price, the demand curve shifts to the left, from D 1 to D 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 8 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Demand Many variables other than price can influence market demand. • Income Normal good A good for which the demand increases as income rises and decreases as income falls. Inferior good A good for which the demand increases as income falls and decreases as income rises. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 9 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Demand Many variables other than price can influence market demand. • Income Normal good A good for which the demand increases as income rises and decreases as income falls. Inferior good A good for which the demand increases as income falls and decreases as income rises. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 9 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Demand • Prices of related goods Substitutes Goods and services that can be used for the same purpose. Complements Goods and services that are used together. • Tastes Consumers can be influenced by an advertising campaign for a product. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 10 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Demand • Prices of related goods Substitutes Goods and services that can be used for the same purpose. Complements Goods and services that are used together. • Tastes Consumers can be influenced by an advertising campaign for a product. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 10 of 46
 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Demand • Population and demographics Demographics The characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender. • Expected future prices Consumers choose not only which products to buy but also when to buy them. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 11 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Demand • Population and demographics Demographics The characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender. • Expected future prices Consumers choose not only which products to buy but also when to buy them. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 11 of 46
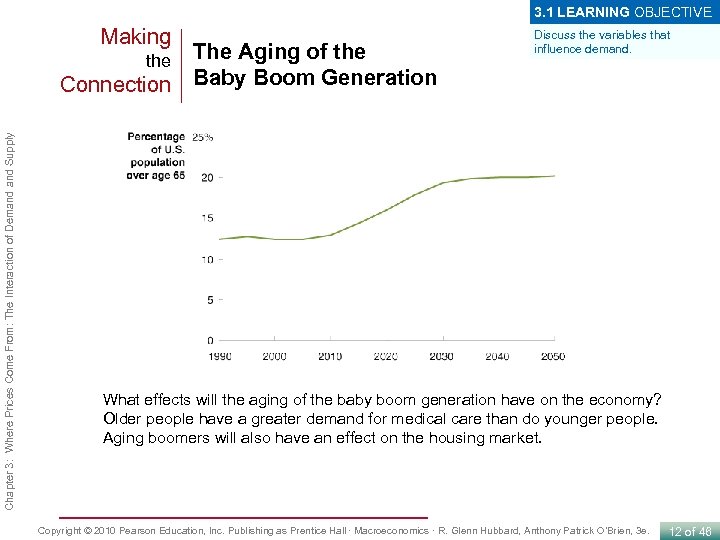 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Making The Aging of the Connection Baby Boom Generation Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply the Discuss the variables that influence demand. What effects will the aging of the baby boom generation have on the economy? Older people have a greater demand for medical care than do younger people. Aging boomers will also have an effect on the housing market. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 12 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE Making The Aging of the Connection Baby Boom Generation Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply the Discuss the variables that influence demand. What effects will the aging of the baby boom generation have on the economy? Older people have a greater demand for medical care than do younger people. Aging boomers will also have an effect on the housing market. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 12 of 46
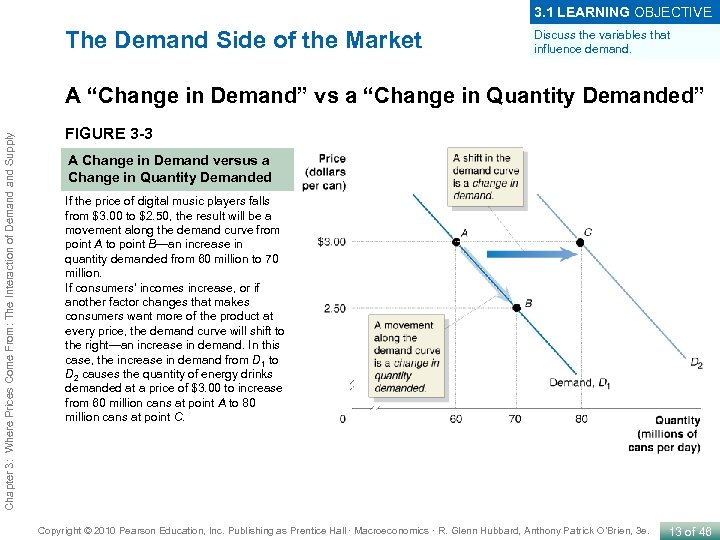 3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply A “Change in Demand” vs a “Change in Quantity Demanded” FIGURE 3 -3 A Change in Demand versus a Change in Quantity Demanded If the price of digital music players falls from $3. 00 to $2. 50, the result will be a movement along the demand curve from point A to point B—an increase in quantity demanded from 60 million to 70 million. If consumers’ incomes increase, or if another factor changes that makes consumers want more of the product at every price, the demand curve will shift to the right—an increase in demand. In this case, the increase in demand from D 1 to D 2 causes the quantity of energy drinks demanded at a price of $3. 00 to increase from 60 million cans at point A to 80 million cans at point C. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 13 of 46
3. 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVE The Demand Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence demand. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply A “Change in Demand” vs a “Change in Quantity Demanded” FIGURE 3 -3 A Change in Demand versus a Change in Quantity Demanded If the price of digital music players falls from $3. 00 to $2. 50, the result will be a movement along the demand curve from point A to point B—an increase in quantity demanded from 60 million to 70 million. If consumers’ incomes increase, or if another factor changes that makes consumers want more of the product at every price, the demand curve will shift to the right—an increase in demand. In this case, the increase in demand from D 1 to D 2 causes the quantity of energy drinks demanded at a price of $3. 00 to increase from 60 million cans at point A to 80 million cans at point C. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 13 of 46
 3. 2 Learning Objective Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Quantity supplied The amount of a good or service that a firm is willing and able to supply at a given price. Supply Schedules and Supply Curves Supply schedule A table that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied. Supply curve A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 14 of 46
3. 2 Learning Objective Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Quantity supplied The amount of a good or service that a firm is willing and able to supply at a given price. Supply Schedules and Supply Curves Supply schedule A table that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied. Supply curve A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 14 of 46
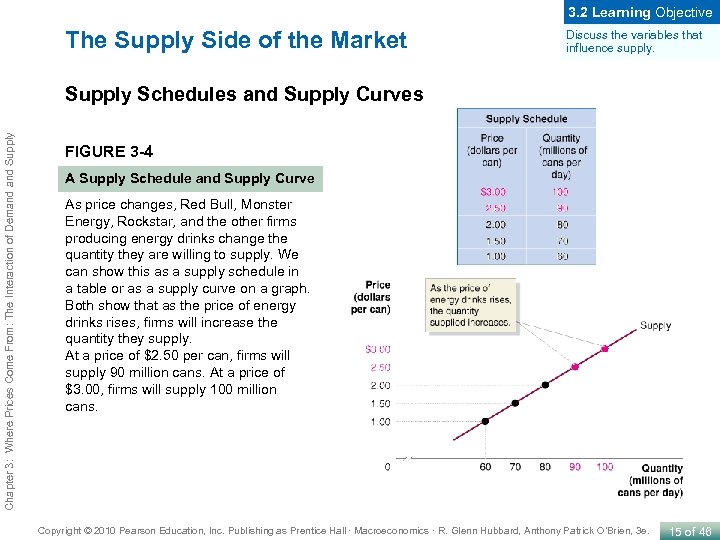 3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Schedules and Supply Curves FIGURE 3 -4 A Supply Schedule and Supply Curve As price changes, Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms producing energy drinks change the quantity they are willing to supply. We can show this as a supply schedule in a table or as a supply curve on a graph. Both show that as the price of energy drinks rises, firms will increase the quantity they supply. At a price of $2. 50 per can, firms will supply 90 million cans. At a price of $3. 00, firms will supply 100 million cans. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 15 of 46
3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Schedules and Supply Curves FIGURE 3 -4 A Supply Schedule and Supply Curve As price changes, Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms producing energy drinks change the quantity they are willing to supply. We can show this as a supply schedule in a table or as a supply curve on a graph. Both show that as the price of energy drinks rises, firms will increase the quantity they supply. At a price of $2. 50 per can, firms will supply 90 million cans. At a price of $3. 00, firms will supply 100 million cans. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 15 of 46
 3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Law of Supply Law of supply The rule that, holding everything else constant, increases in price cause increases in the quantity supplied, and decreases in price cause decreases in the quantity supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 16 of 46
3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Law of Supply Law of supply The rule that, holding everything else constant, increases in price cause increases in the quantity supplied, and decreases in price cause decreases in the quantity supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 16 of 46
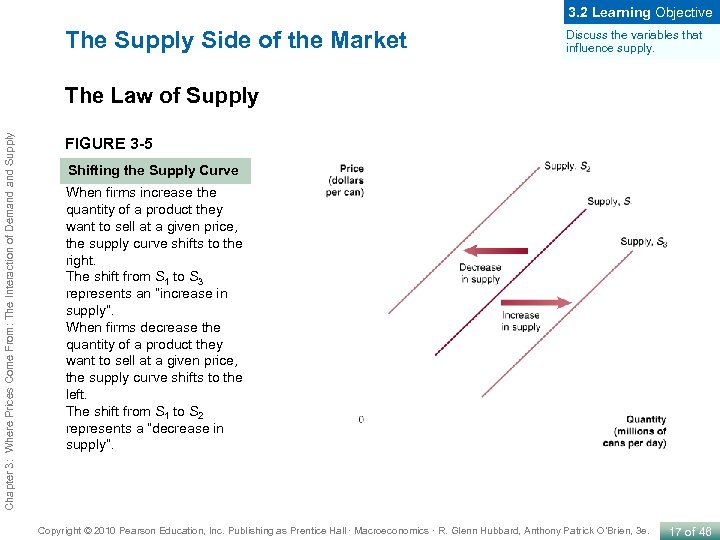 3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Law of Supply FIGURE 3 -5 Shifting the Supply Curve When firms increase the quantity of a product they want to sell at a given price, the supply curve shifts to the right. The shift from S 1 to S 3 represents an “increase in supply”. When firms decrease the quantity of a product they want to sell at a given price, the supply curve shifts to the left. The shift from S 1 to S 2 represents a “decrease in supply”. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 17 of 46
3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Law of Supply FIGURE 3 -5 Shifting the Supply Curve When firms increase the quantity of a product they want to sell at a given price, the supply curve shifts to the right. The shift from S 1 to S 3 represents an “increase in supply”. When firms decrease the quantity of a product they want to sell at a given price, the supply curve shifts to the left. The shift from S 1 to S 2 represents a “decrease in supply”. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 17 of 46
 3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Supply The following are the most important variables that shift market supply: • • Prices of inputs Technological change A positive or negative change in the ability of a firm to produce a given level of output with a given quantity of inputs. • • • Prices of substitutes in production Number of firms in the market Expected future prices Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 18 of 46
3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Variables That Shift Market Supply The following are the most important variables that shift market supply: • • Prices of inputs Technological change A positive or negative change in the ability of a firm to produce a given level of output with a given quantity of inputs. • • • Prices of substitutes in production Number of firms in the market Expected future prices Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 18 of 46
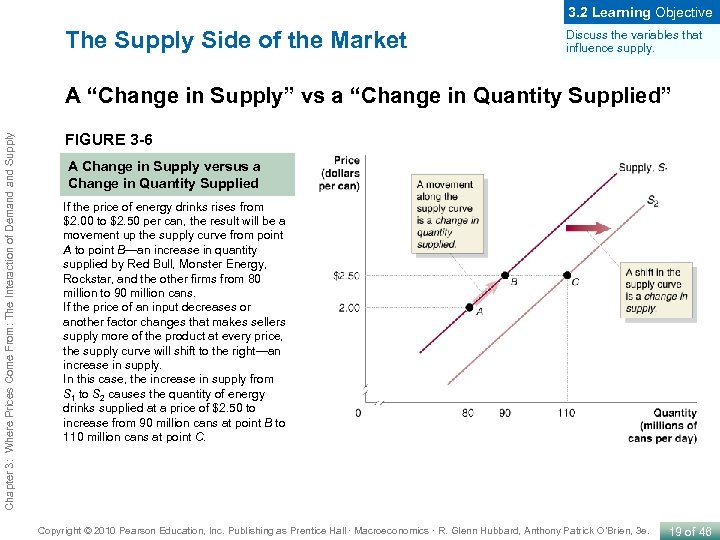 3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply A “Change in Supply” vs a “Change in Quantity Supplied” FIGURE 3 -6 A Change in Supply versus a Change in Quantity Supplied If the price of energy drinks rises from $2. 00 to $2. 50 per can, the result will be a movement up the supply curve from point A to point B—an increase in quantity supplied by Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms from 80 million to 90 million cans. If the price of an input decreases or another factor changes that makes sellers supply more of the product at every price, the supply curve will shift to the right—an increase in supply. In this case, the increase in supply from S 1 to S 2 causes the quantity of energy drinks supplied at a price of $2. 50 to increase from 90 million cans at point B to 110 million cans at point C. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 19 of 46
3. 2 Learning Objective The Supply Side of the Market Discuss the variables that influence supply. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply A “Change in Supply” vs a “Change in Quantity Supplied” FIGURE 3 -6 A Change in Supply versus a Change in Quantity Supplied If the price of energy drinks rises from $2. 00 to $2. 50 per can, the result will be a movement up the supply curve from point A to point B—an increase in quantity supplied by Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms from 80 million to 90 million cans. If the price of an input decreases or another factor changes that makes sellers supply more of the product at every price, the supply curve will shift to the right—an increase in supply. In this case, the increase in supply from S 1 to S 2 causes the quantity of energy drinks supplied at a price of $2. 50 to increase from 90 million cans at point B to 110 million cans at point C. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 19 of 46
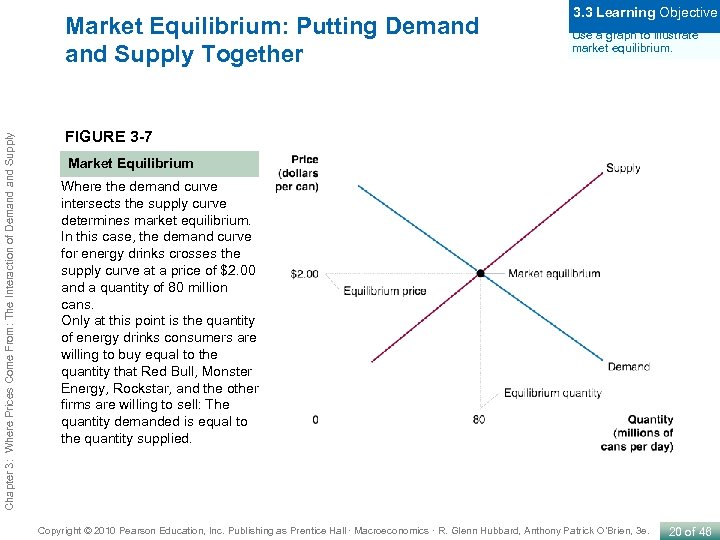 Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. FIGURE 3 -7 Market Equilibrium Where the demand curve intersects the supply curve determines market equilibrium. In this case, the demand curve for energy drinks crosses the supply curve at a price of $2. 00 and a quantity of 80 million cans. Only at this point is the quantity of energy drinks consumers are willing to buy equal to the quantity that Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms are willing to sell: The quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 20 of 46
Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. FIGURE 3 -7 Market Equilibrium Where the demand curve intersects the supply curve determines market equilibrium. In this case, the demand curve for energy drinks crosses the supply curve at a price of $2. 00 and a quantity of 80 million cans. Only at this point is the quantity of energy drinks consumers are willing to buy equal to the quantity that Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms are willing to sell: The quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 20 of 46
 Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Market equilibrium A situation in which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Competitive market equilibrium A market equilibrium with many buyers and many sellers. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 21 of 46
Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Market equilibrium A situation in which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Competitive market equilibrium A market equilibrium with many buyers and many sellers. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 21 of 46
 Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. How Markets Eliminate Surpluses and Shortages Surplus A situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. Shortage A situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 22 of 46
Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. How Markets Eliminate Surpluses and Shortages Surplus A situation in which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. Shortage A situation in which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 22 of 46
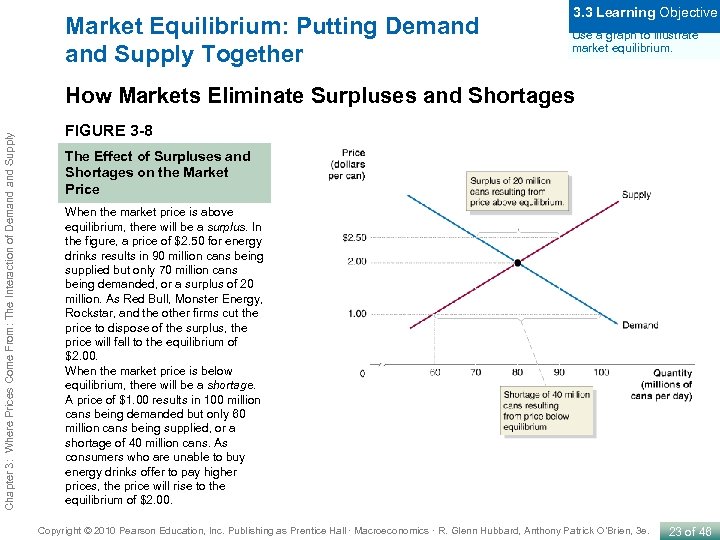 Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply How Markets Eliminate Surpluses and Shortages FIGURE 3 -8 The Effect of Surpluses and Shortages on the Market Price When the market price is above equilibrium, there will be a surplus. In the figure, a price of $2. 50 for energy drinks results in 90 million cans being supplied but only 70 million cans being demanded, or a surplus of 20 million. As Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms cut the price to dispose of the surplus, the price will fall to the equilibrium of $2. 00. When the market price is below equilibrium, there will be a shortage. A price of $1. 00 results in 100 million cans being demanded but only 60 million cans being supplied, or a shortage of 40 million cans. As consumers who are unable to buy energy drinks offer to pay higher prices, the price will rise to the equilibrium of $2. 00. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 23 of 46
Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply How Markets Eliminate Surpluses and Shortages FIGURE 3 -8 The Effect of Surpluses and Shortages on the Market Price When the market price is above equilibrium, there will be a surplus. In the figure, a price of $2. 50 for energy drinks results in 90 million cans being supplied but only 70 million cans being demanded, or a surplus of 20 million. As Red Bull, Monster Energy, Rockstar, and the other firms cut the price to dispose of the surplus, the price will fall to the equilibrium of $2. 00. When the market price is below equilibrium, there will be a shortage. A price of $1. 00 results in 100 million cans being demanded but only 60 million cans being supplied, or a shortage of 40 million cans. As consumers who are unable to buy energy drinks offer to pay higher prices, the price will rise to the equilibrium of $2. 00. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 23 of 46
 Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply Both Count Keep in mind that the interaction of demand supply determines the equilibrium price. Neither consumers nor firms can dictate what the equilibrium price will be. No firm can sell anything at any price unless it can find a willing buyer, and no consumer can buy anything at any price without finding a willing seller. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 24 of 46
Market Equilibrium: Putting Demand Supply Together 3. 3 Learning Objective Use a graph to illustrate market equilibrium. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand and Supply Both Count Keep in mind that the interaction of demand supply determines the equilibrium price. Neither consumers nor firms can dictate what the equilibrium price will be. No firm can sell anything at any price unless it can find a willing buyer, and no consumer can buy anything at any price without finding a willing seller. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 24 of 46
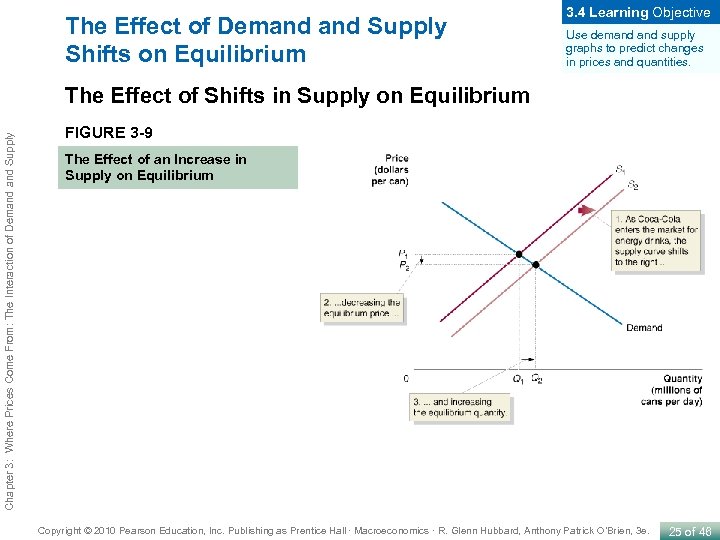 The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Supply on Equilibrium FIGURE 3 -9 The Effect of an Increase in Supply on Equilibrium Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 25 of 46
The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Supply on Equilibrium FIGURE 3 -9 The Effect of an Increase in Supply on Equilibrium Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 25 of 46
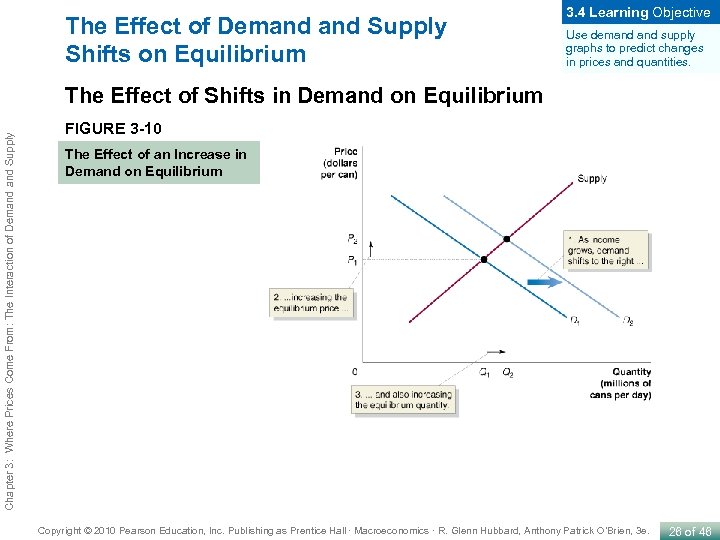 The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Demand on Equilibrium FIGURE 3 -10 The Effect of an Increase in Demand on Equilibrium Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 26 of 46
The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Demand on Equilibrium FIGURE 3 -10 The Effect of an Increase in Demand on Equilibrium Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 26 of 46
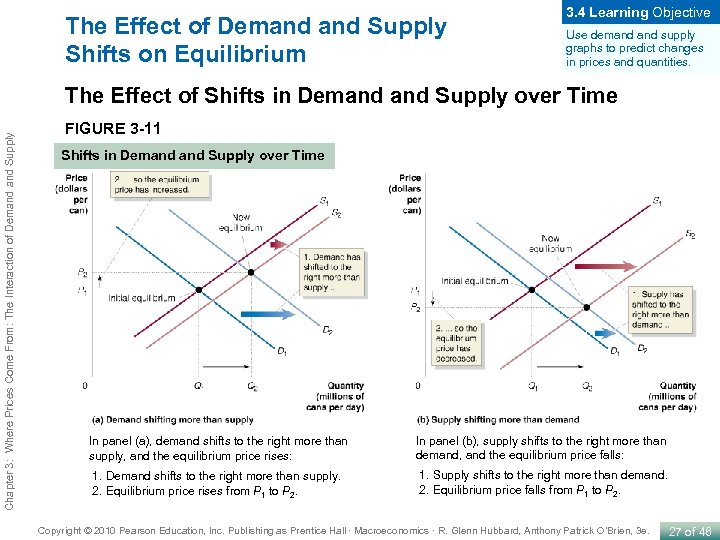 The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Demand Supply over Time FIGURE 3 -11 Shifts in Demand Supply over Time In panel (a), demand shifts to the right more than supply, and the equilibrium price rises: In panel (b), supply shifts to the right more than demand, and the equilibrium price falls: 1. Demand shifts to the right more than supply. 2. Equilibrium price rises from P 1 to P 2. 1. Supply shifts to the right more than demand. 2. Equilibrium price falls from P 1 to P 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 27 of 46
The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Demand Supply over Time FIGURE 3 -11 Shifts in Demand Supply over Time In panel (a), demand shifts to the right more than supply, and the equilibrium price rises: In panel (b), supply shifts to the right more than demand, and the equilibrium price falls: 1. Demand shifts to the right more than supply. 2. Equilibrium price rises from P 1 to P 2. 1. Supply shifts to the right more than demand. 2. Equilibrium price falls from P 1 to P 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 27 of 46
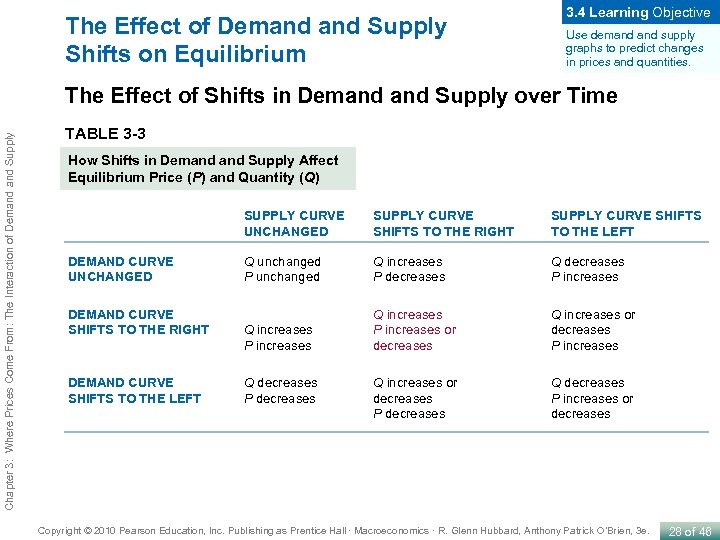 The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Demand Supply over Time TABLE 3 -3 How Shifts in Demand Supply Affect Equilibrium Price (P) and Quantity (Q) SUPPLY CURVE UNCHANGED DEMAND CURVE SHIFTS TO THE RIGHT DEMAND CURVE SHIFTS TO THE LEFT SUPPLY CURVE SHIFTS TO THE RIGHT SUPPLY CURVE SHIFTS TO THE LEFT Q unchanged P unchanged Q increases P decreases Q decreases P increases Q increases P increases or decreases Q increases or decreases P increases Q increases or decreases P decreases Q decreases P increases or decreases Q decreases P decreases Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 28 of 46
The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply The Effect of Shifts in Demand Supply over Time TABLE 3 -3 How Shifts in Demand Supply Affect Equilibrium Price (P) and Quantity (Q) SUPPLY CURVE UNCHANGED DEMAND CURVE SHIFTS TO THE RIGHT DEMAND CURVE SHIFTS TO THE LEFT SUPPLY CURVE SHIFTS TO THE RIGHT SUPPLY CURVE SHIFTS TO THE LEFT Q unchanged P unchanged Q increases P decreases Q decreases P increases Q increases P increases or decreases Q increases or decreases P increases Q increases or decreases P decreases Q decreases P increases or decreases Q decreases P decreases Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 28 of 46
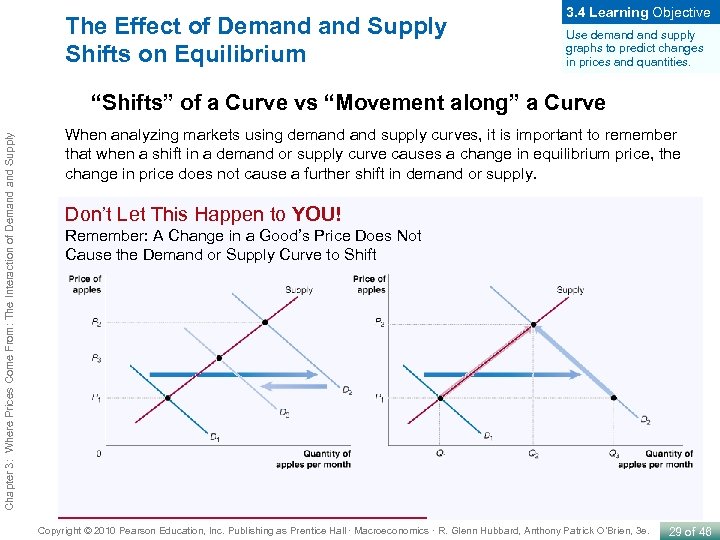 The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply “Shifts” of a Curve vs “Movement along” a Curve When analyzing markets using demand supply curves, it is important to remember that when a shift in a demand or supply curve causes a change in equilibrium price, the change in price does not cause a further shift in demand or supply. Don’t Let This Happen to YOU! Remember: A Change in a Good’s Price Does Not Cause the Demand or Supply Curve to Shift Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 29 of 46
The Effect of Demand Supply Shifts on Equilibrium 3. 4 Learning Objective Use demand supply graphs to predict changes in prices and quantities. Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply “Shifts” of a Curve vs “Movement along” a Curve When analyzing markets using demand supply curves, it is important to remember that when a shift in a demand or supply curve causes a change in equilibrium price, the change in price does not cause a further shift in demand or supply. Don’t Let This Happen to YOU! Remember: A Change in a Good’s Price Does Not Cause the Demand or Supply Curve to Shift Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 29 of 46
 Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply KEY TERMS Ceteris paribus (“all else equal”) condition Competitive market equilibrium Complements Demand curve Demand schedule Demographics Income effect (I. E. ) Inferior good Law of demand Law of supply Market demand Market equilibrium Normal good Perfectly competitive market Quantity demanded Quantity supplied Shortage Substitutes Substitution effect (S. E. ) Supply curve Supply schedule Surplus Technological change Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 30 of 46
Chapter 3: Where Prices Come From: The Interaction of Demand Supply KEY TERMS Ceteris paribus (“all else equal”) condition Competitive market equilibrium Complements Demand curve Demand schedule Demographics Income effect (I. E. ) Inferior good Law of demand Law of supply Market demand Market equilibrium Normal good Perfectly competitive market Quantity demanded Quantity supplied Shortage Substitutes Substitution effect (S. E. ) Supply curve Supply schedule Surplus Technological change Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall · Macroeconomics · R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 3 e. 30 of 46


