Chapter 3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60
 Chapter 3 Voyage Through the Life Mr. Dennis G. Relojo, MP Centro Escolar University Department of Psychology
Chapter 3 Voyage Through the Life Mr. Dennis G. Relojo, MP Centro Escolar University Department of Psychology
 Developmental Psychology § Developmental Psychology is the study of human behaviour from birth to adulthood. § Draws themes from both cognitive and social psychology. § Integrates research from fields such as genetics and linguistics and the interaction between genetic and social factors in influencing behaviour. Source: www. careersinpsychology. co. uk Centro Escolar University 2
Developmental Psychology § Developmental Psychology is the study of human behaviour from birth to adulthood. § Draws themes from both cognitive and social psychology. § Integrates research from fields such as genetics and linguistics and the interaction between genetic and social factors in influencing behaviour. Source: www. careersinpsychology. co. uk Centro Escolar University 2
 1. 2. 3. 4. Prenatal Development Childhood Adolescence Adulthood Centro Escolar University 3
1. 2. 3. 4. Prenatal Development Childhood Adolescence Adulthood Centro Escolar University 3
 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT Centro Escolar University 4
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT Centro Escolar University 4
 § When an egg becomes fertilized by the sperm, the resulting one-celled entity , called a zygote, immediately begins to develop (Feldman, 2008). The first two weeks is called the germinal period. § The next stage is the embryonic period. During this stage the major body organs systems take form (Rathus, 2012). Centro Escolar University 5
§ When an egg becomes fertilized by the sperm, the resulting one-celled entity , called a zygote, immediately begins to develop (Feldman, 2008). The first two weeks is called the germinal period. § The next stage is the embryonic period. During this stage the major body organs systems take form (Rathus, 2012). Centro Escolar University 5
 § As it develops, the embryo is suspended within a protective amniotic sac in the mother’s uterus. § The sac is surrounded by a clear membrane and contains amniotic fluid. § From week 8 until birth, the developing individual enters the fetal period and is called a fetus. Centro Escolar University 6
§ As it develops, the embryo is suspended within a protective amniotic sac in the mother’s uterus. § The sac is surrounded by a clear membrane and contains amniotic fluid. § From week 8 until birth, the developing individual enters the fetal period and is called a fetus. Centro Escolar University 6
 § 1 -2 weeks: Germinal period (Zygote) § 2 -8 weeks: Embryonic period (Embryo) § 8 weeks-birth: Fetal period (Fetus) Centro Escolar University 7
§ 1 -2 weeks: Germinal period (Zygote) § 2 -8 weeks: Embryonic period (Embryo) § 8 weeks-birth: Fetal period (Fetus) Centro Escolar University 7
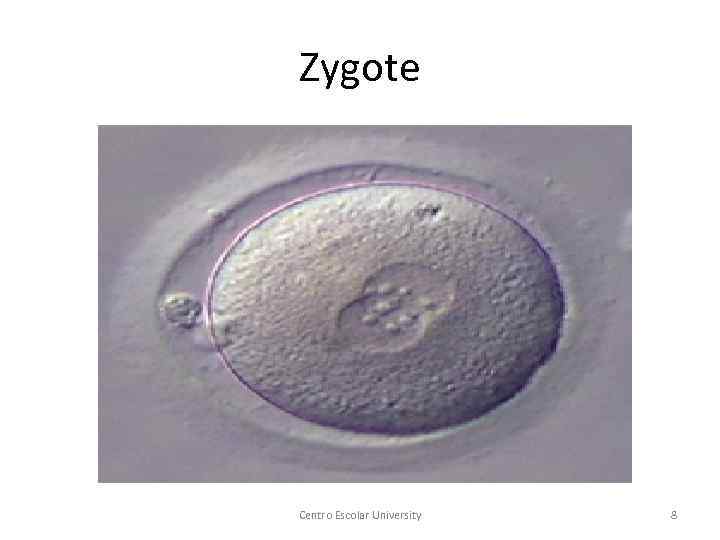 Zygote Centro Escolar University 8
Zygote Centro Escolar University 8
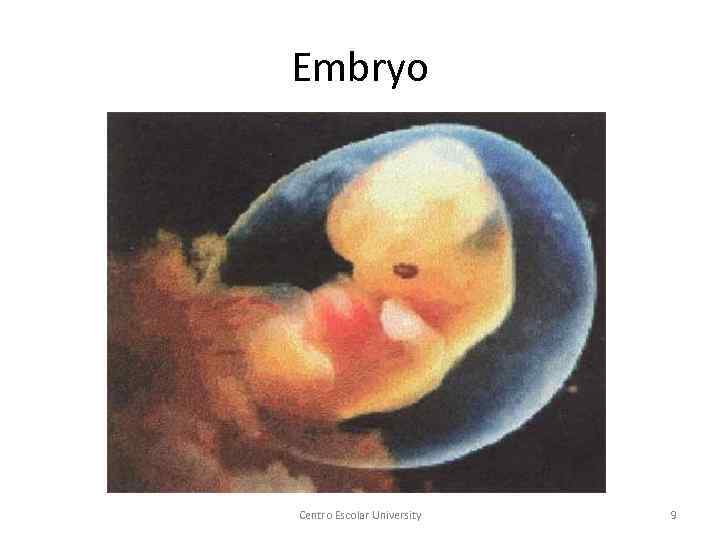 Embryo Centro Escolar University 9
Embryo Centro Escolar University 9
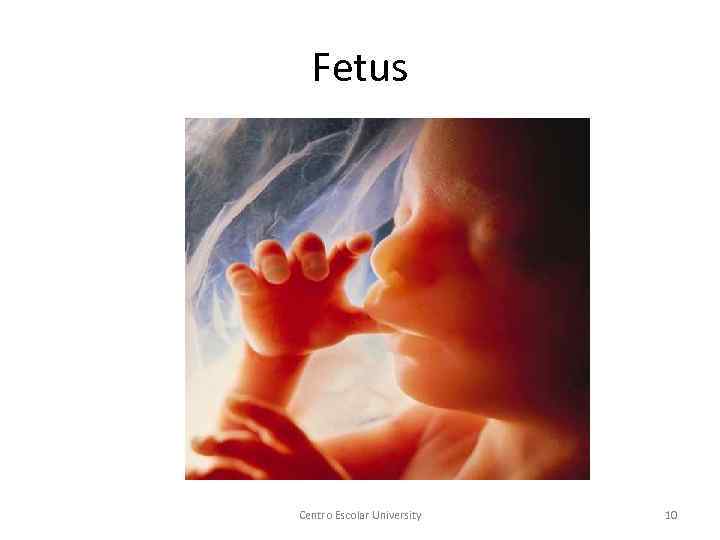 Fetus Centro Escolar University 10
Fetus Centro Escolar University 10
 Common Genetic Difficulties § Phenylketonuria (PKU) A child born with the inherited disease phenylketonuria cannot produce an enzyme that is required for normal development. This results in an accumulation of poisons that eventually cause profound mental retardation (Walter et al. , 2002). Centro Escolar University 11
Common Genetic Difficulties § Phenylketonuria (PKU) A child born with the inherited disease phenylketonuria cannot produce an enzyme that is required for normal development. This results in an accumulation of poisons that eventually cause profound mental retardation (Walter et al. , 2002). Centro Escolar University 11
 § Sickle-cell anaemia About 12, 500 people in the UK have sickle cell anaemia. Sickle cell anaemia develops when your body makes an abnormal form of the protein in your blood that carries oxygen, called haemoglobin. Source: British United Provident Association Centro Escolar University 12
§ Sickle-cell anaemia About 12, 500 people in the UK have sickle cell anaemia. Sickle cell anaemia develops when your body makes an abnormal form of the protein in your blood that carries oxygen, called haemoglobin. Source: British United Provident Association Centro Escolar University 12
 § Cystic fibrosis The disease is caused by a scarring of the pancreas, which can give rise to a difficulty in breathing as well other symptoms, which can include: sinus infections, poor growth, diarrhea, infertility. Centro Escolar University 13
§ Cystic fibrosis The disease is caused by a scarring of the pancreas, which can give rise to a difficulty in breathing as well other symptoms, which can include: sinus infections, poor growth, diarrhea, infertility. Centro Escolar University 13
 § Tay-Sachs Disease disorder most found in Jews of eastern European ancestry, usually die by age 3 or 4 because of the body’s inability to break down fat ( Navon & Proia, 1989). § Down Syndrome often related to the mother’s age; mothers over 35 and younger than 18, in particular, stand a higher risk of having a child with the syndrome (Roizen & Patterson, 2003). Centro Escolar University 14
§ Tay-Sachs Disease disorder most found in Jews of eastern European ancestry, usually die by age 3 or 4 because of the body’s inability to break down fat ( Navon & Proia, 1989). § Down Syndrome often related to the mother’s age; mothers over 35 and younger than 18, in particular, stand a higher risk of having a child with the syndrome (Roizen & Patterson, 2003). Centro Escolar University 14
 Activity Guess the Creature Centro Escolar University 15
Activity Guess the Creature Centro Escolar University 15
 His head was molded into a long melon shape and came to a point at the back. Centro Escolar University 16
His head was molded into a long melon shape and came to a point at the back. Centro Escolar University 16
 He was covered with a thick greasy white material known as “vernix”, which made him slippery to hold, and also allowed him to slip easily through the birth canal. Centro Escolar University 17
He was covered with a thick greasy white material known as “vernix”, which made him slippery to hold, and also allowed him to slip easily through the birth canal. Centro Escolar University 17
 … In addition to a shock of black hair on his head, his body was covered with dark, fine hair known as “lanugo”. His ears, his back, his shoulders, and even his cheeks were furry… Centro Escolar University 18
… In addition to a shock of black hair on his head, his body was covered with dark, fine hair known as “lanugo”. His ears, his back, his shoulders, and even his cheeks were furry… Centro Escolar University 18
 What is it? NEONATE Centro Escolar University 19
What is it? NEONATE Centro Escolar University 19
 CHILDHOOD Centro Escolar University 20
CHILDHOOD Centro Escolar University 20
 § Childhood begins with birth and is the period of life before puberty (Rathus, 2012; Collins Dictionary). § Babies usually double their birth weight in about five months and triple it by their first birthday (Kuczmarski et al. , 2000). Centro Escolar University 21
§ Childhood begins with birth and is the period of life before puberty (Rathus, 2012; Collins Dictionary). § Babies usually double their birth weight in about five months and triple it by their first birthday (Kuczmarski et al. , 2000). Centro Escolar University 21
 In terms of developmental stages, childhood is divided into… Centro Escolar University 22
In terms of developmental stages, childhood is divided into… Centro Escolar University 22
 Toddlerhood (1 -2) Centro Escolar University 23
Toddlerhood (1 -2) Centro Escolar University 23
 Early Childhood (2 -6) Centro Escolar University 24
Early Childhood (2 -6) Centro Escolar University 24
 Middle Childhood (6 -10) Centro Escolar University 25
Middle Childhood (6 -10) Centro Escolar University 25
 Adolescence (10 -19) Centro Escolar University 26
Adolescence (10 -19) Centro Escolar University 26
 § § Physical Development Cognitive Development Attachment Parenting Styles Centro Escolar University 27
§ § Physical Development Cognitive Development Attachment Parenting Styles Centro Escolar University 27
 Physical Development § Reflexes are simple, unlearned, stereotypical responses elicited by specific stimuli. § Examples of reflexes: rooting, sucking, Moro reflex, Palmar reflex, Babinski reflex, Centro Escolar University 28
Physical Development § Reflexes are simple, unlearned, stereotypical responses elicited by specific stimuli. § Examples of reflexes: rooting, sucking, Moro reflex, Palmar reflex, Babinski reflex, Centro Escolar University 28
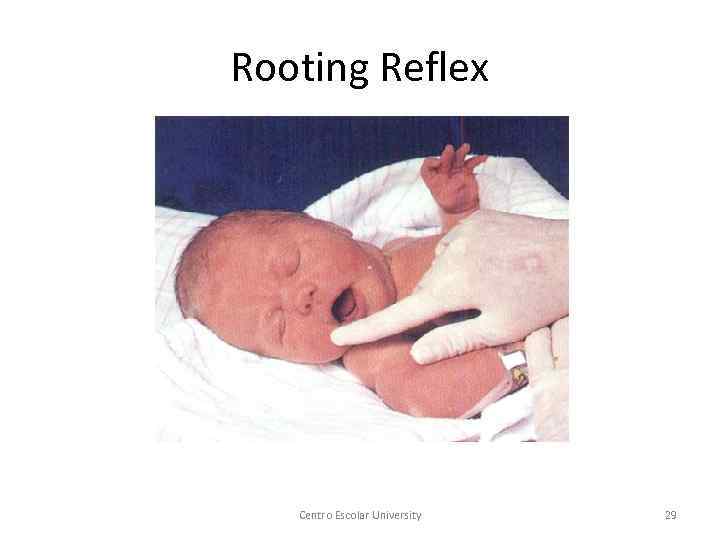 Rooting Reflex Centro Escolar University 29
Rooting Reflex Centro Escolar University 29
 Sucking Reflex Centro Escolar University 30
Sucking Reflex Centro Escolar University 30
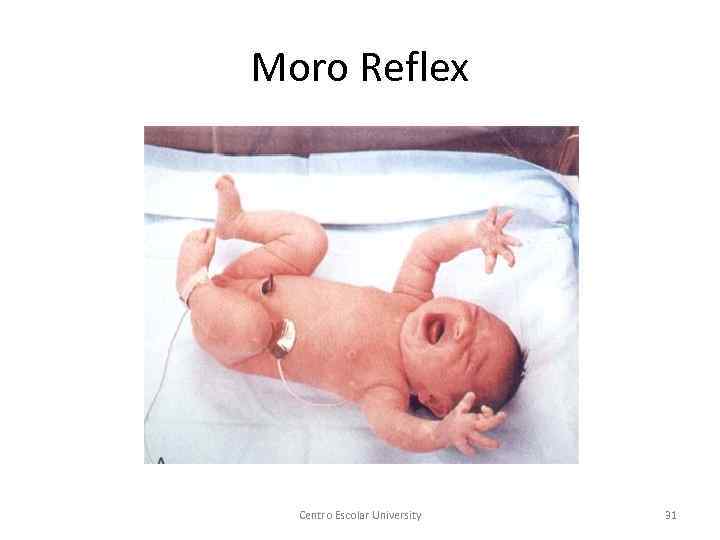 Moro Reflex Centro Escolar University 31
Moro Reflex Centro Escolar University 31
 Palmar Reflex Centro Escolar University 32
Palmar Reflex Centro Escolar University 32
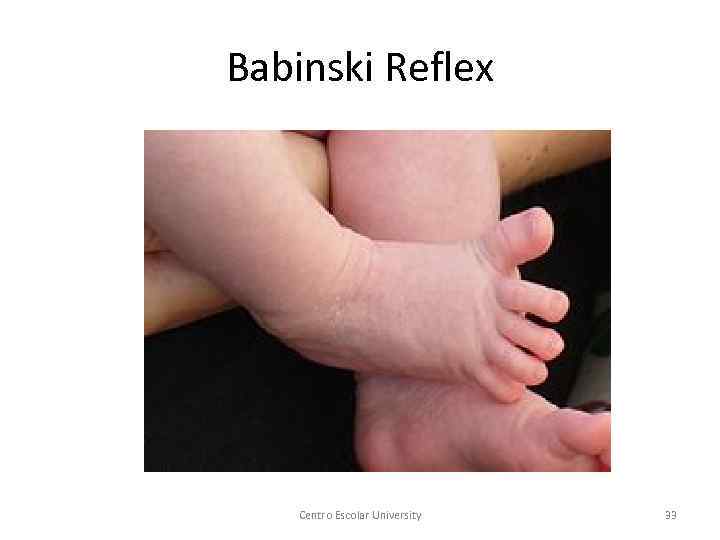 Babinski Reflex Centro Escolar University 33
Babinski Reflex Centro Escolar University 33
 Motor Development § The motor development of the child refers to the progression from simple acts like lifting the head to running around (Rathus, 2012). § Maturation and experience both play key roles in motor development (Muir, 2000; Pryce et al. , 2001; Roncesvalles et al. , 2001). Centro Escolar University 34
Motor Development § The motor development of the child refers to the progression from simple acts like lifting the head to running around (Rathus, 2012). § Maturation and experience both play key roles in motor development (Muir, 2000; Pryce et al. , 2001; Roncesvalles et al. , 2001). Centro Escolar University 34
 Perceptual Development § As early as four months babies have not only learned to distinguish colours, but have developed a particular preference for a certain colour as well. Source: www. kidsdevelopment. co. uk § Newborns are nearsighted, but by about four months, infants focus on distant objects (Rathus, 2012). Centro Escolar University 35
Perceptual Development § As early as four months babies have not only learned to distinguish colours, but have developed a particular preference for a certain colour as well. Source: www. kidsdevelopment. co. uk § Newborns are nearsighted, but by about four months, infants focus on distant objects (Rathus, 2012). Centro Escolar University 35
 Cognitive Development § The ways in which children mentally represent and think about the world– that is their cognitive development (Rathus, 2012). § Because cognitive functioning develops over many years, young children have ideas about the world that differ considerably from those of adults (Rathus, 2012). Centro Escolar University 36
Cognitive Development § The ways in which children mentally represent and think about the world– that is their cognitive development (Rathus, 2012). § Because cognitive functioning develops over many years, young children have ideas about the world that differ considerably from those of adults (Rathus, 2012). Centro Escolar University 36
 Jean Piaget Centro Escolar University 37
Jean Piaget Centro Escolar University 37
 Cognitive-Developmental Theory § Assimilation means responding to a new stimulus through existing cognitive structures. § Accommodation is the creation of new ways of responding to objects or looking at the world. Centro Escolar University 38
Cognitive-Developmental Theory § Assimilation means responding to a new stimulus through existing cognitive structures. § Accommodation is the creation of new ways of responding to objects or looking at the world. Centro Escolar University 38
 Example of Assimilation q. A flower has petals, smells good, and has stem. q. A rose has petals, smells good, and has stem. q. A rose is a flower. Centro Escolar University 39
Example of Assimilation q. A flower has petals, smells good, and has stem. q. A rose has petals, smells good, and has stem. q. A rose is a flower. Centro Escolar University 39
 Example of Accommodation q. Whales are not fish. q. Whales are mammals without legs that live in the sea. Centro Escolar University 40
Example of Accommodation q. Whales are not fish. q. Whales are mammals without legs that live in the sea. Centro Escolar University 40
 Thought Exercise 1 Erik knows that the Saint Bernard is a large dog instead of a little pony. This is an example of what Piaget called ____. Accommodation or Assimilation? Centro Escolar University 41
Thought Exercise 1 Erik knows that the Saint Bernard is a large dog instead of a little pony. This is an example of what Piaget called ____. Accommodation or Assimilation? Centro Escolar University 41
 Answer: Accommodation Centro Escolar University 42
Answer: Accommodation Centro Escolar University 42
 Explanation: Erik believes that "All big four legged animals are ponies". He sees a breed of dog (Saint Bernard) that he's never seen before and says, "That's a pony. " But his parents tell him it isn't a pony, but a dog, a large one. So the child accommodates. Centro Escolar University 43
Explanation: Erik believes that "All big four legged animals are ponies". He sees a breed of dog (Saint Bernard) that he's never seen before and says, "That's a pony. " But his parents tell him it isn't a pony, but a dog, a large one. So the child accommodates. Centro Escolar University 43
 Thought Exercise 2 A 2 year old child sees a man who is bald on top of his head and has long frizzy hair on the sides. To his father’s horror, the toddler shouts “Clown, clown” Centro Escolar University 44
Thought Exercise 2 A 2 year old child sees a man who is bald on top of his head and has long frizzy hair on the sides. To his father’s horror, the toddler shouts “Clown, clown” Centro Escolar University 44
 Answer: Assimilation Centro Escolar University 45
Answer: Assimilation Centro Escolar University 45
 Explanation: The child may have seen a clown in the past- someone that is bald on top and has long frizzy hairs on the sides. And so he assimilates this when he saw the man. Centro Escolar University 46
Explanation: The child may have seen a clown in the past- someone that is bald on top and has long frizzy hairs on the sides. And so he assimilates this when he saw the man. Centro Escolar University 46
 Thought Exercise 3 When Jon was growing up his parents told him that tattoos are bad. He assimilated such information as "probably rides a motorcycle, " "is dirty, " and "probably has been in jail" into a schema during childhood. When he got to college, he met a lot of people with tattoos who aren’t bad. Centro Escolar University 47
Thought Exercise 3 When Jon was growing up his parents told him that tattoos are bad. He assimilated such information as "probably rides a motorcycle, " "is dirty, " and "probably has been in jail" into a schema during childhood. When he got to college, he met a lot of people with tattoos who aren’t bad. Centro Escolar University 47
 Answer: Accommodation Centro Escolar University 48
Answer: Accommodation Centro Escolar University 48
 Explanation: When Jon was a kid he assimilated that tattoos are bad because that is what his parents told him. When he got to college he met people who did not fit into his schema, and thus had to do some accommodation to accept those people. Centro Escolar University 49
Explanation: When Jon was a kid he assimilated that tattoos are bad because that is what his parents told him. When he got to college he met people who did not fit into his schema, and thus had to do some accommodation to accept those people. Centro Escolar University 49
 Stages of Cognitive Development § § Sensorimotor (Birth- 2 Years) Preoperational (2 -7 Years) Concrete Operational (7 -12 Years) Formal Operational (12 and Above) Centro Escolar University 50
Stages of Cognitive Development § § Sensorimotor (Birth- 2 Years) Preoperational (2 -7 Years) Concrete Operational (7 -12 Years) Formal Operational (12 and Above) Centro Escolar University 50
 Sensorimotor § Differentiates self from objects § Recognises self as agent of action and begins to act intentionally: e. g. pulls a string to set mobile in motion or shakes a rattle to make a noise. § Achieves object permanence: realises that things continue to exist even when no longer present to the sense Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 51
Sensorimotor § Differentiates self from objects § Recognises self as agent of action and begins to act intentionally: e. g. pulls a string to set mobile in motion or shakes a rattle to make a noise. § Achieves object permanence: realises that things continue to exist even when no longer present to the sense Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 51
 Preoperational § Learns to use language and to represent objects by images and words Thinking is still egocentric: has difficulty taking the viewpoint of others. § Classifies objects by a single feature: e. g. groups together all the red blocks regardless of shape or all the square blocks regardless of colour. Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 52
Preoperational § Learns to use language and to represent objects by images and words Thinking is still egocentric: has difficulty taking the viewpoint of others. § Classifies objects by a single feature: e. g. groups together all the red blocks regardless of shape or all the square blocks regardless of colour. Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 52
 Concrete Operational § Can think logically about objects and events § Achieves conservation of number, mass , and weight. § Classifies objects according to several features and can order them in series along a single dimension such as size Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 53
Concrete Operational § Can think logically about objects and events § Achieves conservation of number, mass , and weight. § Classifies objects according to several features and can order them in series along a single dimension such as size Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 53
 Formal Operational § Can think logically about abstract propositions and test hypotheses systematically § Becomes concerned with the hypothetical, the future, and ideological problems Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 54
Formal Operational § Can think logically about abstract propositions and test hypotheses systematically § Becomes concerned with the hypothetical, the future, and ideological problems Source: www. learningandteaching. info Centro Escolar University 54
 Lev Vygotsky Centro Escolar University 55
Lev Vygotsky Centro Escolar University 55
 Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory § Lev Vygotsky’s theory focuses on the transmission of information and cognitive skills from generation to generation (Rathus, 2012). § Believed that community plays a central role in the process of "making meaning“ (www. simplypsychology. org) Centro Escolar University 56
Vygotsky’s Sociocultural Theory § Lev Vygotsky’s theory focuses on the transmission of information and cognitive skills from generation to generation (Rathus, 2012). § Believed that community plays a central role in the process of "making meaning“ (www. simplypsychology. org) Centro Escolar University 56
 Zone of Proximal Development § Zone of Proximal Development is the distance between the actual developmental level as determined by independent problem solving and the level of potential development as determined through problem solving under adult guidance, or in collaboration with more capable peers (Vygotsky, 1978). Centro Escolar University 57
Zone of Proximal Development § Zone of Proximal Development is the distance between the actual developmental level as determined by independent problem solving and the level of potential development as determined through problem solving under adult guidance, or in collaboration with more capable peers (Vygotsky, 1978). Centro Escolar University 57
 ` Centro Escolar University 58
` Centro Escolar University 58
 Seatwork ½ Yellow Paper, cross-wise, 10 points. Read Parenting Styles (p. 84 -85). Identify the parenting styles of your parents and discuss how it has influenced your personality development. Centro Escolar University 59
Seatwork ½ Yellow Paper, cross-wise, 10 points. Read Parenting Styles (p. 84 -85). Identify the parenting styles of your parents and discuss how it has influenced your personality development. Centro Escolar University 59
 Assignment 1. Follow me on Twitter @Dennis. Relojo Visit vk. com/behaviourcentre for instructions (50 Points) 2. Read pages 80 -83 Centro Escolar University 60
Assignment 1. Follow me on Twitter @Dennis. Relojo Visit vk. com/behaviourcentre for instructions (50 Points) 2. Read pages 80 -83 Centro Escolar University 60


