Ch_3_Attitudes.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Chapter 3: Values, Attitudes, and Diversity in the Workplace Fundamentals of Organizational Behaviour 5 th Canadian Edition Langton / Robbins / Judge Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -1
Chapter 3: Values, Attitudes, and Diversity in the Workplace Fundamentals of Organizational Behaviour 5 th Canadian Edition Langton / Robbins / Judge Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -1
 Attitudes • Positive or negative feelings concerning objects, people, or events. • Attitudes are less stable than values. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -2
Attitudes • Positive or negative feelings concerning objects, people, or events. • Attitudes are less stable than values. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -2
 Types of Attitudes • Job Satisfaction – An individual’s general attitude toward his or her job. • Organizational Commitment – A state in which an employee identifies with a particular organization and its goals, and wishes to maintain membership in the organization. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -3
Types of Attitudes • Job Satisfaction – An individual’s general attitude toward his or her job. • Organizational Commitment – A state in which an employee identifies with a particular organization and its goals, and wishes to maintain membership in the organization. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -3
 What Causes Job Satisfaction? • Key sources of Job Satisfaction – Work itself, pay advancement opportunities, supervision, coworkers • Enjoying the work itself is almost always most strongly correlated with high levels of job satisfaction. • Once a person reaches the level of comfortable living the relationship between pay and satisfaction virtually disappears. • People with positive core self-evaluations , believe in their inner worth and basic competence, and are more satisfied with their work. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -4
What Causes Job Satisfaction? • Key sources of Job Satisfaction – Work itself, pay advancement opportunities, supervision, coworkers • Enjoying the work itself is almost always most strongly correlated with high levels of job satisfaction. • Once a person reaches the level of comfortable living the relationship between pay and satisfaction virtually disappears. • People with positive core self-evaluations , believe in their inner worth and basic competence, and are more satisfied with their work. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -4
 Job Satisfaction and Individual Performance • Satisfaction affects: – Individual productivity – Organizational citizenship behaviour – Job satisfaction and customer satisfaction Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -5
Job Satisfaction and Individual Performance • Satisfaction affects: – Individual productivity – Organizational citizenship behaviour – Job satisfaction and customer satisfaction Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -5
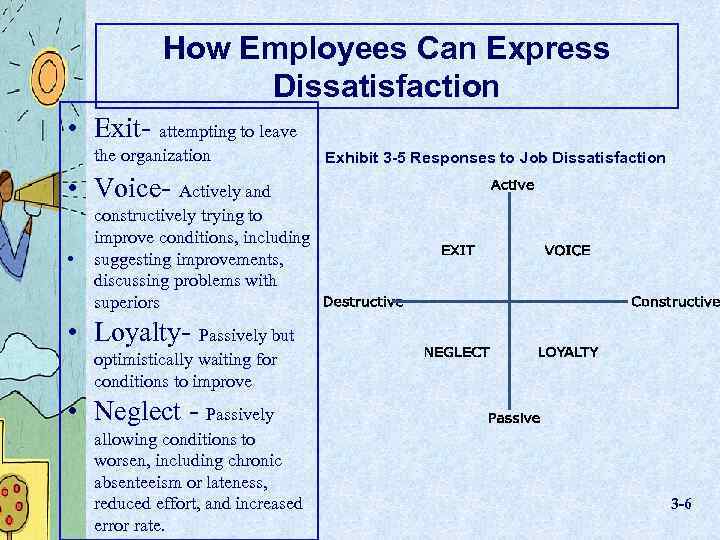 How Employees Can Express Dissatisfaction • Exit- attempting to leave the organization Exhibit 3 -5 Responses to Job Dissatisfaction • Voice- Actively and • constructively trying to improve conditions, including suggesting improvements, discussing problems with superiors • Loyalty- Passively but optimistically waiting for conditions to improve • Neglect - Passively allowing conditions to worsen, including chronic absenteeism or lateness, reduced effort, and increased error rate. 3 -6
How Employees Can Express Dissatisfaction • Exit- attempting to leave the organization Exhibit 3 -5 Responses to Job Dissatisfaction • Voice- Actively and • constructively trying to improve conditions, including suggesting improvements, discussing problems with superiors • Loyalty- Passively but optimistically waiting for conditions to improve • Neglect - Passively allowing conditions to worsen, including chronic absenteeism or lateness, reduced effort, and increased error rate. 3 -6
 Managers Often Don’t Get it • Many managers are not concerned with job satisfaction measures. • Many other managers overestimate the job satisfaction of their employees. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -7
Managers Often Don’t Get it • Many managers are not concerned with job satisfaction measures. • Many other managers overestimate the job satisfaction of their employees. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -7
 Organizational Commitment • Three Types of Commitment – Affective commitment • An individual’s relationship to the organization. – Normative commitment • The obligation an individual feels to staying with an organization. – Continuance commitment • An individual’s calculation that it is in his or her best interest to stay with the organization based on the perceived costs of leaving it. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -8
Organizational Commitment • Three Types of Commitment – Affective commitment • An individual’s relationship to the organization. – Normative commitment • The obligation an individual feels to staying with an organization. – Continuance commitment • An individual’s calculation that it is in his or her best interest to stay with the organization based on the perceived costs of leaving it. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -8
![Five Reasons Employees Commit Themselves • They are proud of [the company’s] aspirations, accomplishments, Five Reasons Employees Commit Themselves • They are proud of [the company’s] aspirations, accomplishments,](https://present5.com/presentation/93083640_138105729/image-9.jpg) Five Reasons Employees Commit Themselves • They are proud of [the company’s] aspirations, accomplishments, and legacy; they share its values. • They know what each person is expected to do, how performance is measured, and why it matters. • They are in control of their own destinies; they savour the high-risk, high-reward work environment. • They are recognized mostly for the quality of their individual performance. • They have fun and enjoy the supportive and highly interactive environment. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -9
Five Reasons Employees Commit Themselves • They are proud of [the company’s] aspirations, accomplishments, and legacy; they share its values. • They know what each person is expected to do, how performance is measured, and why it matters. • They are in control of their own destinies; they savour the high-risk, high-reward work environment. • They are recognized mostly for the quality of their individual performance. • They have fun and enjoy the supportive and highly interactive environment. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -9
 Employee Engagement • An individual’s involvement with, satisfaction with, and enthusiasm for work he or she does. • Highly engaged employees have a passion for their work and feel a deep connection to the company. • Firms that have employees with a higher level of engagement tend to see positive results: – – Higher customer satisfaction More productive employees Higher profits Lower levels of turnover and accidents Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -10
Employee Engagement • An individual’s involvement with, satisfaction with, and enthusiasm for work he or she does. • Highly engaged employees have a passion for their work and feel a deep connection to the company. • Firms that have employees with a higher level of engagement tend to see positive results: – – Higher customer satisfaction More productive employees Higher profits Lower levels of turnover and accidents Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -10
 Summary and Implications 1. What are Values? – 2. How can we understand values across cultures? – 4. Hofstede found that managers and employees vary on five value dimensions of national culture. This insight is expanded on by his GLOBE program. What are attitudes and why are they important? – 5. Values guide how we make decisions about and evaluations of behaviours and events. Attitudes are positive or negative feelings about objects, people, or events. They affect the way people respond to situations. How do we respond to diversity in the workplace? – Many organizations have introduced diversity training programs to improve cultural awareness. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -11
Summary and Implications 1. What are Values? – 2. How can we understand values across cultures? – 4. Hofstede found that managers and employees vary on five value dimensions of national culture. This insight is expanded on by his GLOBE program. What are attitudes and why are they important? – 5. Values guide how we make decisions about and evaluations of behaviours and events. Attitudes are positive or negative feelings about objects, people, or events. They affect the way people respond to situations. How do we respond to diversity in the workplace? – Many organizations have introduced diversity training programs to improve cultural awareness. Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -11
 Practical CASE INCIDENT, Gourmet Foods Works on Employee Attitudes p. 95 Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -12
Practical CASE INCIDENT, Gourmet Foods Works on Employee Attitudes p. 95 Langton, Robbins and Judge, Organizational Behaviour, Fifth Cdn. Ed. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education Canada 3 -12


