 Chapter 3: Two Dimensional Motion and Vectors (Now the fun really starts)
Chapter 3: Two Dimensional Motion and Vectors (Now the fun really starts)
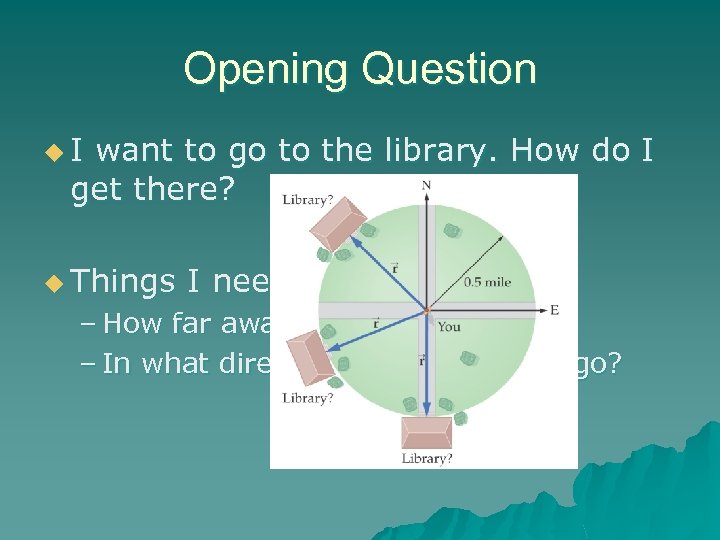 Opening Question u. I want to go to the library. How do I get there? u Things I need to know: – How far away is it? – In what direction(s) do I need to go?
Opening Question u. I want to go to the library. How do I get there? u Things I need to know: – How far away is it? – In what direction(s) do I need to go?
 One dimensional motion vs two dimensional motion u One dimensional motion: Limited to moving in one dimension (i. e. back and forth or up and down) u Two dimensional motion: Able to move in two dimensions (i. e. forward then left then back)
One dimensional motion vs two dimensional motion u One dimensional motion: Limited to moving in one dimension (i. e. back and forth or up and down) u Two dimensional motion: Able to move in two dimensions (i. e. forward then left then back)
 Scalars and Vectors u Scalar: A physical quantity that has magnitude but no direction – Examples: – Speed, Distance, Weight, Volume u Vector: A physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction – Examples: – Velocity, Displacement, Acceleration
Scalars and Vectors u Scalar: A physical quantity that has magnitude but no direction – Examples: – Speed, Distance, Weight, Volume u Vector: A physical quantity that has both magnitude and direction – Examples: – Velocity, Displacement, Acceleration
 Vectors are represented by symbols u Book uses boldface type to indicate vectors u Scalars u Use are designated with italics arrows to draw vectors
Vectors are represented by symbols u Book uses boldface type to indicate vectors u Scalars u Use are designated with italics arrows to draw vectors
 Vectors can be added graphically u When adding vectors make sure that the units are the same u Resultant vector: A vector representing the sum of two or more vectors
Vectors can be added graphically u When adding vectors make sure that the units are the same u Resultant vector: A vector representing the sum of two or more vectors
 Adding Vectors Graphically u Draw situation using a reasonable scale (i. e. 50 m = 1 cm) u Draw each vector head to tail using the right scale u Use a ruler and protractor to find the resultant vector
Adding Vectors Graphically u Draw situation using a reasonable scale (i. e. 50 m = 1 cm) u Draw each vector head to tail using the right scale u Use a ruler and protractor to find the resultant vector
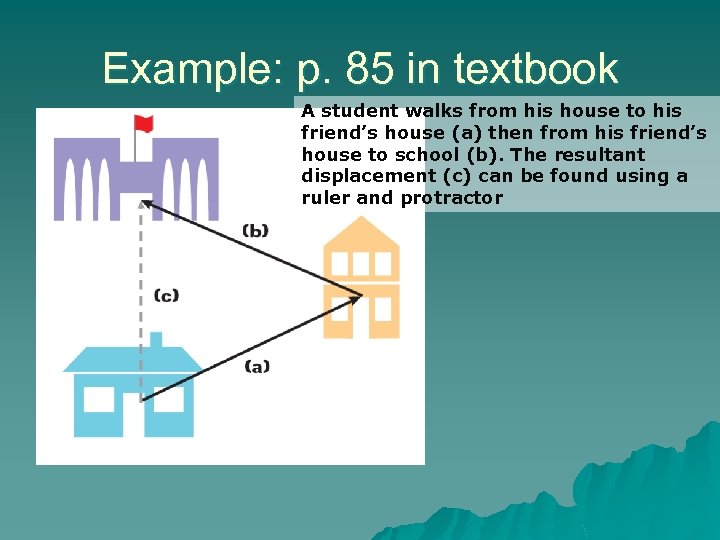 Example: p. 85 in textbook A student walks from his house to his friend’s house (a) then from his friend’s house to school (b). The resultant displacement (c) can be found using a ruler and protractor
Example: p. 85 in textbook A student walks from his house to his friend’s house (a) then from his friend’s house to school (b). The resultant displacement (c) can be found using a ruler and protractor
 Properties of vectors u Vectors u To can be added in any order subtract a vector add its opposite
Properties of vectors u Vectors u To can be added in any order subtract a vector add its opposite
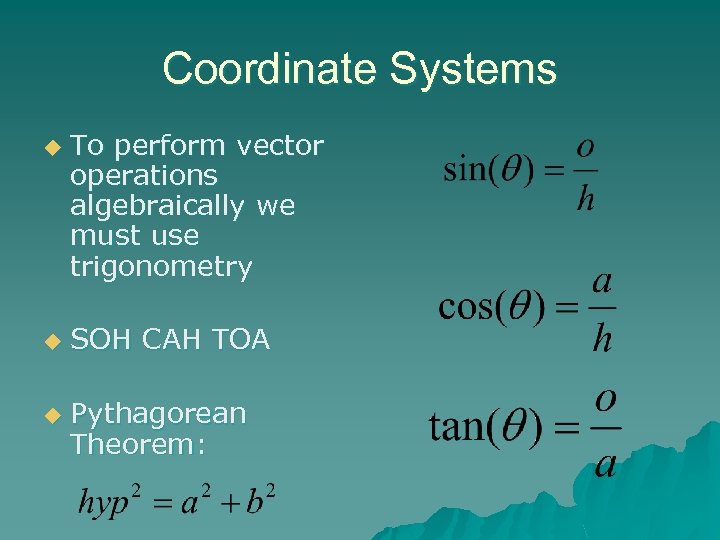 Coordinate Systems u u u To perform vector operations algebraically we must use trigonometry SOH CAH TOA Pythagorean Theorem:
Coordinate Systems u u u To perform vector operations algebraically we must use trigonometry SOH CAH TOA Pythagorean Theorem:
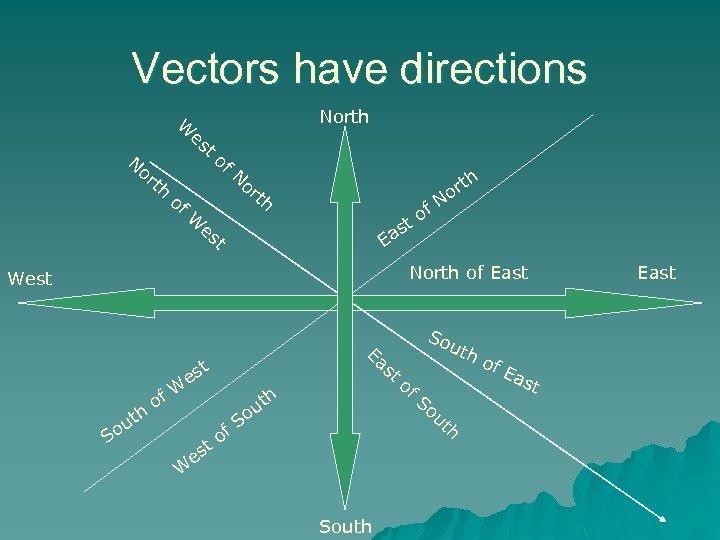 Vectors have directions North W es N t or th of of N th or r No of t W th es as E t North of East West Ea s t es h ut o t f. W to S W h ut o o es So uth of So ut f. S South h of Ea st East
Vectors have directions North W es N t or th of of N th or r No of t W th es as E t North of East West Ea s t es h ut o t f. W to S W h ut o o es So uth of So ut f. S South h of Ea st East
 Examples p. 91 #2 u While following directions on a treasure map, a pirate walks 45. 0 m north then turns around and walks 7. 5 m east. What single straight-line displacement could the pirate have taken to reach the treasure?
Examples p. 91 #2 u While following directions on a treasure map, a pirate walks 45. 0 m north then turns around and walks 7. 5 m east. What single straight-line displacement could the pirate have taken to reach the treasure?
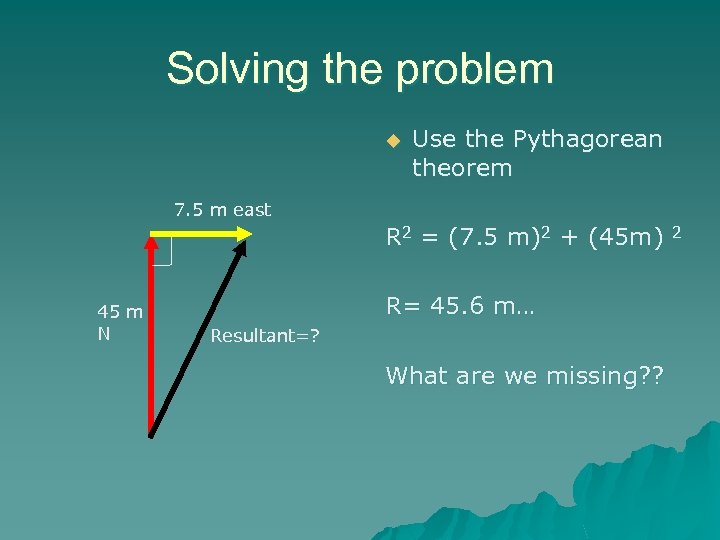 Solving the problem u Use the Pythagorean theorem 7. 5 m east R 2 = (7. 5 m)2 + (45 m) 45 m N R= 45. 6 m… Resultant=? What are we missing? ? 2
Solving the problem u Use the Pythagorean theorem 7. 5 m east R 2 = (7. 5 m)2 + (45 m) 45 m N R= 45. 6 m… Resultant=? What are we missing? ? 2
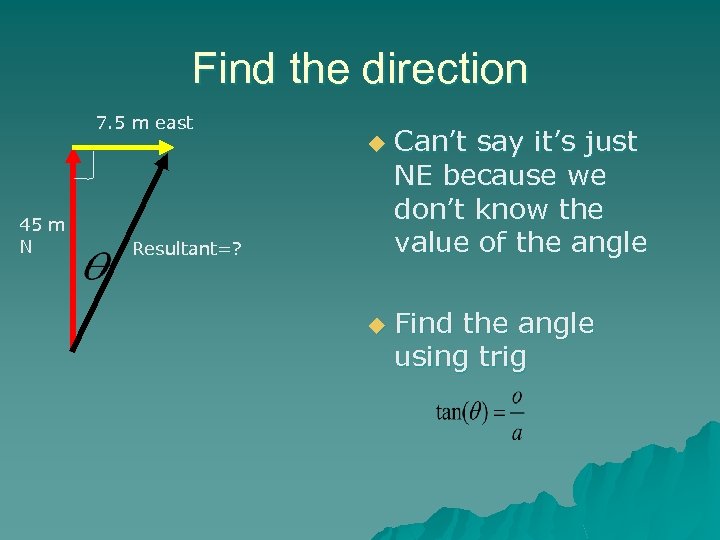 Find the direction 7. 5 m east u 45 m N Resultant=? u Can’t say it’s just NE because we don’t know the value of the angle Find the angle using trig
Find the direction 7. 5 m east u 45 m N Resultant=? u Can’t say it’s just NE because we don’t know the value of the angle Find the angle using trig
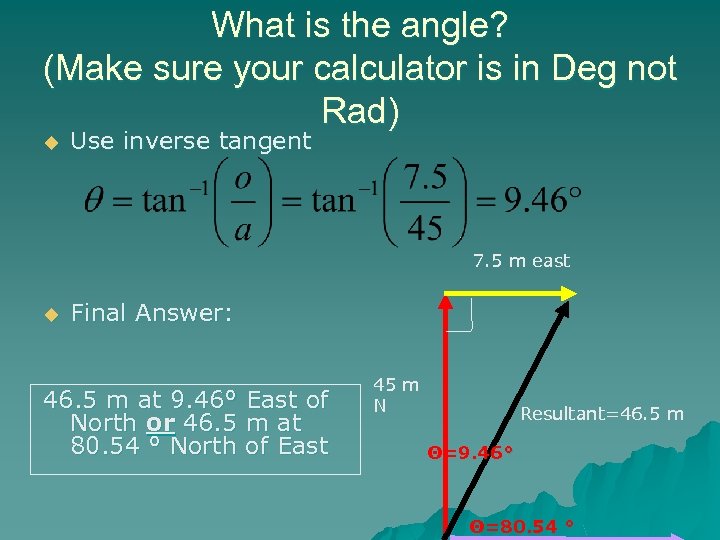 What is the angle? (Make sure your calculator is in Deg not Rad) u Use inverse tangent 7. 5 m east u Final Answer: 46. 5 m at 9. 46° East of North or 46. 5 m at 80. 54 ° North of East 45 m N Resultant=46. 5 m Θ=9. 46° Θ=80. 54 °
What is the angle? (Make sure your calculator is in Deg not Rad) u Use inverse tangent 7. 5 m east u Final Answer: 46. 5 m at 9. 46° East of North or 46. 5 m at 80. 54 ° North of East 45 m N Resultant=46. 5 m Θ=9. 46° Θ=80. 54 °