ad71d5da29c3aa94a95e52ed25c60a35.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Chapter 3 The Trading Industry
Chapter 3 The Trading Industry
 Terminology Ø Agency vs. proprietary traders (trading) • Ø Long vs. short positions • Ø Brokers are agency traders Short covering Buy vs. sell side • Liquidity demanders vs. liquidity providers
Terminology Ø Agency vs. proprietary traders (trading) • Ø Long vs. short positions • Ø Brokers are agency traders Short covering Buy vs. sell side • Liquidity demanders vs. liquidity providers
 Ø People and institutions who use market services are on the buy-side. Ø Those who provide market services are on the sell-side. Ø These sides have nothing to do with whether you are a buyer or seller of a specific security.
Ø People and institutions who use market services are on the buy-side. Ø Those who provide market services are on the sell-side. Ø These sides have nothing to do with whether you are a buyer or seller of a specific security.
 Buy-side players - Investors Individuals Ø Corporate pension fund sponsors Ø Charitable trusts Ø Legal trusts Ø Endowments Ø => Stocks and bonds Investment managers Ø Corporate investment funds Ø Governmental funds Ø
Buy-side players - Investors Individuals Ø Corporate pension fund sponsors Ø Charitable trusts Ø Legal trusts Ø Endowments Ø => Stocks and bonds Investment managers Ø Corporate investment funds Ø Governmental funds Ø
 Buy-side players – Borrowers and Hedgers Ø Ø Ø Homeowners Students Corporations => Mortgages, Bonds, Notes Ø Ø Ø Farmers Manufacturers Miners Shippers Financial Institutions => Forwards, Futures, Swaps, and Options
Buy-side players – Borrowers and Hedgers Ø Ø Ø Homeowners Students Corporations => Mortgages, Bonds, Notes Ø Ø Ø Farmers Manufacturers Miners Shippers Financial Institutions => Forwards, Futures, Swaps, and Options
 Sell-side players Ø Dealers trade for their own accounts. Day traders • Market makers • Floor traders • Ø Brokers trade for other people’s accounts. Retail and institutional • Full-service and discount • Ø Broker-dealers do both. Specialists • Wire houses •
Sell-side players Ø Dealers trade for their own accounts. Day traders • Market makers • Floor traders • Ø Brokers trade for other people’s accounts. Retail and institutional • Full-service and discount • Ø Broker-dealers do both. Specialists • Wire houses •
 Sell-side trade facilitators Ø Exchanges provide systems that help traders arrange their trades. Ø Clearing houses help settle trades and guarantee that traders will perform. Ø Depositories and custodians hold securities.
Sell-side trade facilitators Ø Exchanges provide systems that help traders arrange their trades. Ø Clearing houses help settle trades and guarantee that traders will perform. Ø Depositories and custodians hold securities.
 A typical set of relationships A sponsor owns funds. Ø An investment manager makes portfolio decisions. Ø A broker implements trades. Ø A dealer supplies liquidity. Ø A clearing house guarantees trades. Ø A depository holds the security. Ø Consultants advise everyone. Ø
A typical set of relationships A sponsor owns funds. Ø An investment manager makes portfolio decisions. Ø A broker implements trades. Ø A dealer supplies liquidity. Ø A clearing house guarantees trades. Ø A depository holds the security. Ø Consultants advise everyone. Ø
 Primary vs. secondary security sales Ø Primary New issue • Key factor: issuer receives the proceeds from the sale. • Ø Secondary Existing owner sells to another party. • Issuing firm doesn’t receive proceeds and is not directly involved. •
Primary vs. secondary security sales Ø Primary New issue • Key factor: issuer receives the proceeds from the sale. • Ø Secondary Existing owner sells to another party. • Issuing firm doesn’t receive proceeds and is not directly involved. •
 Primary markets: Public offerings Ø Public offerings: registered with the SEC and sale is made to the investing public. • Shelf registration (Rule 415, since 1982) Ø Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) • Evidence of underpricing • Performance
Primary markets: Public offerings Ø Public offerings: registered with the SEC and sale is made to the investing public. • Shelf registration (Rule 415, since 1982) Ø Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) • Evidence of underpricing • Performance
 US primary listing market New York Stock Exchange Ø American Stock Exchange Ø NASDAQ Ø Over-the-Counter (OTC) Ø Nasdaq small cap • OTCBB • Pink Sheets • (N) (A) (Q) (S) (U)
US primary listing market New York Stock Exchange Ø American Stock Exchange Ø NASDAQ Ø Over-the-Counter (OTC) Ø Nasdaq small cap • OTCBB • Pink Sheets • (N) (A) (Q) (S) (U)
 Primary markets: Private placements Private placement: sale to a limited number of sophisticated investors not requiring the protection of registration. Ø Dominated by institutions. Ø Very active market for debt securities. Ø Not active for stock offerings. Ø
Primary markets: Private placements Private placement: sale to a limited number of sophisticated investors not requiring the protection of registration. Ø Dominated by institutions. Ø Very active market for debt securities. Ø Not active for stock offerings. Ø
 Organization of secondary markets Organized exchanges Ø OTC market Ø Third market Ø Fourth market Ø
Organization of secondary markets Organized exchanges Ø OTC market Ø Third market Ø Fourth market Ø
 Organized Exchanges Auction markets with centralized order flow. Ø Dealership function: can be competitive or assigned by the exchange (Specialists). Ø Securities: stock, futures contracts, options, and to a lesser extent, bonds. Ø Examples: NYSE, AMEX, Regionals, CBOE. Ø
Organized Exchanges Auction markets with centralized order flow. Ø Dealership function: can be competitive or assigned by the exchange (Specialists). Ø Securities: stock, futures contracts, options, and to a lesser extent, bonds. Ø Examples: NYSE, AMEX, Regionals, CBOE. Ø
 NYSE Ø The NYSE is a hybrid market. It has: • • • Ø floor traders (like a futures pit) an electronic limit order book (like Euronext) a designated dealer (the specialist) to maintain liquidity and otherwise coordinate trading. This mix is the outcome of political, technological and economic forces over the last 200 years.
NYSE Ø The NYSE is a hybrid market. It has: • • • Ø floor traders (like a futures pit) an electronic limit order book (like Euronext) a designated dealer (the specialist) to maintain liquidity and otherwise coordinate trading. This mix is the outcome of political, technological and economic forces over the last 200 years.
 NYSE’s Marke. Trac: http: //marketrac. nyse. com/mt/
NYSE’s Marke. Trac: http: //marketrac. nyse. com/mt/
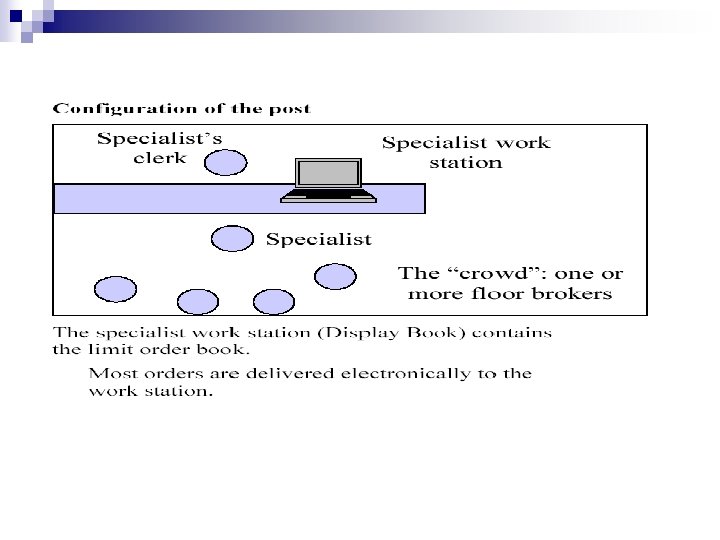
 NYSE The NYSE was first a floor market (loosely resembling the futures pits). Ø Many of the trading rules reflect the “floor” aspect of the market. Ø The NYSE next evolved strong central dealers (late 1800’s). Ø The specialist, in the sense of a trader who specializes in a particular stock. Ø
NYSE The NYSE was first a floor market (loosely resembling the futures pits). Ø Many of the trading rules reflect the “floor” aspect of the market. Ø The NYSE next evolved strong central dealers (late 1800’s). Ø The specialist, in the sense of a trader who specializes in a particular stock. Ø
 NYSE Ø Beginning in the 1980’s, electronic order entry has come to play an increasing role. The exchange has always permitted limit orders, but the book has become more important over time. Ø The basic reading for this material is the NYSE Floor Official Manual, abbreviated FOM.
NYSE Ø Beginning in the 1980’s, electronic order entry has come to play an increasing role. The exchange has always permitted limit orders, but the book has become more important over time. Ø The basic reading for this material is the NYSE Floor Official Manual, abbreviated FOM.
 What does the NYSE do? Trading and trading services. Ø The NYSE charges (directly and indirectly) for trades that occur and for software supplied to its members. Ø Listing Ø To be listed on the NYSE, a corporation must meet/maintain certain financial standards and pay listing fees. Ø http: //www. nasdaq. com/about/appa. pdf Ø
What does the NYSE do? Trading and trading services. Ø The NYSE charges (directly and indirectly) for trades that occur and for software supplied to its members. Ø Listing Ø To be listed on the NYSE, a corporation must meet/maintain certain financial standards and pay listing fees. Ø http: //www. nasdaq. com/about/appa. pdf Ø
 US regional exchanges Pacific Exchange / Archipelago Ø Chicago (formerly Midwestern) Stock Exchange Ø Boston Stock Exchange Ø Philadelphia Stock Exchange Ø Cincinnati Stock Exchange Ø (P) (M) (B) (X) (C)
US regional exchanges Pacific Exchange / Archipelago Ø Chicago (formerly Midwestern) Stock Exchange Ø Boston Stock Exchange Ø Philadelphia Stock Exchange Ø Cincinnati Stock Exchange Ø (P) (M) (B) (X) (C)
 Third markets Ø Trading of listed securities away from the exchange. Ø Institutional market: to facilitate trades of larger blocks of securities. Ø Involves services of dealers and brokers
Third markets Ø Trading of listed securities away from the exchange. Ø Institutional market: to facilitate trades of larger blocks of securities. Ø Involves services of dealers and brokers
 Fourth Market Ø Trading in exchange-listed stocks within Alternative Trading Systems (ATS), such as ECNs (Instinet, Island, Archipelago) Ø Institutions trading directly with institutions Ø No middleman involved in the transaction
Fourth Market Ø Trading in exchange-listed stocks within Alternative Trading Systems (ATS), such as ECNs (Instinet, Island, Archipelago) Ø Institutions trading directly with institutions Ø No middleman involved in the transaction
 Major international stock markets Europe • London Stock Exchange (LSE) • Euro. Next (Paris/Netherlands/Belgium) • Deutsche Borse (DB) • Milan Stock Exchange • Swiss Stock Exchange Stockholm/Copenhagen/Helsinki/Oslo (OM) Ø Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) Ø
Major international stock markets Europe • London Stock Exchange (LSE) • Euro. Next (Paris/Netherlands/Belgium) • Deutsche Borse (DB) • Milan Stock Exchange • Swiss Stock Exchange Stockholm/Copenhagen/Helsinki/Oslo (OM) Ø Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) Ø
 Ø Asia • • • Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) Taiwan Stock Exchange Korean Stock Exchange (KSE) Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) Hong Kong Stock Exchange
Ø Asia • • • Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) Taiwan Stock Exchange Korean Stock Exchange (KSE) Australian Stock Exchange (ASX) Hong Kong Stock Exchange
 International market structures Ø London Stock Exchange Dealer market similar to NASDAQ • Stock Exchange Automated Quotation • Greater Anonymity • Ø Tokyo Stock Exchange No market making service • Sartori provides bookkeeping service • Feature a floor and electronic trading •
International market structures Ø London Stock Exchange Dealer market similar to NASDAQ • Stock Exchange Automated Quotation • Greater Anonymity • Ø Tokyo Stock Exchange No market making service • Sartori provides bookkeeping service • Feature a floor and electronic trading •
 KSE n http: //www. kse. or. kr/
KSE n http: //www. kse. or. kr/
 The regulators Ø Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) • Ø Securities markets, equity options markets, and cash-settled equity index options markets Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) • Commodity spot, forward, and futures markets
The regulators Ø Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) • Ø Securities markets, equity options markets, and cash-settled equity index options markets Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) • Commodity spot, forward, and futures markets


