efc997adccf320f25ef2427eae39a789.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62

Chapter 3 The Global Trade Environment: Regional Market Characteristics and Preferential Trade Agreements 3 -1

In Chapter 2 Market definition – People or organizations with needs and wants; both have the willingness and ability to buy or sell The global economic environment plays a large role in the development of new markets for organizations 2

Economic Systems 4 main types of economic systems – Market Capitalism – Centrally planned socialism – Centrally planned capitalism – Market socialism 3
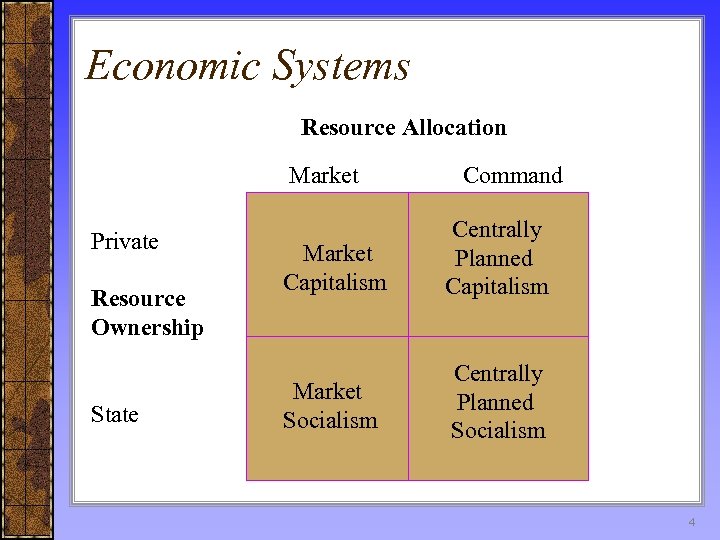
Economic Systems Resource Allocation Market Private Resource Ownership State Command Market Capitalism Centrally Planned Capitalism Market Socialism Centrally Planned Socialism 4
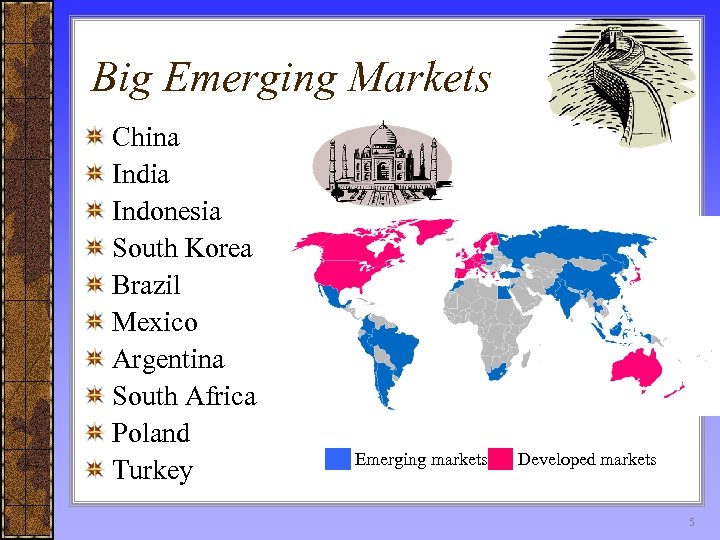
Big Emerging Markets China India Indonesia South Korea Brazil Mexico Argentina South Africa Poland Turkey ██ Emerging markets██ Developed markets 5

Rapidly Developing Economies The term "rapidly developing economies" is now being used to denote emerging markets such as – The United Arab Emirates, – Chile and – Malaysia that are undergoing rapid growth. 6

Stages of Market Development World Bank has defined four categories of development – High-income countries – Upper-middle income countries – Low-income countries Based upon Gross National Product (GNP) 7

Influencing the World Economy Group of Seven (G-7) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development The Triad 8

GATT General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade – treaty among nations to promote trade among members • Handled trade disputes • Lacked enforcement power • Replaced by World Trade Organization in 1995 9

The World Trade Organization Mission: The WTO states that its aims are to increase international trade by promoting lower trade barriers and providing a platform for the negotiation of trade and to their business Provides forum for trade-related negotiations among 150 members – based in Geneva – serves as dispute mediators – empowered with ability to enforce rulings Countries found in violation of WTO rules are expected to change policies or else face sanctions 10
Members 11

Recent WTO Cases ACP: Africa, Caribbean and Pacific 12

Preferential Trade Agreements Many countries seek to lower barriers to trade within their regions – Free Trade Areas – Customs Unions – Common Market – Economic Unions 13
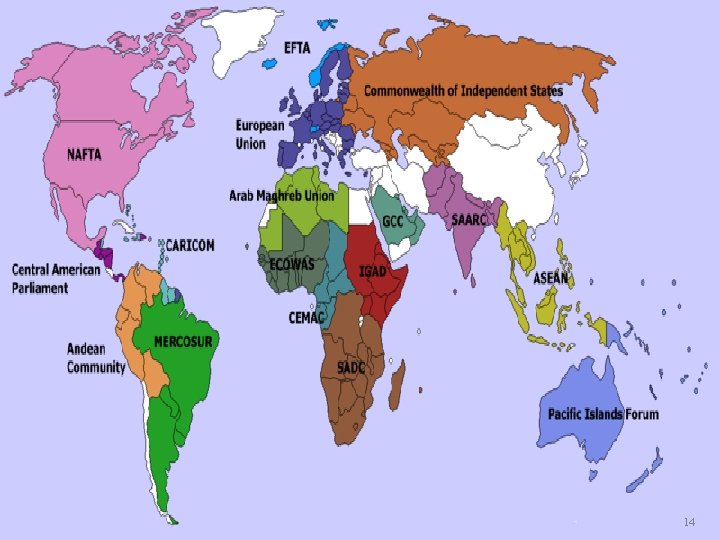
14

North America Canada, United States, Mexico NAFTA established free trade area – all three nations pledge to promote economic growth through tariff reductions and expanded trade and investment – no common external tariffs – restrictions on labor and other movements remain 15

Economic Integration in the Americas The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) created the world’s largest free market. – 390 million U. S. , Canadian, and Mexican consumers 16
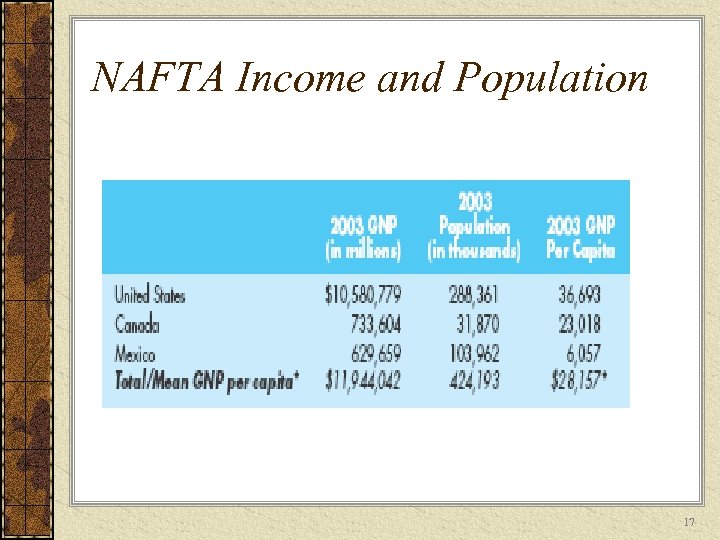
NAFTA Income and Population 17
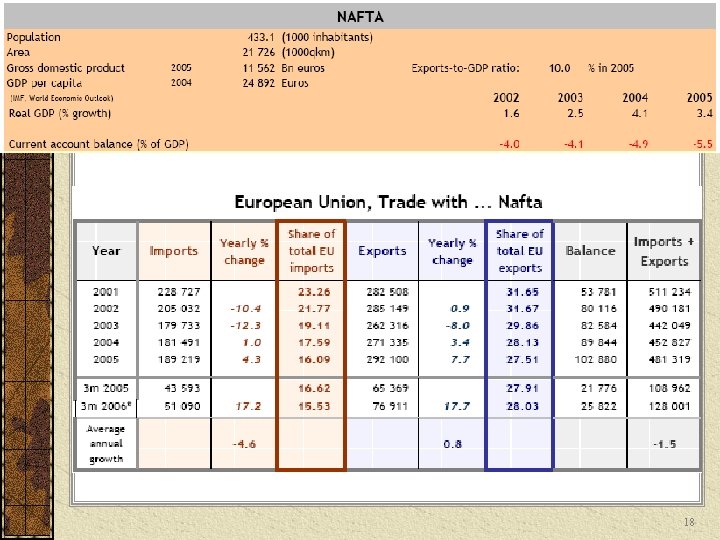
18
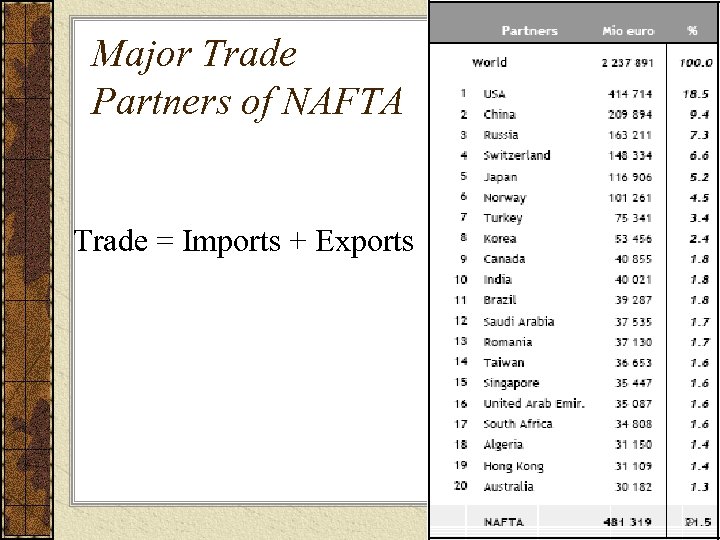
Major Trade Partners of NAFTA Trade = Imports + Exports 19
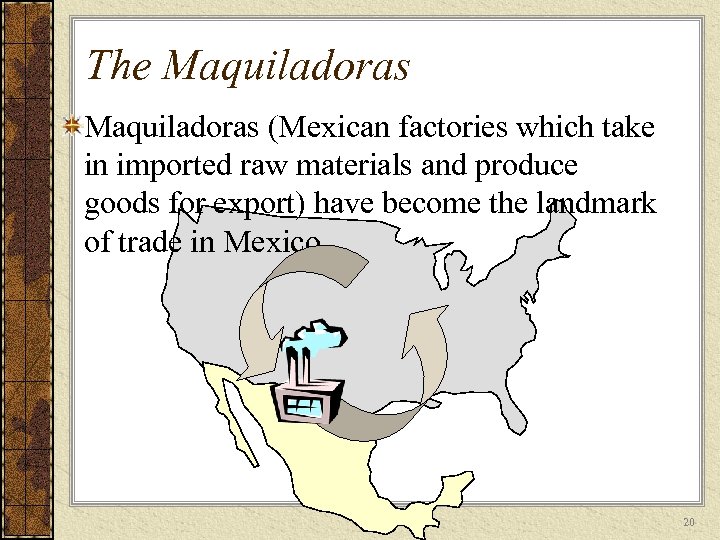
The Maquiladoras (Mexican factories which take in imported raw materials and produce goods for export) have become the landmark of trade in Mexico 20

Latin America Caribbean, Central, and South America 4 preferential trade agreements in place – Central American Integration System – Andean Community – Common Market of the South – Caribbean Community and Common Market 21
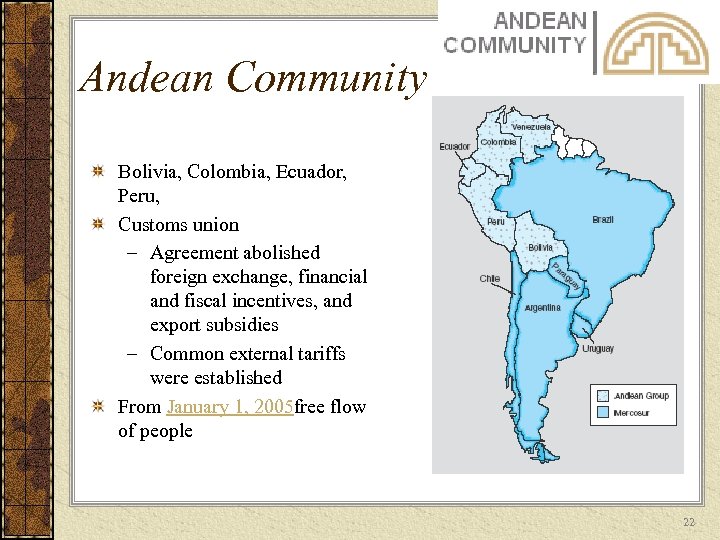
Andean Community Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Customs union – Agreement abolished foreign exchange, financial and fiscal incentives, and export subsidies – Common external tariffs were established From January 1, 2005 free flow of people 22
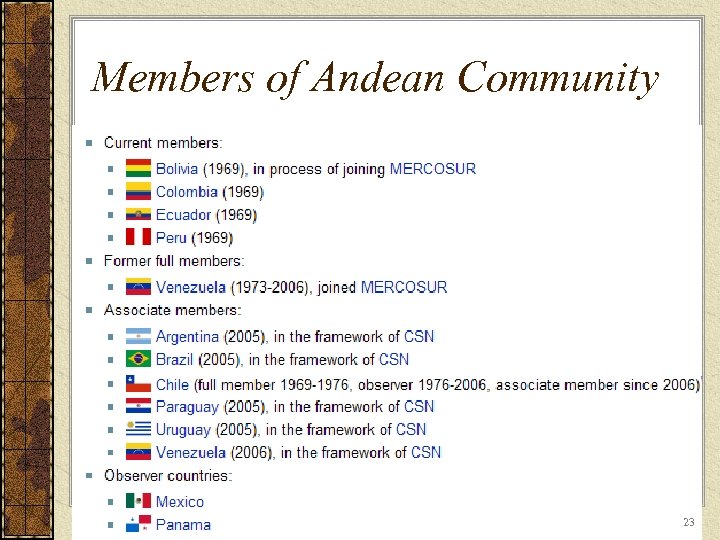
Members of Andean Community 23

Common Market of the South (Mercosur) Common Market of the South Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, and Paraguay sign a three-step treaty – 1991 -94 creation of a FTA – 1995 CU – eventually common market (modeled after the EU) 24
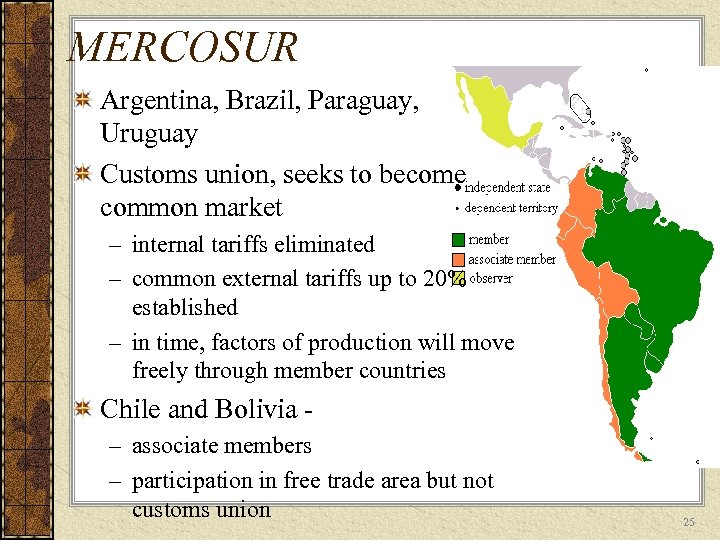
MERCOSUR Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay Customs union, seeks to become common market – internal tariffs eliminated – common external tariffs up to 20% established – in time, factors of production will move freely through member countries Chile and Bolivia - – associate members – participation in free trade area but not customs union 25
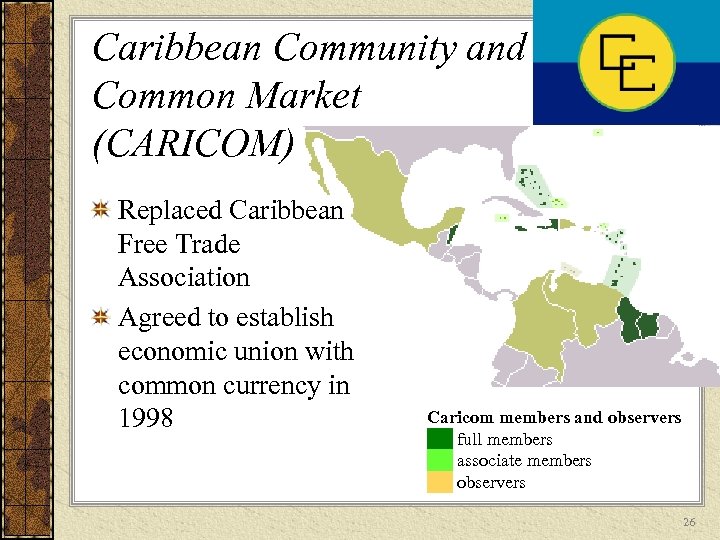
Caribbean Community and Common Market (CARICOM) Replaced Caribbean Free Trade Association Agreed to establish economic union with common currency in 1998 Caricom members and observers ██ full members ██ associate members ██ observers 26

NICs: Newly Industrialized Countries Africa: South Africa, Egypt North America: Mexico (OECD member, 1994) South America: Argentina, Brazil Asia: China, The GCC states, India; Republic of, Malaysia, Philippines and Thailand Europe: Turkey (EU official candidate) 27
Asia-Pacific Includes 23 countries and 56% of world population – Japan – Newly industrializing economies – Association of Southeast Asian Nations 28
Japan Generates 14% of world’s GNP Key factors – population density – geographic isolation Recent economic struggles despite status as high income country Strong culture requires flexibility and commitment from global marketers 29

Newly Industrializing Economies (NIEs) Strong economic growth in recent decades – foreign investment – export-driven industrial development Sometimes called the 4 Tigers of Asia – South Korea – Taiwan – Singapore – Hong Kong 亞洲四小龍 30

亞洲四小龍 (4 Little Dragons of Asia) The common characteristics of the East Asian Tigers are: Focused on exports to richer industrialized nations Trade surplus with aforementioned countries Sustained rate of double-digit growth for decades Non-democratic and relatively authoritarian political systems during the early years High level of U. S. treasury bond holdings High savings rate A high degree of what is referred to as economic freedom. Hong Kong, Singapore, Taiwan and South Korea are 1 st, 2 nd, 37 th, and 45 th respectively. 31

Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) became fully operational on January 1, 2003 – Tariffs of 20+% will be reduced to 0 - 5% – (2006 for Vietnam, 2008 for Laos and Myanmar, and 2010 for Cambodia). Singapore represents great success among ASEAN nations 32
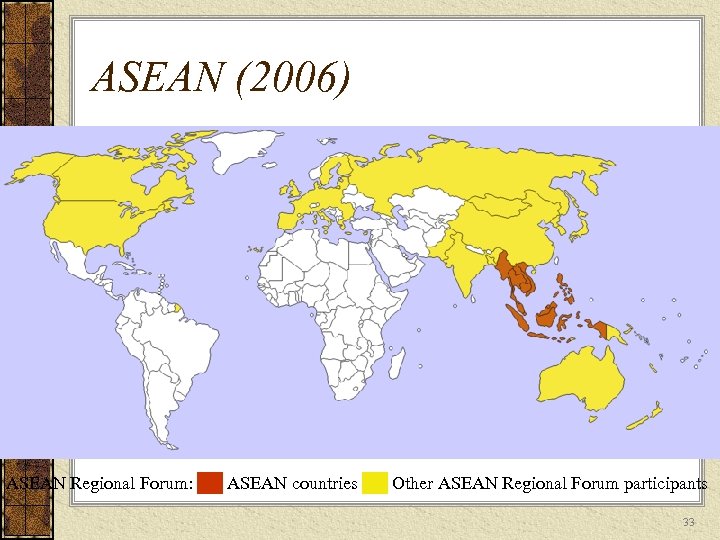
ASEAN (2006) ASEAN Regional Forum: ██ ASEAN countries ██ Other ASEAN Regional Forum participants 33

European Union European Free Trade Area European Economic Area The Lome Convention Central European Free Trade Association (CEFTA) 34

European Union Initially began with the 1958 Treaty of Rome Objective to harmonize national laws and regulations so that goods, services, people and money could flow freely across national boundaries 1991 Maastricht Treaty set stage for transition to an economic union with a central bank and single currency (the Euro) 35
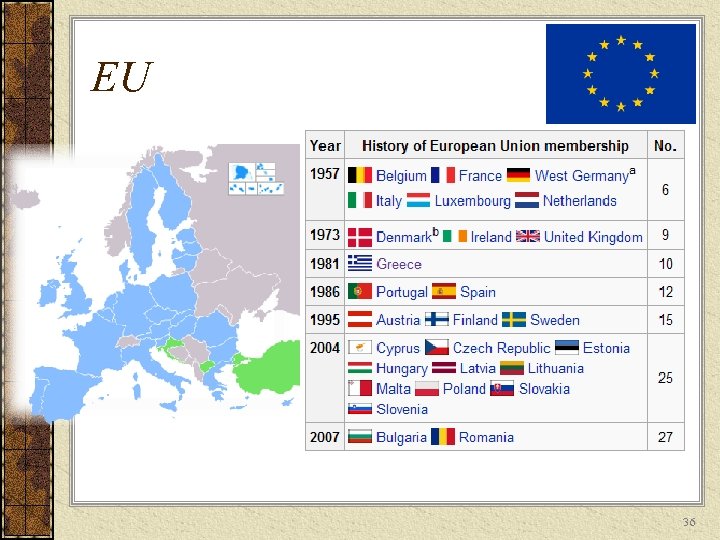
EU 36
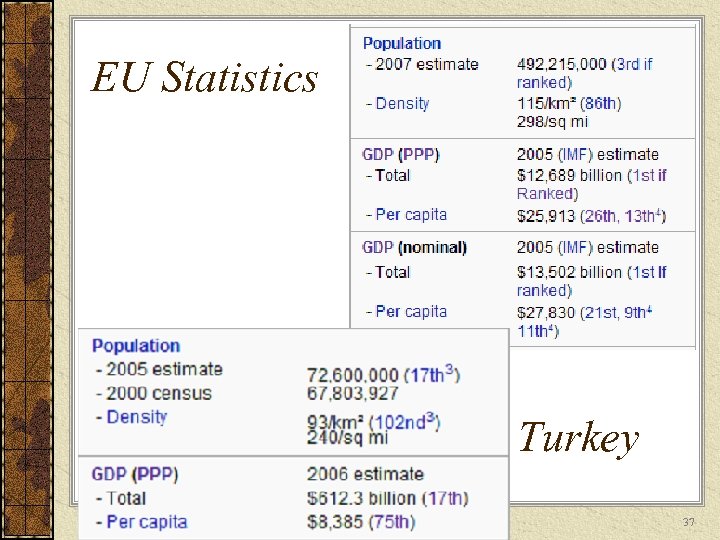
EU Statistics Turkey 37

European Free Trade Area and the European Economic Area EFTA: Norway, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Switzerland Free trade area Members (excluding Switzerland) chose to establish European Economic Area (EEA) – Non-EU members of the EEA are expected to adopt EU guidelines – EEA Members: Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, without Switzerland – and the 27 EU Member States along with the European Community. Norway, Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Switzerland maintain free trade agreements with other countries as well 38

The Lome Convention An accord between EU and 71 countries in Africa, Caribbean, and the Pacific Promotes trade and provides poor countries with financial assistance from a European Development Fund Currently working to establish a successor agreement 39

Central European Free Trade Association (CEFTA) Allows for cooperation in many areas including: – infrastructure and telecommunications – sub-regional projects – inter-enterprise cooperation – tourism and retail trade 40
41

The Middle East Afghanistan, Cyprus, Bahrain, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen – Primarily Arab, some Persian and Jews – 95% Muslim 3 key regional organizations – Gulf Cooperation Council – Arab Maghreb Union – Arab Cooperation Council 42

ﺍﻟﺨﻠﻴﺠﻲ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﺎﻭﻥ ﻣﺠﻠﺲ (Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf GDP: $536, 223 Yemen is currently (as of 2006) in negotiations for GCC membership, and hopes to join by 2016 43

ﺍﺗﺤﺎﺩﺍﻟﻤﻐﺮﺏﺍﻟﻌﺮﺑﻲ (Arab Maghreb Union ) Arab Maghreb Union is a Pan-Arab trade agreement aiming for economic and political unity in Northern Africa. 44

Arab Cooperation Council (ACC) founded in February 1989 by North Yemen, Iraq, Jordan, and Egypt the organization did not survive the crisis that followed Iraq's invasion of Kuwait on August 2, 1990 45

Africa 53 nations over three distinct areas – Republic of South Africa – North Africa – Black Africa Regional agreements – Economic Community of West African States – East African Cooperation – South African Development Community 46
47

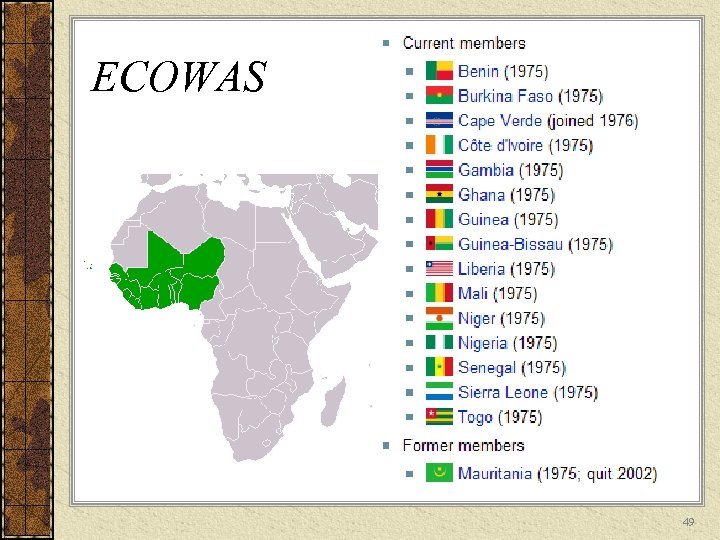
Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) Free trade area with unified monetary zone ECOWAS Travel certificate has entered into circulation in Burkina Faso, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria and Sierra Leone. ECOWAS Passport is printed and operational in Benin, Mali and Senegal 48
ECOWAS 49
East African Community plans to introduce a monetary union with a common currency by 2009 plans for a common market and a political union with a common President (initially on a rotation basis) & a common parliament by 2010 50

South African Development Community (SADC) Mechanism to promote trade, cooperation, and economic integration by black-ruled states Ultimately seeks to form customs union 51
SADC 52

Looking Ahead to Chapter 4 Social and Cultural Environments 53

Free Trade Areas Two or more countries agree to abolish all internal barriers to trade amongst themselves It is the second stage of economic integration Countries continue independent trade policies with countries outside agreement 54

Free Trade Areas Turkey has bilateral agreements with the following countries and blocs: – – – – – Bosnia and Herzegovina Croatia Egypt Israel Morocco Macedonia Palestinian Authority Tunisia The European Free Trade Association GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) - proposed Return 55

Customs Unions Evolution of Free Trade Area Includes the elimination of internal barriers to trade (as in FTA) AND Establishes common external barriers to trade 56

List of Customs Unions Southern African Customs Union East African Community Gulf Cooperation Council MERCOSUR Central American Customs Union EU - Turkey Customs Union (since 1996) EU - Andorra Customs Union EU - San Marino Customs Union Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA) Andean Community (CAN) Israel - Palestinian territories (since 1994) Switzerland - Liechtenstein (since 1924) Return 57

Common Market Includes the elimination of internal barriers to trade (as in free trade area) AND Establishes common external barriers to trade (as in customs union) AND Allows for the free movement of factors of production, such as labor, capital, and information 58

List of Common Markets the European Community (EC) European Economic Area (EEA) between the EC, Norway, Iceland Liechtenstein the Caribbean Community single market (CARICOM) Return 59

Economic Unions Includes the elimination of internal barriers to trade (as in free trade area) AND Establishes common external barriers to trade (as in customs union) AND Allows for the free movement of factors of production, such as labor, capital, and information (as in common market) AND Coordinates and harmonizes economic and social policy within the union 60

Economic Unions Full evolution of economic union – creation of unified central bank – use of single currency – common policies on issues ranging from agriculture to taxation – requires extensive political unity Return 61
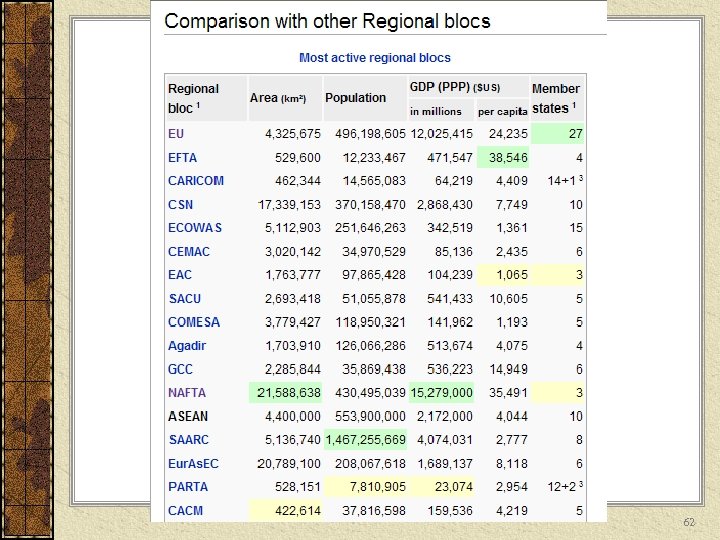
62
efc997adccf320f25ef2427eae39a789.ppt