e2429360fc80c76fb45c79d19b2a0cd9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 84
 Chapter 3 The External Assessment Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 10 th Edition Fred David Power. Point Slides by Anthony F. Chelte Western New England College Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 1
Chapter 3 The External Assessment Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 10 th Edition Fred David Power. Point Slides by Anthony F. Chelte Western New England College Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 1
 Chapter Outline The Nature of the External Audit The Industrial Organization (I/O) View Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 2
Chapter Outline The Nature of the External Audit The Industrial Organization (I/O) View Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 2
 Chapter Outline (cont’d) Political, Governmental, and Legal Forces Technological Forces Competitive Forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 3
Chapter Outline (cont’d) Political, Governmental, and Legal Forces Technological Forces Competitive Forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 3
 Chapter Outline (cont’d) Porter’s Five-Forces Model Sources of External Information Forecasting Tools & Techniques Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 4
Chapter Outline (cont’d) Porter’s Five-Forces Model Sources of External Information Forecasting Tools & Techniques Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 4
 Chapter Outline (cont’d) Global Challenge The External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 5
Chapter Outline (cont’d) Global Challenge The External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 5
 External Assessment It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to change. – Charles Darwin Nothing focuses the mind better than the constant sight of a competitor who wants to wipe you off the map. – Wayne Calloway, Former CEO, Pepsi. Co Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 6
External Assessment It is not the strongest of the species that survive, nor the most intelligent, but the one most responsive to change. – Charles Darwin Nothing focuses the mind better than the constant sight of a competitor who wants to wipe you off the map. – Wayne Calloway, Former CEO, Pepsi. Co Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 6
 External Strategic Management Audit -- Environmental Scanning -- Industry Analysis Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 7
External Strategic Management Audit -- Environmental Scanning -- Industry Analysis Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 7
 External Strategic Management Audit Identify & Evaluate factors beyond the control of a single firm q q q Increased foreign competition Population shifts Information technology Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 8
External Strategic Management Audit Identify & Evaluate factors beyond the control of a single firm q q q Increased foreign competition Population shifts Information technology Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 8
 External Strategic Management Audit Purpose of External Audit q Identify Opportunities n Threats n Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 9
External Strategic Management Audit Purpose of External Audit q Identify Opportunities n Threats n Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 9
 Key External Forces • Economic forces • Social, cultural, demographic & environmental forces • Political, governmental & legal forces • Technological forces • Competitive forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 10
Key External Forces • Economic forces • Social, cultural, demographic & environmental forces • Political, governmental & legal forces • Technological forces • Competitive forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 10
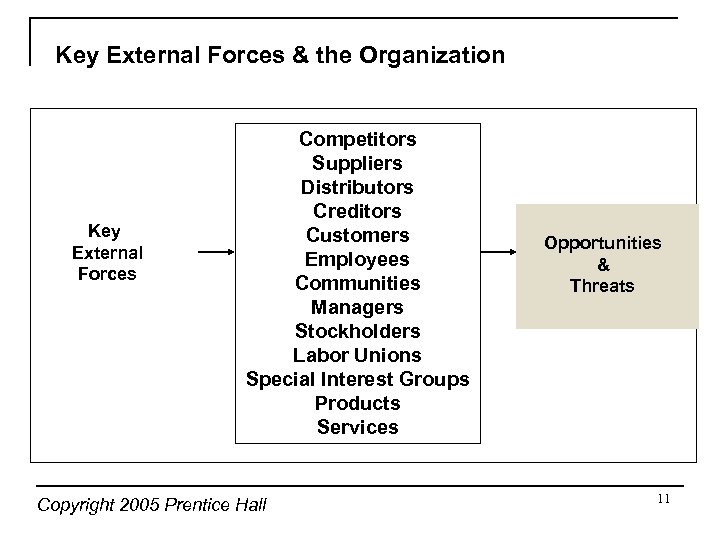 Key External Forces & the Organization Key External Forces Competitors Suppliers Distributors Creditors Customers Employees Communities Managers Stockholders Labor Unions Special Interest Groups Products Services Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall Opportunities & Threats 11
Key External Forces & the Organization Key External Forces Competitors Suppliers Distributors Creditors Customers Employees Communities Managers Stockholders Labor Unions Special Interest Groups Products Services Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall Opportunities & Threats 11
 External Audit Gather competitive intelligence – n n n n Social Cultural Demographic Environmental Economic Political, legal governmental Technological Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 12
External Audit Gather competitive intelligence – n n n n Social Cultural Demographic Environmental Economic Political, legal governmental Technological Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 12
 External Audit – Sources of Information • Internet • Libraries • Suppliers • Distributors • Customers • Competition Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 13
External Audit – Sources of Information • Internet • Libraries • Suppliers • Distributors • Customers • Competition Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 13
 Performing External Audit -- Key Factors n n Vary over time Vary by industry Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 14
Performing External Audit -- Key Factors n n Vary over time Vary by industry Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 14
 Performing External Audit -Variables • Market share • Breadth of competing products • World economies • Foreign affiliates • Proprietary account advantages Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 15
Performing External Audit -Variables • Market share • Breadth of competing products • World economies • Foreign affiliates • Proprietary account advantages Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 15
 Performing External Audit -Variables • Price competitiveness • Technological advancements • Interest rates • Pollution abatement Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 16
Performing External Audit -Variables • Price competitiveness • Technological advancements • Interest rates • Pollution abatement Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 16
 Performing External Audit Long-term orientation External Factors Measurable Applicable to competing firms Hierarchical Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 17
Performing External Audit Long-term orientation External Factors Measurable Applicable to competing firms Hierarchical Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 17
 Industrial Organization (I/O) View -- Industry factors more important than internal factors n Performance determined by industry forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 18
Industrial Organization (I/O) View -- Industry factors more important than internal factors n Performance determined by industry forces Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 18
 I/O Perspective Firm Performance Industry Properties Economies of Scale Barriers to market entry Product differentiation Level of competitiveness Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 19
I/O Perspective Firm Performance Industry Properties Economies of Scale Barriers to market entry Product differentiation Level of competitiveness Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 19
 Economic Forces • Availability of credit • Level of disposable income • Interest rates • Inflation rates Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 20
Economic Forces • Availability of credit • Level of disposable income • Interest rates • Inflation rates Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 20
 Economic Forces • Money market rates • Fed Gov’t deficits • GDP trend • Consumption patterns Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 21
Economic Forces • Money market rates • Fed Gov’t deficits • GDP trend • Consumption patterns Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 21
 Key Economic Variables Unemployment trends Worker productivity levels Value of the dollar in world markets Stock market trends Foreign economic conditions Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 22
Key Economic Variables Unemployment trends Worker productivity levels Value of the dollar in world markets Stock market trends Foreign economic conditions Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 22
 Key Economic Variables Import/Export factors Demand shifts for goods/services Income differences by region/customer Price fluctuations Exportation of labor and capital Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 23
Key Economic Variables Import/Export factors Demand shifts for goods/services Income differences by region/customer Price fluctuations Exportation of labor and capital Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 23
 Key Economic Variables Monetary policies Fiscal policies Tax rates OPEC policies ECC policies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 24
Key Economic Variables Monetary policies Fiscal policies Tax rates OPEC policies ECC policies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 24
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Major Impact – • Products • Services • Markets • Customers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 25
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Major Impact – • Products • Services • Markets • Customers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 25
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces U. S. Facts • Aging population • Less Caucasian • Widening gap between rich & poor • 2025 = 18. 5% population >65 years • 2075 = no ethnic or racial majority Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 26
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces U. S. Facts • Aging population • Less Caucasian • Widening gap between rich & poor • 2025 = 18. 5% population >65 years • 2075 = no ethnic or racial majority Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 26
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Facts • World population > 6 billion • U. S. population < 300 million Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 27
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Facts • World population > 6 billion • U. S. population < 300 million Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 27
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Population characteristics require global strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 28
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Population characteristics require global strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 28
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Global trends • 2003 – China largest exporter to U. S. • 2003 Asia receives highest foreign direct investment Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 29
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Global trends • 2003 – China largest exporter to U. S. • 2003 Asia receives highest foreign direct investment Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 29
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Global trends • China’s labor rates less than Mexico • China provides more site location incentives than Mexico Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 30
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Global trends • China’s labor rates less than Mexico • China provides more site location incentives than Mexico Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 30
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Export Trends • Mexico-exports to U. S. 1. 2% growth (2002) • China-exports to U. S. 19% growth (2002) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 31
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Export Trends • Mexico-exports to U. S. 1. 2% growth (2002) • China-exports to U. S. 19% growth (2002) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 31
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Export Trends • Mexico-corporate income tax rate 34% • China-corporate income tax rate 17% Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 32
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Export Trends • Mexico-corporate income tax rate 34% • China-corporate income tax rate 17% Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 32
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces 21 st Century Trends • More educated consumers • Aging population • Minorities more influential • Local rather than federal solutions Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 33
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces 21 st Century Trends • More educated consumers • Aging population • Minorities more influential • Local rather than federal solutions Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 33
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces (cont’d) 21 st Century Trends • Fixation with youth decreasing • Hispanics increase to 15% by 2021 • African American increase to 14% by 2021 Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 34
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces (cont’d) 21 st Century Trends • Fixation with youth decreasing • Hispanics increase to 15% by 2021 • African American increase to 14% by 2021 Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 34
 Key Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Variables Childbearing rates Number of special interest groups Number of marriages & divorces Number of births & deaths Immigration & emigration rates Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 35
Key Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Variables Childbearing rates Number of special interest groups Number of marriages & divorces Number of births & deaths Immigration & emigration rates Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 35
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Actuarial rates Monitor Key Variables Per capita income Attitudes toward business Avg. disposable income Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 36
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Actuarial rates Monitor Key Variables Per capita income Attitudes toward business Avg. disposable income Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 36
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Consumer behavior Monitor Key Variables Ethical concerns Attitudes toward saving Racial equality Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 37
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Consumer behavior Monitor Key Variables Ethical concerns Attitudes toward saving Racial equality Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 37
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Avg. educational level Monitor Key Variables Governmental regulation Attitudes toward customer service Attitudes toward quality Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 38
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Avg. educational level Monitor Key Variables Governmental regulation Attitudes toward customer service Attitudes toward quality Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 38
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Energy conservation Monitor Key Variables Social responsibility Leisure time values Recycling Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 39
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Energy conservation Monitor Key Variables Social responsibility Leisure time values Recycling Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 39
 Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Waste management Monitor Key Variables Air & water pollution Ozone depletion Endangered species Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 40
Social, Cultural, Demographic & Environmental Forces Waste management Monitor Key Variables Air & water pollution Ozone depletion Endangered species Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 40
 Political, Government & Legal Forces Government Regulation Key opportunities & threats Antitrust legislation n Tax rates n Lobbying efforts n Patent laws n Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 41
Political, Government & Legal Forces Government Regulation Key opportunities & threats Antitrust legislation n Tax rates n Lobbying efforts n Patent laws n Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 41
 Political, Government & Legal Forces Increasing Global Interdependence Political variables impact – q q Formulation of strategies Implementation of strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 42
Political, Government & Legal Forces Increasing Global Interdependence Political variables impact – q q Formulation of strategies Implementation of strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 42
 Political, Government & Legal Forces Increasing Global Interdependence Strategists in a global economy -q q q Forecast political climates Legalistic skills Diverse world cultures Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 43
Political, Government & Legal Forces Increasing Global Interdependence Strategists in a global economy -q q q Forecast political climates Legalistic skills Diverse world cultures Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 43
 Political, Government & Legal Forces Globalization of Industry n n Worldwide trend toward similar consumption patterns Global buyers and sellers E-commerce Technology for instant currency transfers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 44
Political, Government & Legal Forces Globalization of Industry n n Worldwide trend toward similar consumption patterns Global buyers and sellers E-commerce Technology for instant currency transfers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 44
 Key Political, Governmental, & Legal Variables Regulation/deregulation Tax law changes Special tariffs PAC’s Voter participation rates Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 45
Key Political, Governmental, & Legal Variables Regulation/deregulation Tax law changes Special tariffs PAC’s Voter participation rates Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 45
 Key Political, Governmental, & Legal Variables (cont’d) Number of patents Changes in patent laws Environmental protection laws Equal employment legislation Government subsidies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 46
Key Political, Governmental, & Legal Variables (cont’d) Number of patents Changes in patent laws Environmental protection laws Equal employment legislation Government subsidies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 46
 Key Political, Governmental, & Legal Variables (cont’d) Anti-trust enforcement Global relationships Import/export regulations Political conditions Location and severity of terrorist activity Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 47
Key Political, Governmental, & Legal Variables (cont’d) Anti-trust enforcement Global relationships Import/export regulations Political conditions Location and severity of terrorist activity Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 47
 Technological Forces Major Impact – • Internet • Communications • Semiconductors Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 48
Technological Forces Major Impact – • Internet • Communications • Semiconductors Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 48
 Technological Forces Significance of IT • Chief Information Officer (CIO) • Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 49
Technological Forces Significance of IT • Chief Information Officer (CIO) • Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 49
 Technological Forces Technology-based issues Essential for nearly every strategic decision Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 50
Technological Forces Technology-based issues Essential for nearly every strategic decision Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 50
 Competitive Forces Collection & evaluation of data on competitors is essential for successful strategy formulation Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 51
Competitive Forces Collection & evaluation of data on competitors is essential for successful strategy formulation Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 51
 Competitive Forces Competition on virtually all industries can be described as intense. Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 52
Competitive Forces Competition on virtually all industries can be described as intense. Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 52
 Competitive Forces Identifying Rival Firms Strengths • Weaknesses • Capabilities • Opportunities • Threats • Objectives • Strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 53
Competitive Forces Identifying Rival Firms Strengths • Weaknesses • Capabilities • Opportunities • Threats • Objectives • Strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 53
 Key Questions Concerning Competitors Their strengths Their weaknesses Their objectives and strategies Their responses to external variables Their vulnerability to our alternative strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 54
Key Questions Concerning Competitors Their strengths Their weaknesses Their objectives and strategies Their responses to external variables Their vulnerability to our alternative strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 54
 Key Questions Concerning Competitors (cont’d) Our vulnerability to strategic counterattack Our product/service positioning Entry and exit of firms in the industry Key factors for our current position in industry Sales/profit rankings of competitors over time Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 55
Key Questions Concerning Competitors (cont’d) Our vulnerability to strategic counterattack Our product/service positioning Entry and exit of firms in the industry Key factors for our current position in industry Sales/profit rankings of competitors over time Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 55
 Key Questions Concerning Competitors (cont’d) Nature of supplier & distributor relationships The threat of substitute products/services Should we keep our strategies secret from employees and stakeholders? Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 56
Key Questions Concerning Competitors (cont’d) Nature of supplier & distributor relationships The threat of substitute products/services Should we keep our strategies secret from employees and stakeholders? Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 56
 Competitive Forces Sources of Corporate Information • Moody’s Manuals • Standard Corporation Descriptions • Value Line Investment Surveys • Dun’s Business Rankings • Standard & Poor’s Industry Surveys • Industry Week • Forbes, Fortune, Business Week Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 57
Competitive Forces Sources of Corporate Information • Moody’s Manuals • Standard Corporation Descriptions • Value Line Investment Surveys • Dun’s Business Rankings • Standard & Poor’s Industry Surveys • Industry Week • Forbes, Fortune, Business Week Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 57
 Competitive Forces 7 Characteristics of most Competitive U. S. Firms: 1. Market share matters 2. Understand what business you are in 3. Broke or not, fix it 4. Innovate or evaporate Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 58
Competitive Forces 7 Characteristics of most Competitive U. S. Firms: 1. Market share matters 2. Understand what business you are in 3. Broke or not, fix it 4. Innovate or evaporate Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 58
 Competitive Forces 7 Characteristics of most Competitive U. S. Firms: 5. Acquisition is essential to growth 6. People make a difference 7. No substitute for quality Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 59
Competitive Forces 7 Characteristics of most Competitive U. S. Firms: 5. Acquisition is essential to growth 6. People make a difference 7. No substitute for quality Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 59
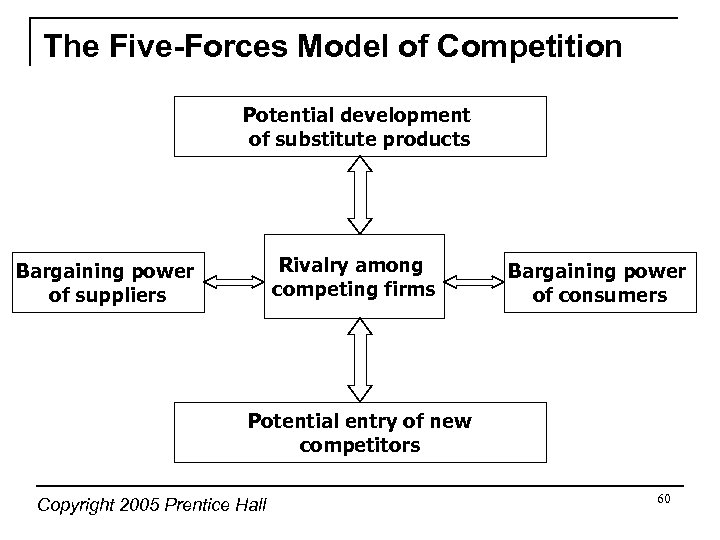 The Five-Forces Model of Competition Potential development of substitute products Rivalry among competing firms Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of consumers Potential entry of new competitors Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 60
The Five-Forces Model of Competition Potential development of substitute products Rivalry among competing firms Bargaining power of suppliers Bargaining power of consumers Potential entry of new competitors Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 60
 The Five-Forces Model Rivalry Among Competing Firms n n Most powerful of the five forces Focus on competitive advantage of strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 61
The Five-Forces Model Rivalry Among Competing Firms n n Most powerful of the five forces Focus on competitive advantage of strategies Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 61
 The Five-Forces Model Potential Entry of New Competitors n n Barriers to entry are important Quality, pricing, and marketing can overcome barriers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 62
The Five-Forces Model Potential Entry of New Competitors n n Barriers to entry are important Quality, pricing, and marketing can overcome barriers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 62
 The Five-Forces Model Potential Development of Substitute Products n n Pressures increase when consumer’s switching costs decrease Firm’s plans for increased capacity & market penetration Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 63
The Five-Forces Model Potential Development of Substitute Products n n Pressures increase when consumer’s switching costs decrease Firm’s plans for increased capacity & market penetration Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 63
 The Five-Forces Model Bargaining Power of Suppliers n n Large number of suppliers & few substitutes affects intensity of competition Backward integration can gain control or ownership of suppliers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 64
The Five-Forces Model Bargaining Power of Suppliers n n Large number of suppliers & few substitutes affects intensity of competition Backward integration can gain control or ownership of suppliers Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 64
 The Five-Forces Model Bargaining Power of Consumers n n Customers concentrated or buy in volume affects intensity of competition Consumer power is higher where products are standard or undifferentiated Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 65
The Five-Forces Model Bargaining Power of Consumers n n Customers concentrated or buy in volume affects intensity of competition Consumer power is higher where products are standard or undifferentiated Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 65
 The Global Challenge Faced by U. S. Firms -- • Gain & maintain exports to other nations • Defend domestic markets against imported goods Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 66
The Global Challenge Faced by U. S. Firms -- • Gain & maintain exports to other nations • Defend domestic markets against imported goods Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 66
 The Global Challenge Multinational Corporations (MNC’s) Simultaneously globally competitive & nationally responsive Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 67
The Global Challenge Multinational Corporations (MNC’s) Simultaneously globally competitive & nationally responsive Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 67
 The Global Challenge Globalization Worldwide integration of: §Strategy formulation §Strategy implementation §Strategy evaluation Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 68
The Global Challenge Globalization Worldwide integration of: §Strategy formulation §Strategy implementation §Strategy evaluation Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 68
 The Global Challenge Globalization of Industries §Similar consumption patterns §Global buyers and sellers §E-commerce §Instant transmission of money & information Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 69
The Global Challenge Globalization of Industries §Similar consumption patterns §Global buyers and sellers §E-commerce §Instant transmission of money & information Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 69
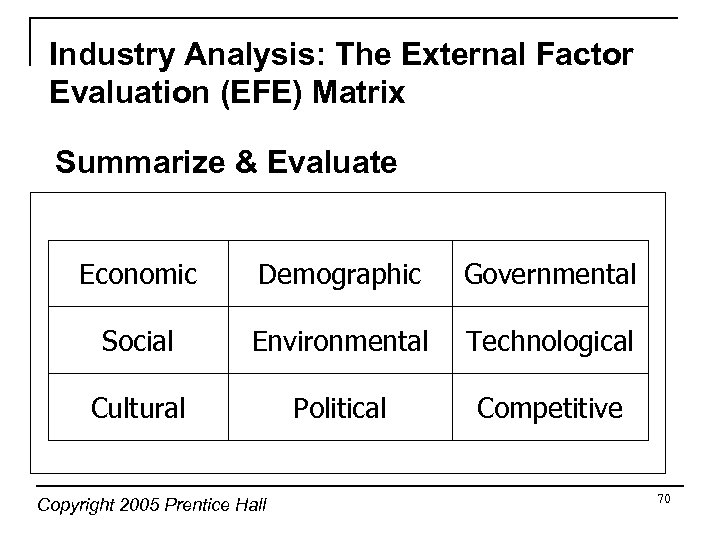 Industry Analysis: The External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix Summarize & Evaluate Economic Demographic Governmental Social Environmental Technological Cultural Political Competitive Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 70
Industry Analysis: The External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix Summarize & Evaluate Economic Demographic Governmental Social Environmental Technological Cultural Political Competitive Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 70
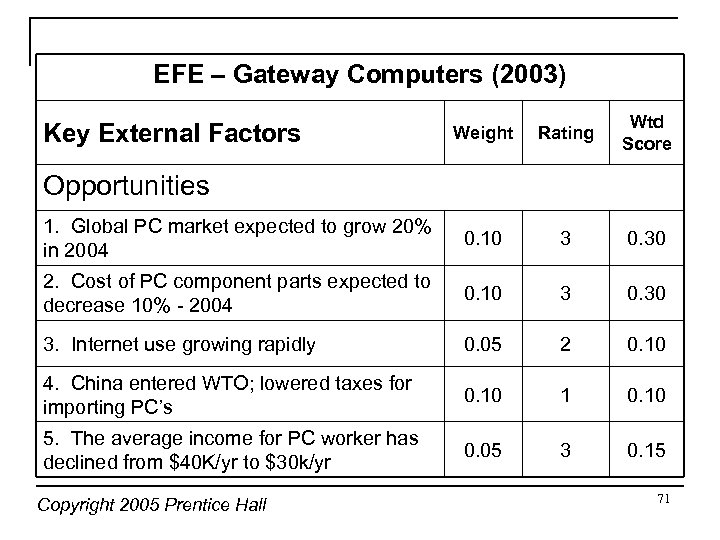 EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) Weight Rating Wtd Score 1. Global PC market expected to grow 20% in 2004 0. 10 3 0. 30 2. Cost of PC component parts expected to decrease 10% - 2004 0. 10 3 0. 30 3. Internet use growing rapidly 0. 05 2 0. 10 4. China entered WTO; lowered taxes for importing PC’s 0. 10 1 0. 10 5. The average income for PC worker has declined from $40 K/yr to $30 k/yr 0. 05 3 0. 15 Key External Factors Opportunities Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 71
EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) Weight Rating Wtd Score 1. Global PC market expected to grow 20% in 2004 0. 10 3 0. 30 2. Cost of PC component parts expected to decrease 10% - 2004 0. 10 3 0. 30 3. Internet use growing rapidly 0. 05 2 0. 10 4. China entered WTO; lowered taxes for importing PC’s 0. 10 1 0. 10 5. The average income for PC worker has declined from $40 K/yr to $30 k/yr 0. 05 3 0. 15 Key External Factors Opportunities Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 71
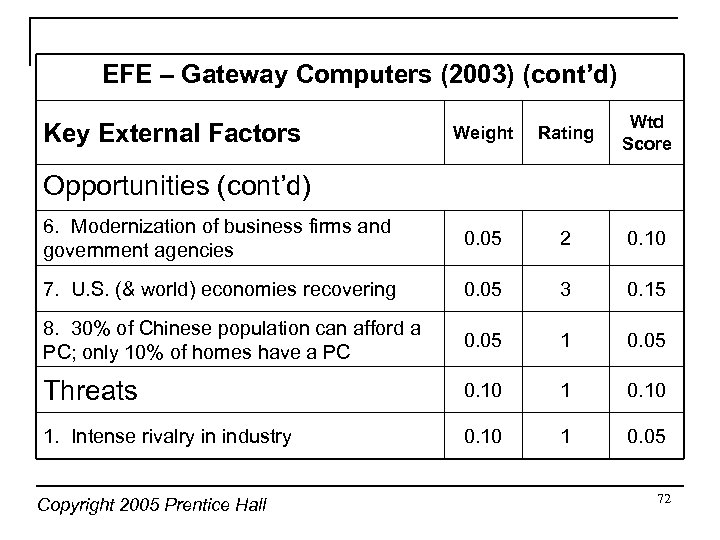 EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) (cont’d) Weight Rating Wtd Score 6. Modernization of business firms and government agencies 0. 05 2 0. 10 7. U. S. (& world) economies recovering 0. 05 3 0. 15 8. 30% of Chinese population can afford a PC; only 10% of homes have a PC 0. 05 1 0. 05 Threats 0. 10 1. Intense rivalry in industry 0. 10 1 0. 05 Key External Factors Opportunities (cont’d) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 72
EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) (cont’d) Weight Rating Wtd Score 6. Modernization of business firms and government agencies 0. 05 2 0. 10 7. U. S. (& world) economies recovering 0. 05 3 0. 15 8. 30% of Chinese population can afford a PC; only 10% of homes have a PC 0. 05 1 0. 05 Threats 0. 10 1. Intense rivalry in industry 0. 10 1 0. 05 Key External Factors Opportunities (cont’d) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 72
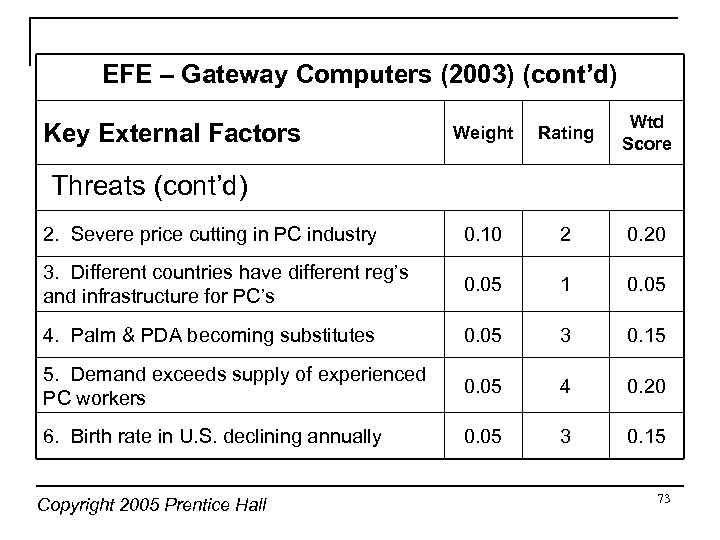 EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) (cont’d) Weight Rating Wtd Score 2. Severe price cutting in PC industry 0. 10 2 0. 20 3. Different countries have different reg’s and infrastructure for PC’s 0. 05 1 0. 05 4. Palm & PDA becoming substitutes 0. 05 3 0. 15 5. Demand exceeds supply of experienced PC workers 0. 05 4 0. 20 6. Birth rate in U. S. declining annually 0. 05 3 0. 15 Key External Factors Threats (cont’d) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 73
EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) (cont’d) Weight Rating Wtd Score 2. Severe price cutting in PC industry 0. 10 2 0. 20 3. Different countries have different reg’s and infrastructure for PC’s 0. 05 1 0. 05 4. Palm & PDA becoming substitutes 0. 05 3 0. 15 5. Demand exceeds supply of experienced PC workers 0. 05 4 0. 20 6. Birth rate in U. S. declining annually 0. 05 3 0. 15 Key External Factors Threats (cont’d) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 73
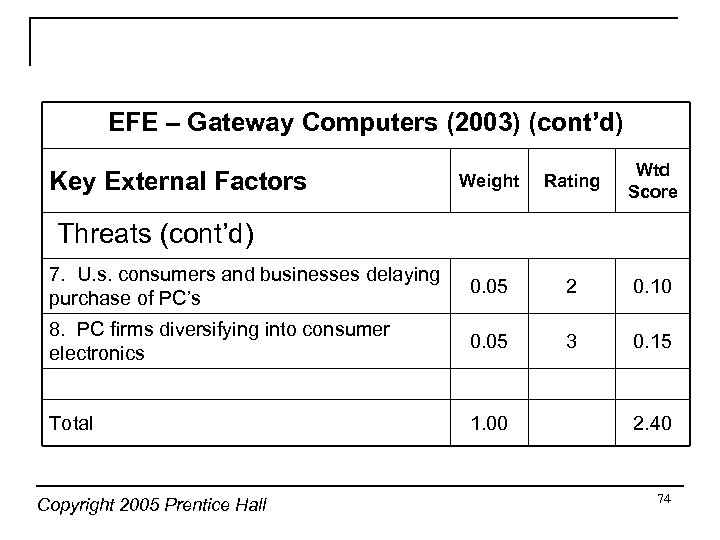 EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) (cont’d) Weight Rating Wtd Score 7. U. s. consumers and businesses delaying purchase of PC’s 0. 05 2 0. 10 8. PC firms diversifying into consumer electronics 0. 05 3 0. 15 Total 1. 00 Key External Factors Threats (cont’d) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 2. 40 74
EFE – Gateway Computers (2003) (cont’d) Weight Rating Wtd Score 7. U. s. consumers and businesses delaying purchase of PC’s 0. 05 2 0. 10 8. PC firms diversifying into consumer electronics 0. 05 3 0. 15 Total 1. 00 Key External Factors Threats (cont’d) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 2. 40 74
 Industry Analysis EFE Total weighted score of 4. 0 n Organization response is outstanding to threats and weaknesses Total weighted score of 1. 0 n Firm’s strategies not capitalizing on opportunities or avoiding threats Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 75
Industry Analysis EFE Total weighted score of 4. 0 n Organization response is outstanding to threats and weaknesses Total weighted score of 1. 0 n Firm’s strategies not capitalizing on opportunities or avoiding threats Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 75
 Industry Analysis EFE Important -- Understanding the factors used in the EFE Matrix is more important than the actual weights and ratings assigned. Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 76
Industry Analysis EFE Important -- Understanding the factors used in the EFE Matrix is more important than the actual weights and ratings assigned. Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 76
 Industry Analysis: Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) Identifies firm’s major competitors and their strengths & weaknesses in relation to a sample firm’s strategic positions Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 77
Industry Analysis: Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) Identifies firm’s major competitors and their strengths & weaknesses in relation to a sample firm’s strategic positions Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 77
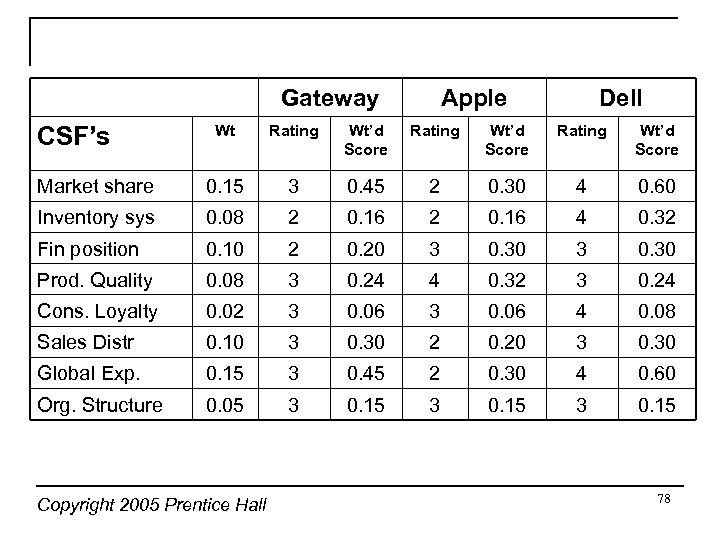 Gateway Apple Dell Wt Rating Wt’d Score Market share 0. 15 3 0. 45 2 0. 30 4 0. 60 Inventory sys 0. 08 2 0. 16 4 0. 32 Fin position 0. 10 2 0. 20 3 0. 30 Prod. Quality 0. 08 3 0. 24 4 0. 32 3 0. 24 Cons. Loyalty 0. 02 3 0. 06 4 0. 08 Sales Distr 0. 10 3 0. 30 2 0. 20 3 0. 30 Global Exp. 0. 15 3 0. 45 2 0. 30 4 0. 60 Org. Structure 0. 05 3 0. 15 CSF’s Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 78
Gateway Apple Dell Wt Rating Wt’d Score Market share 0. 15 3 0. 45 2 0. 30 4 0. 60 Inventory sys 0. 08 2 0. 16 4 0. 32 Fin position 0. 10 2 0. 20 3 0. 30 Prod. Quality 0. 08 3 0. 24 4 0. 32 3 0. 24 Cons. Loyalty 0. 02 3 0. 06 4 0. 08 Sales Distr 0. 10 3 0. 30 2 0. 20 3 0. 30 Global Exp. 0. 15 3 0. 45 2 0. 30 4 0. 60 Org. Structure 0. 05 3 0. 15 CSF’s Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 78
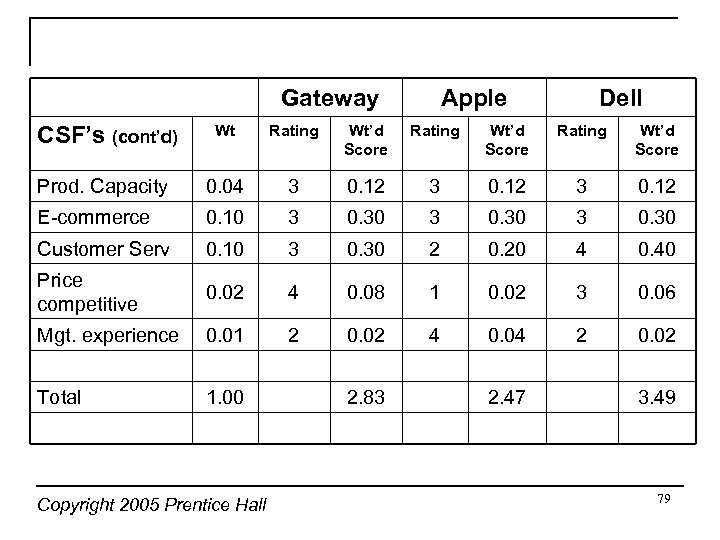 Gateway Apple Dell CSF’s (cont’d) Wt Rating Wt’d Score Prod. Capacity 0. 04 3 0. 12 E-commerce 0. 10 3 0. 30 Customer Serv 0. 10 3 0. 30 2 0. 20 4 0. 40 Price competitive 0. 02 4 0. 08 1 0. 02 3 0. 06 Mgt. experience 0. 01 2 0. 02 4 0. 04 2 0. 02 Total 1. 00 Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 2. 83 2. 47 3. 49 79
Gateway Apple Dell CSF’s (cont’d) Wt Rating Wt’d Score Prod. Capacity 0. 04 3 0. 12 E-commerce 0. 10 3 0. 30 Customer Serv 0. 10 3 0. 30 2 0. 20 4 0. 40 Price competitive 0. 02 4 0. 08 1 0. 02 3 0. 06 Mgt. experience 0. 01 2 0. 02 4 0. 04 2 0. 02 Total 1. 00 Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 2. 83 2. 47 3. 49 79
 Industry Analysis CPM Important -- Just because one firm receives a 3. 2 rating and another receives a 2. 8 rating, it does not follow that the first firm is 20 percent better than the second. Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 80
Industry Analysis CPM Important -- Just because one firm receives a 3. 2 rating and another receives a 2. 8 rating, it does not follow that the first firm is 20 percent better than the second. Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 80
 For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts AOL Competitive Analysis Chief Information Officer (CIO) Competitive Intelligence (CI) Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) Competitive Advantage Decruiting Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 81
For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts AOL Competitive Analysis Chief Information Officer (CIO) Competitive Intelligence (CI) Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM) Competitive Advantage Decruiting Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 81
 For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts Director of Competitive Analysis External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFE) Downsizing External Forces Environmental Scanning Industry Analysis External Audit Industrial Organizational (I/O) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 82
For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts Director of Competitive Analysis External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFE) Downsizing External Forces Environmental Scanning Industry Analysis External Audit Industrial Organizational (I/O) Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 82
 For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts Information Technology (IT) Lifecare Facilities Internet Porter’s Five-Forces Model Learning from the Partner Rightsizing Linear Regression World Wide Web Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 83
For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts Information Technology (IT) Lifecare Facilities Internet Porter’s Five-Forces Model Learning from the Partner Rightsizing Linear Regression World Wide Web Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 83
 For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts Tax Harmonization Foreign Direct Investment Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 84
For Review (Chapter 3) Key Terms & Concepts Tax Harmonization Foreign Direct Investment Copyright 2005 Prentice Hall 84


