a3e8c3d59c34cb2ae4f0086b7d254275.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 176

 Chapter 3 Systems and Infrastructure Life Cycle Management
Chapter 3 Systems and Infrastructure Life Cycle Management
 Course Agenda
Course Agenda
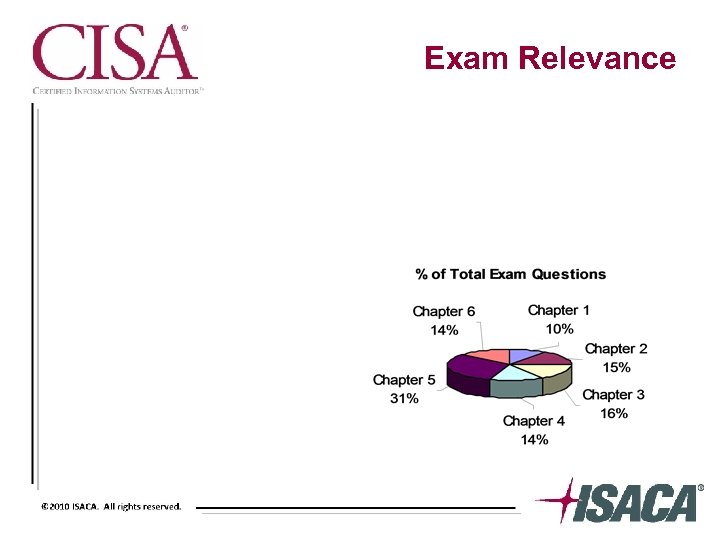 Exam Relevance
Exam Relevance
 Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives (continued)
Learning Objectives (continued)
 Learning Objectives (continued)
Learning Objectives (continued)
 3. 2. 1 Portfolio/Program Management
3. 2. 1 Portfolio/Program Management
 3. 2. 1 Portfolio/Program Management (continued)
3. 2. 1 Portfolio/Program Management (continued)
 3. 2. 1 Portfolio/Program Management (continued)
3. 2. 1 Portfolio/Program Management (continued)
 3. 2. 2 Business Case Development and Approval
3. 2. 2 Business Case Development and Approval
 3. 2. 3 Benefits Realization Techniques
3. 2. 3 Benefits Realization Techniques
 3. 3. 1 General Aspects
3. 3. 1 General Aspects
 3. 3. 2 Project Context and Environment
3. 3. 2 Project Context and Environment
 3. 3. 3 Project Organizational Forms
3. 3. 3 Project Organizational Forms
 3. 3. 4 Project Communication and Culture
3. 3. 4 Project Communication and Culture
 3. 3. 5 Project Objectives
3. 3. 5 Project Objectives
 3. 3. 6 Roles and Responsibilities of Groups and Individuals
3. 3. 6 Roles and Responsibilities of Groups and Individuals
 3. 3. 6 Roles and Responsibilities of Groups and Individuals (continued)
3. 3. 6 Roles and Responsibilities of Groups and Individuals (continued)
 3. 3. 6 Roles and Responsibilities of Groups and Individuals (continued)
3. 3. 6 Roles and Responsibilities of Groups and Individuals (continued)
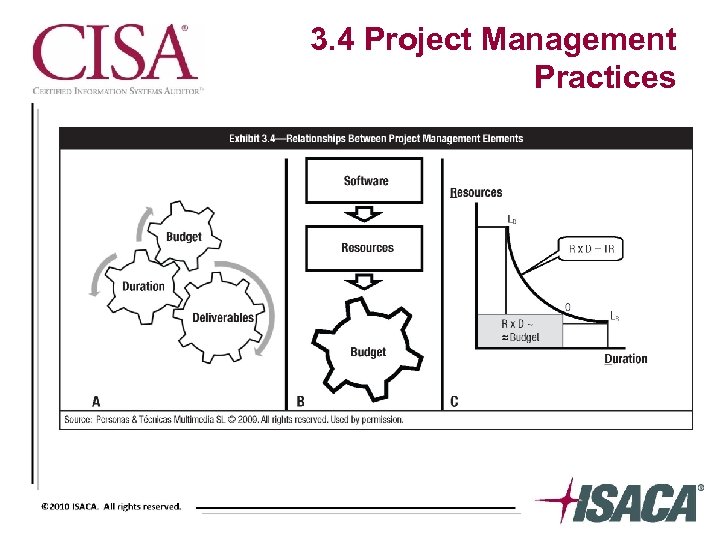 3. 4 Project Management Practices
3. 4 Project Management Practices
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning
3. 4. 2 Project Planning
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
3. 4. 2 Project Planning (continued)
 3. 4. 3 General Project Management
3. 4. 3 General Project Management
 3. 4. 4 Project Controlling
3. 4. 4 Project Controlling
 3. 4. 5 Closing a Project
3. 4. 5 Closing a Project
 3. 5 Business Application Development
3. 5 Business Application Development
 3. 5 Business Application Development (continued)
3. 5 Business Application Development (continued)
 3. 5 Business Application Development (continued)
3. 5 Business Application Development (continued)
 3. 5. 1 Traditional SDLC Approach
3. 5. 1 Traditional SDLC Approach
 3. 5. 1 Traditional SDLC Approach (continued)
3. 5. 1 Traditional SDLC Approach (continued)
 3. 5. 2 Integrated Resource Management Systems
3. 5. 2 Integrated Resource Management Systems
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 Practice Question
Practice Question
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 Practice Question
Practice Question
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
3. 5. 3 Description of Traditional SDLC Phases (continued)
 3. 5. 4 Risks Associated with Software Development
3. 5. 4 Risks Associated with Software Development
 3. 5. 5 Use of Structured Analysis, Design and Development Techniques
3. 5. 5 Use of Structured Analysis, Design and Development Techniques
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
 3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
3. 6. 1 Electronic Commerce (continued)
 Practice Question
Practice Question
 3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange
3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange
 3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange (continued)
3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange (continued)
 3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange (continued)
3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange (continued)
 3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange (continued)
3. 6. 2 Electronic Data Interchange (continued)
 3. 6. 4 Controls in EDI Environment
3. 6. 4 Controls in EDI Environment
 3. 6. 4 Controls in EDI Environment (continued)
3. 6. 4 Controls in EDI Environment (continued)
 3. 6. 4 Controls In EDI Environment (continued)
3. 6. 4 Controls In EDI Environment (continued)
 3. 6. 4 Controls in EDI Environment (continued)
3. 6. 4 Controls in EDI Environment (continued)
 Practice Question
Practice Question
 3. 6. 5 Electronic Mail
3. 6. 5 Electronic Mail
 3. 6. 5 Electronic Mail (continued)
3. 6. 5 Electronic Mail (continued)
 3. 6. 5 Electronic Mail (continued)
3. 6. 5 Electronic Mail (continued)
 3. 6. 7 Electronic Banking
3. 6. 7 Electronic Banking
 3. 6. 7 Electronic Banking (continued)
3. 6. 7 Electronic Banking (continued)
 3. 6. 7 Electronic Banking (continued)
3. 6. 7 Electronic Banking (continued)
 3. 6. 8 Electronic Finance
3. 6. 8 Electronic Finance
 3. 6. 11 Electronic Funds Transfer
3. 6. 11 Electronic Funds Transfer
 3. 6. 12 Controls in an EFT Environment
3. 6. 12 Controls in an EFT Environment
 3. 6. 15 Automated Teller Machine
3. 6. 15 Automated Teller Machine
 3. 6. 20 Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems
3. 6. 20 Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems
 3. 6. 20 Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems (continued)
3. 6. 20 Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems (continued)
 3. 6. 20 Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems (continued)
3. 6. 20 Artificial Intelligence and Expert Systems (continued)
 3. 6. 21 Business Intelligence
3. 6. 21 Business Intelligence
 3. 6. 21 Business Intelligence (continued)
3. 6. 21 Business Intelligence (continued)
 3. 6. 22 Decision Support System A decision support system (DSS) is an interactive system that provides the user with easy access to decision models and data from a wide range of sources, to support semistructured decision-making tasks typically for business purposes
3. 6. 22 Decision Support System A decision support system (DSS) is an interactive system that provides the user with easy access to decision models and data from a wide range of sources, to support semistructured decision-making tasks typically for business purposes
 3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
 3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
 3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
 3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
3. 6. 22 Decision Support System (continued)
 3. 7 Alternative Forms of Software Project Organization
3. 7 Alternative Forms of Software Project Organization
 3. 7. 1 Agile Development
3. 7. 1 Agile Development
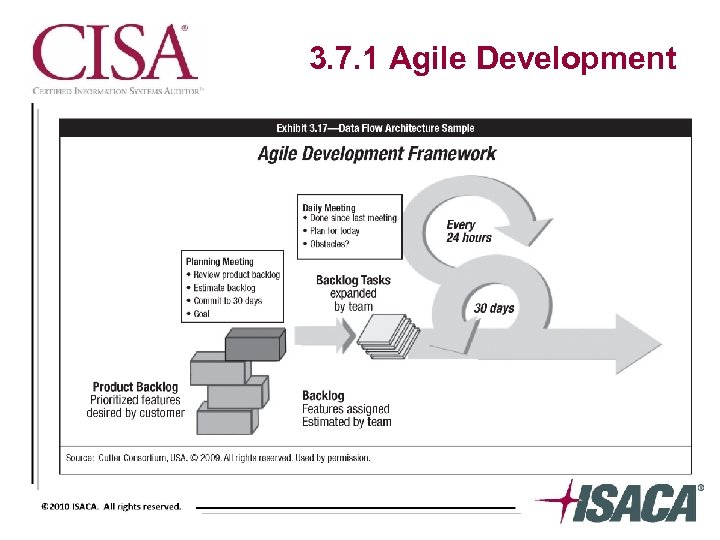 3. 7. 1 Agile Development
3. 7. 1 Agile Development
 3. 7. 2 Prototyping
3. 7. 2 Prototyping
 3. 7. 3 Rapid Application Development
3. 7. 3 Rapid Application Development
 3. 8. 1 Data-oriented System Development
3. 8. 1 Data-oriented System Development
 3. 8. 2 Object-oriented System Development
3. 8. 2 Object-oriented System Development
 3. 8. 3 Component-based Development
3. 8. 3 Component-based Development
 3. 8. 3 Component-based Development (continued)
3. 8. 3 Component-based Development (continued)
 3. 8. 4 Web-based Application Development
3. 8. 4 Web-based Application Development
 3. 8. 6 Reverse Engineering
3. 8. 6 Reverse Engineering
 3. 9 Infrastructure Development/Acquisition Practices
3. 9 Infrastructure Development/Acquisition Practices
 3. 9 Infrastructure Development/Acquisition Practices (continued)
3. 9 Infrastructure Development/Acquisition Practices (continued)
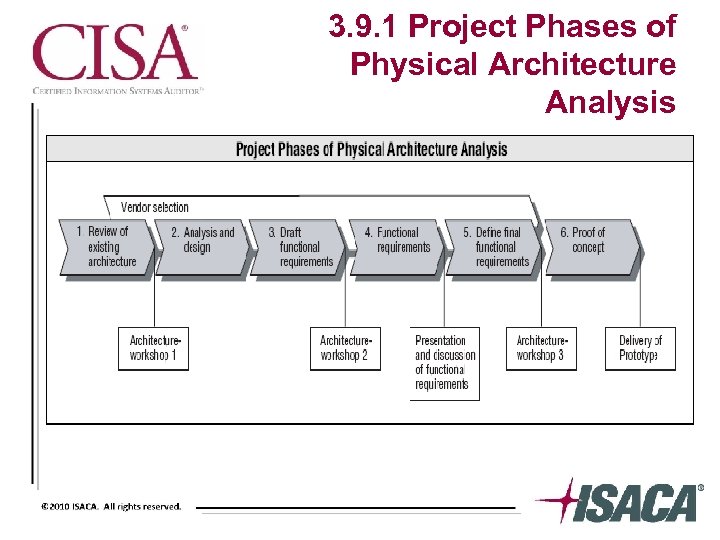 3. 9. 1 Project Phases of Physical Architecture Analysis
3. 9. 1 Project Phases of Physical Architecture Analysis
 3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure
3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure
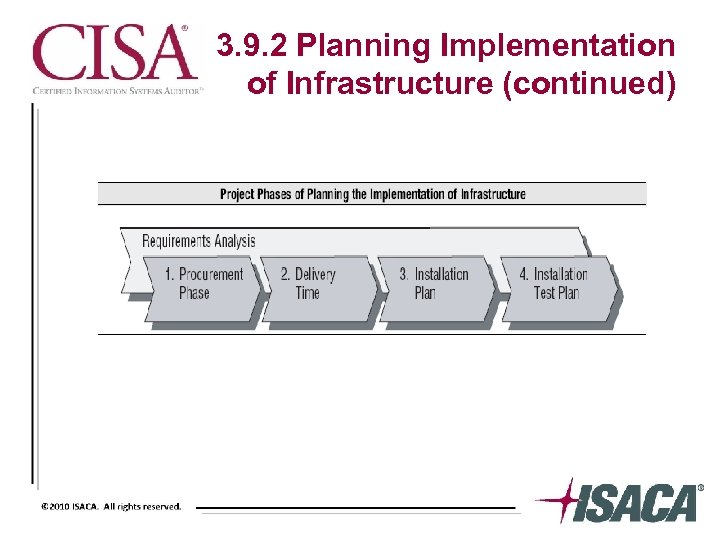 3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
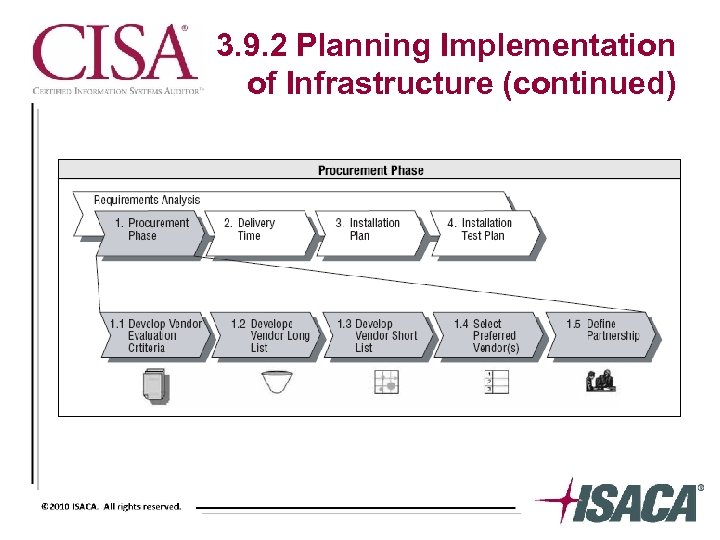 3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
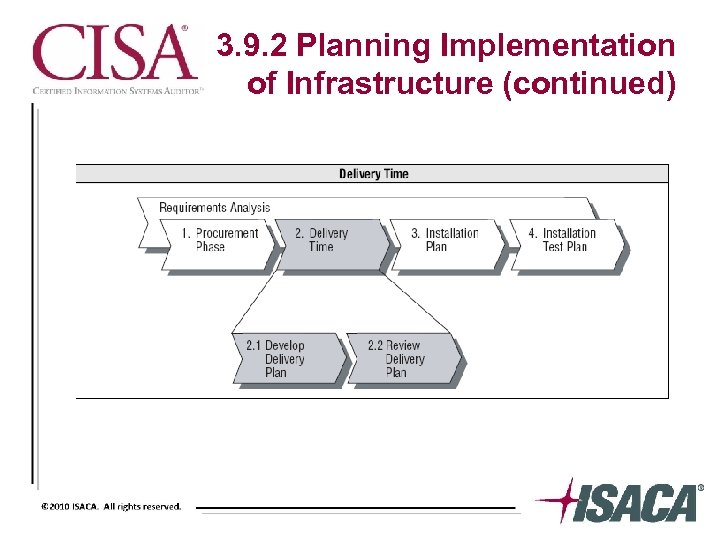 3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
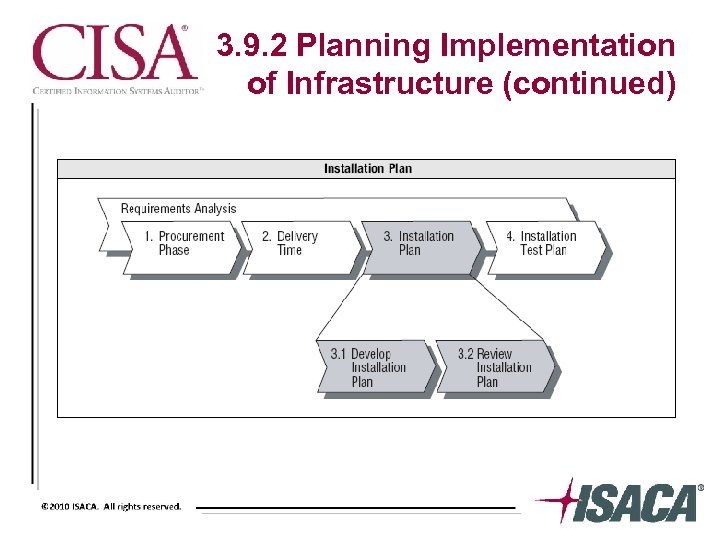 3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
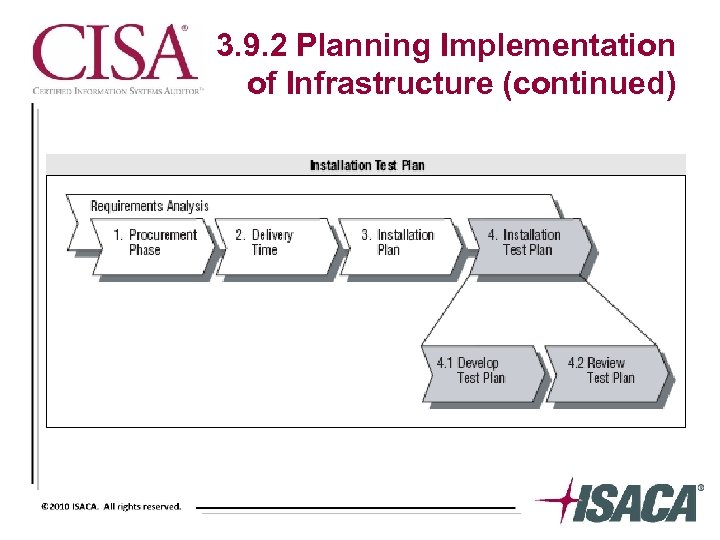 3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
3. 9. 2 Planning Implementation of Infrastructure (continued)
 3. 9. 4 Hardware Acquisition
3. 9. 4 Hardware Acquisition
 3. 9. 4 Hardware Acquisition (continued)
3. 9. 4 Hardware Acquisition (continued)
 3. 9. 5 System Software Acquisition
3. 9. 5 System Software Acquisition
 3. 9. 7 System Software Change Control Procedures
3. 9. 7 System Software Change Control Procedures
 3. 10. 1 Change Management Process Overview
3. 10. 1 Change Management Process Overview
 3. 10. 1 Change Management Process Overview (continued)
3. 10. 1 Change Management Process Overview (continued)
 3. 10. 2 Configuration Management
3. 10. 2 Configuration Management
 3. 10. 2 Configuration Management (continued)
3. 10. 2 Configuration Management (continued)
 3. 11. 2 Computer-aided Software Engineering
3. 11. 2 Computer-aided Software Engineering
 3. 11. 2 Computer-aided Software Engineering (continued)
3. 11. 2 Computer-aided Software Engineering (continued)
 3. 11. 3 Fourth-generation Languages
3. 11. 3 Fourth-generation Languages
 3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects (continued)
3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects (continued)
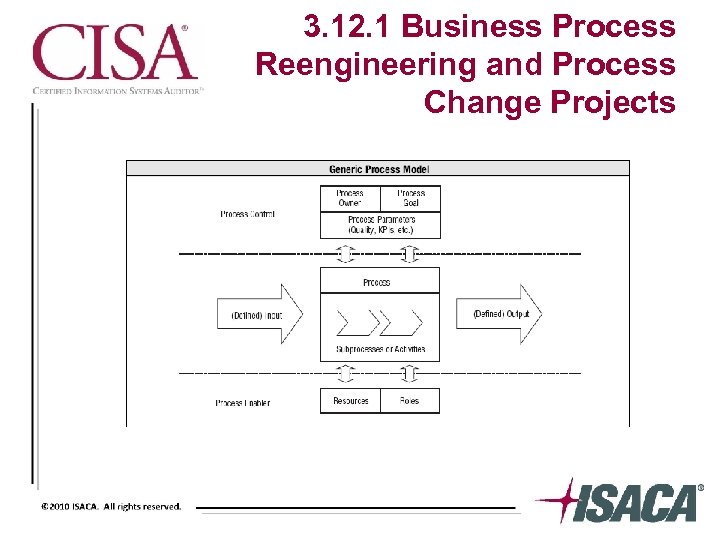 3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects
3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects
 3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects (continued)
3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects (continued)
 3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects (continued)
3. 12. 1 Business Process Reengineering and Process Change Projects (continued)
 Practice Question
Practice Question
 Practice Question 3 -4 During which of the following steps in the business process reengineering should the benchmarking team visit the benchmarking partner?
Practice Question 3 -4 During which of the following steps in the business process reengineering should the benchmarking team visit the benchmarking partner?
 3. 13 Application Controls
3. 13 Application Controls
 3. 13 Application Controls (continued)
3. 13 Application Controls (continued)
 3. 1 Input/Origination Controls
3. 1 Input/Origination Controls
 3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
 3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
 3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
 3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
3. 1 Input/Origination Controls (continued)
 3. 13. 2 Processing Procedures and Controls
3. 13. 2 Processing Procedures and Controls
 3. 13. 2 Processing Procedures and Controls (continued)
3. 13. 2 Processing Procedures and Controls (continued)
 3. 13. 2 Processing Procedures and Controls (continued)
3. 13. 2 Processing Procedures and Controls (continued)
 Practice Question 3 -5 A hash total of employee numbers is part of the input to a payroll master file update program. The program compares the hash total with the corresponding control total. What is the purpose of this procedure?
Practice Question 3 -5 A hash total of employee numbers is part of the input to a payroll master file update program. The program compares the hash total with the corresponding control total. What is the purpose of this procedure?
 3. 13. 3 Output Controls
3. 13. 3 Output Controls
 3. 13. 4 Business Process Control Assurance
3. 13. 4 Business Process Control Assurance
 3. 14 Auditing Application Controls
3. 14 Auditing Application Controls
 3. 14. 4 Data Integrity Testing
3. 14. 4 Data Integrity Testing
 3. 14. 5 Data Integrity in Online Transaction Processing Systems
3. 14. 5 Data Integrity in Online Transaction Processing Systems
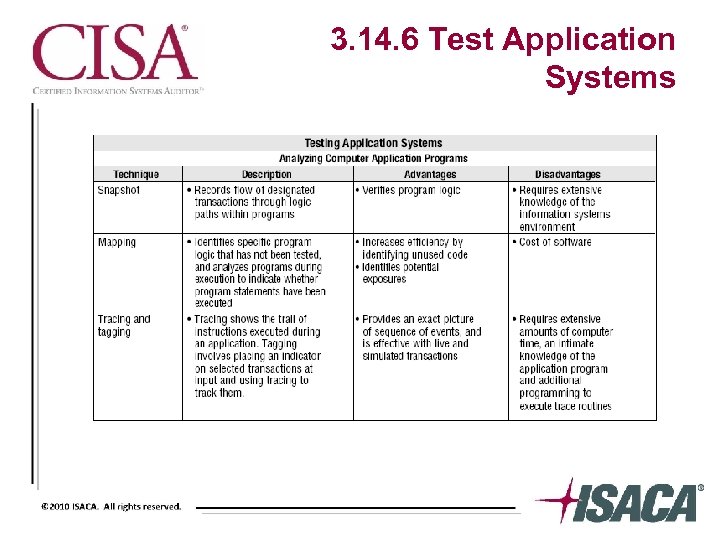 3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems
3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems
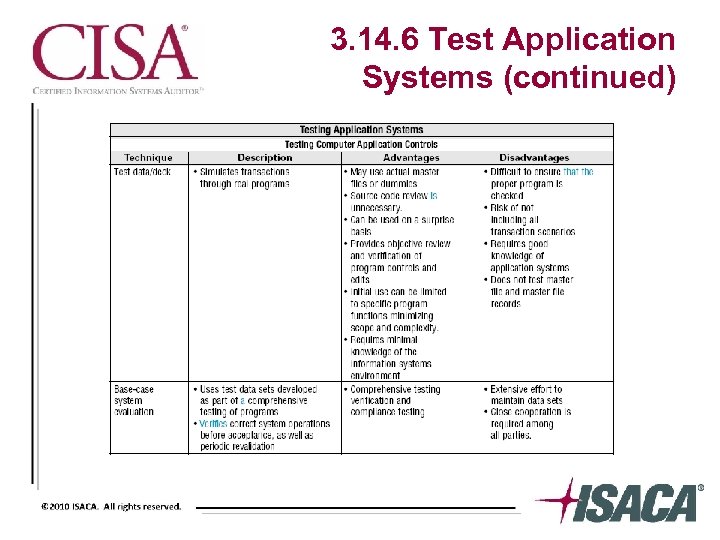 3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems (continued)
3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems (continued)
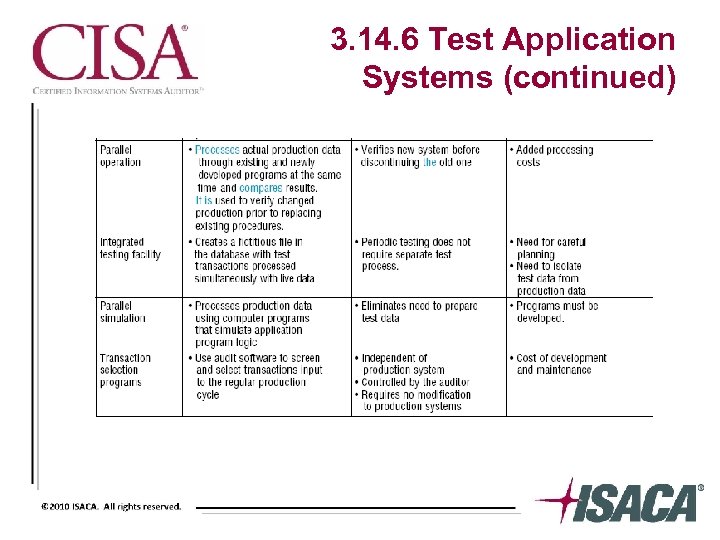 3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems (continued)
3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems (continued)
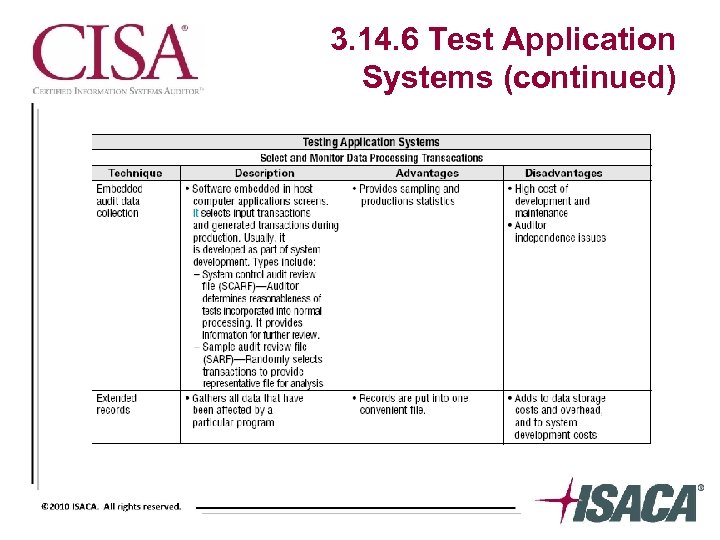 3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems (continued)
3. 14. 6 Test Application Systems (continued)
 3. 14. 7 Continuous Online Auditing
3. 14. 7 Continuous Online Auditing
 3. 14. 8 Online Auditing Techniques
3. 14. 8 Online Auditing Techniques
 3. 15 Auditing Systems Development, Acquisition and Maintenance
3. 15 Auditing Systems Development, Acquisition and Maintenance
 3. 15. 1 Project Management
3. 15. 1 Project Management
 3. 15. 2 Feasibility Study
3. 15. 2 Feasibility Study
 3. 15. 3 Requirements Definition
3. 15. 3 Requirements Definition
 Practice Question 3 -6 When auditing the requirements phase of a software acquisition, an IS auditor should:
Practice Question 3 -6 When auditing the requirements phase of a software acquisition, an IS auditor should:
 3. 15. 4 Software Acquisition Process
3. 15. 4 Software Acquisition Process
 Practice Question
Practice Question
 3. 15. 5 Detailed Design and Development
3. 15. 5 Detailed Design and Development
 Practice Question 3 -8 User specifications for a project using the traditional SDLC methodology have not been met. An IS auditor looking for a cause should look in which of the following areas?
Practice Question 3 -8 User specifications for a project using the traditional SDLC methodology have not been met. An IS auditor looking for a cause should look in which of the following areas?
 3. 15. 6 Testing
3. 15. 6 Testing
 3. 15. 7 Implementation Phase
3. 15. 7 Implementation Phase
 3. 15. 8 Postimplementation Review
3. 15. 8 Postimplementation Review
 3. 15. 9 System Change Procedures and the Program Migration Process
3. 15. 9 System Change Procedures and the Program Migration Process
 3. 15. 9 System Change Procedures and the Program Migration Process (continued)
3. 15. 9 System Change Procedures and the Program Migration Process (continued)
 Case Study A Scenario A major retailer asked the IS auditor to review their readiness for complying with credit card company requirements for protecting cardholder information. The IS auditor subsequently learned the following information. The retailer uses wireless point-of-sale registers that connect to application servers located at each store. These registers use wired equivalent protection (WEP) encryption. The application server, usually located in the middle of the store’s customer service area, forwards all sales data over a frame relay network to database servers located at the retailer’s corporate headquarters, and using strong encryption over an Internet virtual private network (VPN) to the credit card processor for approval of the sale.
Case Study A Scenario A major retailer asked the IS auditor to review their readiness for complying with credit card company requirements for protecting cardholder information. The IS auditor subsequently learned the following information. The retailer uses wireless point-of-sale registers that connect to application servers located at each store. These registers use wired equivalent protection (WEP) encryption. The application server, usually located in the middle of the store’s customer service area, forwards all sales data over a frame relay network to database servers located at the retailer’s corporate headquarters, and using strong encryption over an Internet virtual private network (VPN) to the credit card processor for approval of the sale.
 Case Study A Scenario (continued)
Case Study A Scenario (continued)
 Case Study A Question
Case Study A Question
 Case Study A Question
Case Study A Question
 Case Study B Scenario
Case Study B Scenario
 Case Study B Scenario (continued) Additional problems show up—errors already corrected started occurring again and functional modifications already tested tend to present other errors. The project, already late, is now in a critical situation. The IS auditor, after collecting the evidence, requests an immediate meeting with the head of the project steering committee to communicate findings and suggest actions capable to improve the situation.
Case Study B Scenario (continued) Additional problems show up—errors already corrected started occurring again and functional modifications already tested tend to present other errors. The project, already late, is now in a critical situation. The IS auditor, after collecting the evidence, requests an immediate meeting with the head of the project steering committee to communicate findings and suggest actions capable to improve the situation.
 Case Study B Question
Case Study B Question
 Case Study B Question
Case Study B Question
 Conclusion
Conclusion


