401c62e35af45795f3b002aadd4be9f8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41

Chapter 3 Supply and Demand Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -1

Chapter Objectives • Define and explain demand in a product or service market • Define and explain supply • Determine the equilibrium point in the market for a specific good, given data on supply and demand at different price levels Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -2

Chapter Objectives • Understand what causes shifts in demand supply • Understand how price ceilings cause shortages • Understand how price floors cause surpluses Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -3

Demand • The schedule of quantities of a good or service that people are willing and able to buy at different prices – Sometimes a schedule is also called a table Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -4
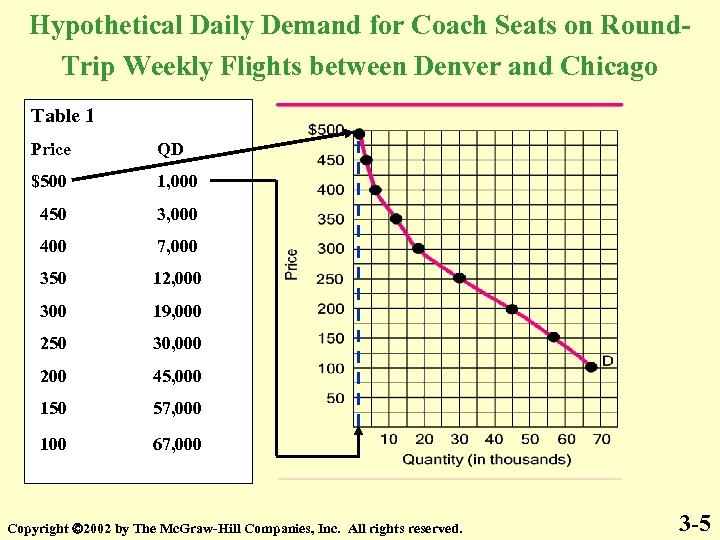
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -5
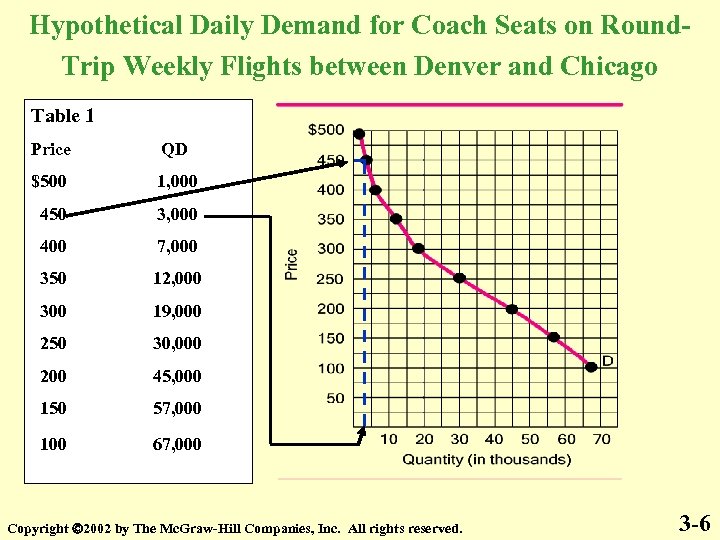
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -6
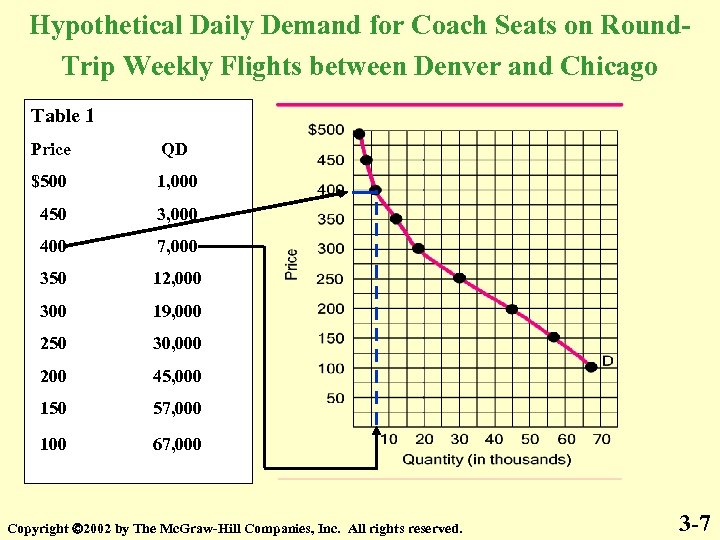
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -7
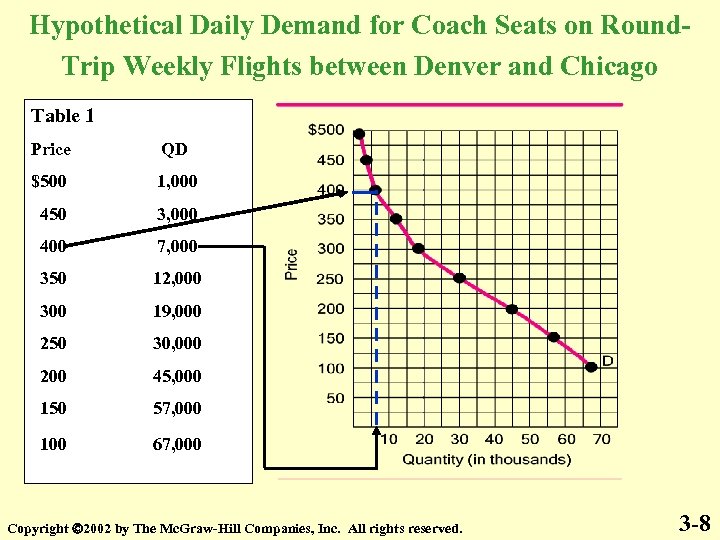
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -8
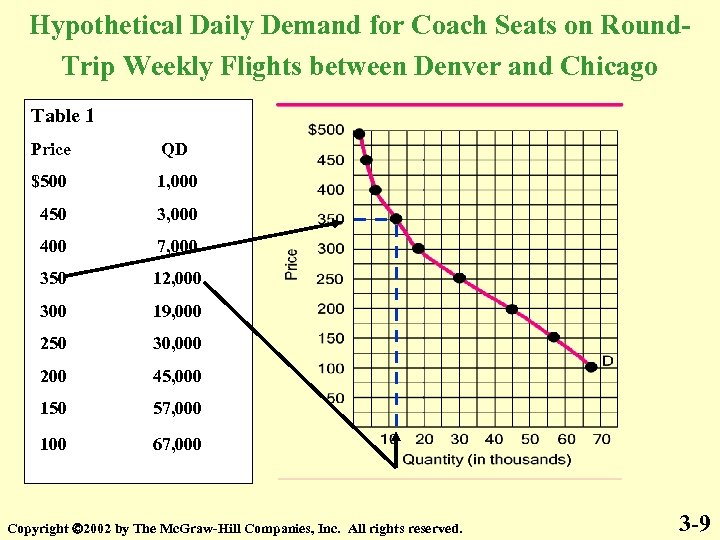
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -9
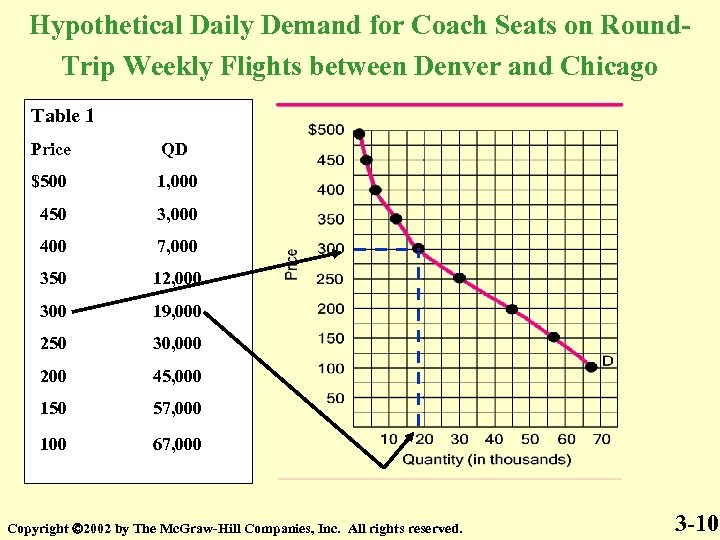
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -10
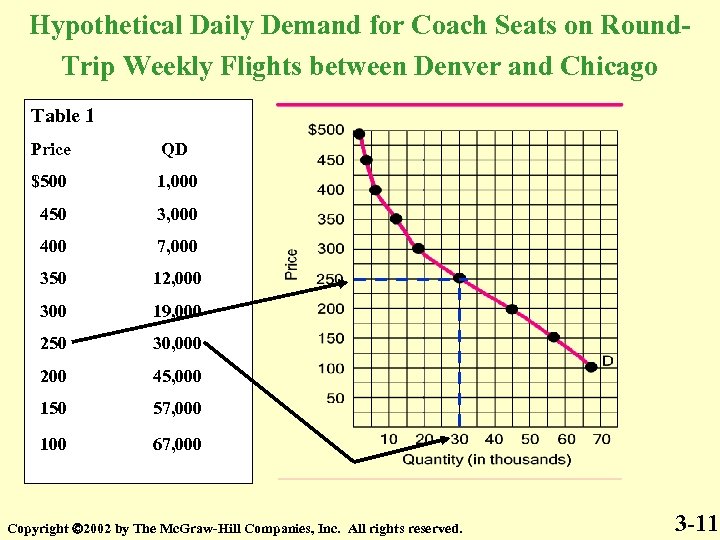
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -11
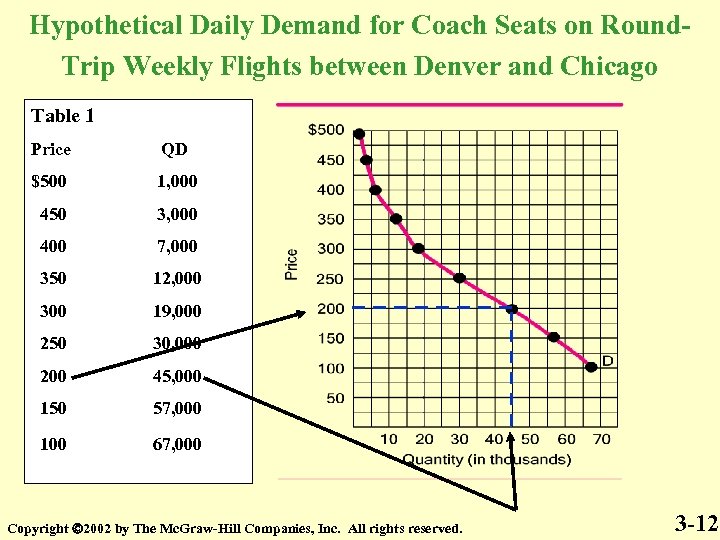
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -12
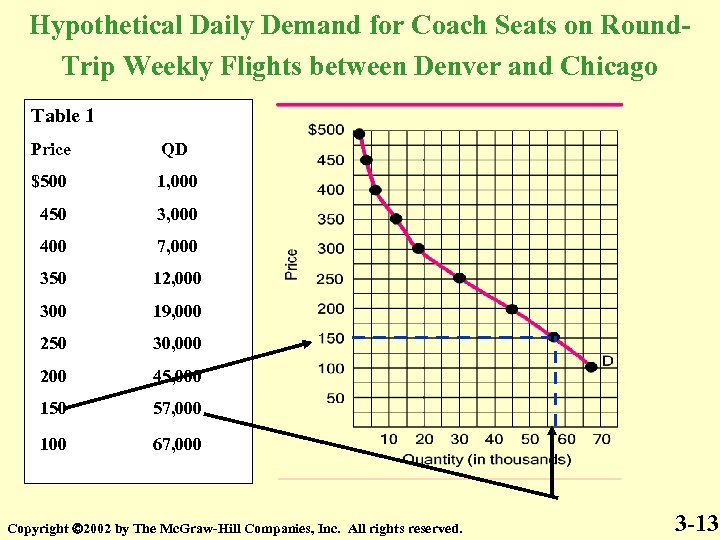
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -13
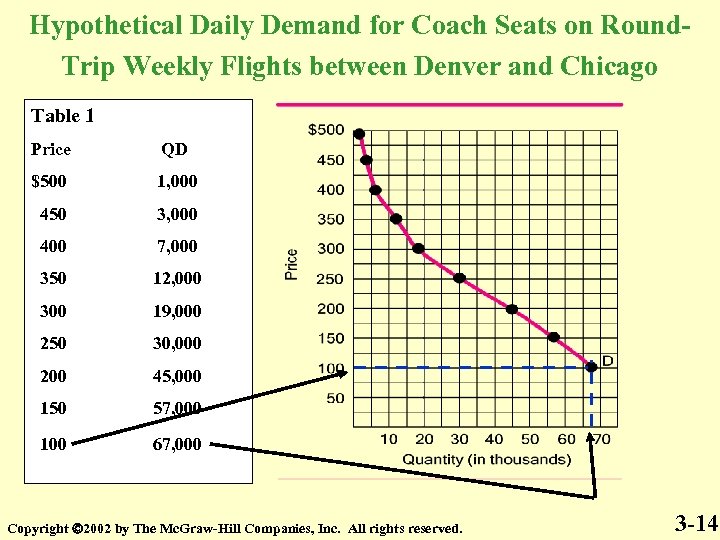
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round. Trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -14
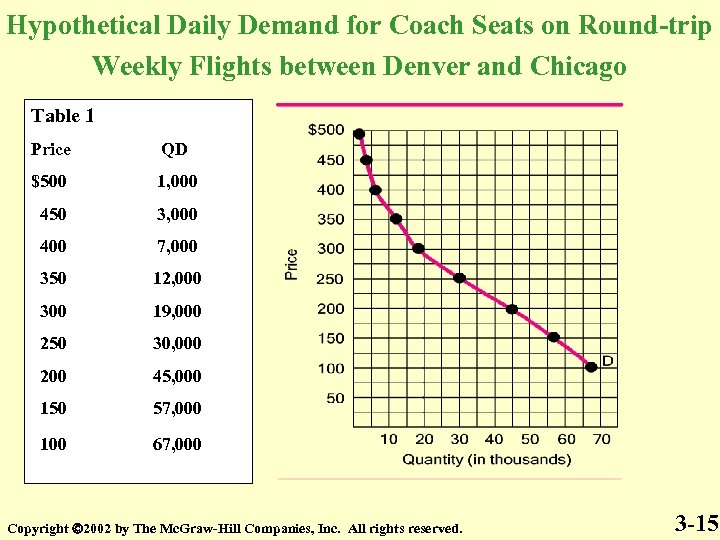
Hypothetical Daily Demand for Coach Seats on Round-trip Weekly Flights between Denver and Chicago Table 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -15
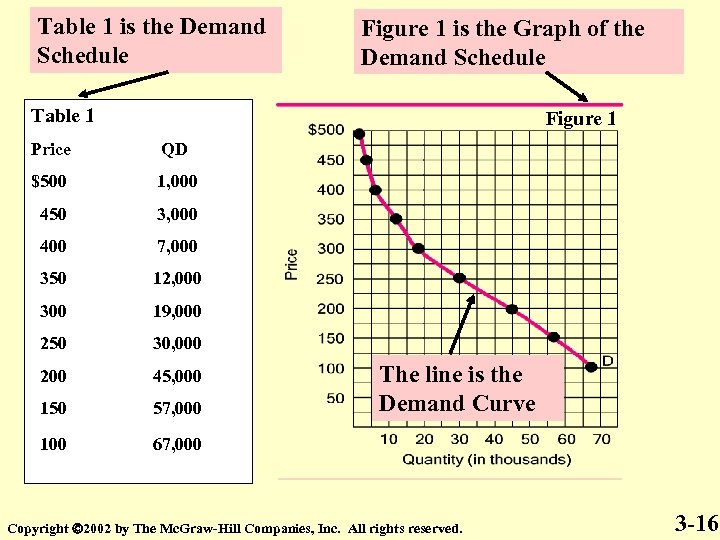
Table 1 is the Demand Schedule Figure 1 is the Graph of the Demand Schedule Table 1 Figure 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 The line is the Demand Curve Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -16
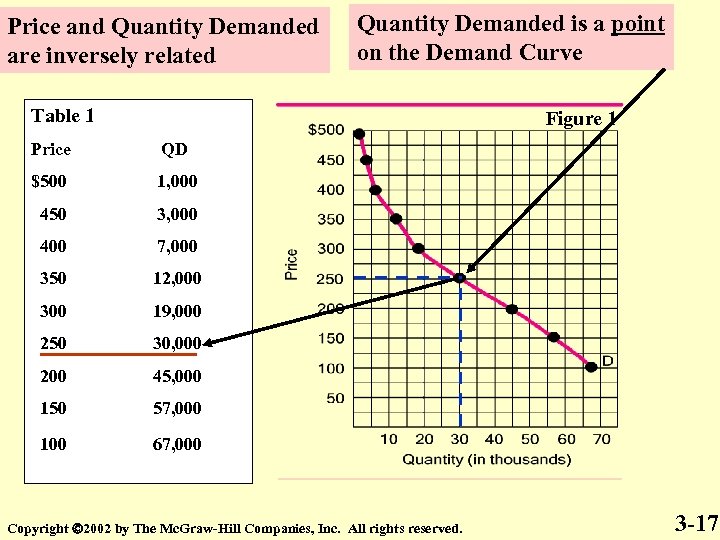
Price and Quantity Demanded are inversely related Quantity Demanded is a point on the Demand Curve Table 1 Figure 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -17
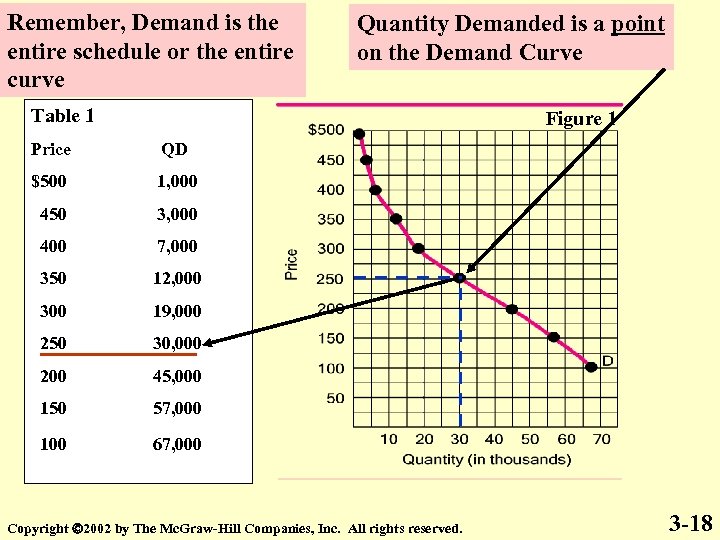
Remember, Demand is the entire schedule or the entire curve Quantity Demanded is a point on the Demand Curve Table 1 Figure 1 Price QD $500 1, 000 450 3, 000 400 7, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 250 30, 000 200 45, 000 150 57, 000 100 67, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -18

Supply • Is the “schedule” of quantities of a good or service that people are willing to sell at various prices Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -19
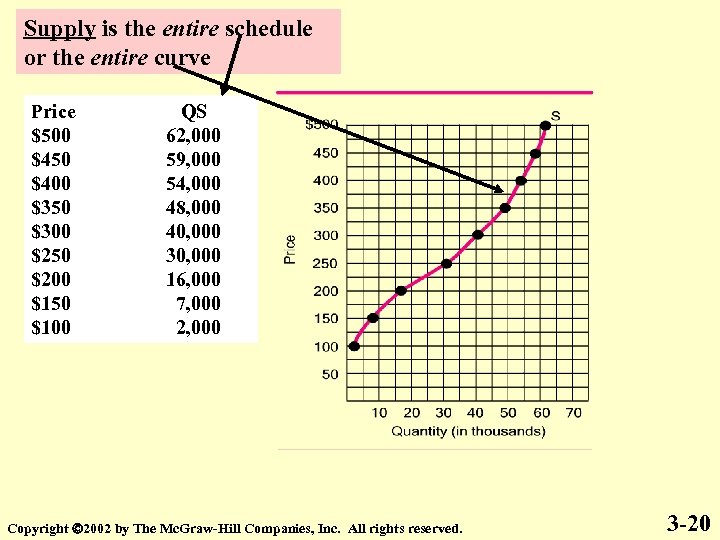
Supply is the entire schedule or the entire curve Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -20
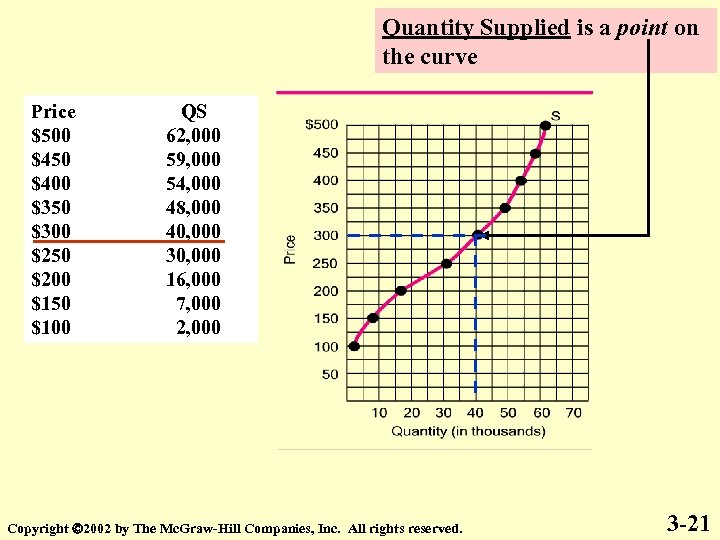
Quantity Supplied is a point on the curve Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -21
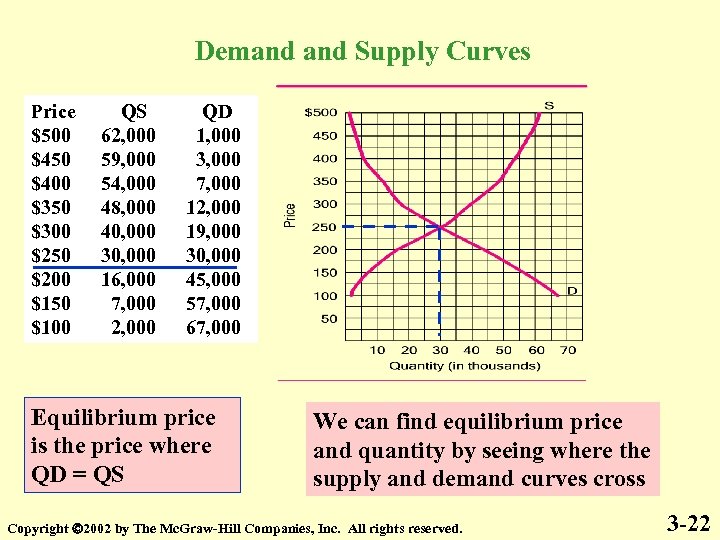
Demand Supply Curves Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 QD 1, 000 3, 000 7, 000 12, 000 19, 000 30, 000 45, 000 57, 000 67, 000 Equilibrium price is the price where QD = QS We can find equilibrium price and quantity by seeing where the supply and demand curves cross Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -22
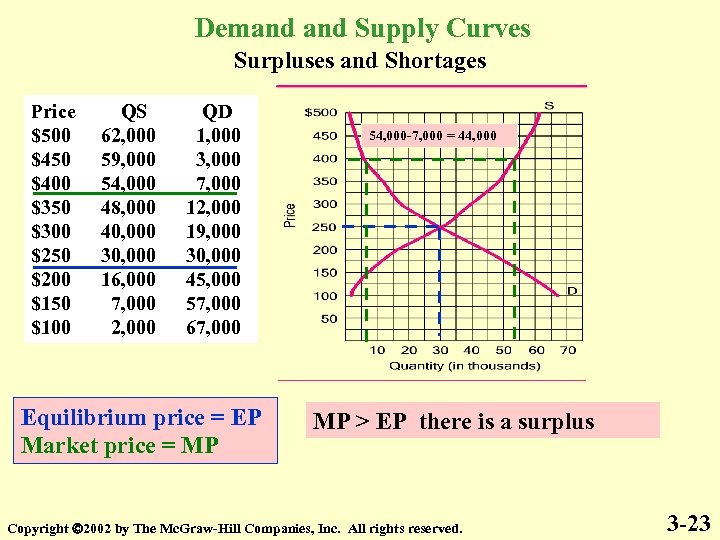
Demand Supply Curves Surpluses and Shortages Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 QD 1, 000 3, 000 7, 000 12, 000 19, 000 30, 000 45, 000 57, 000 67, 000 Equilibrium price = EP Market price = MP 54, 000 -7, 000 = 44, 000 MP > EP there is a surplus Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -23
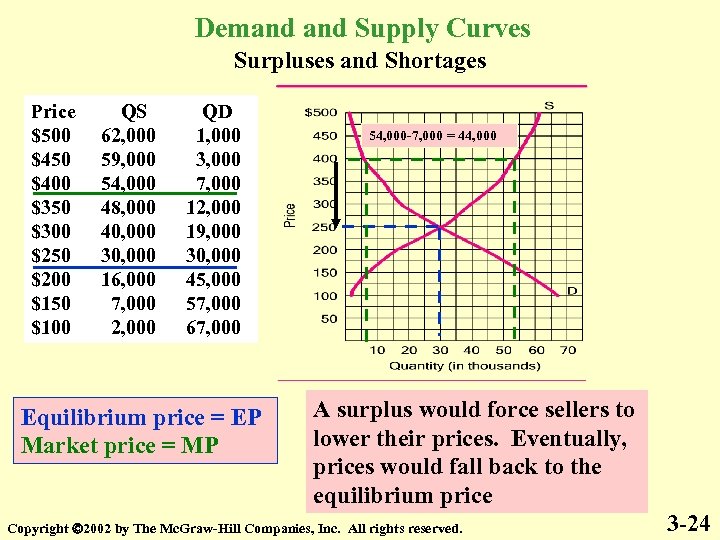
Demand Supply Curves Surpluses and Shortages Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 QD 1, 000 3, 000 7, 000 12, 000 19, 000 30, 000 45, 000 57, 000 67, 000 Equilibrium price = EP Market price = MP 54, 000 -7, 000 = 44, 000 A surplus would force sellers to lower their prices. Eventually, prices would fall back to the equilibrium price Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -24
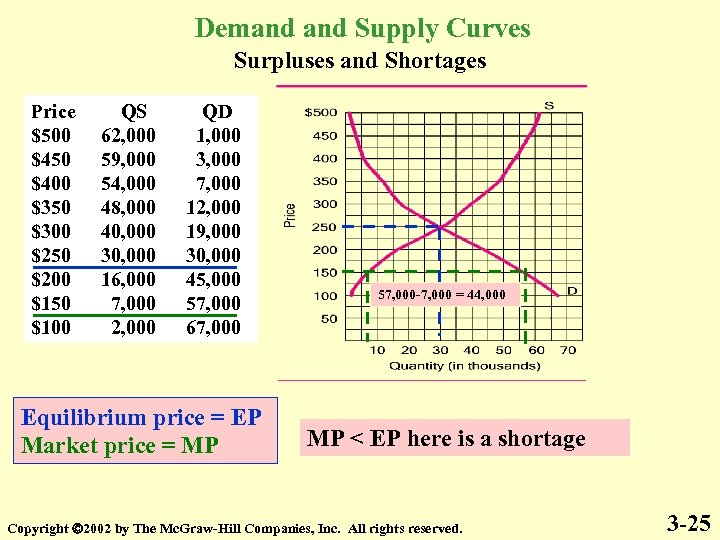
Demand Supply Curves Surpluses and Shortages Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 QD 1, 000 3, 000 7, 000 12, 000 19, 000 30, 000 45, 000 57, 000 67, 000 Equilibrium price = EP Market price = MP 57, 000 -7, 000 = 44, 000 MP < EP here is a shortage Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -25
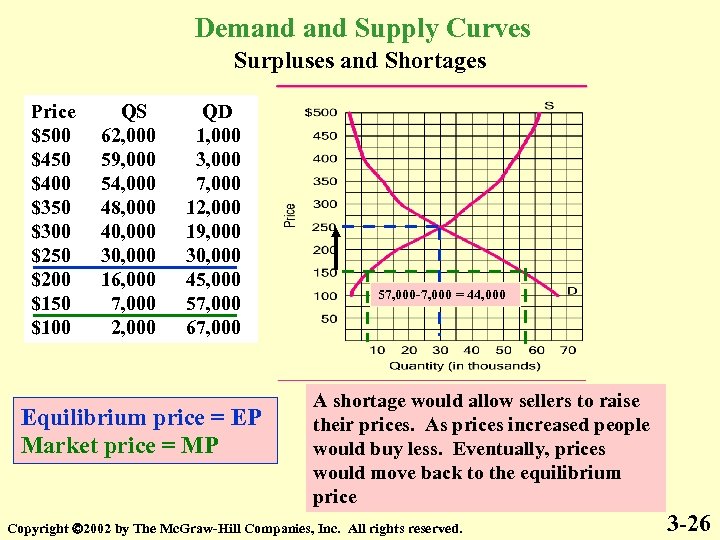
Demand Supply Curves Surpluses and Shortages Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 QD 1, 000 3, 000 7, 000 12, 000 19, 000 30, 000 45, 000 57, 000 67, 000 Equilibrium price = EP Market price = MP 57, 000 -7, 000 = 44, 000 A shortage would allow sellers to raise their prices. As prices increased people would buy less. Eventually, prices would move back to the equilibrium price Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -26
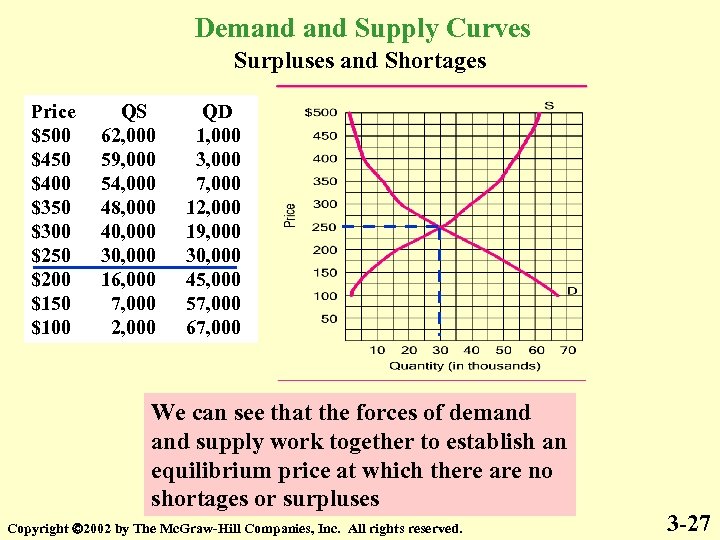
Demand Supply Curves Surpluses and Shortages Price $500 $450 $400 $350 $300 $250 $200 $150 $100 QS 62, 000 59, 000 54, 000 48, 000 40, 000 30, 000 16, 000 7, 000 2, 000 QD 1, 000 3, 000 7, 000 12, 000 19, 000 30, 000 45, 000 57, 000 67, 000 We can see that the forces of demand supply work together to establish an equilibrium price at which there are no shortages or surpluses Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -27
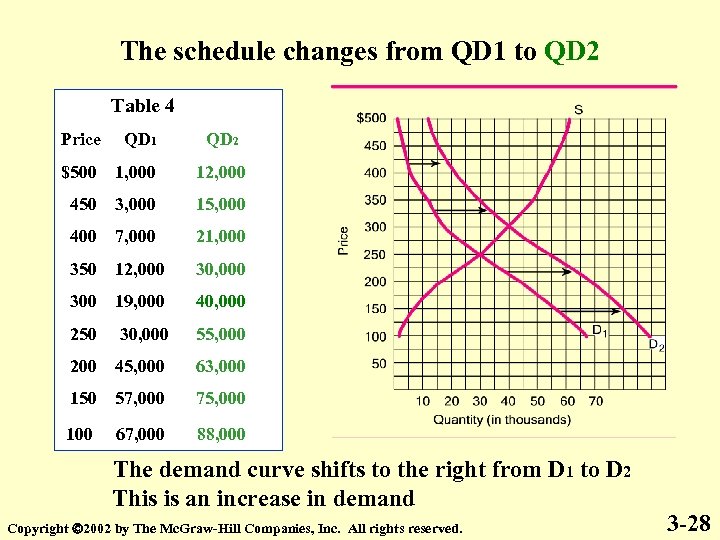
The schedule changes from QD 1 to QD 2 Table 4 Price QD 1 QD 2 $500 1, 000 12, 000 450 3, 000 15, 000 400 7, 000 21, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 40, 000 250 30, 000 55, 000 200 45, 000 63, 000 150 57, 000 75, 000 100 67, 000 88, 000 The demand curve shifts to the right from D 1 to D 2 This is an increase in demand Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -28
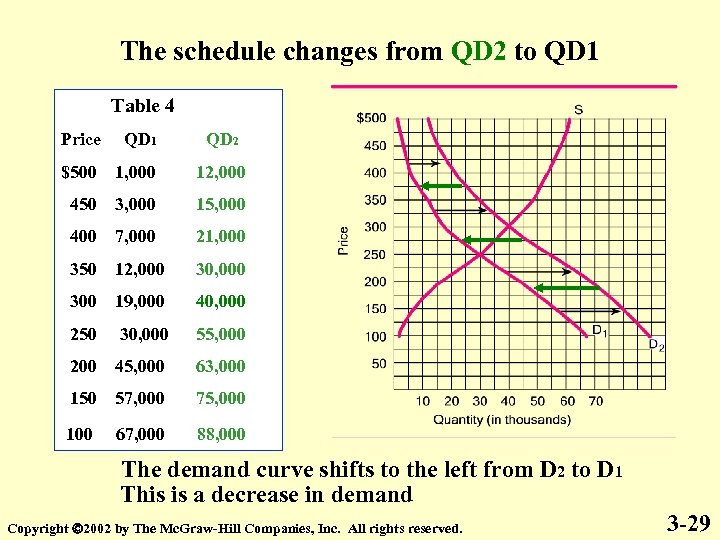
The schedule changes from QD 2 to QD 1 Table 4 Price QD 1 QD 2 $500 1, 000 12, 000 450 3, 000 15, 000 400 7, 000 21, 000 350 12, 000 300 19, 000 40, 000 250 30, 000 55, 000 200 45, 000 63, 000 150 57, 000 75, 000 100 67, 000 88, 000 The demand curve shifts to the left from D 2 to D 1 This is a decrease in demand Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -29
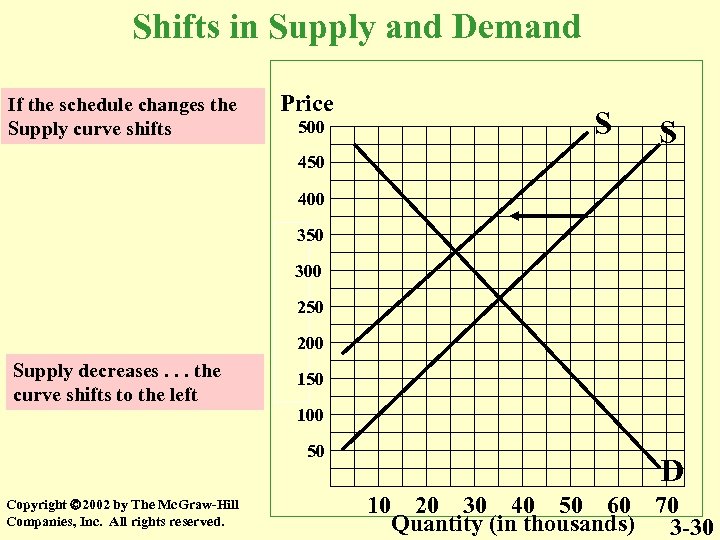
Shifts in Supply and Demand If the schedule changes the Supply curve shifts Price 500 S S 450 400 350 300 250 200 Supply decreases. . . the curve shifts to the left 150 100 50 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (in thousands) 3 -30
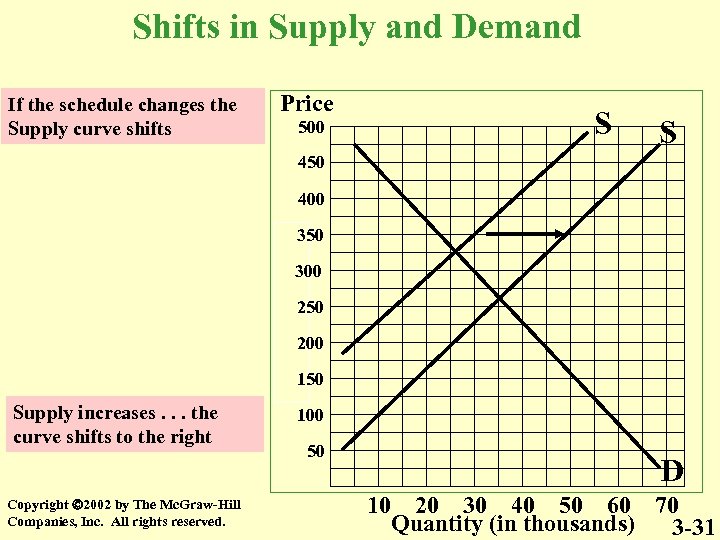
Shifts in Supply and Demand If the schedule changes the Supply curve shifts Price 500 S S 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 Supply increases. . . the curve shifts to the right Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 100 50 D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (in thousands) 3 -31
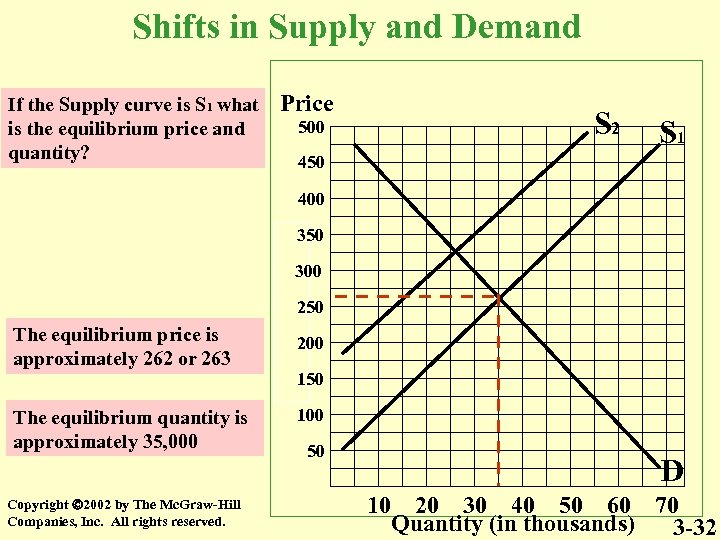
Shifts in Supply and Demand If the Supply curve is S 1 what is the equilibrium price and quantity? Price 500 S 2 S 1 450 400 350 300 250 The equilibrium price is approximately 262 or 263 200 150 The equilibrium quantity is approximately 35, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 100 50 D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (in thousands) 3 -32
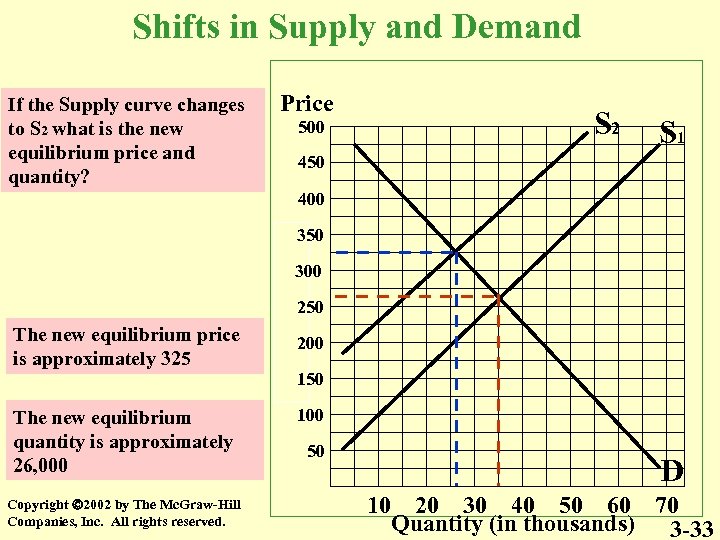
Shifts in Supply and Demand If the Supply curve changes to S 2 what is the new equilibrium price and quantity? Price 500 S 2 S 1 450 400 350 300 250 The new equilibrium price is approximately 325 200 150 The new equilibrium quantity is approximately 26, 000 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 100 50 D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (in thousands) 3 -33
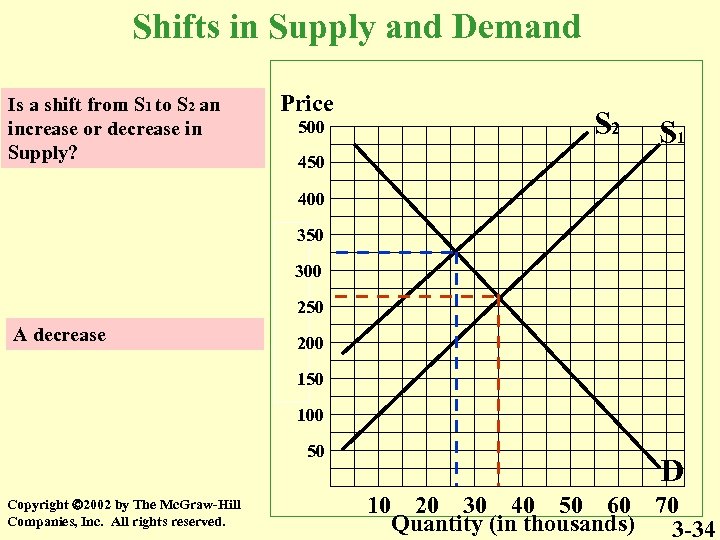
Shifts in Supply and Demand Is a shift from S 1 to S 2 an increase or decrease in Supply? Price 500 S 2 S 1 450 400 350 300 250 A decrease 200 150 100 50 Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Quantity (in thousands) 3 -34
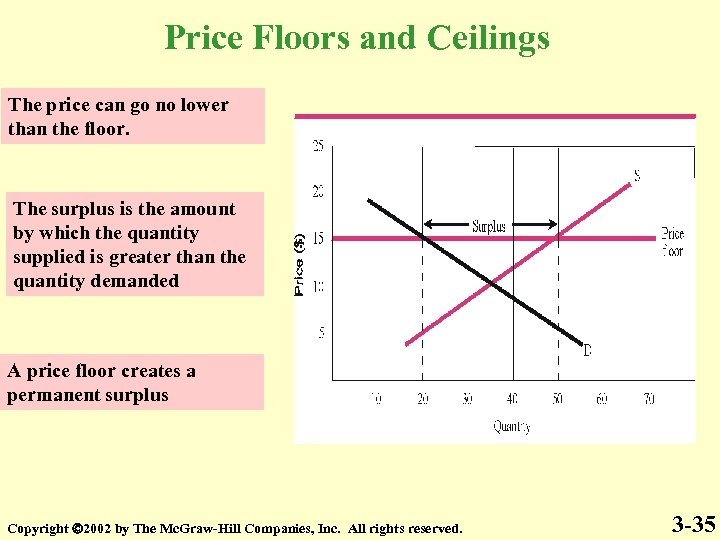
Price Floors and Ceilings The price can go no lower than the floor. The surplus is the amount by which the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded A price floor creates a permanent surplus Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -35
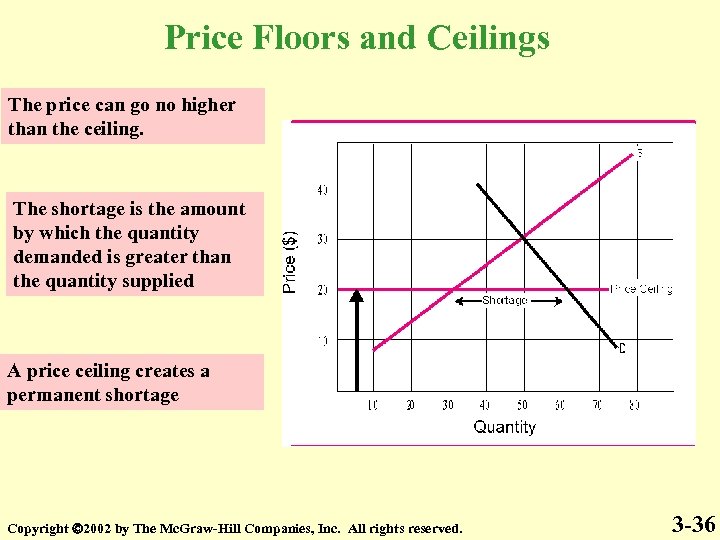
Price Floors and Ceilings The price can go no higher than the ceiling. The shortage is the amount by which the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied A price ceiling creates a permanent shortage Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -36

Applications of Supply and Demand • Interest rates are set by – Supply and demand • Wage rates are set by – Supply and demand • Rents are determined by – Supply and demand • Prices of nearly all goods are determined by – Supply and demand • Prices of nearly all services are determined by – Supply and demand Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -37
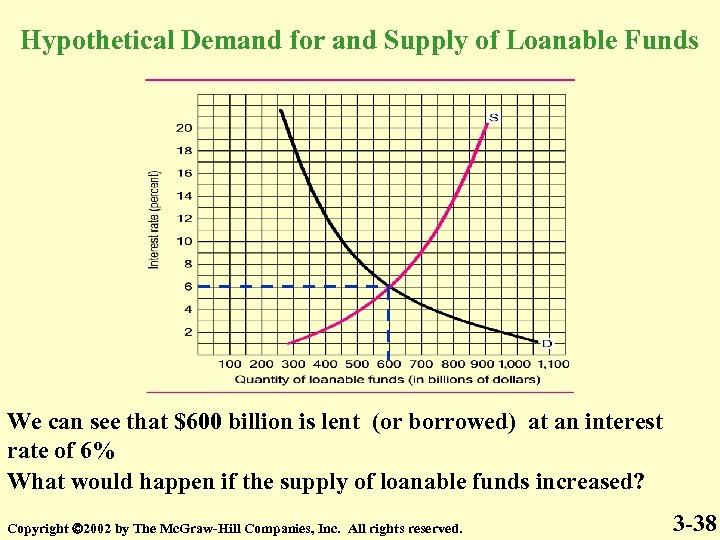
Hypothetical Demand for and Supply of Loanable Funds We can see that $600 billion is lent (or borrowed) at an interest rate of 6% What would happen if the supply of loanable funds increased? Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -38
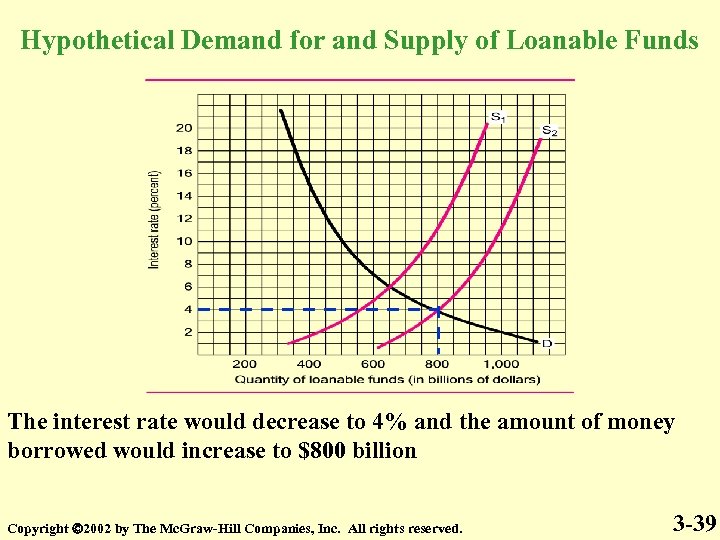
Hypothetical Demand for and Supply of Loanable Funds The interest rate would decrease to 4% and the amount of money borrowed would increase to $800 billion Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -39
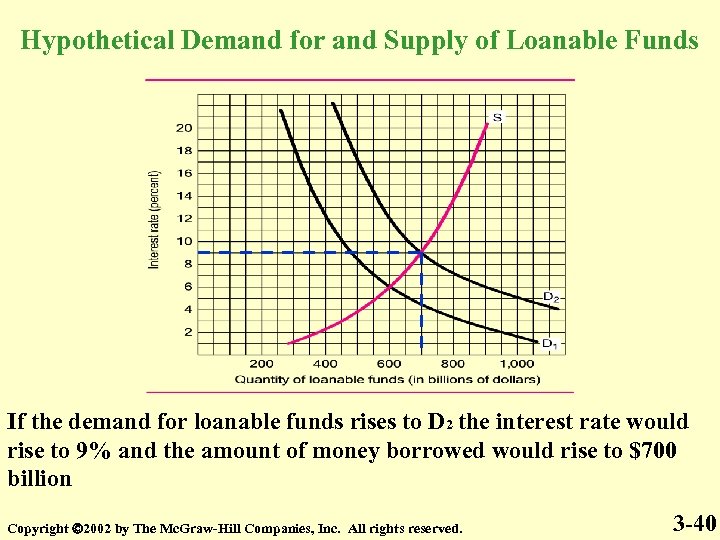
Hypothetical Demand for and Supply of Loanable Funds If the demand for loanable funds rises to D 2 the interest rate would rise to 9% and the amount of money borrowed would rise to $700 billion Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -40

Price Mechanism (The Forces of Supply & Demand) • Operates an automatic guidance system – Sometimes this is called the “invisible hand” – Efficiently allocates the limited means of production toward the satisfaction of human wants – Provides consumers with an endless stream of goods and services • In a sense, the price system has failed poor people – Many are working 50 or 60 hours a week, but they are still poor Copyright 2002 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 3 -41
401c62e35af45795f3b002aadd4be9f8.ppt