837976ec513da0450ee9e845411b82b4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Chapter 3 Strategic Initiatives for Implementing Competitive Advantages Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved
Chapter 3 Strategic Initiatives for Implementing Competitive Advantages Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved
 Learning Outcomes 3. 1 List and describe the four basic components of supply chain management 3. 2 Explain customer relationship management systems and how they can help organizations understand their customers 3 -2
Learning Outcomes 3. 1 List and describe the four basic components of supply chain management 3. 2 Explain customer relationship management systems and how they can help organizations understand their customers 3 -2
 Learning Outcomes 3. 3 Summarize the importance of enterprise resource planning systems 3. 4 Identify how an organization can use business process reengineering to improve its business 3 -3
Learning Outcomes 3. 3 Summarize the importance of enterprise resource planning systems 3. 4 Identify how an organization can use business process reengineering to improve its business 3 -3
 Leadership 3 -4
Leadership 3 -4
 Strategic Initiatives • To gain competitive advantage organizations can undertake high-profile strategic initiatives including: – Supply chain management (SCM) – Customer relationship management (CRM) – Enterprise resource planning (ERP) – Business process reengineering (BPR) 3 -5
Strategic Initiatives • To gain competitive advantage organizations can undertake high-profile strategic initiatives including: – Supply chain management (SCM) – Customer relationship management (CRM) – Enterprise resource planning (ERP) – Business process reengineering (BPR) 3 -5
 Supply Chain Management • A supply chain is a system of organizations, people, technology, activities, information and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer • Supply Chain Management (SCM) – involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximize total supply chain effectiveness and profitability 3 -6
Supply Chain Management • A supply chain is a system of organizations, people, technology, activities, information and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer • Supply Chain Management (SCM) – involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximize total supply chain effectiveness and profitability 3 -6
 Supply Chain Management • Four basic components of supply chain management include: 1. 2. 3. 4. Supply chain strategy – strategy for managing all resources to meet customer demand Supply chain partner – partners throughout the supply chain that deliver finished products, raw materials, and services including pricing, delivery, and payment processes Supply chain operation – schedule for production activities including testing, packaging, and preparation for delivery Supply chain logistics – product delivery process including orders, warehouses, carriers, defective product returns, and invoicing. 3 -7
Supply Chain Management • Four basic components of supply chain management include: 1. 2. 3. 4. Supply chain strategy – strategy for managing all resources to meet customer demand Supply chain partner – partners throughout the supply chain that deliver finished products, raw materials, and services including pricing, delivery, and payment processes Supply chain operation – schedule for production activities including testing, packaging, and preparation for delivery Supply chain logistics – product delivery process including orders, warehouses, carriers, defective product returns, and invoicing. 3 -7
 • SCM software can enable an organization to generate efficiencies by automating and improving the information flow throughout and among the different supply chain component. 3 -8
• SCM software can enable an organization to generate efficiencies by automating and improving the information flow throughout and among the different supply chain component. 3 -8
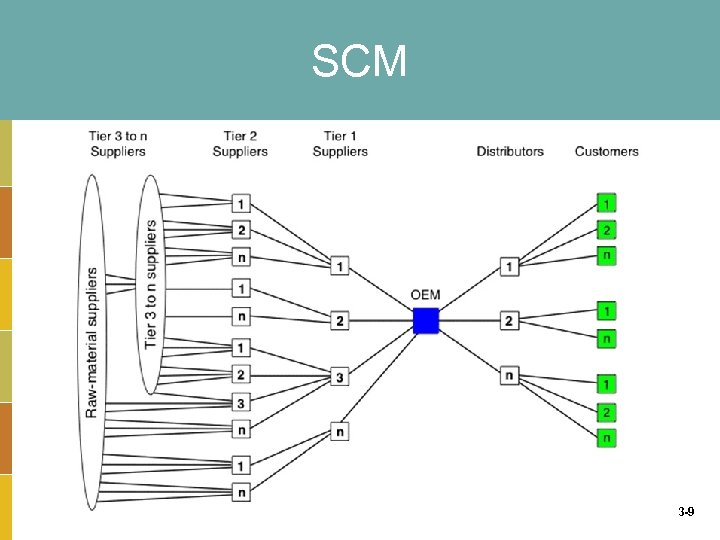 SCM 3 -9
SCM 3 -9
 Serious supply chain problem 3 -10
Serious supply chain problem 3 -10
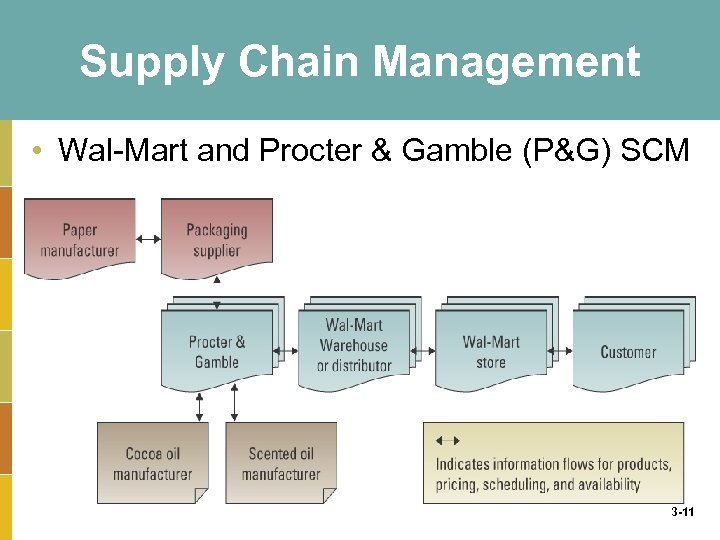 Supply Chain Management • Wal-Mart and Procter & Gamble (P&G) SCM 3 -11
Supply Chain Management • Wal-Mart and Procter & Gamble (P&G) SCM 3 -11
 • The SCM system save time, reduce inventory and decrease order-processing cost for P&G passes on these saving to Wal-Mart in the form of discounted prices. 3 -12
• The SCM system save time, reduce inventory and decrease order-processing cost for P&G passes on these saving to Wal-Mart in the form of discounted prices. 3 -12
 Supply Chain Management • Effective and efficient SCM systems can enable an organization to: – Decrease the power of its buyers – Increase its own supplier power – Increase switching costs to reduce threat of substitute products or services – Create entry barriers thereby reducing the threat of new entrants – Increase efficiencies while seeking a competitive advantage through cost leadership 3 -13
Supply Chain Management • Effective and efficient SCM systems can enable an organization to: – Decrease the power of its buyers – Increase its own supplier power – Increase switching costs to reduce threat of substitute products or services – Create entry barriers thereby reducing the threat of new entrants – Increase efficiencies while seeking a competitive advantage through cost leadership 3 -13
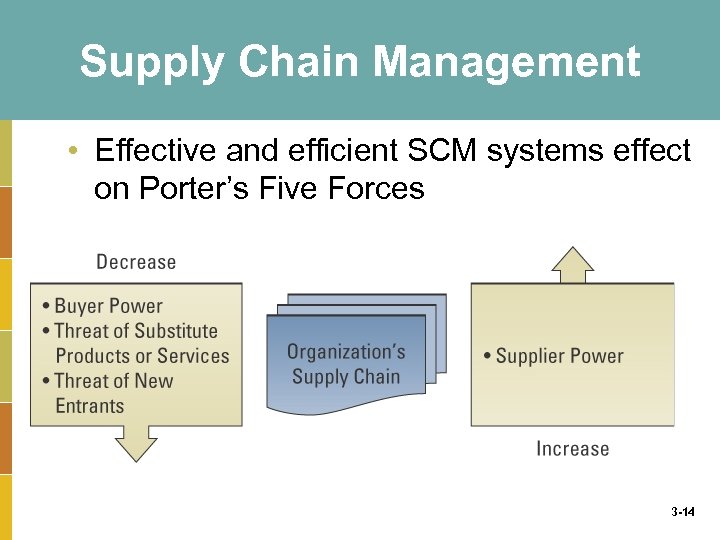 Supply Chain Management • Effective and efficient SCM systems effect on Porter’s Five Forces 3 -14
Supply Chain Management • Effective and efficient SCM systems effect on Porter’s Five Forces 3 -14
 No supply problem here 3 -15
No supply problem here 3 -15
 Videos • Keeping the Global Supply Chain Moving (6 mins) • Fresh Produce Supply Chain Management ( 2 mins) 3 -16
Videos • Keeping the Global Supply Chain Moving (6 mins) • Fresh Produce Supply Chain Management ( 2 mins) 3 -16
 Customer Relationship Management • Customer relationship management • (CRM) • involves managing all aspects of a customer’s relationship with an organization to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization's profitability 3 -17
Customer Relationship Management • Customer relationship management • (CRM) • involves managing all aspects of a customer’s relationship with an organization to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization's profitability 3 -17
 Customer Relationship Management • CRM is not just technology, but a strategy, process, and business goal that an organization must embrace on an enterprisewide level • CRM can enable an organization to: – – Identify types of customers Design individual customer marketing campaigns Treat each customer as an individual Understand customer buying behaviors 3 -18
Customer Relationship Management • CRM is not just technology, but a strategy, process, and business goal that an organization must embrace on an enterprisewide level • CRM can enable an organization to: – – Identify types of customers Design individual customer marketing campaigns Treat each customer as an individual Understand customer buying behaviors 3 -18
 Charles Schwab’s CRM Case • Charles Schwab recouped the cost of a multimilliondollar CRM system in less than two years – The system allowed Schwab to segment its customers in terms of serious and nonserious investors – The CRM system looked for customers that had automatic withdrawal from a bank account as a sign of a serious investor – The CRM system looked for stagnant balances as a sign of a nonserious investor – Charles Schwab could then focus efforts on selling to serious investors, and spend less time attempting to sell to nonserious investors 3 -19
Charles Schwab’s CRM Case • Charles Schwab recouped the cost of a multimilliondollar CRM system in less than two years – The system allowed Schwab to segment its customers in terms of serious and nonserious investors – The CRM system looked for customers that had automatic withdrawal from a bank account as a sign of a serious investor – The CRM system looked for stagnant balances as a sign of a nonserious investor – Charles Schwab could then focus efforts on selling to serious investors, and spend less time attempting to sell to nonserious investors 3 -19
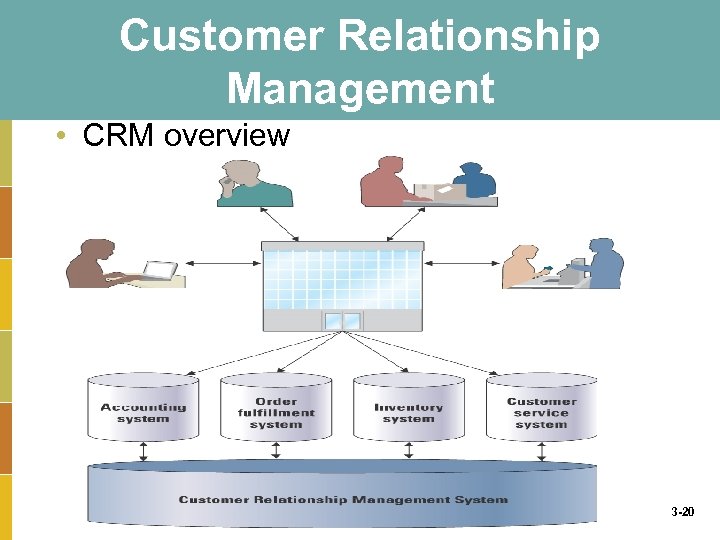 Customer Relationship Management • CRM overview 3 -20
Customer Relationship Management • CRM overview 3 -20
 Videos • What is CRM? ( 7 mins) 3 -21
Videos • What is CRM? ( 7 mins) 3 -21
 Business Process Reengineering • Business process – a standardized set of activities that accomplish a specific task, such as processing a customer’s order • Business process reengineering (BPR) – the analysis and redesign of workflow within and between enterprises – The purpose of BPR is to make all business processes best-in-class 3 -22
Business Process Reengineering • Business process – a standardized set of activities that accomplish a specific task, such as processing a customer’s order • Business process reengineering (BPR) – the analysis and redesign of workflow within and between enterprises – The purpose of BPR is to make all business processes best-in-class 3 -22
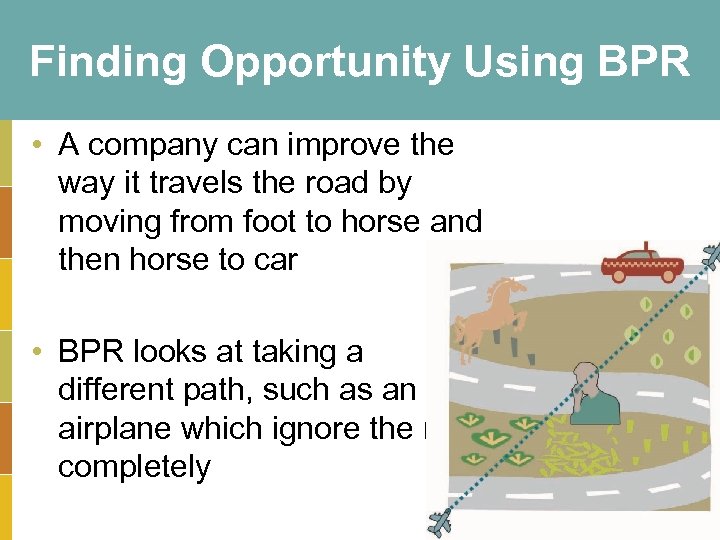 Finding Opportunity Using BPR • A company can improve the way it travels the road by moving from foot to horse and then horse to car • BPR looks at taking a different path, such as an airplane which ignore the road completely 3 -23
Finding Opportunity Using BPR • A company can improve the way it travels the road by moving from foot to horse and then horse to car • BPR looks at taking a different path, such as an airplane which ignore the road completely 3 -23
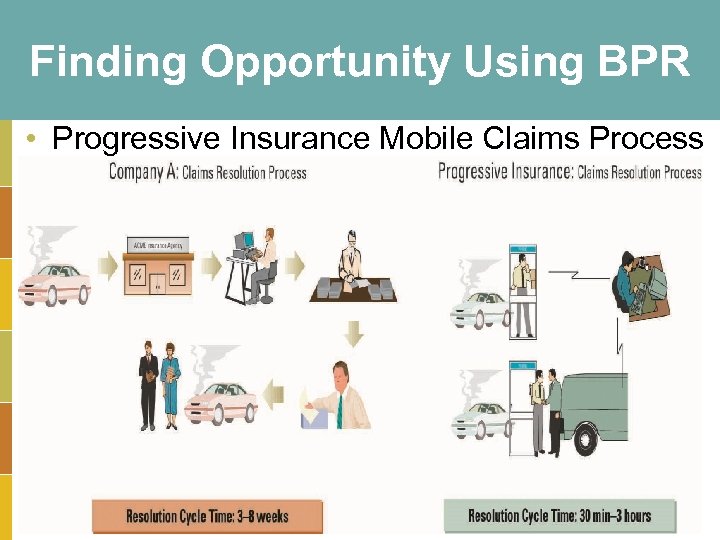 Finding Opportunity Using BPR • Progressive Insurance Mobile Claims Process 3 -24
Finding Opportunity Using BPR • Progressive Insurance Mobile Claims Process 3 -24
 Videos • Business Process Management ( 6 mins) • Workflow - Improving Business Processes ( 2 mins) 3 -25
Videos • Business Process Management ( 6 mins) • Workflow - Improving Business Processes ( 2 mins) 3 -25
 Enterprise Resource Planning • Enterprise resource planning (ERP) – integrates all departments and functions throughout an organization into a single IT system so that employees can make decisions by viewing enterprisewide information on all business operations 3 -26
Enterprise Resource Planning • Enterprise resource planning (ERP) – integrates all departments and functions throughout an organization into a single IT system so that employees can make decisions by viewing enterprisewide information on all business operations 3 -26
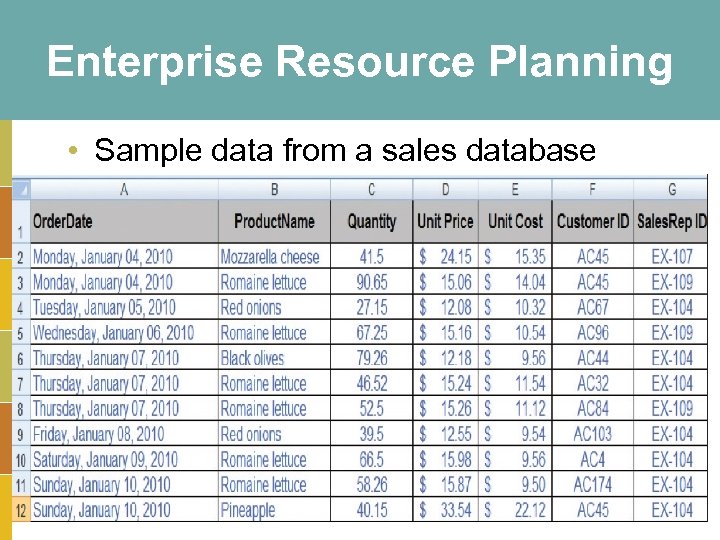 Enterprise Resource Planning • Sample data from a sales database 3 -27
Enterprise Resource Planning • Sample data from a sales database 3 -27
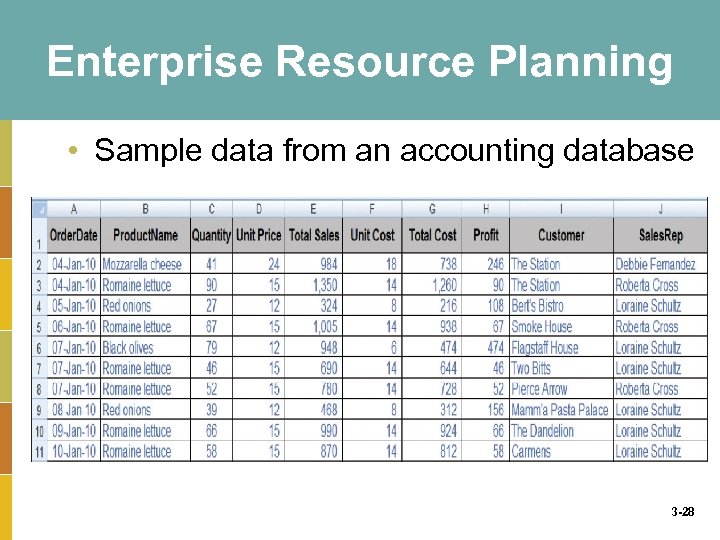 Enterprise Resource Planning • Sample data from an accounting database 3 -28
Enterprise Resource Planning • Sample data from an accounting database 3 -28
 Professor Liengme on a bad day 3 -29
Professor Liengme on a bad day 3 -29
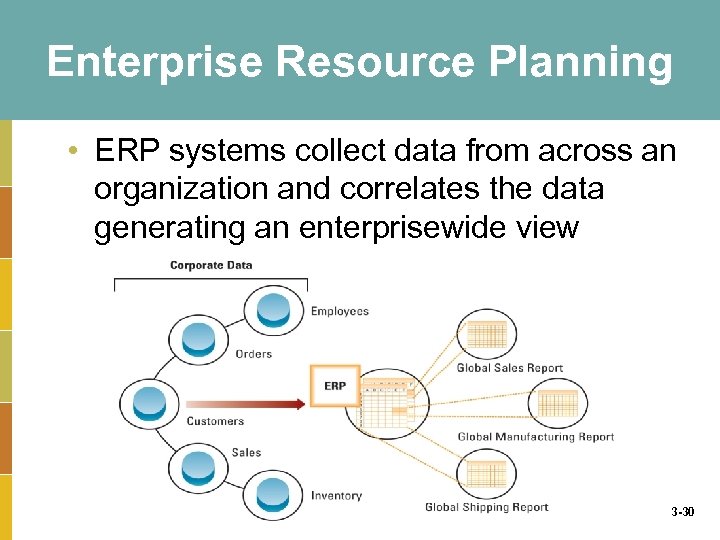 Enterprise Resource Planning • ERP systems collect data from across an organization and correlates the data generating an enterprisewide view 3 -30
Enterprise Resource Planning • ERP systems collect data from across an organization and correlates the data generating an enterprisewide view 3 -30


