35839e53e6c4cd95c968731063f6a3f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Chapter 3 Retailing in Electronic Commerce (E-Tailing)
Chapter 3 Retailing in Electronic Commerce (E-Tailing)
 Opening Case: Amazon. com u B 2 C business model where customers look for a: a a Low price Fast shipment Good return policy Helpful customer service u Customer profile different from traditional bookstore u From Buy-and-sell to Sell-Order-Deliver CK Farn 2
Opening Case: Amazon. com u B 2 C business model where customers look for a: a a Low price Fast shipment Good return policy Helpful customer service u Customer profile different from traditional bookstore u From Buy-and-sell to Sell-Order-Deliver CK Farn 2
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Largest Bookstore in the world u Offers millions of items a a a Books and music DVDs and videos Toys and video games Electronics and software Home improvement products CK Farn 3
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Largest Bookstore in the world u Offers millions of items a a a Books and music DVDs and videos Toys and video games Electronics and software Home improvement products CK Farn 3
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Started business in 1995 a Sales û 1996 = $15. 7 million û 2000 = $1. 8 billion a Products û 1999 = 5 million titles û 2000 = 13 million books, music, DVD/video titles CK Farn 4
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Started business in 1995 a Sales û 1996 = $15. 7 million û 2000 = $1. 8 billion a Products û 1999 = 5 million titles û 2000 = 13 million books, music, DVD/video titles CK Farn 4
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Auctions a Hosts and operates auctions for individuals and small businesses a z. Shops, Amazon marketplace, Amazon payment processing û Provide the opportunity for small businesses to develop custom storefront û Storefronts are supported by Amazon’s backend order fulfillment processing CK Farn 5
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Auctions a Hosts and operates auctions for individuals and small businesses a z. Shops, Amazon marketplace, Amazon payment processing û Provide the opportunity for small businesses to develop custom storefront û Storefronts are supported by Amazon’s backend order fulfillment processing CK Farn 5
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) Features a Easy browsing and searching a Useful product information a Reviews, recommendations, and personalization CK Farn u Broad selection and low prices u Secure payment system (1 Click order technology) u Gifts department u Online community u Secured payments 6
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) Features a Easy browsing and searching a Useful product information a Reviews, recommendations, and personalization CK Farn u Broad selection and low prices u Secure payment system (1 Click order technology) u Gifts department u Online community u Secured payments 6
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Customer relationship management a Creates interesting and informative front-end a Highly automated and efficient back-end support a Personalized service û Return customers are welcomed back by name û Customer wish lists available û E-mails customers purchase recommendations based on their purchasing history CK Farn 7
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Customer relationship management a Creates interesting and informative front-end a Highly automated and efficient back-end support a Personalized service û Return customers are welcomed back by name û Customer wish lists available û E-mails customers purchase recommendations based on their purchasing history CK Farn 7
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Financial performance a Overall losses rather than profits a Ability to move into new areas of business should move them toward profitability, but makes money from books a High level of customer service and customer loyalty adds value CK Farn 8
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Financial performance a Overall losses rather than profits a Ability to move into new areas of business should move them toward profitability, but makes money from books a High level of customer service and customer loyalty adds value CK Farn 8
 Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Diversification through business alliances a Online sale of cars - greenlight. com a Online health and beauty aids drugstore. com a Wireless phones – multiple business partners a Toys - Toysr. Us. com CK Farn 9
Opening Case: Amazon. com (cont. ) u Diversification through business alliances a Online sale of cars - greenlight. com a Online health and beauty aids drugstore. com a Wireless phones – multiple business partners a Toys - Toysr. Us. com CK Farn 9
 E-Tailing and B 2 C Market Growth u Business-to-business (B 2 B) a Requires precise record keeping, trackability, accountability, and formal contracts, usually with high volume of transactions and large amount payments a Also online retailing u Business-to-consumer (B 2 C) a Ability to create direct relationships with consumer without intermediaries like distributors, wholesalers, or dealers CK Farn 10
E-Tailing and B 2 C Market Growth u Business-to-business (B 2 B) a Requires precise record keeping, trackability, accountability, and formal contracts, usually with high volume of transactions and large amount payments a Also online retailing u Business-to-consumer (B 2 C) a Ability to create direct relationships with consumer without intermediaries like distributors, wholesalers, or dealers CK Farn 10
 E-Tailing and B 2 C Market Growth (cont. ) u The B 2 C Market success is derived from: a Offering quality merchandise at good prices a Excellent customer service a Convenience CK Farn 11
E-Tailing and B 2 C Market Growth (cont. ) u The B 2 C Market success is derived from: a Offering quality merchandise at good prices a Excellent customer service a Convenience CK Farn 11
 E-Tailing and B 2 C Market Growth (cont. ) u Characteristics of goods leading to high online sales volumes a a Brand recognition and guarantees Digitized products Frequently purchased, inexpensive items Well-known items with standard specifications CK Farn 12
E-Tailing and B 2 C Market Growth (cont. ) u Characteristics of goods leading to high online sales volumes a a Brand recognition and guarantees Digitized products Frequently purchased, inexpensive items Well-known items with standard specifications CK Farn 12
 Consumer Purchase Process and Marketing Plan u Purchase decision process a Prepurchase steps û Awareness of need for purchase û Identify basic need or want a Actual purchase û Establish decision criteria û Seek recommendations and information û Make purchase a Postpurchase steps û Assistance with installation or setup û Online help desks and instruction manuals CK Farn 13
Consumer Purchase Process and Marketing Plan u Purchase decision process a Prepurchase steps û Awareness of need for purchase û Identify basic need or want a Actual purchase û Establish decision criteria û Seek recommendations and information û Make purchase a Postpurchase steps û Assistance with installation or setup û Online help desks and instruction manuals CK Farn 13
 Figure 3 -1 The Consumer Purchase Decision Process CK Farn 14
Figure 3 -1 The Consumer Purchase Decision Process CK Farn 14
 Consumer Purchase Process and Marketing Plan (cont. ) Types of online shoppers u Time-starved consumers u Shopping avoiders u New technologists u Time-sensitive materialists or clickand-mortar consumers CK Farn u u Traditionalists Hunter-gatherers Brand loyalists Single shoppers Which are your targets? 15
Consumer Purchase Process and Marketing Plan (cont. ) Types of online shoppers u Time-starved consumers u Shopping avoiders u New technologists u Time-sensitive materialists or clickand-mortar consumers CK Farn u u Traditionalists Hunter-gatherers Brand loyalists Single shoppers Which are your targets? 15
 Decision Criteria u Value proposition a customer service, better prices, higher quality u Personal service a treat the customer as a unique individual u Convenience a self-contained site that serves all the customer’s needs u Other criteria a service after the sale CK Farn 16
Decision Criteria u Value proposition a customer service, better prices, higher quality u Personal service a treat the customer as a unique individual u Convenience a self-contained site that serves all the customer’s needs u Other criteria a service after the sale CK Farn 16
 A Marketing Plan u Influence the consumer’s decision process through the “marketing mix” a Product—portfolio of items available a Price of the products a Promotion of products (advertisements and giveaways) a Packaging and delivery CK Farn 17
A Marketing Plan u Influence the consumer’s decision process through the “marketing mix” a Product—portfolio of items available a Price of the products a Promotion of products (advertisements and giveaways) a Packaging and delivery CK Farn 17
 Online Purchasing Aids u Shopping portals a Comprehensive portals û Links to many different sellers û Shopping comparison sites û Comparison tools are available a Niche oriented û Specialize in a certain line of products (dogtoys. com) û Some collect referral fee only û Others have formal relationships with affiliates CK Farn 18
Online Purchasing Aids u Shopping portals a Comprehensive portals û Links to many different sellers û Shopping comparison sites û Comparison tools are available a Niche oriented û Specialize in a certain line of products (dogtoys. com) û Some collect referral fee only û Others have formal relationships with affiliates CK Farn 18
 Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) u Shopbots and agents—tools that scout the Web for specific search criteria requested by consumers a a Mysimon. com - best prices on multiple items Auto. Bytel. com – cars Zdnet. com/computershopper – computers Office. com – office supplies CK Farn 19
Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) u Shopbots and agents—tools that scout the Web for specific search criteria requested by consumers a a Mysimon. com - best prices on multiple items Auto. Bytel. com – cars Zdnet. com/computershopper – computers Office. com – office supplies CK Farn 19
 Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) u Business ratings sites—sites that rate e-tailers a Bizrate. com—compiles results provided by a network of shoppers a Gomez. com—consumer identifies relative importance of different criteria CK Farn 20
Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) u Business ratings sites—sites that rate e-tailers a Bizrate. com—compiles results provided by a network of shoppers a Gomez. com—consumer identifies relative importance of different criteria CK Farn 20
 Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) Trust verification sites—evaluate and verify trustworthiness and integrity of e-tailers u TRUSTe seal of assurance a a u Secure Assure E-tailers pay TRUSTe for use of seal Hope consumers use seal as proxy u for actual research about their site u BBBOn. Line a Yearly license fees based on company’s annual revenue CK Farn a Yearly license fees based on company’s annual revenue Ernst and Young a a Created its own service for auditing e-tailers Offers some guarantee of integrity of business practices 21
Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) Trust verification sites—evaluate and verify trustworthiness and integrity of e-tailers u TRUSTe seal of assurance a a u Secure Assure E-tailers pay TRUSTe for use of seal Hope consumers use seal as proxy u for actual research about their site u BBBOn. Line a Yearly license fees based on company’s annual revenue CK Farn a Yearly license fees based on company’s annual revenue Ernst and Young a a Created its own service for auditing e-tailers Offers some guarantee of integrity of business practices 21
 Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) u Other shopping tools a Escrow services— 3 rd party to assure quality û Proper exchange of money and goods û Research information û Payment-processing support a Communities of consumers û Epinions. com—searchable recommendations on products û Price. Grabber. com—comparison shopping CK Farn 22
Online Purchasing Aids (cont. ) u Other shopping tools a Escrow services— 3 rd party to assure quality û Proper exchange of money and goods û Research information û Payment-processing support a Communities of consumers û Epinions. com—searchable recommendations on products û Price. Grabber. com—comparison shopping CK Farn 22
 E-Tailing Business Models u Subscription models a charge monthly or annual subscription fee for service u Transaction fee models a charge service fee based on the level of transaction offered u Advertising-supported models a charge fee to advertisers instead of customers u Sponsorship models a companies sponsor the business through donations (usually supplemental income) CK Farn 23
E-Tailing Business Models u Subscription models a charge monthly or annual subscription fee for service u Transaction fee models a charge service fee based on the level of transaction offered u Advertising-supported models a charge fee to advertisers instead of customers u Sponsorship models a companies sponsor the business through donations (usually supplemental income) CK Farn 23
 Figure 3 -2 Disintermediation in the B 2 C Supply Chain Source: M. Warkentin, et al. (2000). Used with permission of Dr. Merrill Warkentin. CK Farn 24
Figure 3 -2 Disintermediation in the B 2 C Supply Chain Source: M. Warkentin, et al. (2000). Used with permission of Dr. Merrill Warkentin. CK Farn 24
 E-Tailing Business Models (cont. ) u Direct marketing—sell directly to consumers a Manufactures can sell directly to customers û Disintermediation—removal of business process layers in the value chain û Shortens the distribution chain – Eliminates inefficiencies – Shortens delivery time – Builds closer relationships with consumers a Click-and-mortar û Additional marketing channel to the conventional one û Effectively supports build-to-order requests CK Farn 25
E-Tailing Business Models (cont. ) u Direct marketing—sell directly to consumers a Manufactures can sell directly to customers û Disintermediation—removal of business process layers in the value chain û Shortens the distribution chain – Eliminates inefficiencies – Shortens delivery time – Builds closer relationships with consumers a Click-and-mortar û Additional marketing channel to the conventional one û Effectively supports build-to-order requests CK Farn 25
 E-Tailing Business Models (cont. ) u Pure-play e-tailers—sell over the Internet without a physical sales channel a General purpose e-tailers (Amazon. com) û Broad range of products û Large number of consumers a Specialty or niche e-tailers (Cat. Toys. com) û One specific product area û High demand items in the area û Effective practices for customer appeal CK Farn 26
E-Tailing Business Models (cont. ) u Pure-play e-tailers—sell over the Internet without a physical sales channel a General purpose e-tailers (Amazon. com) û Broad range of products û Large number of consumers a Specialty or niche e-tailers (Cat. Toys. com) û One specific product area û High demand items in the area û Effective practices for customer appeal CK Farn 26
 E-Tailing Business Models (cont. ) u Traditional retailers with Web sites a Physical store a May include mail-order or catalog sales a Multichannel store operates both û Physical store û E-tail site CK Farn 27
E-Tailing Business Models (cont. ) u Traditional retailers with Web sites a Physical store a May include mail-order or catalog sales a Multichannel store operates both û Physical store û E-tail site CK Farn 27
 Digital Delivery u Digital (“soft”) goods a Music, movies, videos, software, newspapers, magazines, graphics, etc. a Can be delivered in “hard” or “soft” form û Computer program on CD-ROM with owner’s manual and warranty card û Download from Web site after payment CK Farn 28
Digital Delivery u Digital (“soft”) goods a Music, movies, videos, software, newspapers, magazines, graphics, etc. a Can be delivered in “hard” or “soft” form û Computer program on CD-ROM with owner’s manual and warranty card û Download from Web site after payment CK Farn 28
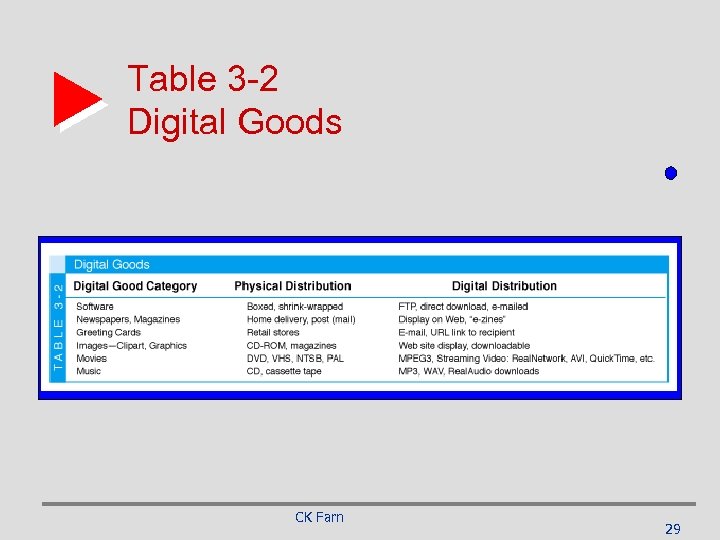 Table 3 -2 Digital Goods CK Farn 29
Table 3 -2 Digital Goods CK Farn 29
 Digital Delivery (cont. ) u Napster experience—person-to-person sharing tool a Enables individual users to download music files from each other’s computers a Phenomenal growth of Napster community a New version of its file-swapping software includes a “buy button” linked to CDNow a May be beneficial to overall music sales as individuals easily sample a broader range of music CK Farn 30
Digital Delivery (cont. ) u Napster experience—person-to-person sharing tool a Enables individual users to download music files from each other’s computers a Phenomenal growth of Napster community a New version of its file-swapping software includes a “buy button” linked to CDNow a May be beneficial to overall music sales as individuals easily sample a broader range of music CK Farn 30
 Digital Delivery (cont. ) u New developments a Custom-publishing music CD sites—collection of personal favorites a Disintermediation of traditional print media û Journals and magazines û Newspapers (e. g. , Wall Street Journal) CK Farn 31
Digital Delivery (cont. ) u New developments a Custom-publishing music CD sites—collection of personal favorites a Disintermediation of traditional print media û Journals and magazines û Newspapers (e. g. , Wall Street Journal) CK Farn 31
 Successful Click-and-Mortar Strategies u Click-and-mortar hybrid strategies a Speak with one voice—link all back-end systems to create an integrated customer experience a Empower the customer—powerful channel for service and information a Leverage the channels—offs advantages of each channel to customers from all channels û Return item purchased online at physical store û Order via the Web at the physical store items not available there CK Farn 32
Successful Click-and-Mortar Strategies u Click-and-mortar hybrid strategies a Speak with one voice—link all back-end systems to create an integrated customer experience a Empower the customer—powerful channel for service and information a Leverage the channels—offs advantages of each channel to customers from all channels û Return item purchased online at physical store û Order via the Web at the physical store items not available there CK Farn 32
 Successful Click-and-Mortar Strategies (cont. ) u Circuit City Case: transform to click-and-mortar (Circuit. City. com) a Educates customers about features and capabilities of products a Customers can perform powerful searches to find most appropriate products a Offers extensive amount of information on electronics etc. , organized very flexibly a Online purchases are smooth, secure and seamless CK Farn 33
Successful Click-and-Mortar Strategies (cont. ) u Circuit City Case: transform to click-and-mortar (Circuit. City. com) a Educates customers about features and capabilities of products a Customers can perform powerful searches to find most appropriate products a Offers extensive amount of information on electronics etc. , organized very flexibly a Online purchases are smooth, secure and seamless CK Farn 33
 Successful Click-and-Mortar Strategies (cont. ) u Amazon and Toys R Us: alliance of pureplay with traditional retailer a Toys R Us had limited logistics capabilities including distribution centers a Amazon failed in the toy market lacking supplier relationships with toy manufacturers a Alliance allows each partner to leverage each others core strengths a Innovative model still working out problems CK Farn 34
Successful Click-and-Mortar Strategies (cont. ) u Amazon and Toys R Us: alliance of pureplay with traditional retailer a Toys R Us had limited logistics capabilities including distribution centers a Amazon failed in the toy market lacking supplier relationships with toy manufacturers a Alliance allows each partner to leverage each others core strengths a Innovative model still working out problems CK Farn 34
 Disintermediation & Reintermediaries u Disintermediation—manufacturer sells directly to consumer u Reintermediaries—new intermediary roles in the digital environment offer new ways to: a Reach new customers a Bring value to customers a Generate revenues CK Farn 35
Disintermediation & Reintermediaries u Disintermediation—manufacturer sells directly to consumer u Reintermediaries—new intermediary roles in the digital environment offer new ways to: a Reach new customers a Bring value to customers a Generate revenues CK Farn 35
 Channel Conflict & Personalization u Channel conflict— members antagonistic over: a a Incentives Rewards Policies Support CK Farn u Personalization—custom designed marketing plan a Tailored to buying patterns a Appeal to sense of value a Excellent customer service a Mass customization 36
Channel Conflict & Personalization u Channel conflict— members antagonistic over: a a Incentives Rewards Policies Support CK Farn u Personalization—custom designed marketing plan a Tailored to buying patterns a Appeal to sense of value a Excellent customer service a Mass customization 36
 E-Tailing : Lessons Learned u Profitability—online marginal sales don’t lead to marginal profits u Branding—drive to establish brand can lead to excessive spending u Performance—Web sites need to function in a fast, user-friendly manner u Static design—dynamic sites with rich databases of information appeal most to customers CK Farn 37
E-Tailing : Lessons Learned u Profitability—online marginal sales don’t lead to marginal profits u Branding—drive to establish brand can lead to excessive spending u Performance—Web sites need to function in a fast, user-friendly manner u Static design—dynamic sites with rich databases of information appeal most to customers CK Farn 37
 Managerial Issues u u u First-mover advantage or wait and learn Strategic positioning Trust New risk exposure Financial viability Successes CK Farn 38
Managerial Issues u u u First-mover advantage or wait and learn Strategic positioning Trust New risk exposure Financial viability Successes CK Farn 38


