cd034554541319671d74e91f531b59b0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Chapter 3 Mesopotamia
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia
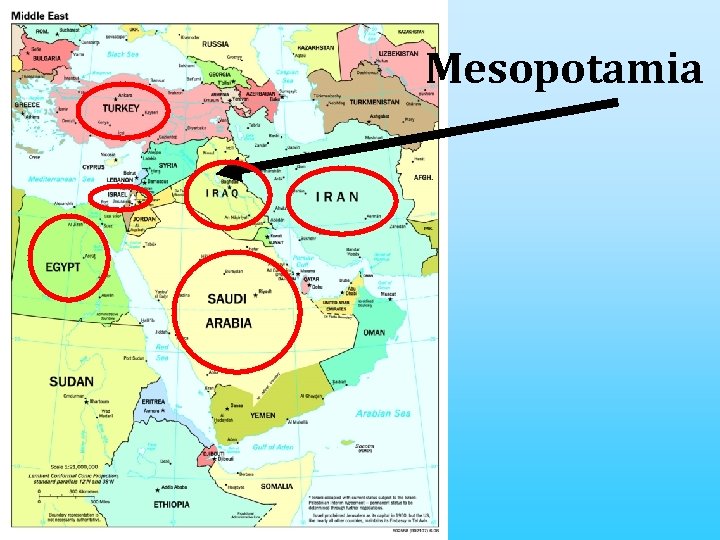 Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
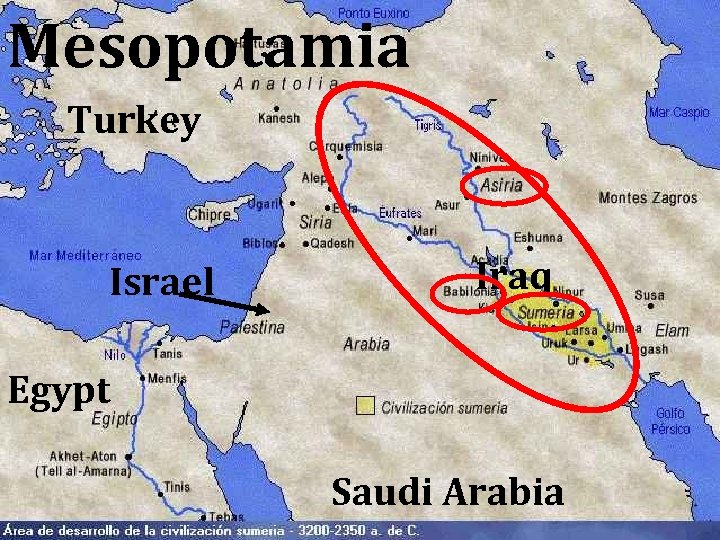 Mesopotamia Turkey Israel Iraq Egypt Saudi Arabia
Mesopotamia Turkey Israel Iraq Egypt Saudi Arabia
 Around 15, 000 B. C. , people began migrating. Why?
Around 15, 000 B. C. , people began migrating. Why?
 People began migrating in search of… • Water • Land • Fertile soil • Climate
People began migrating in search of… • Water • Land • Fertile soil • Climate
 Also… about 15, 000 B. C. , farming began to evolve. Where did this “revolution” begin?
Also… about 15, 000 B. C. , farming began to evolve. Where did this “revolution” begin?
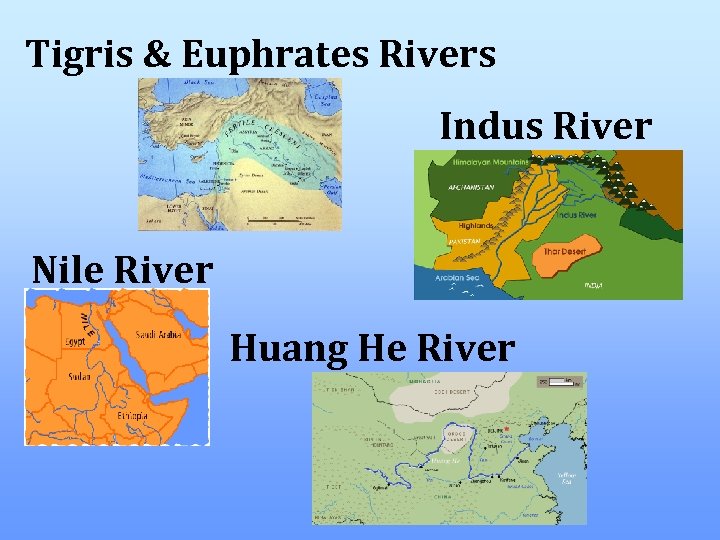 Tigris & Euphrates Rivers Indus River Nile River Huang He River
Tigris & Euphrates Rivers Indus River Nile River Huang He River
 Section 1 The Rise of Sumer
Section 1 The Rise of Sumer
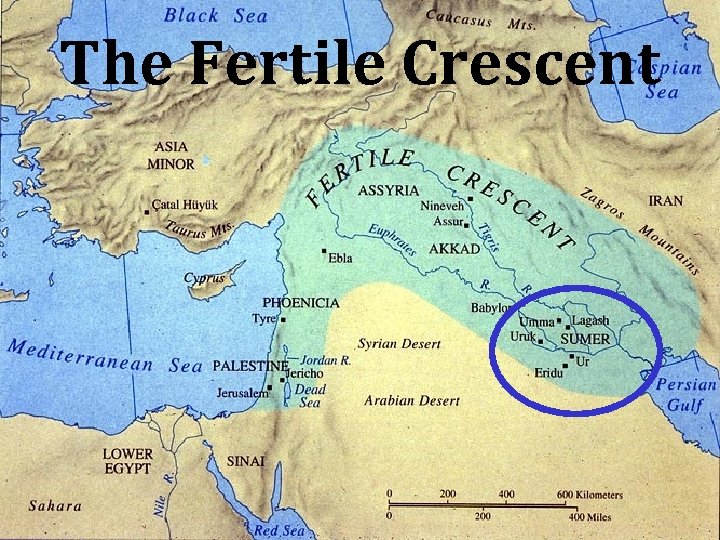 The Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent
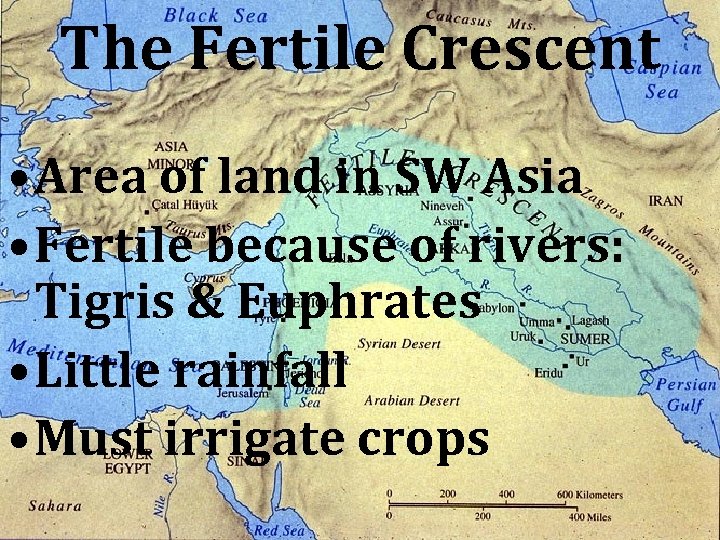 The Fertile Crescent • Area of land in SW Asia • Fertile because of rivers: Tigris & Euphrates • Little rainfall • Must irrigate crops
The Fertile Crescent • Area of land in SW Asia • Fertile because of rivers: Tigris & Euphrates • Little rainfall • Must irrigate crops
 Mesopotamia • Greek: Meso – between +Pot – river “land between the rivers” • Located between Tigris & Euphrates • Present day Iraq • “Cradle of Civilization”
Mesopotamia • Greek: Meso – between +Pot – river “land between the rivers” • Located between Tigris & Euphrates • Present day Iraq • “Cradle of Civilization”
 The Rise of Sumer • Earliest known civilization • Located in Mesopotamia • People built up natural levees higher to control flooding • Built canals and used them to irrigate crops • Crops included: barley (chief crop), wheat, sesame, flax, fruit, dates
The Rise of Sumer • Earliest known civilization • Located in Mesopotamia • People built up natural levees higher to control flooding • Built canals and used them to irrigate crops • Crops included: barley (chief crop), wheat, sesame, flax, fruit, dates
 5 Characteristics of Civilization • Food Surplus • Specialization of Labor • Government • Social Classes • Signs of Culture
5 Characteristics of Civilization • Food Surplus • Specialization of Labor • Government • Social Classes • Signs of Culture
 Ur – Food Surplus • Grew crops using irrigation • Used surplus to trade for other goods • Ur was major center for trade and commerce
Ur – Food Surplus • Grew crops using irrigation • Used surplus to trade for other goods • Ur was major center for trade and commerce
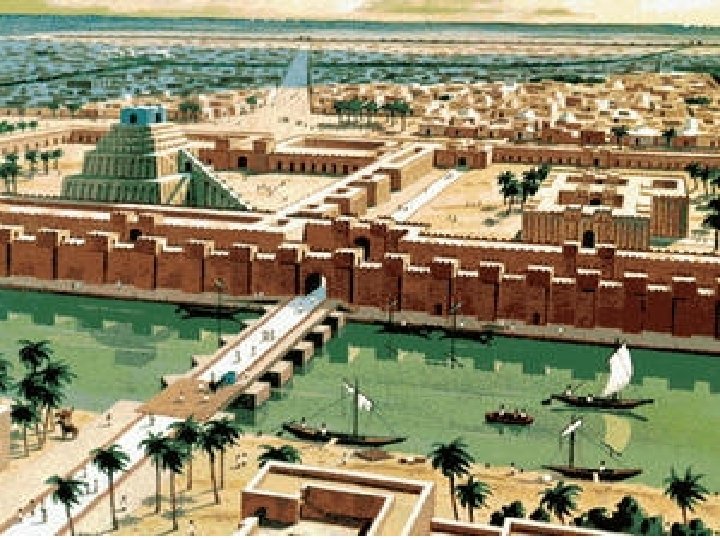

 Specialization of Labor • Houses made of mud and crushed reed bricks (no stone or timber available) • City was surrounded by wall
Specialization of Labor • Houses made of mud and crushed reed bricks (no stone or timber available) • City was surrounded by wall
 Government • Made laws • City-states: city and farmland around it • Priests ran city-states
Government • Made laws • City-states: city and farmland around it • Priests ran city-states
 Signs of Culture • Religion • Language • Dress • Customs • Social Classes
Signs of Culture • Religion • Language • Dress • Customs • Social Classes
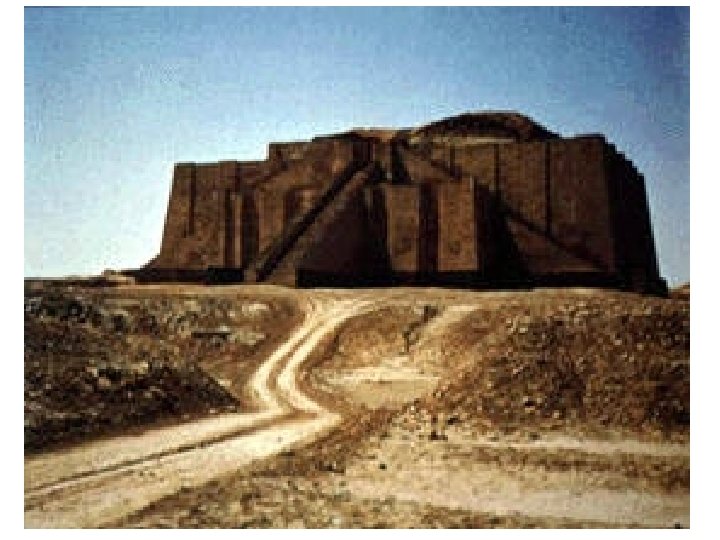
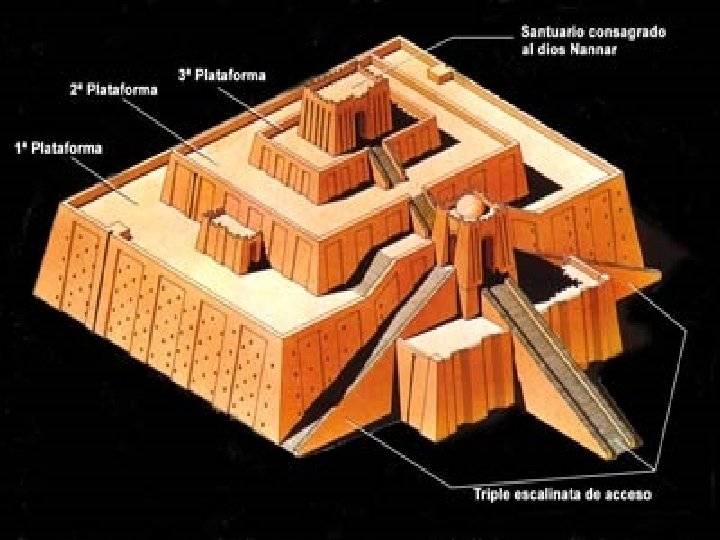
 Religion • Ziggurat – temple in the middle of each Sumerian city • Ziggurat – “mountain of god” or “hill of heaven” • Only priest entered ziggurats
Religion • Ziggurat – temple in the middle of each Sumerian city • Ziggurat – “mountain of god” or “hill of heaven” • Only priest entered ziggurats
 Religious Beliefs • Forces of nature were gods • Humans were created from mud of rivers to serve gods • Only priest knew will of gods • Priests……… became very powerful.
Religious Beliefs • Forces of nature were gods • Humans were created from mud of rivers to serve gods • Only priest knew will of gods • Priests……… became very powerful.
 Social Classes • Upper Class • Middle Class • Lower Class
Social Classes • Upper Class • Middle Class • Lower Class
 Upper Class • Houses in center of city • Priests and merchants • Priests controlled land, schools, etc. • Only rich males could go to school
Upper Class • Houses in center of city • Priests and merchants • Priests controlled land, schools, etc. • Only rich males could go to school
 Priest makes account of supplies
Priest makes account of supplies





 Middle Class • Houses outside upper class houses • Government officials, shop keepers, artisans (skilled workers)
Middle Class • Houses outside upper class houses • Government officials, shop keepers, artisans (skilled workers)
 Lower Class • Houses outside middle class • Farmers, unskilled workers, fishermen
Lower Class • Houses outside middle class • Farmers, unskilled workers, fishermen
 Sumerian Schools • Called tablet houses • Students were taught to write cuneiform
Sumerian Schools • Called tablet houses • Students were taught to write cuneiform
 Cuneiform • Sumerian writing using hundreds of markings shaped in wedges • Writing was developed to keep track of business dealings • Students became scribes (writers) in the temple, palace, government, army, for merchants , or became public writers
Cuneiform • Sumerian writing using hundreds of markings shaped in wedges • Writing was developed to keep track of business dealings • Students became scribes (writers) in the temple, palace, government, army, for merchants , or became public writers
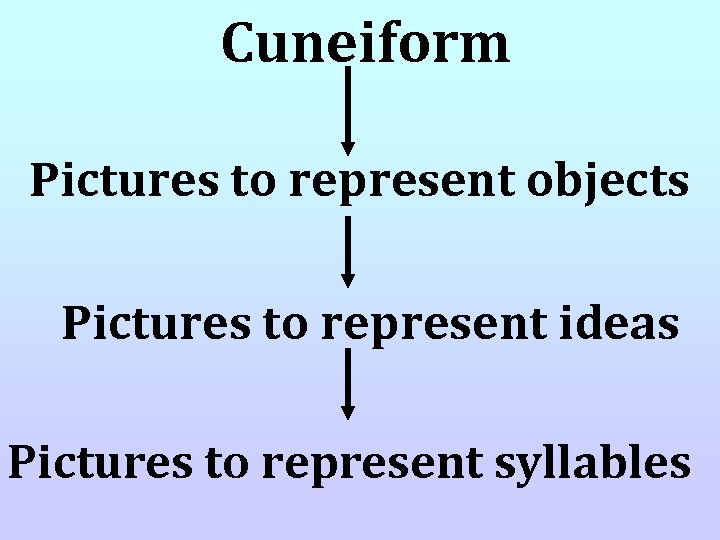 Cuneiform Pictures to represent objects Pictures to represent ideas Pictures to represent syllables
Cuneiform Pictures to represent objects Pictures to represent ideas Pictures to represent syllables
 The Round School Tablet from the Babylonian city of Nippur during Hammurabi Dynasty
The Round School Tablet from the Babylonian city of Nippur during Hammurabi Dynasty

 The Philadelphia Tablet found near Baghdad, Iraq 3100 -2900 B. C.
The Philadelphia Tablet found near Baghdad, Iraq 3100 -2900 B. C.

 Vargy’s monogram http: //www. upennmuseum. com/cuneiform. cgi
Vargy’s monogram http: //www. upennmuseum. com/cuneiform. cgi
 Women’s Rights • Women could…. …buy and sell land …run businesses …buy and sell slaves • Women could… …be divorced …be sold or rented for 3 years
Women’s Rights • Women could…. …buy and sell land …run businesses …buy and sell slaves • Women could… …be divorced …be sold or rented for 3 years
 Priests or Kings? • Sumerian priests were kings over city-states • Received advice from an assembly • In time of war, city-state would choose a military leader
Priests or Kings? • Sumerian priests were kings over city-states • Received advice from an assembly • In time of war, city-state would choose a military leader
 • About 3, 000 B. C. , this military leader took the place of priests as permanent kings. • Kingship became hereditary (passed on from parent to child)
• About 3, 000 B. C. , this military leader took the place of priests as permanent kings. • Kingship became hereditary (passed on from parent to child)
 Gilgamesh of Uruk • Famous priest-king • Story written about 1700 B. C. • Gilgamesh searches for a way to live forever after the death of his friend Enkidu.
Gilgamesh of Uruk • Famous priest-king • Story written about 1700 B. C. • Gilgamesh searches for a way to live forever after the death of his friend Enkidu.


