22 ВАРИАНТ.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Chapter 3 Lecture Outlines Management’s Social and Ethical Responsibilities Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Chapter 3 Lecture Outlines Management’s Social and Ethical Responsibilities Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Objectives 1. Define corporate social responsibility and summarize the arguments for and against it. 2. Identify and describe the four social responsibility strategies. 3. Explain the role of enlightened self-interest in social responsibility. 4. Summarize three practical lessons from business ethics research. 5. Identify and describe at least four of the ten general ethical principles. 6. Discuss what management can do to improve business ethics Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2
Chapter Objectives 1. Define corporate social responsibility and summarize the arguments for and against it. 2. Identify and describe the four social responsibility strategies. 3. Explain the role of enlightened self-interest in social responsibility. 4. Summarize three practical lessons from business ethics research. 5. Identify and describe at least four of the ten general ethical principles. 6. Discuss what management can do to improve business ethics Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2
 Social Responsibility: Definition and Debate • Corporate Social Responsibility – The idea that business has social obligations above and beyond making a profit. – Business has an obligation to constituent groups in society other than stockholders and beyond that prescribed by law. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 3
Social Responsibility: Definition and Debate • Corporate Social Responsibility – The idea that business has social obligations above and beyond making a profit. – Business has an obligation to constituent groups in society other than stockholders and beyond that prescribed by law. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 3
 Social Responsibility: Definition and Debate (cont’d) • What Does Social Responsibility Involve? – Voluntary action – Action before lawsuits or other actions that are taken to force a firm to take action on a matter. – An emphasis on means, not ends – How the decision to act was reached, not the decision itself. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 4
Social Responsibility: Definition and Debate (cont’d) • What Does Social Responsibility Involve? – Voluntary action – Action before lawsuits or other actions that are taken to force a firm to take action on a matter. – An emphasis on means, not ends – How the decision to act was reached, not the decision itself. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 4
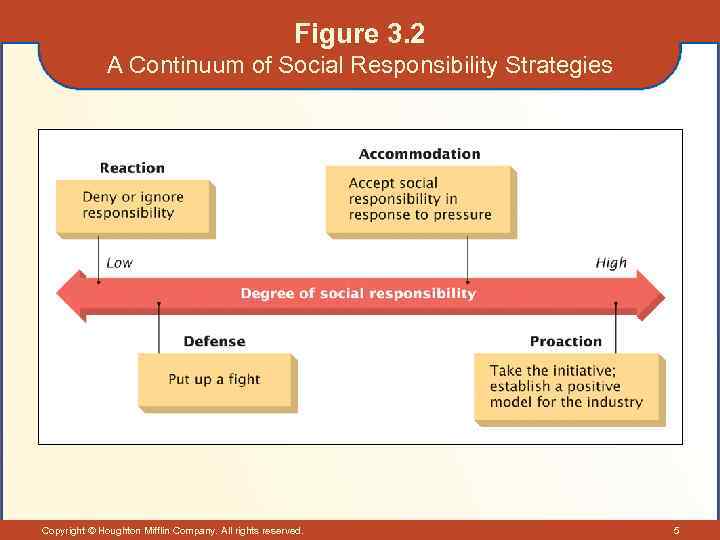 Figure 3. 2 A Continuum of Social Responsibility Strategies Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 5
Figure 3. 2 A Continuum of Social Responsibility Strategies Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 5
 Social Responsibility Strategies • Reactive Strategy – Denying responsibility while striving to maintain the status quo by resisting change. • Defensive Strategy – Resisting additional social responsibilities with legal and public relations tactics. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 6
Social Responsibility Strategies • Reactive Strategy – Denying responsibility while striving to maintain the status quo by resisting change. • Defensive Strategy – Resisting additional social responsibilities with legal and public relations tactics. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 6
 Social Responsibility Strategies (cont’d) • Accommodation Strategy – Assuming social responsibility only in response to pressure from interest groups or the government. • Proactive Strategy – Taking the initiative in formulating and putting in place new programs that serve as role models for industry. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7
Social Responsibility Strategies (cont’d) • Accommodation Strategy – Assuming social responsibility only in response to pressure from interest groups or the government. • Proactive Strategy – Taking the initiative in formulating and putting in place new programs that serve as role models for industry. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7
 Who Benefits from Corporate Social Responsibility? • Altruism – The unselfish devotion to the interests of others. • Research Findings – There is a positive correlation between industry leadership on a socially responsible issue (pollution control) and profitability. – Corporate social responsibility is a competitive advantage in recruiting talented people. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 8
Who Benefits from Corporate Social Responsibility? • Altruism – The unselfish devotion to the interests of others. • Research Findings – There is a positive correlation between industry leadership on a socially responsible issue (pollution control) and profitability. – Corporate social responsibility is a competitive advantage in recruiting talented people. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 8
 Who Benefits from Corporate Social Responsibility? (cont’d) • Enlightened Self-Interest – A business ultimately helps itself by helping solve social problems. • An Array of Benefits for the Organization – – – Tax-free incentives to employees. Retention of talented employees. Help in recruiting the talented and socially conscious. Help in swaying public opinion. Improved community living standards. …Others. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9
Who Benefits from Corporate Social Responsibility? (cont’d) • Enlightened Self-Interest – A business ultimately helps itself by helping solve social problems. • An Array of Benefits for the Organization – – – Tax-free incentives to employees. Retention of talented employees. Help in recruiting the talented and socially conscious. Help in swaying public opinion. Improved community living standards. …Others. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9
 The Ethical Dimension of Management • Ethics – The study of moral obligation involving the distinction between right and wrong. • Business Ethics – The study of the complex business practices and behaviors that give rise to ethical issues in organizations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 10
The Ethical Dimension of Management • Ethics – The study of moral obligation involving the distinction between right and wrong. • Business Ethics – The study of the complex business practices and behaviors that give rise to ethical issues in organizations. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 10
 Practical Lessons from Business Ethics Research: Ethical Hot Spots • Balancing work and family • Poor internal communications • Need to meet sales, budget, or profit goals • Poor leadership • Little or no recognition of achievements • Work hours, work load • Company politics • Lack of management support • Personal financial worries Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. • Insufficient resources 11
Practical Lessons from Business Ethics Research: Ethical Hot Spots • Balancing work and family • Poor internal communications • Need to meet sales, budget, or profit goals • Poor leadership • Little or no recognition of achievements • Work hours, work load • Company politics • Lack of management support • Personal financial worries Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. • Insufficient resources 11
 Practical Lessons from Business Ethics Research (cont’d) • Pressure from Above – The problem of superiors pressuring subordinates is widespread. • Responding to Pressure from Above – Consciously avoid putting undue pressure on subordinates. – Be prepared to deal with excessive organization pressure. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 12
Practical Lessons from Business Ethics Research (cont’d) • Pressure from Above – The problem of superiors pressuring subordinates is widespread. • Responding to Pressure from Above – Consciously avoid putting undue pressure on subordinates. – Be prepared to deal with excessive organization pressure. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 12
 Practical Lessons from Business Ethics Research (cont’d) • Ambiguous Situations – Situations where there are no clear-cut ethical guidelines. – Ethical codes can help satisfy employees’ need formal guidelines. • A Call to Action – The deliberate and conscious actions of a manager to do the right thing is an ethical and personal matter. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 13
Practical Lessons from Business Ethics Research (cont’d) • Ambiguous Situations – Situations where there are no clear-cut ethical guidelines. – Ethical codes can help satisfy employees’ need formal guidelines. • A Call to Action – The deliberate and conscious actions of a manager to do the right thing is an ethical and personal matter. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 13
 General Ethical Principles • Self-Interests • Universal rules • Personal virtues • Individual rights • Religious injunctions • Economic efficiency • Government requirements • Distributive justice • Utilitarian benefits • Contributive justice Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 14
General Ethical Principles • Self-Interests • Universal rules • Personal virtues • Individual rights • Religious injunctions • Economic efficiency • Government requirements • Distributive justice • Utilitarian benefits • Contributive justice Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 14
 Encouraging Ethical Conduct • Ethics Training – Amoral managers: managers who are neither moral or immoral, but ethically lazy. – Key features of effective ethics training programs – Top management support. – Open discussion. – A clear focus on ethical issues. – Integration of ethics into the organization. – A mechanism for anonymously reporting ethical violations. – Reward ethical conduct. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 15
Encouraging Ethical Conduct • Ethics Training – Amoral managers: managers who are neither moral or immoral, but ethically lazy. – Key features of effective ethics training programs – Top management support. – Open discussion. – A clear focus on ethical issues. – Integration of ethics into the organization. – A mechanism for anonymously reporting ethical violations. – Reward ethical conduct. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 15
 Encouraging Ethical Conduct (cont’d) • Whistle-Blowing – The reporting of perceived unethical matters. – Reducing the fear of retaliation against whistleblowers – Anonymous hotlines and web sites – Personal, confidential guidance • Ethical Advocate – An ethics specialist who plays a role of critical questioner in top-management’s decision-making. – Serves as the Board of directors’ social conscience. – Helps prevent groupthink and blind conformity Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 16
Encouraging Ethical Conduct (cont’d) • Whistle-Blowing – The reporting of perceived unethical matters. – Reducing the fear of retaliation against whistleblowers – Anonymous hotlines and web sites – Personal, confidential guidance • Ethical Advocate – An ethics specialist who plays a role of critical questioner in top-management’s decision-making. – Serves as the Board of directors’ social conscience. – Helps prevent groupthink and blind conformity Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 16
 Encouraging Ethical Conduct (cont’d) • Code of Ethics – Published statement of moral expectations for employee conduct – Requirements for an effective ethics code – Must describe specific practices as unethical (e. g. , kickbacks, payoffs, gifts, falsification of records, and misleading product claims). – Must be firmly supported and fairly enforced by top management. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 17
Encouraging Ethical Conduct (cont’d) • Code of Ethics – Published statement of moral expectations for employee conduct – Requirements for an effective ethics code – Must describe specific practices as unethical (e. g. , kickbacks, payoffs, gifts, falsification of records, and misleading product claims). – Must be firmly supported and fairly enforced by top management. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 17


