 Chapter 3 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java 1
Chapter 3 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java 1
 Objectives 2
Objectives 2
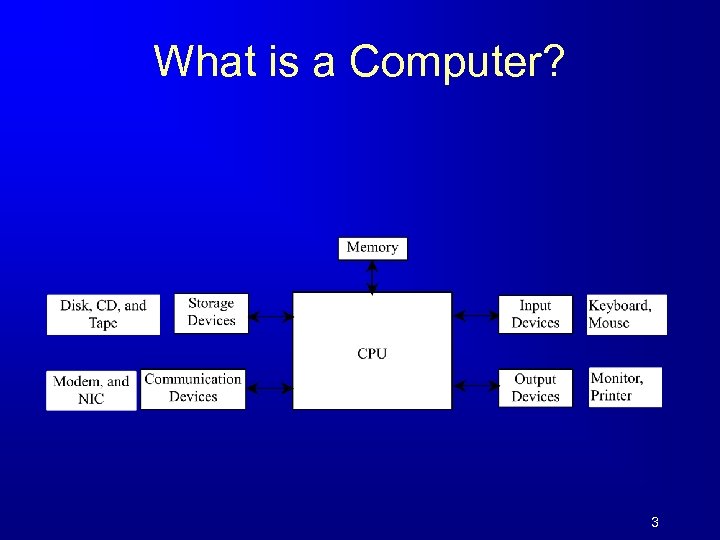 What is a Computer? 3
What is a Computer? 3
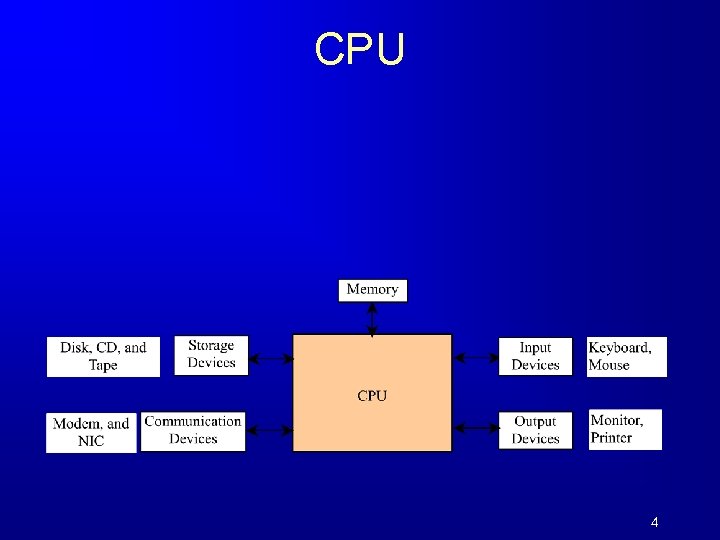 CPU 4
CPU 4
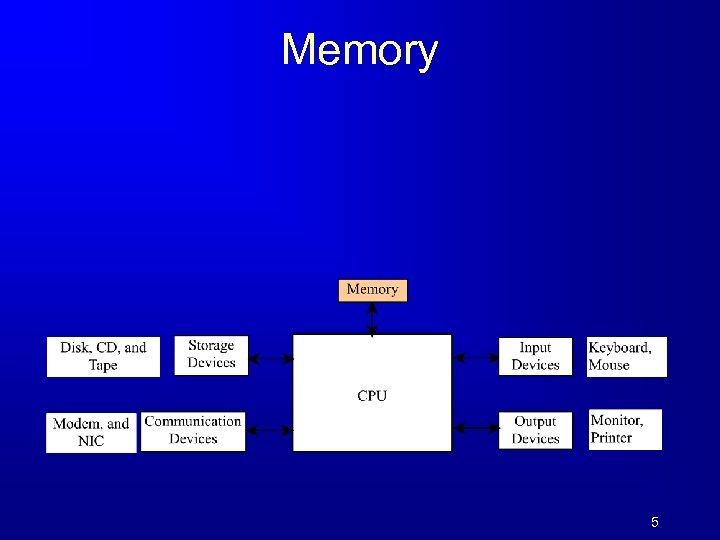 Memory 5
Memory 5
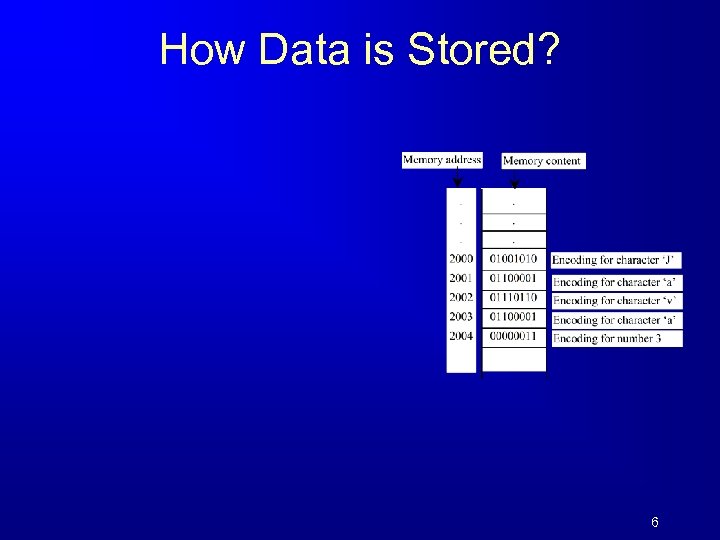 How Data is Stored? 6
How Data is Stored? 6
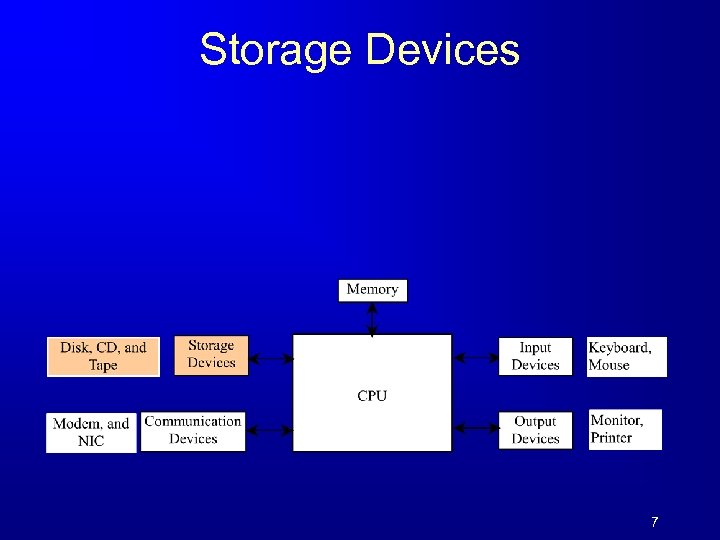 Storage Devices 7
Storage Devices 7
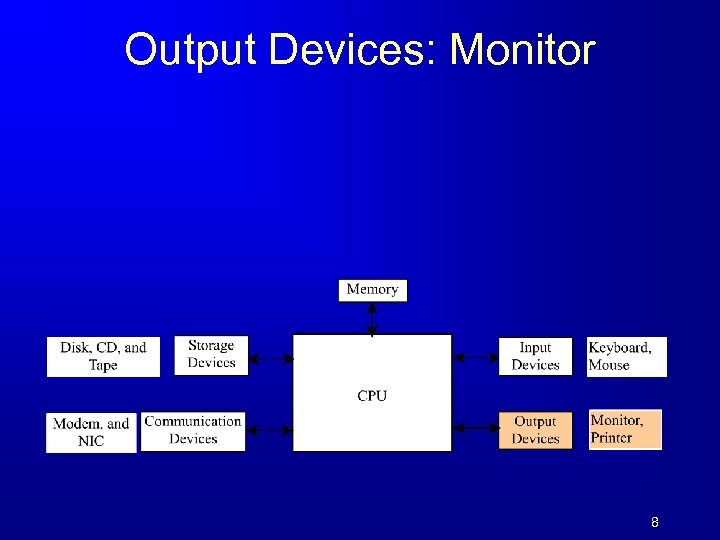 Output Devices: Monitor 8
Output Devices: Monitor 8
 Monitor Resolution and Dot Pitch 9
Monitor Resolution and Dot Pitch 9
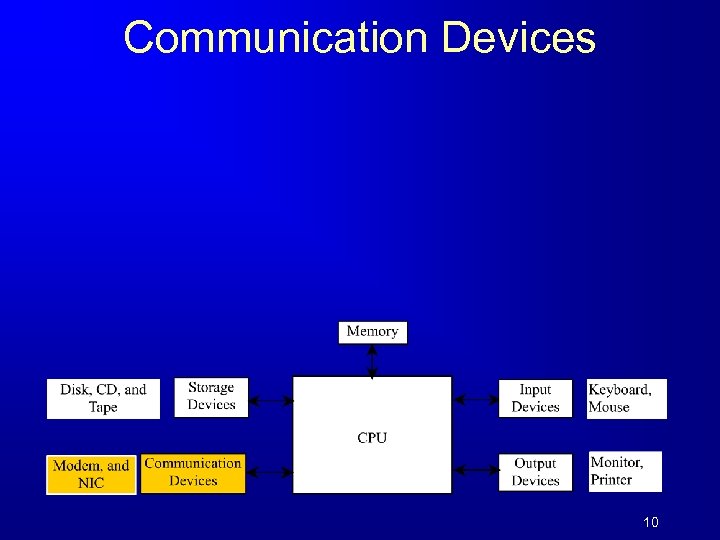 Communication Devices 10
Communication Devices 10
 Programs 11
Programs 11
 Programming Languages 12
Programming Languages 12
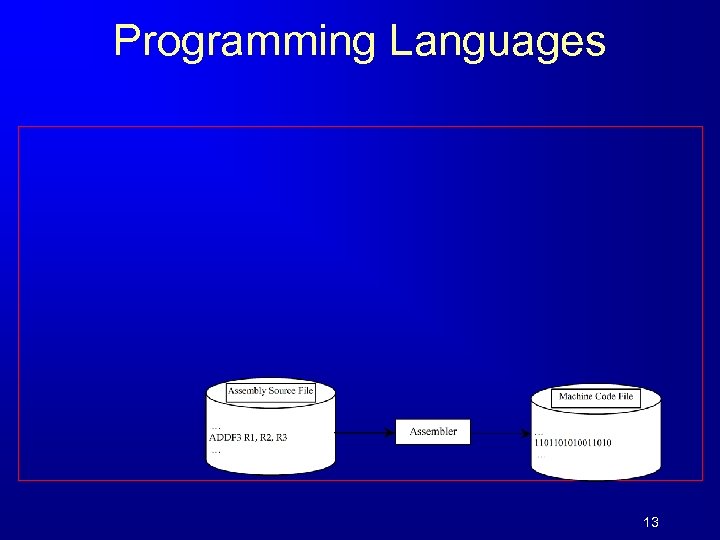 Programming Languages 13
Programming Languages 13
 Programming Languages 14
Programming Languages 14
 Popular High-Level Languages 15
Popular High-Level Languages 15
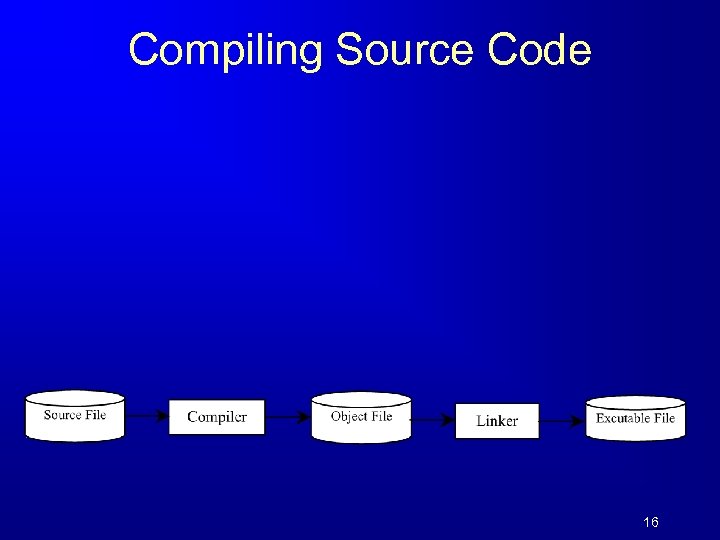 Compiling Source Code 16
Compiling Source Code 16
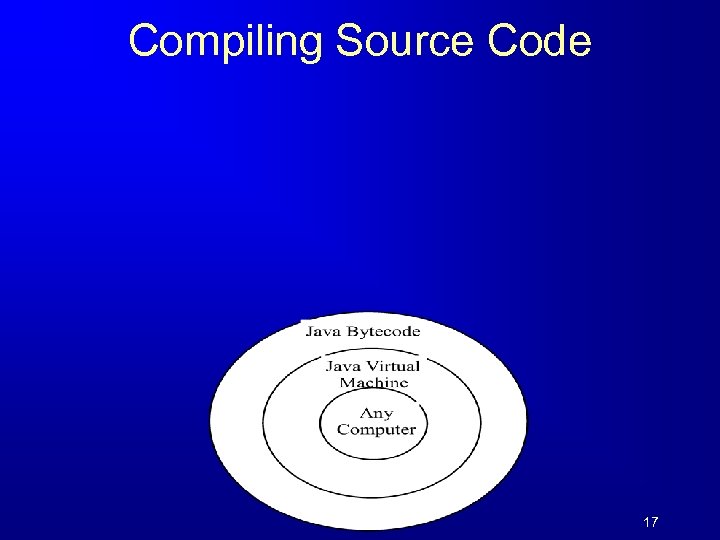 Compiling Source Code 17
Compiling Source Code 17
 Operating Systems 18
Operating Systems 18
 Number Systems 19
Number Systems 19
 Number Systems 20
Number Systems 20
 Number Systems, cont. 21
Number Systems, cont. 21
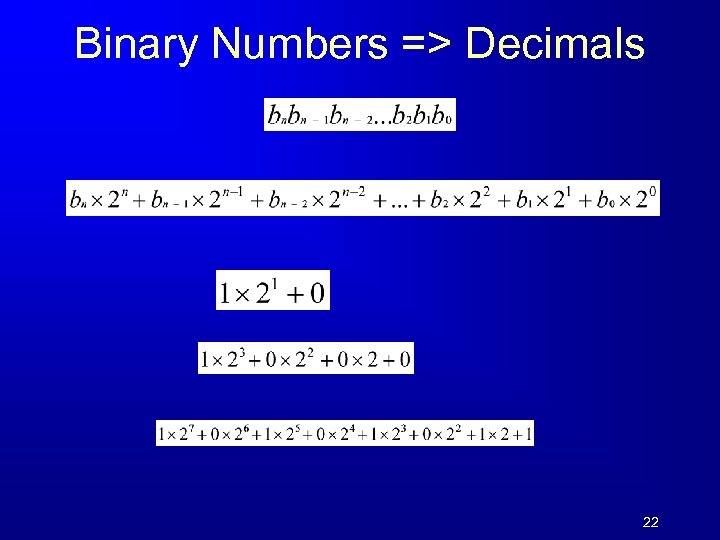 Binary Numbers => Decimals 22
Binary Numbers => Decimals 22
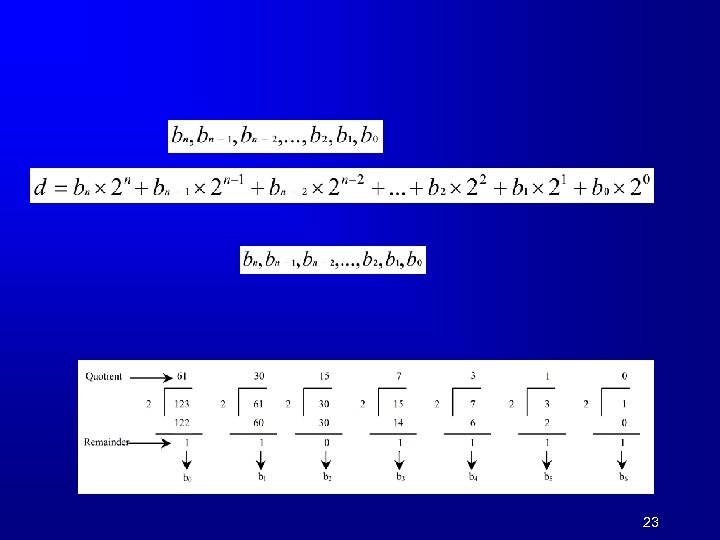 23
23
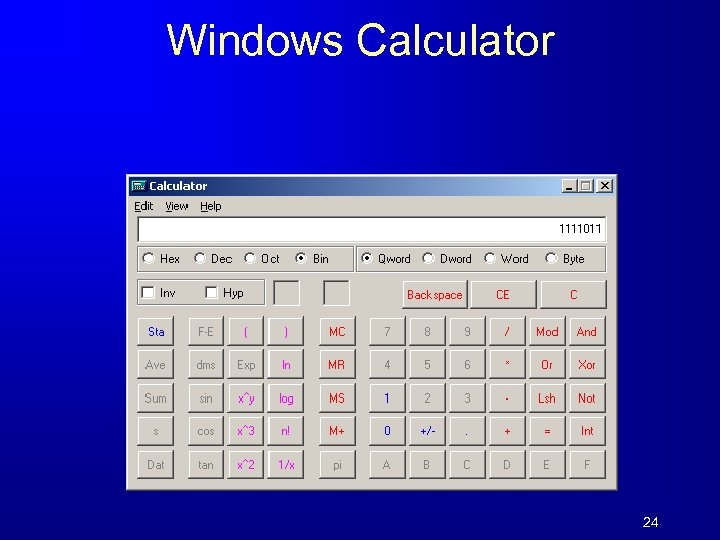 Windows Calculator 24
Windows Calculator 24
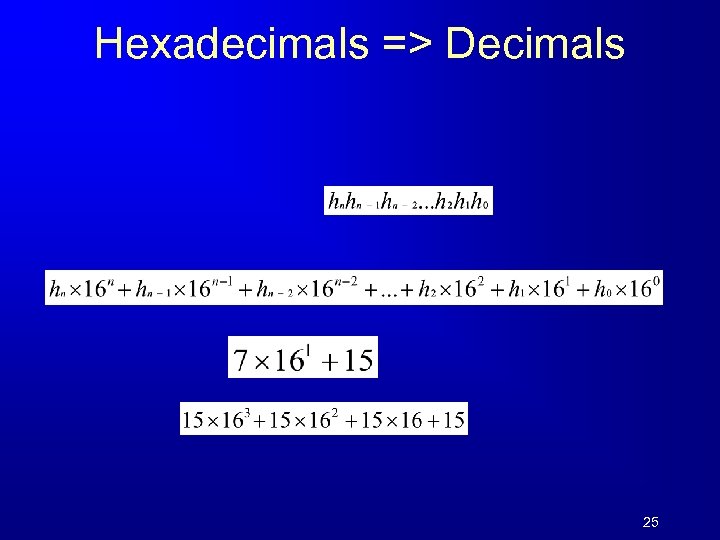 Hexadecimals => Decimals 25
Hexadecimals => Decimals 25
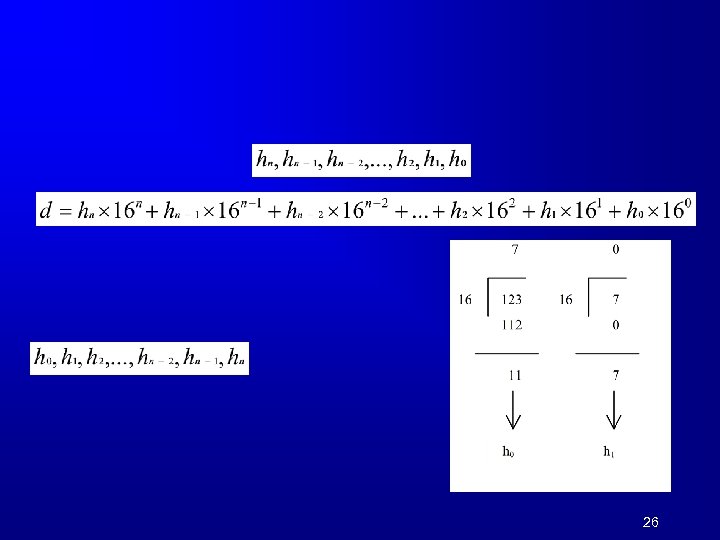 26
26
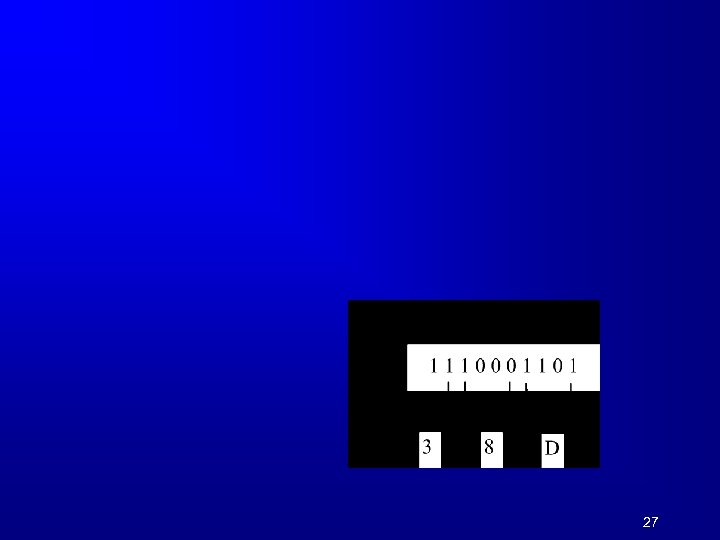 27
27
 28
28
 29
29
 30
30
 31
31
 32
32
 Java’s History 33
Java’s History 33
 Characteristics of Java 34
Characteristics of Java 34
 Characteristics of Java 35
Characteristics of Java 35
 Characteristics of Java 36
Characteristics of Java 36
 Characteristics of Java 37
Characteristics of Java 37
 Characteristics of Java 38
Characteristics of Java 38
 Characteristics of Java 39
Characteristics of Java 39
 Characteristics of Java 40
Characteristics of Java 40
 Characteristics of Java 41
Characteristics of Java 41
 Characteristics of Java 42
Characteristics of Java 42
 Characteristics of Java 43
Characteristics of Java 43
 Characteristics of Java 44
Characteristics of Java 44
 Characteristics of Java 45
Characteristics of Java 45
 46
46
 JDK Versions 47
JDK Versions 47
 JDK Editions 48
JDK Editions 48
 Java IDE Tools 49
Java IDE Tools 49
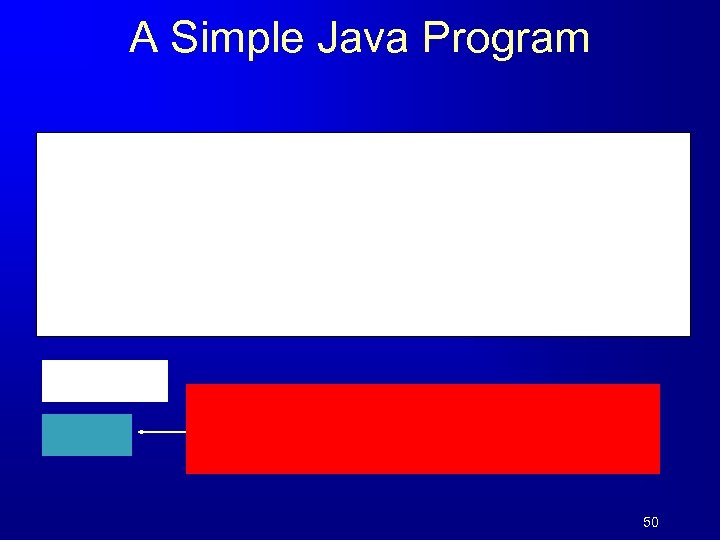 A Simple Java Program 50
A Simple Java Program 50
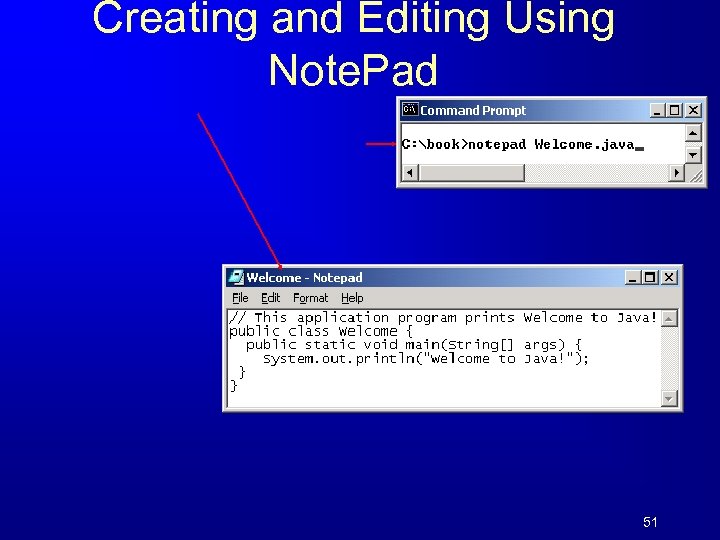 Creating and Editing Using Note. Pad 51
Creating and Editing Using Note. Pad 51
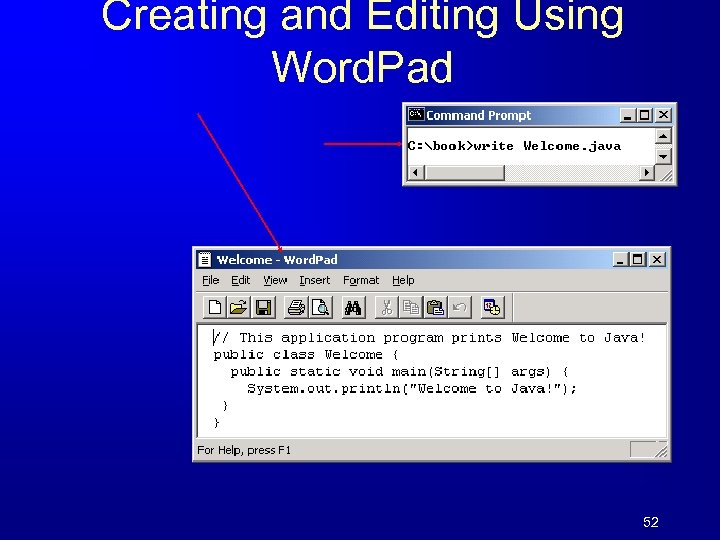 Creating and Editing Using Word. Pad 52
Creating and Editing Using Word. Pad 52
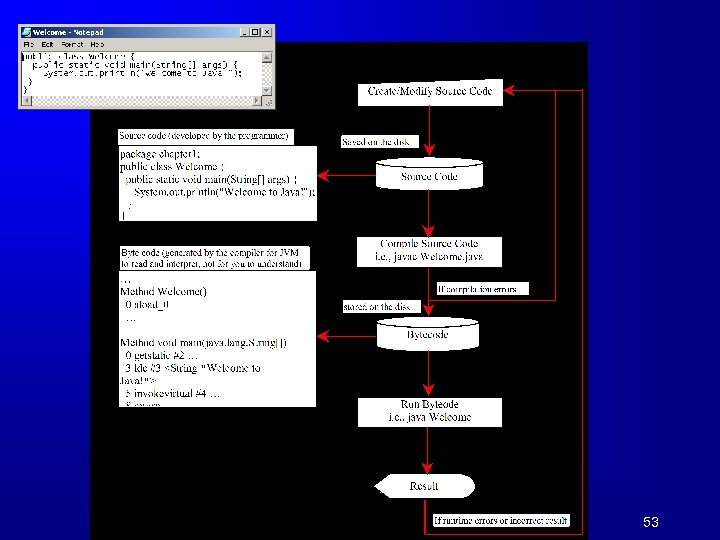 53
53
 Supplements on the Companion Website 54
Supplements on the Companion Website 54
 Compiling and Running Java from the Command Window 55
Compiling and Running Java from the Command Window 55
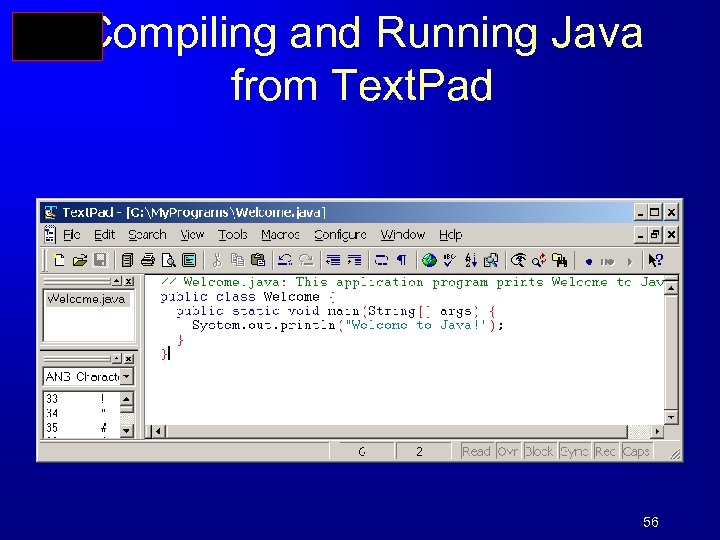 Compiling and Running Java from Text. Pad 56
Compiling and Running Java from Text. Pad 56
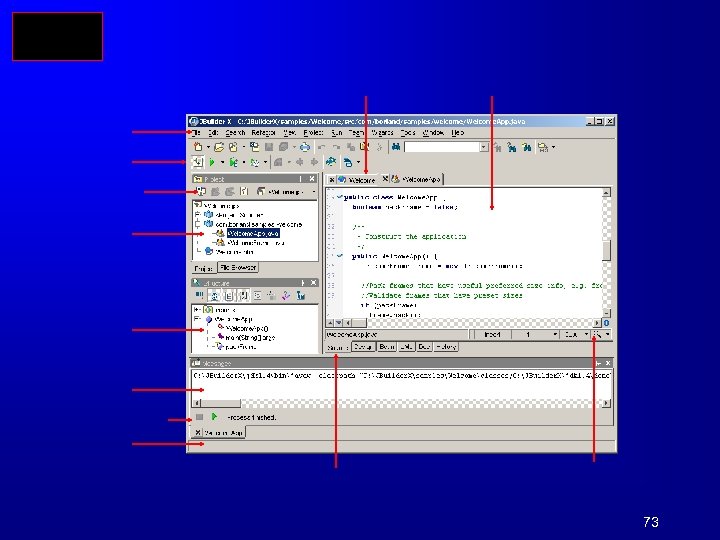
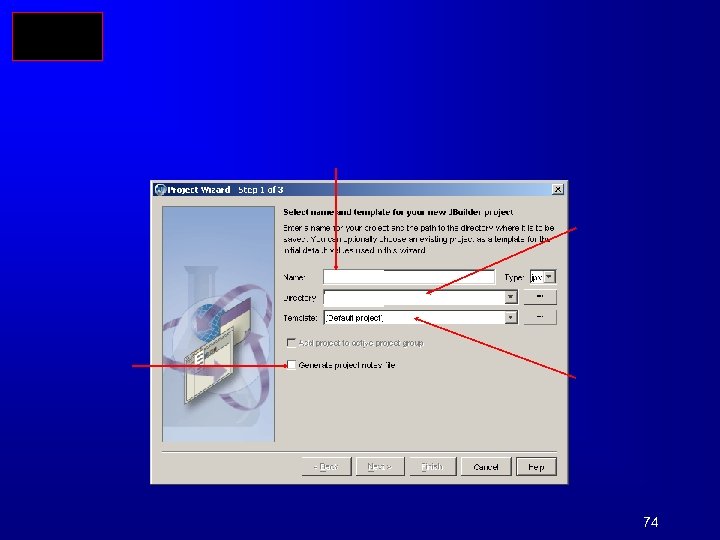
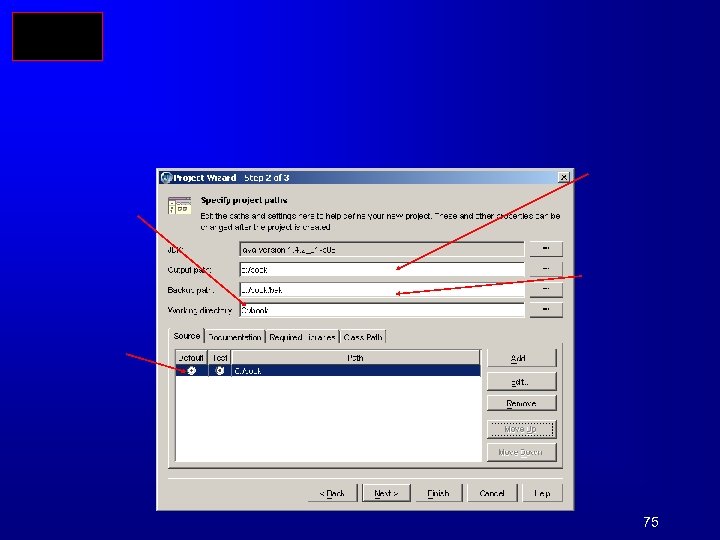
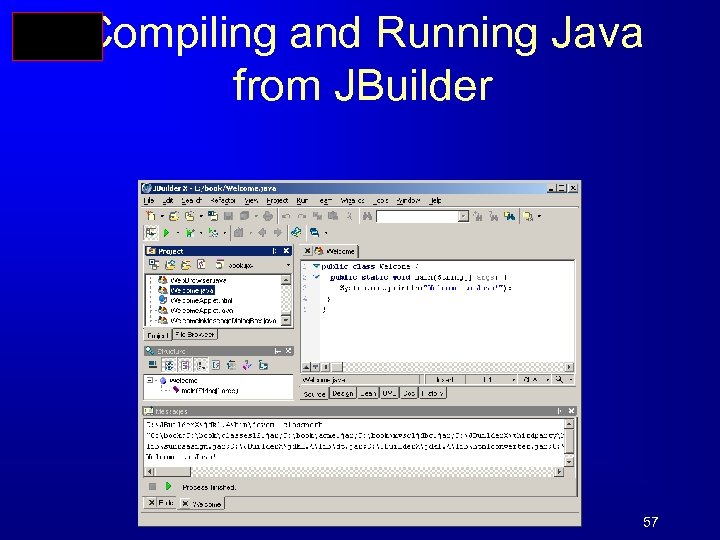 Compiling and Running Java from JBuilder 57
Compiling and Running Java from JBuilder 57
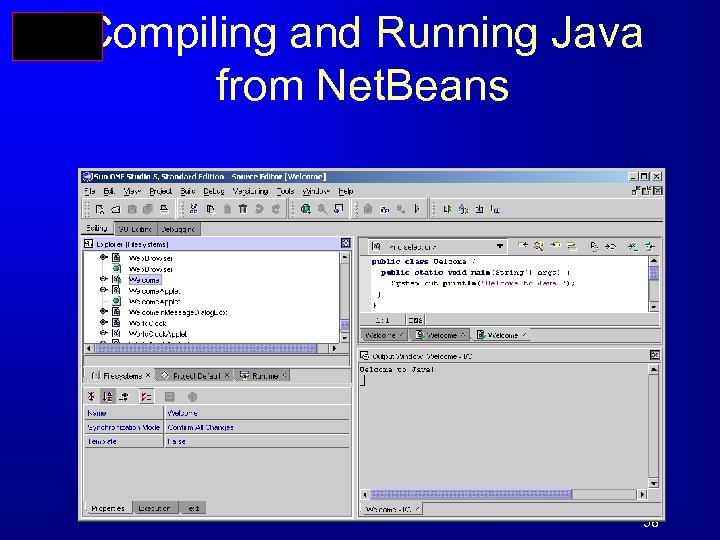 Compiling and Running Java from Net. Beans 58
Compiling and Running Java from Net. Beans 58
 Anatomy of a Java Program 59
Anatomy of a Java Program 59
 Comments 60
Comments 60
 Package 61
Package 61
 Reserved Words 62
Reserved Words 62
 Modifiers 63
Modifiers 63
 Statements 64
Statements 64
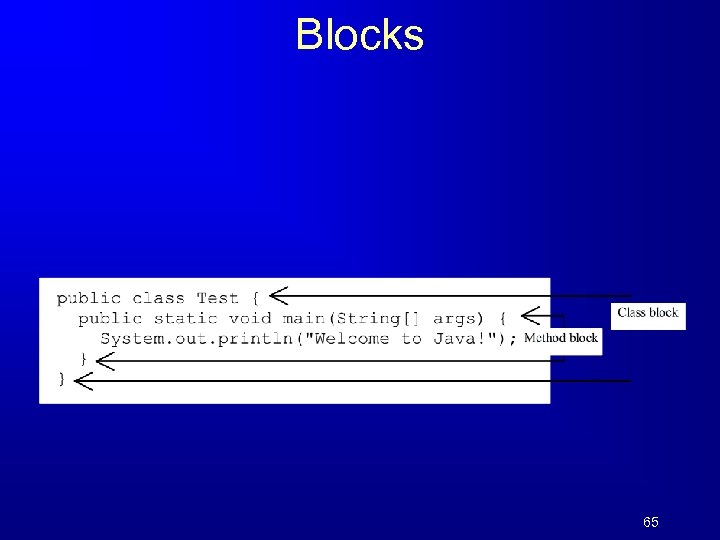 Blocks 65
Blocks 65
 Classes 66
Classes 66
 Methods 67
Methods 67
 main Method 68
main Method 68
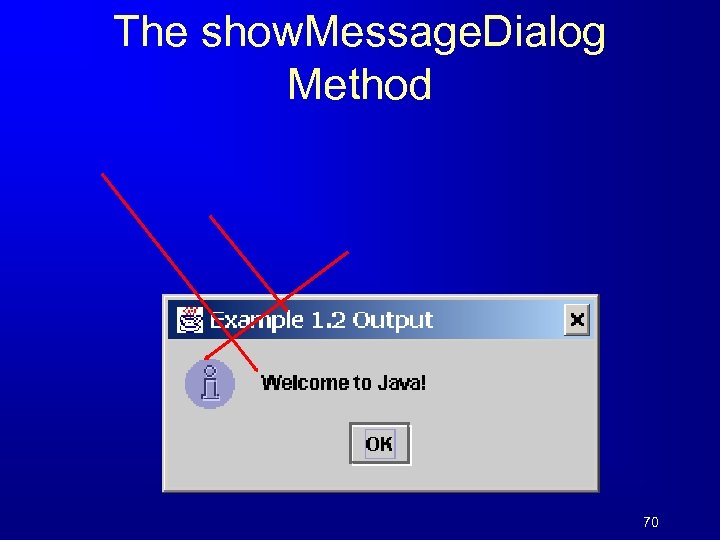
 Displaying Text in a Message Dialog Box 69
Displaying Text in a Message Dialog Box 69
 The show. Message. Dialog Method 70
The show. Message. Dialog Method 70
 Two Ways to Invoke the Method 71
Two Ways to Invoke the Method 71
 The exit Method 72
The exit Method 72
 73
73
 74
74
 75
75
 76
76
 77
77