f3b79686e1b37b582d64c0c0da303a28.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43

Chapter 3 Information Systems in Business Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 1

Learning Objectives • Identify various business functions and the role of ISs in these functions • Explain how ISs in the basic business functions relate to each other • Show ISs of different business functions support each other Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 2

Learning Objectives (Cont. ) • Explain how information technology is used in the most common business functions to make business processes more effective and more efficient • Explain the notion of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems • Identify business areas where information technology facilitates the work of managers and knowledge workers Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 3

Effectiveness and Efficiency • ISs can help companies attain more effective and efficient business processes – Effectiveness • The degree to which a task is accomplished • The degree to which the company achieves outcomes better than the competitors do • “To get the right things done” by Peter F. Drucker – Efficiency • Determined by the relationship between resources expended and benefits gained in achieving a goal • To do the things right Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 4

Effectiveness and Efficiency (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 5

Effectiveness and Efficiency (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 6

Accounting • AISs automatically post transactions in the books and automate generation of reports for management and legal requirements • Three types of AISs – Transaction processing systems (TPS) – Cost accounting systems – Managerial accounting systems Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 7

Accounting (Cont. ) • Electronic Data Processing (EDP) Audits – Ensure electronic systems comply with standard regulations and acceptable rules – Ensure systems cannot be manipulated to circumvent acceptable principles – To be an EDP auditor ($) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 8
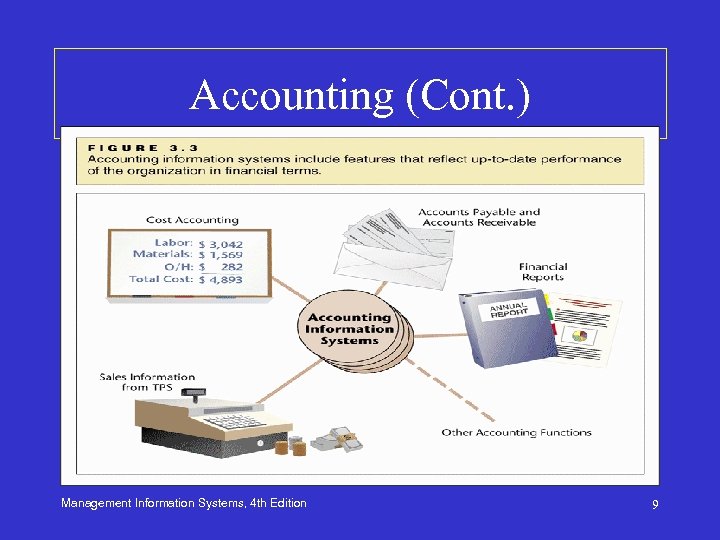
Accounting (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 9

Finance • The job of financial managers is to manage money as efficiently as possible by: – Collecting payables as soon as possible – Making payments by the latest time allowed by contract or law – Ensuring sufficient funds are available for day-today operations – Taking advantage of opportunities to accrue the highest yield on funds not used for current activities Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 10
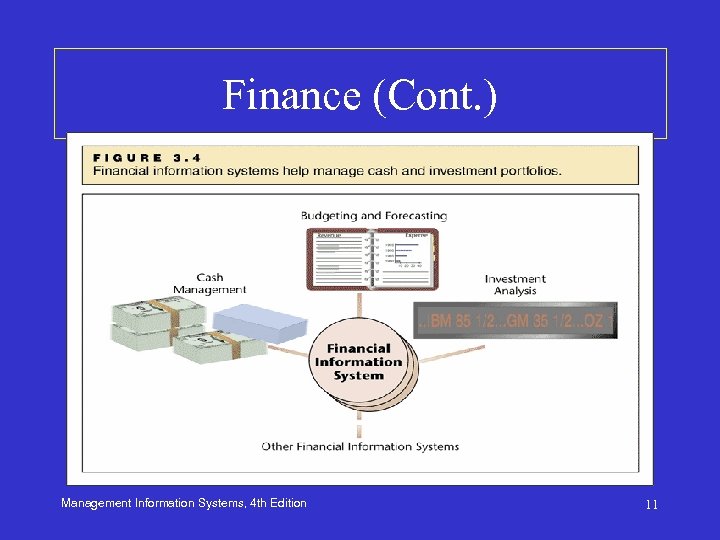
Finance (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 11

Cash Management • Financial ISs help balance the need to accrue interest against the need to have cash available • Cash management systems (CMS): – Handle cash transactions specifically • Electronic fund transfer (EFT): – Electronic transfer of cash from one bank account to another Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 12

Investment Analysis and Service • Analyze and project prices of a specific stock or bond in real time • Transmit buy and sell orders electronically • Provide clients with a detailed statement • Monitor account information and news online Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 13
Engineering • ISs reduce engineering lead time or time to market – Key to maintaining a competitive edge – Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Systems • Help engineers and technicians design new products and quickly modify and store drawings electronically – Rapid Prototyping: • Creating one-of-a-kind products to test design in three dimensions • Concurrent engineering and communication through Internet • Product Data Management (PDM) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 14
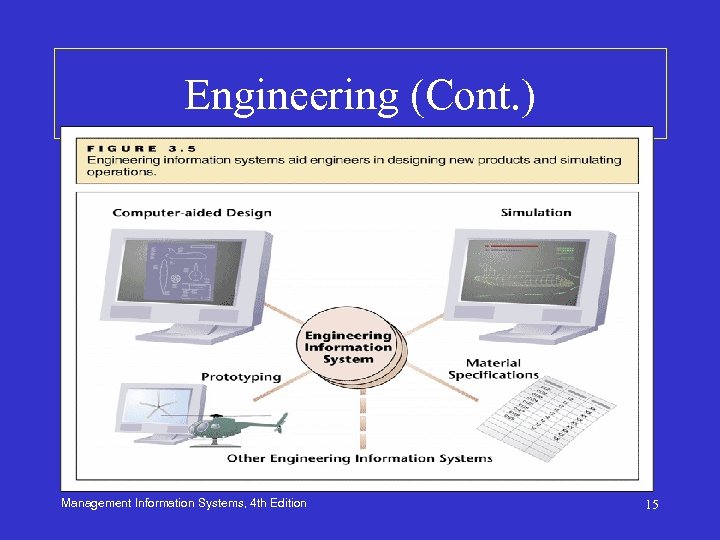
Engineering (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 15

Manufacturing & Inventory Control • IT helps in these manufacturing activities: – Plant activity scheduling – Material Requirement Planning/assessment – Material reallocation between orders – Dynamic inventory management – Grouping work orders by “characteristics” – Resource qualification for task completion Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 16
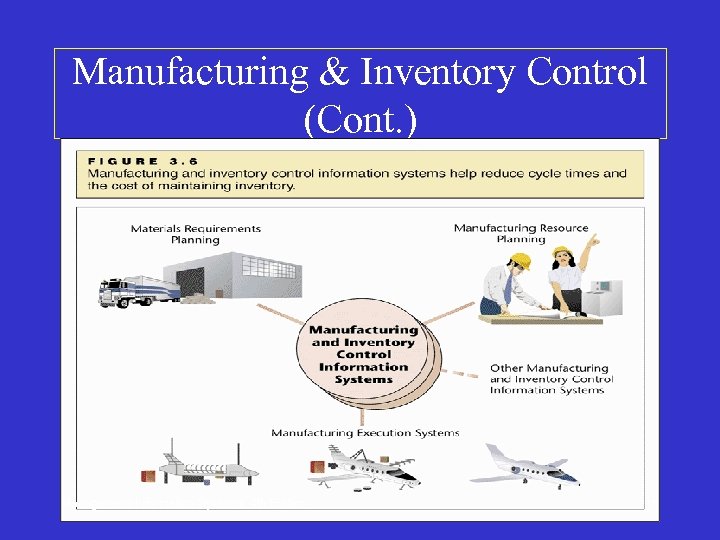
Manufacturing & Inventory Control (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 17

Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) • Take customer demand as initial input – Deployment according to the bill of materials (BOM) – Number of product units needed and when they are needed (Main Production Scheduling) • Use long-range forecasts to put long-lead material on order • Help reduce inventory cost while ensuring availability – EOQ inventory under a specific lead time and a consumption rate Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 18
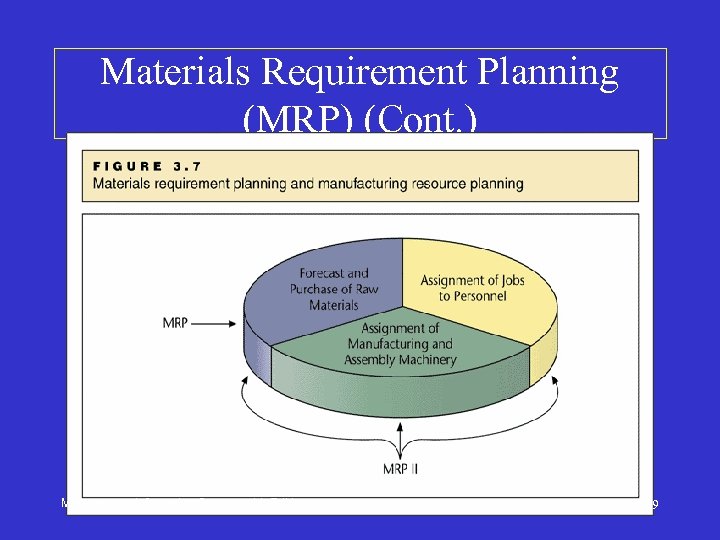
Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 19

Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) • Combines MRP with other manufacturing-related activities to plan the manufacturing process such as: – Shop activity control and purchasing – Source of demand – Customer order entry and forecasting • MPS (master production scheduling) – Support functions such as financial management, sales analysis, and data collection Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 20
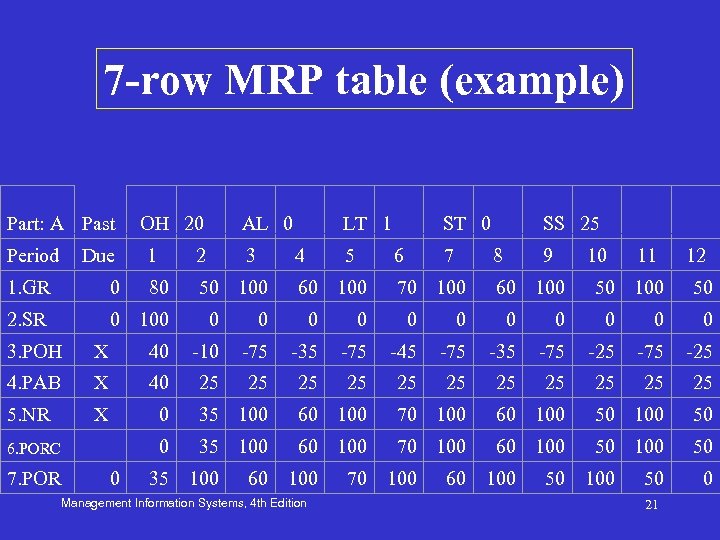
7 -row MRP table (example) Part: A Past Period Due OH 20 AL 0 1 2 3 80 50 100 LT 1 4 5 ST 0 6 60 100 7 SS 25 8 70 100 9 10 60 100 11 50 100 12 1. GR 0 50 2. SR 0 100 0 0 3. POH X 40 -10 -75 -35 -75 -45 -75 -35 -75 -25 4. PAB X 40 25 25 25 5. NR X 0 35 100 60 100 70 100 60 100 50 6. PORC 7. POR 0 35 100 60 100 Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 70 100 60 100 50 21 0

The algorithm of MRP • • Procedure MRP; 單階BOM 展開 MPS 之PORt, 加入其子件成為其GRt LLC 1; While MPS 有未被處理項 Do – While BOM中 LLC 有任一項未被處理 Do • PAB 0 OH-AL+max(SR 0, 0); • For t=1 to T Do – IF t=1 then POH 1 PAB 0+SR 1 -GR 1 -max(GR 0, 0) » Else POHt PABt-1+SRt-GRt; – Endif – IF POHt<SS then NRt SS-POHt, PORCt=max(NRt, LS); » Else NRt 0, PORCt 0; Management Endif – Information Systems, 4 th Edition 22
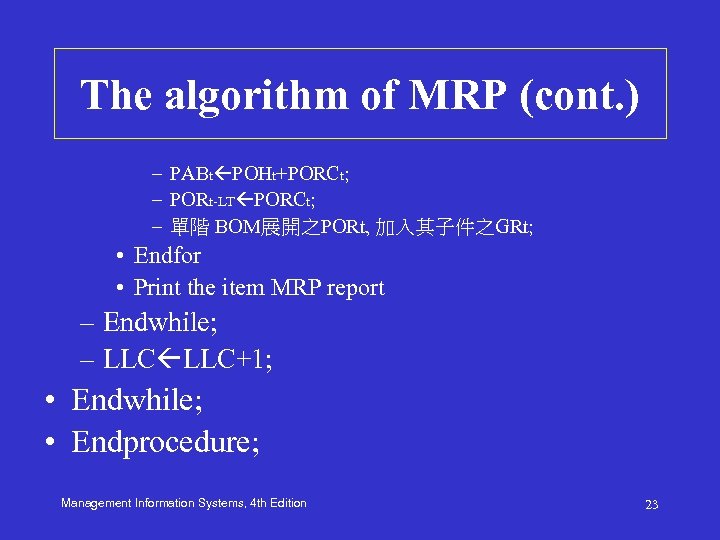
The algorithm of MRP (cont. ) – PABt POHt+PORCt; – PORt-LT PORCt; – 單階 BOM展開之PORt, 加入其子件之GRt; • Endfor • Print the item MRP report – Endwhile; – LLC+1; • Endwhile; • Endprocedure; Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 23

Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) • Track, schedule, and control manufacturing processes • Collect data such as: – Hours machine operates every day of the month – Hours the machine is idle and why – Optimization, rationalization Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 24

Monitoring and Control • Supply chain management (SCM) – Managers know status of product during manufacturing – Recent IS control/adjustment as well as monitor manufacturing process – System at Ford Motor Company designed to ensure no assemble steps are missed Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 25

Marketing, Sales, & Customer Service • Market Research – Statistical (data mining) models help market researchers find the best populations for new and existing products • Targeted Marketing – Database management systems (DBMS) help define potential customers as narrowly as possible Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 26
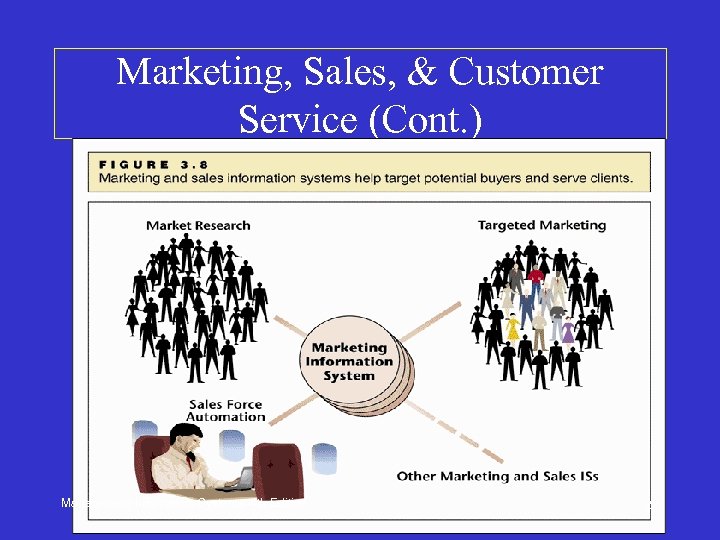
Marketing, Sales, & Customer Service (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 27

Marketing, Sales, & Customer Service (Cont. ) • The Internet as a Marketing and Selling Medium – Web lets companies reach more shoppers and serve them better – Mobile Commerce (M-Commerce) is the newest form of marketing • Location-based, timely, impulse-purchasing, killing-time info-tainment – Commercial announcements/Internet advertisements pervade the Web • Annoying but effective Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 28

Sales Force Automation • Equipping salespeople with information technology to facilitate productivity – IT allows salespeople to present different options for products and services on the spot – Instantly mobile dispatching Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 29

Customer Relationship Management • Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software for companies to better serve and know customer needs – Track past purchase and payments – Update online answers to frequently asked questions (FAQs) – Analyze customer’s contact with company • Web-based Customer Service available 24/7/365 Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 30

Human Resources Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 31

Human Resources (Cont. ) • Employee Record Management – Reduce space needed to store records, time to retrieve them, and costs of both • Promotion and Recruitment – Search databases for qualified personnel – Use intranet to post job vacancies – Use the Web to recruit Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 32

Human Resources (Cont. ) • Training – Multimedia software training is replacing classrooms and teachers – Training software simulates an actual task or situation and includes evaluation tools • Evaluation – Evaluation software helps standardize the evaluation process and adds a certain measure of objectivity and consistency (MBO) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 33

Human Resources (Cont. ) • Compensation and Benefits Management – ISs can help manage compensation efficiently and effectively • Calculate salaries, hourly pay, commissions, and taxes • Automatically generate paychecks or direct deposits – Special software helps manage benefits, such as health insurance, life insurance, retirement plans, and sick and leave days Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 34

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) • All business functions served by one system that supports different activities for internal different departments • Support the external-oriented material/information flow of supply chain management upward and downward, the series of main and supporting activities from order to delivery Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 35
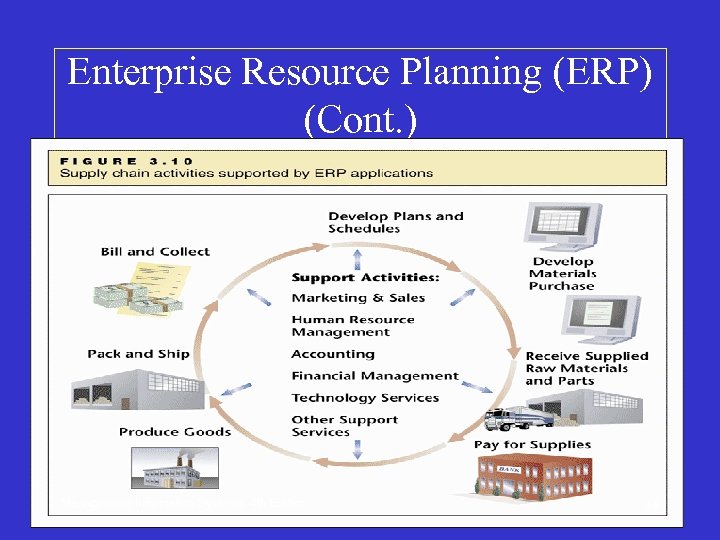
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) (Cont. ) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 36

Groupware and Collaborative Work • Group. Ware lets workers in different locations communicate ideas, brainstorm, and work together as if they were in the same place, esp. , the engineering task • Document Control – Users can distribute and track electronic documents without working with outdated information – PDM • Collaborative Projects – Users can coordinate work on a single document from many different terminals – Collaborative Production Commerce (CPC) Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 37

Ethical and Societal Issues Privacy? What Privacy? • What is Privacy? – One’s right to control information about oneself – Not a constitutional right per se; secured by laws or convention – Increasing number of organizations may access information via better IT hardware and software – Business and civil rights advocates dispute degree of privacy vs. utility of information access Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 38

Ethical and Societal Issues Privacy? What Privacy? • Business Arguments – Necessary to collect basic financial and personal information as cheaply as possible – Consumers benefit eventually from competitive environment augmented by readily available information – Customization possibility Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 39

Ethical and Societal Issues Privacy? What Privacy? • Consumer Arguments – Resent unsolicited mail and telephone calls – Resent being refused credit because of credit bureau mistakes – Frightened by “dossier phenomenon” – Loss of control over information unfair—information gathered for a particular purpose with permission should remain restricted Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 40

Ethical and Societal Issues Privacy? What Privacy? • Seven Commandments of Personal Data Collection and Maintenance – Purpose: Companies should inform people who provide information of specific, exclusive purpose – Relevance: Companies should record and use only data necessary to fulfill their own purposes – Accuracy: Companies should ensure that their data are accurate Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 41

Ethical and Societal Issues Privacy? What Privacy? – Currency: Companies should make sure that all data about an individual are current – Security: Companies should limit data access to only those who need to know – Time Limitation: Companies should retain data only for the time period necessary – Scrutiny: Companies should establish procedures to let individuals review their records and correct inaccuracies Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 42

Summary • There are various business functions and ISs have a role in these functions • ISs relate to each other in basic business functions • IT is used in business functions to make business more effective and more efficient • ERP systems help run different functions upon a common platform Management Information Systems, 4 th Edition 43
f3b79686e1b37b582d64c0c0da303a28.ppt