16a575b72276fc0494543c92f92e8997.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chapter 3 Income and Purchasing Power Copyright 2007 Thomson South-Western
Chapter 3 Income and Purchasing Power Copyright 2007 Thomson South-Western
 Inflation • Is an increase in the general level of prices for goods and services • Is measured by the U. S. government using the Consumer Price Index (CPI) • The CPI measures the change in a list of goods and services that are commonly bought by consumers 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 2
Inflation • Is an increase in the general level of prices for goods and services • Is measured by the U. S. government using the Consumer Price Index (CPI) • The CPI measures the change in a list of goods and services that are commonly bought by consumers 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 2
 Types of Inflation • Disinflation – occurs when prices are rising, but at a slow rate. Happens when demand for the product is not the same throughout the year. • Reflation – occurs when prices are high but then drop due to lower demand. Example—large vehicle when gas prices are high. Slide 3
Types of Inflation • Disinflation – occurs when prices are rising, but at a slow rate. Happens when demand for the product is not the same throughout the year. • Reflation – occurs when prices are high but then drop due to lower demand. Example—large vehicle when gas prices are high. Slide 3
 Type of Inflation • Hyperinflation – occurs when prices are rising so rapidly they are out of control. (Usually an inflation rate of 50 percent or higher). Slide 4
Type of Inflation • Hyperinflation – occurs when prices are rising so rapidly they are out of control. (Usually an inflation rate of 50 percent or higher). Slide 4
 Deflation • Is a decrease in the general level of prices for goods and services • Is the opposite of inflation • Happens when – Events cause consumers to buy less – Producers are able and willing to provide goods at lower prices 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 5
Deflation • Is a decrease in the general level of prices for goods and services • Is the opposite of inflation • Happens when – Events cause consumers to buy less – Producers are able and willing to provide goods at lower prices 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 5
 Causes of Inflation • Demand-pull inflation • Cost-push inflation • Real-cost inflation Demand-pull inflation occurs when consumers want to buy more goods than producers supply. 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 6
Causes of Inflation • Demand-pull inflation • Cost-push inflation • Real-cost inflation Demand-pull inflation occurs when consumers want to buy more goods than producers supply. 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 6
 Causes of Inflation • Demand-pull inflation – when consumers want to buy more goods and services than producers supply. • Cost-push inflation – when producers raise prices because their costs to create products are rising. • Real-cost inflation – when prices rise because resources diminish or become hard to get. Slide 7
Causes of Inflation • Demand-pull inflation – when consumers want to buy more goods and services than producers supply. • Cost-push inflation – when producers raise prices because their costs to create products are rising. • Real-cost inflation – when prices rise because resources diminish or become hard to get. Slide 7
 In Times of Inflation • Mild inflation of 2 or 3 percent can be good for the economy • Workers with fixed pay rates may be able to buy less • Consumers must spend more to meet needs and may be able to save or invest less • Times value of money is a dollar received in the future is worth less than a dollar received today 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 8
In Times of Inflation • Mild inflation of 2 or 3 percent can be good for the economy • Workers with fixed pay rates may be able to buy less • Consumers must spend more to meet needs and may be able to save or invest less • Times value of money is a dollar received in the future is worth less than a dollar received today 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 8
 Check In #1 1. What is inflation and how is inflation measured? 2. How does disinflation, reflation and hyperinflation differ? 3. What is deflation? 4. How does demand-pull inflation differ from cost-push inflation? 5. How does inflation affect spending, saving, and investing decisions? Slide 9
Check In #1 1. What is inflation and how is inflation measured? 2. How does disinflation, reflation and hyperinflation differ? 3. What is deflation? 4. How does demand-pull inflation differ from cost-push inflation? 5. How does inflation affect spending, saving, and investing decisions? Slide 9
 Ethics A Full Day’s Work for a Full Day’s Pay • Ethical behavior requires workers to provide a full day’s work for a full day’s pay • This behavior can lead to positive job ratings or promotions • Poor work habits can lead to poor job ratings or dismissal 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 10
Ethics A Full Day’s Work for a Full Day’s Pay • Ethical behavior requires workers to provide a full day’s work for a full day’s pay • This behavior can lead to positive job ratings or promotions • Poor work habits can lead to poor job ratings or dismissal 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 10
 The Federal Reserve System • Two tools used to manage the effects of rising prices • Monetary policy is the actions by the Federal Reserve System (the Fed). – Discount rate is rate the banks have to pay to borrow money from the Fed. – Federal funds rate is the rate the banks can borrow from the excess reserves of other banks – Prime rate is the rate banks charge to the most creditworthy customers. 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 11
The Federal Reserve System • Two tools used to manage the effects of rising prices • Monetary policy is the actions by the Federal Reserve System (the Fed). – Discount rate is rate the banks have to pay to borrow money from the Fed. – Federal funds rate is the rate the banks can borrow from the excess reserves of other banks – Prime rate is the rate banks charge to the most creditworthy customers. 3 -1 Inflation and Prices Slide 11
 The Federal Reserve System Fiscal policy refers to actions taken by the federal government to manage the economy. Source: The Federal Reserve Board, Monetary Policy, http: //www. federalreserve. gov/policy. htm (accessed October 17, 2006). Slide 12
The Federal Reserve System Fiscal policy refers to actions taken by the federal government to manage the economy. Source: The Federal Reserve Board, Monetary Policy, http: //www. federalreserve. gov/policy. htm (accessed October 17, 2006). Slide 12
 Setting Prices • Prices are affected by – Producers – Consumers – Market forces • Sellers want to set a price – That will support the greatest demand – That will be profitable 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 13
Setting Prices • Prices are affected by – Producers – Consumers – Market forces • Sellers want to set a price – That will support the greatest demand – That will be profitable 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 13
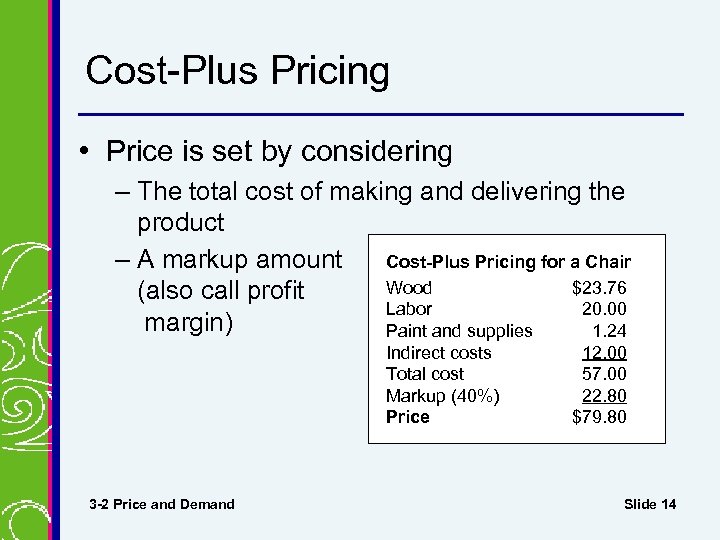 Cost-Plus Pricing • Price is set by considering – The total cost of making and delivering the product Cost-Plus Pricing for a Chair – A markup amount Wood $23. 76 (also call profit Labor 20. 00 margin) Paint and supplies 1. 24 Indirect costs Total cost Markup (40%) Price 3 -2 Price and Demand 12. 00 57. 00 22. 80 $79. 80 Slide 14
Cost-Plus Pricing • Price is set by considering – The total cost of making and delivering the product Cost-Plus Pricing for a Chair – A markup amount Wood $23. 76 (also call profit Labor 20. 00 margin) Paint and supplies 1. 24 Indirect costs Total cost Markup (40%) Price 3 -2 Price and Demand 12. 00 57. 00 22. 80 $79. 80 Slide 14
 Value-Based Pricing • Price is set by considering how much consumers will be willing to pay • Companies often do market research to help in setting prices A mall offers many stores at which to stop for the best prices. 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 15
Value-Based Pricing • Price is set by considering how much consumers will be willing to pay • Companies often do market research to help in setting prices A mall offers many stores at which to stop for the best prices. 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 15
 Market-Based Pricing • Price is set to be competitive with prices of similar products • Companies may set a higher price for products with new features • Unique products that cannot be bought elsewhere may command higher prices 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 16
Market-Based Pricing • Price is set to be competitive with prices of similar products • Companies may set a higher price for products with new features • Unique products that cannot be bought elsewhere may command higher prices 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 16
 Buying Strategies Affect Demand • Economizing – Saving as much as possible – Spending money only when necessary • Optimizing – Getting the highest value for the money spent Taking advantage of sale prices is an example of optimizing. 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 17
Buying Strategies Affect Demand • Economizing – Saving as much as possible – Spending money only when necessary • Optimizing – Getting the highest value for the money spent Taking advantage of sale prices is an example of optimizing. 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 17
 Success Skills Time Management • Using time management strategies can help you be more productive • Scheduling time to plan purchases can help you make better buying decisions This shopper is economizing and following a shopping list. 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 18
Success Skills Time Management • Using time management strategies can help you be more productive • Scheduling time to plan purchases can help you make better buying decisions This shopper is economizing and following a shopping list. 3 -2 Price and Demand Slide 18
 Selling Goods and Services • Sellers use various strategies – Convenience – Customer service – Meeting needs and wants – Creating demand through advertising PR Newswire HOLTON, TEITELMAN AND GURY ADVERTISING 3 -3 Selling and Buying Strategies Slide 19
Selling Goods and Services • Sellers use various strategies – Convenience – Customer service – Meeting needs and wants – Creating demand through advertising PR Newswire HOLTON, TEITELMAN AND GURY ADVERTISING 3 -3 Selling and Buying Strategies Slide 19
 Buying Strategies • Before you shop – Prepare a list of needed items – Decide how much to spend • While you shop – Compare prices – Do not make last-minute purchase decisions • After you buy – Keep receipts and warranties – Inspect the product and evaluate the purchase 3 -3 Selling and Buying Strategies Slide 20
Buying Strategies • Before you shop – Prepare a list of needed items – Decide how much to spend • While you shop – Compare prices – Do not make last-minute purchase decisions • After you buy – Keep receipts and warranties – Inspect the product and evaluate the purchase 3 -3 Selling and Buying Strategies Slide 20
 Check In #2 1. How are prices set when using the cost-plus pricing strategy? 2. How is a market-based pricing strategy different from a value based pricing strategy? 3. What is economizing and how does using this buying strategy affect demand prices in a market economy? 4. What is optimizing and how does using this buying strategy affect demand prices in a market economy? 5. How can using effective time management strategies lead to better buying decisions? Slide 21
Check In #2 1. How are prices set when using the cost-plus pricing strategy? 2. How is a market-based pricing strategy different from a value based pricing strategy? 3. What is economizing and how does using this buying strategy affect demand prices in a market economy? 4. What is optimizing and how does using this buying strategy affect demand prices in a market economy? 5. How can using effective time management strategies lead to better buying decisions? Slide 21


