CH 3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 76
 Chapter 3 - Evaluating a Firm’s Financial Performance 2005, Pearson Prentice Hall
Chapter 3 - Evaluating a Firm’s Financial Performance 2005, Pearson Prentice Hall
 Financial Ratio Analysis § Are our decisions maximizing shareholder wealth?
Financial Ratio Analysis § Are our decisions maximizing shareholder wealth?
 We will want to answer questions about the firm’s § Liquidity § Efficient use of Assets § Leverage (financing) § Profitability
We will want to answer questions about the firm’s § Liquidity § Efficient use of Assets § Leverage (financing) § Profitability
 We will want to answer questions about the firm’s § Liquidity § Efficient use of Assets § Leverage (financing) § Profitability
We will want to answer questions about the firm’s § Liquidity § Efficient use of Assets § Leverage (financing) § Profitability
 Financial Ratios § Tools that help us determine the financial health of a company. § We can compare a company’s financial ratios with its ratios in previous years (trend analysis). § We can compare a company’s financial ratios with those of its industry.
Financial Ratios § Tools that help us determine the financial health of a company. § We can compare a company’s financial ratios with its ratios in previous years (trend analysis). § We can compare a company’s financial ratios with those of its industry.
 Example: Cyber. Dragon Corporation
Example: Cyber. Dragon Corporation
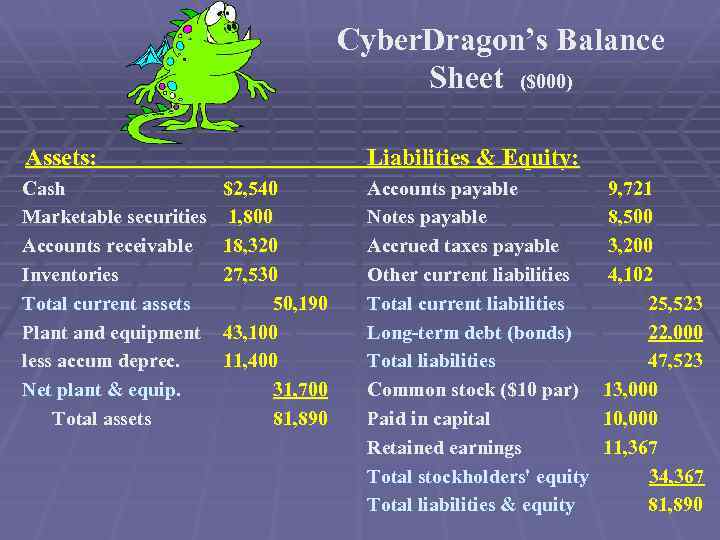 Cyber. Dragon’s Balance Sheet ($000) Assets: Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Plant and equipment less accum deprec. Net plant & equip. Total assets Liabilities & Equity: $2, 540 1, 800 18, 320 27, 530 50, 190 43, 100 11, 400 31, 700 81, 890 Accounts payable Notes payable Accrued taxes payable Other current liabilities Total current liabilities Long-term debt (bonds) Total liabilities Common stock ($10 par) Paid in capital Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities & equity 9, 721 8, 500 3, 200 4, 102 25, 523 22, 000 47, 523 13, 000 10, 000 11, 367 34, 367 81, 890
Cyber. Dragon’s Balance Sheet ($000) Assets: Cash Marketable securities Accounts receivable Inventories Total current assets Plant and equipment less accum deprec. Net plant & equip. Total assets Liabilities & Equity: $2, 540 1, 800 18, 320 27, 530 50, 190 43, 100 11, 400 31, 700 81, 890 Accounts payable Notes payable Accrued taxes payable Other current liabilities Total current liabilities Long-term debt (bonds) Total liabilities Common stock ($10 par) Paid in capital Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities & equity 9, 721 8, 500 3, 200 4, 102 25, 523 22, 000 47, 523 13, 000 10, 000 11, 367 34, 367 81, 890
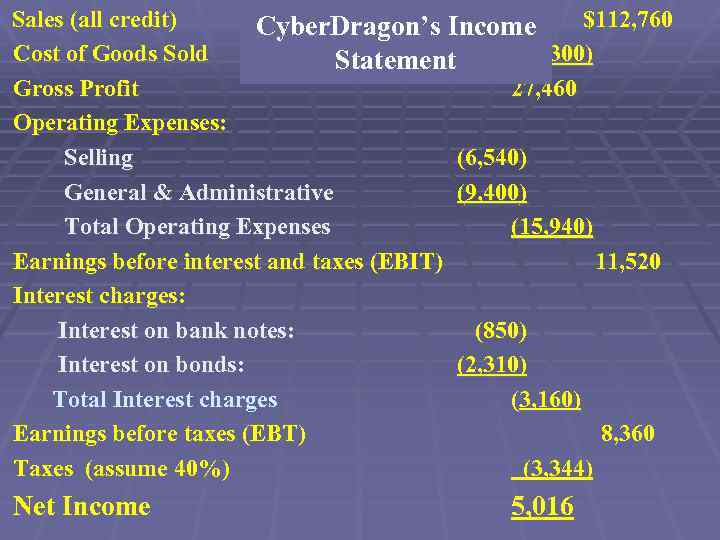 Sales (all credit) $112, 760 Cyber. Dragon’s Income Cost of Goods Sold (85, 300) Statement Gross Profit 27, 460 Operating Expenses: Selling (6, 540) General & Administrative (9, 400) Total Operating Expenses (15, 940) Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) 11, 520 Interest charges: Interest on bank notes: (850) Interest on bonds: (2, 310) Total Interest charges (3, 160) Earnings before taxes (EBT) 8, 360 Taxes (assume 40%) (3, 344) Net Income 5, 016
Sales (all credit) $112, 760 Cyber. Dragon’s Income Cost of Goods Sold (85, 300) Statement Gross Profit 27, 460 Operating Expenses: Selling (6, 540) General & Administrative (9, 400) Total Operating Expenses (15, 940) Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) 11, 520 Interest charges: Interest on bank notes: (850) Interest on bonds: (2, 310) Total Interest charges (3, 160) Earnings before taxes (EBT) 8, 360 Taxes (assume 40%) (3, 344) Net Income 5, 016
 Cyber. Dragon Other Information Dividends paid on common stock Earnings retained in the firm Shares outstanding (000) Market price per share Book value per share Earnings per share Dividends per share $2, 800 2, 216 1, 300 20 26. 44 3. 86 2. 15
Cyber. Dragon Other Information Dividends paid on common stock Earnings retained in the firm Shares outstanding (000) Market price per share Book value per share Earnings per share Dividends per share $2, 800 2, 216 1, 300 20 26. 44 3. 86 2. 15
 1. Liquidity Ratios § Do we have enough liquid assets to meet approaching obligations?
1. Liquidity Ratios § Do we have enough liquid assets to meet approaching obligations?
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio?
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio? current assets current liabilities
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio? current assets current liabilities
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio? 50, 190 25, 523 = 1. 97
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio? 50, 190 25, 523 = 1. 97
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio? 50, 190 25, 523 = 1. 97 If the average current ratio for the industry is 2. 4, is this good or not?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Current Ratio? 50, 190 25, 523 = 1. 97 If the average current ratio for the industry is 2. 4, is this good or not?
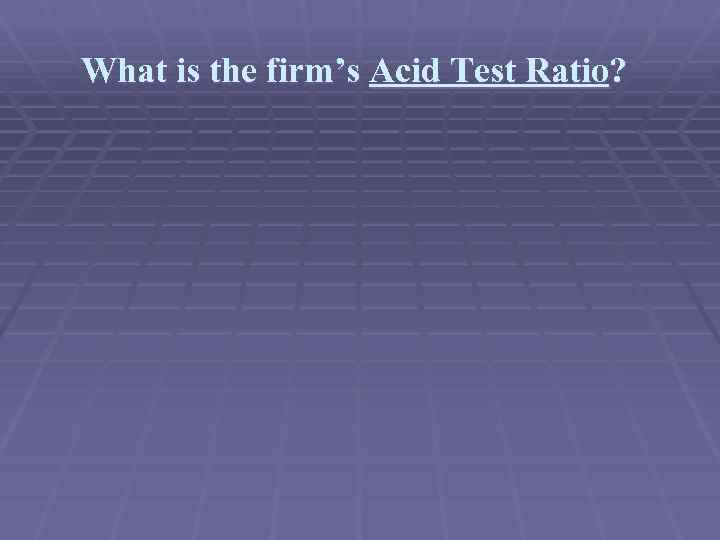 What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio?
What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio?
 What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio? current assets - inventories current liabilities
What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio? current assets - inventories current liabilities
 What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio? 50, 190 - 27, 530 =. 89 25, 523
What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio? 50, 190 - 27, 530 =. 89 25, 523
 What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio? 50, 190 - 27, 530 =. 89 25, 523 Suppose the industry average is. 92. What does this tell us?
What is the firm’s Acid Test Ratio? 50, 190 - 27, 530 =. 89 25, 523 Suppose the industry average is. 92. What does this tell us?
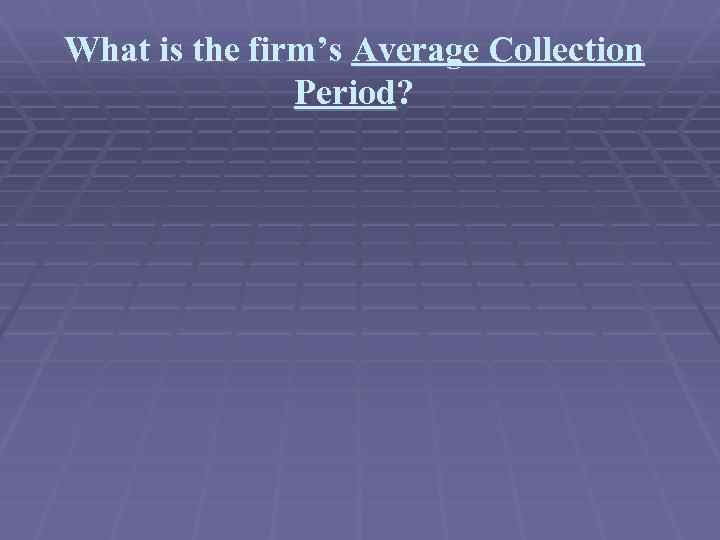 What is the firm’s Average Collection Period?
What is the firm’s Average Collection Period?
 What is the firm’s Average Collection Period? accounts receivable daily credit sales
What is the firm’s Average Collection Period? accounts receivable daily credit sales
 What is the firm’s Average Collection Period? 18, 320 112, 760/365 = 59. 3 days
What is the firm’s Average Collection Period? 18, 320 112, 760/365 = 59. 3 days
 What is the firm’s Average Collection Period? 18, 320 112, 760/365 = 59. 3 days If the industry average is 47 days, what does this tell us?
What is the firm’s Average Collection Period? 18, 320 112, 760/365 = 59. 3 days If the industry average is 47 days, what does this tell us?
 2. Operating Efficiency Ratios § Measure how efficiently the firm’s assets generate operating profits.
2. Operating Efficiency Ratios § Measure how efficiently the firm’s assets generate operating profits.
 What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)?
What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)?
 What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? operating income total assets
What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? operating income total assets
 What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? 11, 520 81, 890 = 14. 07%
What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? 11, 520 81, 890 = 14. 07%
 What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? 11, 520 81, 890 = 14. 07% • Slightly below the industry average of 15%.
What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? 11, 520 81, 890 = 14. 07% • Slightly below the industry average of 15%.
 What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? 11, 520 81, 890 = 14. 07% • Slightly below the industry average of 15%. • The OIROI reflects product pricing and the firm’s ability to keep costs down.
What is the firm’s Operating Income Return on Investment (OIROI)? 11, 520 81, 890 = 14. 07% • Slightly below the industry average of 15%. • The OIROI reflects product pricing and the firm’s ability to keep costs down.
 What is their Operating Profit Margin?
What is their Operating Profit Margin?
 What is their Operating Profit Margin? operating income sales
What is their Operating Profit Margin? operating income sales
 What is their Operating Profit Margin? 11, 520 112, 760 = 10. 22%
What is their Operating Profit Margin? 11, 520 112, 760 = 10. 22%
 What is their Operating Profit Margin? 11, 520 112, 760 = 10. 22% • This is below the industry average of 12%.
What is their Operating Profit Margin? 11, 520 112, 760 = 10. 22% • This is below the industry average of 12%.
 What is their Total Asset Turnover?
What is their Total Asset Turnover?
 What is their Total Asset Turnover? sales total assets
What is their Total Asset Turnover? sales total assets
 What is their Total Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 1. 38 times 81, 890
What is their Total Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 1. 38 times 81, 890
 What is their Total Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 1. 38 times 81, 890 The industry average is 1. 82 times. The firm needs to figure out how to squeeze more sales dollars out of its assets.
What is their Total Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 1. 38 times 81, 890 The industry average is 1. 82 times. The firm needs to figure out how to squeeze more sales dollars out of its assets.
 What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover?
What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover?
 What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover? credit sales accounts receivable
What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover? credit sales accounts receivable
 What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover? 112, 760 18, 320 = 6. 16 times
What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover? 112, 760 18, 320 = 6. 16 times
 What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover? 112, 760 18, 320 = 6. 16 times Cyber. Dragon turns their A/R over 6. 16 times per year. The industry average is 8. 2 times. Is this efficient?
What is the firm’s Accounts Receivable Turnover? 112, 760 18, 320 = 6. 16 times Cyber. Dragon turns their A/R over 6. 16 times per year. The industry average is 8. 2 times. Is this efficient?
 What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover?
What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover?
 What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover? cost of goods sold inventory
What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover? cost of goods sold inventory
 What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover? 85, 300 = 3. 10 times 27, 530
What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover? 85, 300 = 3. 10 times 27, 530
 What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover? 85, 300 = 3. 10 times 27, 530 Cyber. Dragon turns their inventory over 3. 1 times per year. The industry average is 3. 9 times. Is this efficient?
What is the firm’s Inventory Turnover? 85, 300 = 3. 10 times 27, 530 Cyber. Dragon turns their inventory over 3. 1 times per year. The industry average is 3. 9 times. Is this efficient?
 Low inventory turnover: The firm may have too much inventory, which is expensive because: § Inventory takes up costly warehouse space. § Some items may become spoiled or obsolete.
Low inventory turnover: The firm may have too much inventory, which is expensive because: § Inventory takes up costly warehouse space. § Some items may become spoiled or obsolete.
 What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover?
What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover?
 What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover? sales fixed assets
What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover? sales fixed assets
 What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 3. 56 times 31, 700
What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 3. 56 times 31, 700
 What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 3. 56 times 31, 700 If the industry average is 4. 6 times, what does this tell us about Cyber. Dragon?
What is the firm’s Fixed Asset Turnover? 112, 760 = 3. 56 times 31, 700 If the industry average is 4. 6 times, what does this tell us about Cyber. Dragon?
 3. Leverage Ratios (financing decisions) § Measure the impact of using debt capital to finance assets. § Firms use debt to lever (increase) returns on common equity.
3. Leverage Ratios (financing decisions) § Measure the impact of using debt capital to finance assets. § Firms use debt to lever (increase) returns on common equity.
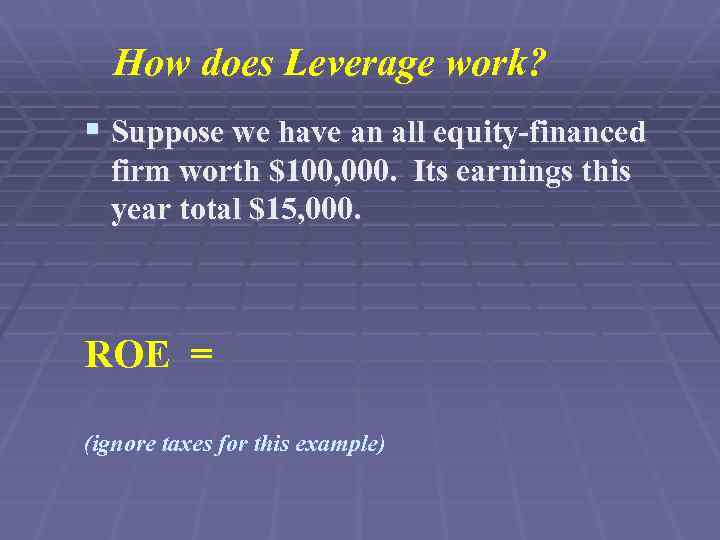 How does Leverage work? § Suppose we have an all equity-financed firm worth $100, 000. Its earnings this year total $15, 000. ROE = (ignore taxes for this example)
How does Leverage work? § Suppose we have an all equity-financed firm worth $100, 000. Its earnings this year total $15, 000. ROE = (ignore taxes for this example)
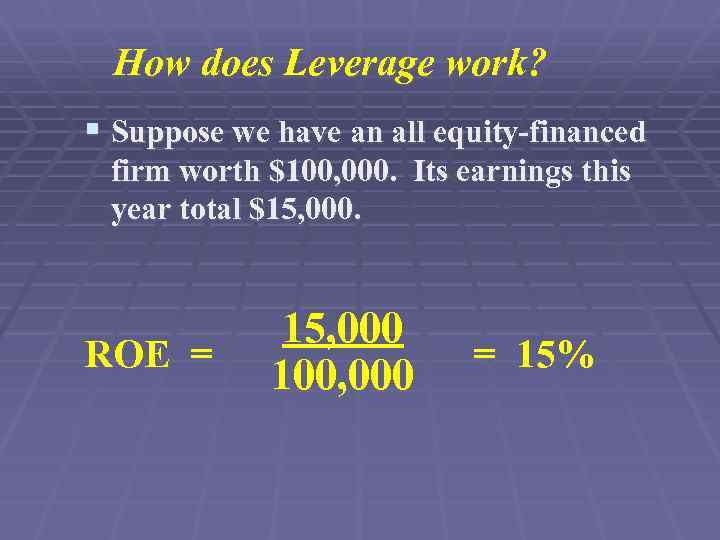 How does Leverage work? § Suppose we have an all equity-financed firm worth $100, 000. Its earnings this year total $15, 000. ROE = 15, 000 100, 000 = 15%
How does Leverage work? § Suppose we have an all equity-financed firm worth $100, 000. Its earnings this year total $15, 000. ROE = 15, 000 100, 000 = 15%
 How does Leverage work? § Suppose the same $100, 000 firm is financed with half equity, and half 8% debt (bonds). Earnings are still $15, 000. ROE =
How does Leverage work? § Suppose the same $100, 000 firm is financed with half equity, and half 8% debt (bonds). Earnings are still $15, 000. ROE =
 How does Leverage work? § Suppose the same $100, 000 firm is financed with half equity, and half 8% debt (bonds). Earnings are still $15, 000. 15, 000 - 4, 000 = ROE = 50, 000
How does Leverage work? § Suppose the same $100, 000 firm is financed with half equity, and half 8% debt (bonds). Earnings are still $15, 000. 15, 000 - 4, 000 = ROE = 50, 000
 How does Leverage work? § Suppose the same $100, 000 firm is financed with half equity, and half 8% debt (bonds). Earnings are still $15, 000. 15, 000 - 4, 000 = 22% ROE = 50, 000
How does Leverage work? § Suppose the same $100, 000 firm is financed with half equity, and half 8% debt (bonds). Earnings are still $15, 000. 15, 000 - 4, 000 = 22% ROE = 50, 000
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio?
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? total debt total assets
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? total debt total assets
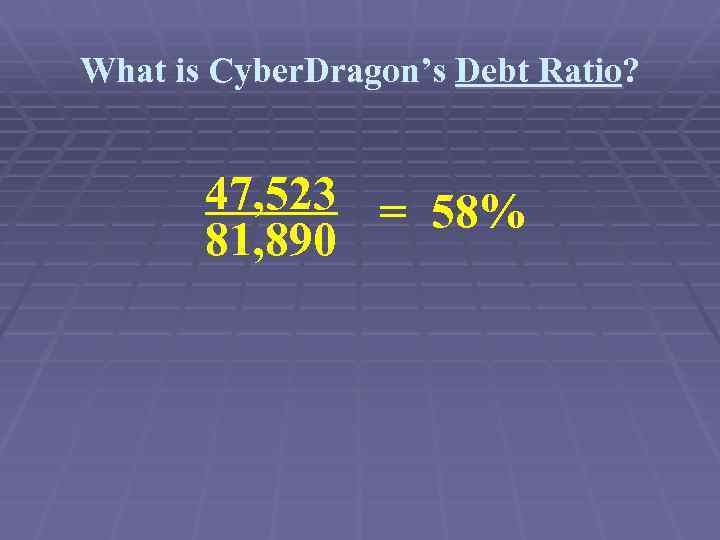 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? 47, 523 = 58% 81, 890
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? 47, 523 = 58% 81, 890
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? 47, 523 = 58% 81, 890 If the industry average is 47%, what does this tell us?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? 47, 523 = 58% 81, 890 If the industry average is 47%, what does this tell us?
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? 47, 523 = 58% 81, 890 If the industry average is 47%, what does this tell us? Can leverage make the firm more profitable? Can leverage make the firm riskier?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Debt Ratio? 47, 523 = 58% 81, 890 If the industry average is 47%, what does this tell us? Can leverage make the firm more profitable? Can leverage make the firm riskier?
 What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio?
What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio?
 What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio? operating income interest expense
What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio? operating income interest expense
 What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio? 11, 520 = 3. 65 times 3, 160
What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio? 11, 520 = 3. 65 times 3, 160
 What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio? 11, 520 = 3. 65 times 3, 160 The industry average is 6. 7 times. This is further evidence that the firm uses more debt financing than average.
What is the firm’s Times Interest Earned Ratio? 11, 520 = 3. 65 times 3, 160 The industry average is 6. 7 times. This is further evidence that the firm uses more debt financing than average.
 4. Return on Equity How well are the firm’s managers maximizing shareholder wealth?
4. Return on Equity How well are the firm’s managers maximizing shareholder wealth?
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)?
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? net income common equity
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? net income common equity
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? 5, 016 = 14. 6% 34, 367
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? 5, 016 = 14. 6% 34, 367
 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? 5, 016 = 14. 6% 34, 367 The industry average is 17. 54%.
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? 5, 016 = 14. 6% 34, 367 The industry average is 17. 54%.
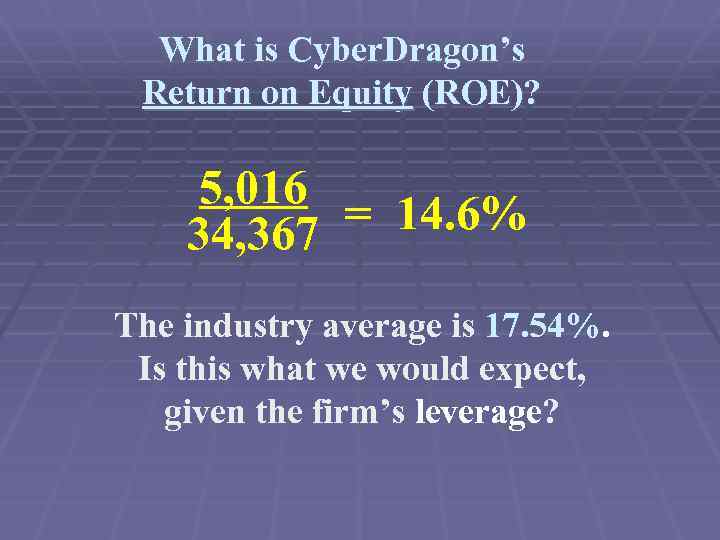 What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? 5, 016 = 14. 6% 34, 367 The industry average is 17. 54%. Is this what we would expect, given the firm’s leverage?
What is Cyber. Dragon’s Return on Equity (ROE)? 5, 016 = 14. 6% 34, 367 The industry average is 17. 54%. Is this what we would expect, given the firm’s leverage?
 Conclusion: § Even though Cyber. Dragon has higher leverage than the industry average, they are much less efficient, and therefore, less profitable.
Conclusion: § Even though Cyber. Dragon has higher leverage than the industry average, they are much less efficient, and therefore, less profitable.
 The Du. Pont Model Brings together: § Profitability § Efficiency § Leverage
The Du. Pont Model Brings together: § Profitability § Efficiency § Leverage
 The Du. Pont Model ROE = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin / (1 - Debt Ratio )
The Du. Pont Model ROE = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin / (1 - Debt Ratio )
 The Du. Pont Model ROE = = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin Net Income Sales x Total Assets Sales / (1 - /(1 - Debt Ratio ) Total Debt Total Assets )
The Du. Pont Model ROE = = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin Net Income Sales x Total Assets Sales / (1 - /(1 - Debt Ratio ) Total Debt Total Assets )
 The Du. Pont Model ROE = = = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin Net Income Sales x Total Assets Sales 5, 016 112, 760 x 112, 760 81, 890 / (1 - /(1 - Debt Ratio ) Total Debt Total Assets / (1 - 47, 523 81, 890 ) )
The Du. Pont Model ROE = = = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin Net Income Sales x Total Assets Sales 5, 016 112, 760 x 112, 760 81, 890 / (1 - /(1 - Debt Ratio ) Total Debt Total Assets / (1 - 47, 523 81, 890 ) )
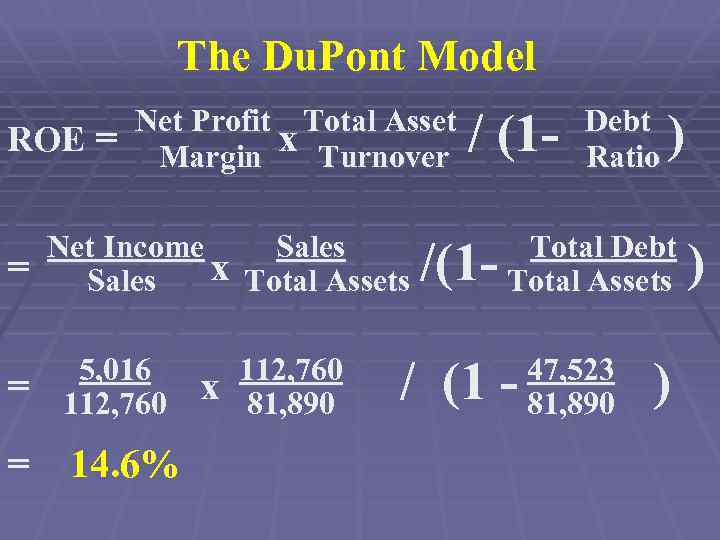 The Du. Pont Model ROE = = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin Net Income Sales x Total Assets Sales = 5, 016 112, 760 = 14. 6% x 112, 760 81, 890 / (1 - /(1 - Debt Ratio ) Total Debt Total Assets / (1 - 47, 523 81, 890 ) )
The Du. Pont Model ROE = = Net Profit Total Asset x Turnover Margin Net Income Sales x Total Assets Sales = 5, 016 112, 760 = 14. 6% x 112, 760 81, 890 / (1 - /(1 - Debt Ratio ) Total Debt Total Assets / (1 - 47, 523 81, 890 ) )


