40c1df9ab963977f8a8de030fc74ce00.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Chapter 3 Discrimination
Chapter 3 Discrimination
 Understanding Discrimination • Discrimination - unequal opportunities because of group membership • Discrimination and deprivation • Two patterns of deprivation relative and absolute • Relative deprivation is based on a discrepancy between cultural expectations and actual realities
Understanding Discrimination • Discrimination - unequal opportunities because of group membership • Discrimination and deprivation • Two patterns of deprivation relative and absolute • Relative deprivation is based on a discrepancy between cultural expectations and actual realities
 • Conditions may improve but continued discrimination may lead to feelings of deprivation • Absolute deprivation - occurs when a group is deprived of the basic necessities that allow for survival in a society • Feelings of relative and absolute deprivation emerge out of discrimination
• Conditions may improve but continued discrimination may lead to feelings of deprivation • Absolute deprivation - occurs when a group is deprived of the basic necessities that allow for survival in a society • Feelings of relative and absolute deprivation emerge out of discrimination
 Total Discrimination • Definition • Total discrimination- current discrimination in the labor market and past discrimination – Poor education and its impact on jobs – Poor health care and job experiences – Past and present actualities
Total Discrimination • Definition • Total discrimination- current discrimination in the labor market and past discrimination – Poor education and its impact on jobs – Poor health care and job experiences – Past and present actualities
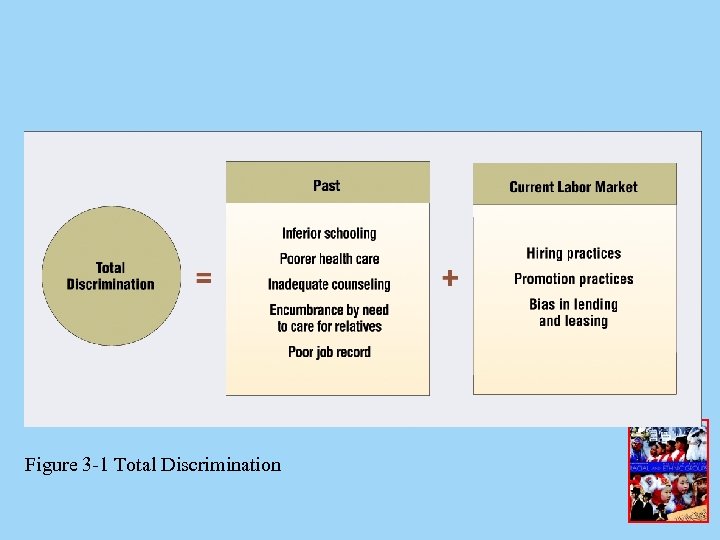 Figure 3 -1 Total Discrimination
Figure 3 -1 Total Discrimination
 Institutional Discrimination • Institutional forms of discrimination are due to the ongoing routines found within a society’s institutions, e. g. economic or education • Institutional forms of discrimination are committed collectively against a group • May be unconscious - in that it is not a function of awareness of discrimination
Institutional Discrimination • Institutional forms of discrimination are due to the ongoing routines found within a society’s institutions, e. g. economic or education • Institutional forms of discrimination are committed collectively against a group • May be unconscious - in that it is not a function of awareness of discrimination
 Examples of Institutional Discrimination • Standards for assessing credit cards don’t work for Hispanics or African Americans. . . • IQ testing favors middle-class children. . . • The entire criminal justice system, from the patrol officer to the judge and jury, are dominated by White males
Examples of Institutional Discrimination • Standards for assessing credit cards don’t work for Hispanics or African Americans. . . • IQ testing favors middle-class children. . . • The entire criminal justice system, from the patrol officer to the judge and jury, are dominated by White males
 • Hiring practices often require several years of experience at jobs only recently opened to members of subordinate groups
• Hiring practices often require several years of experience at jobs only recently opened to members of subordinate groups
 Low-Wage Labor • Informal economy operates outside of governmental processes • Regular and irregular labor market • Regular labor market - operates according to the principles of the conventional labor market
Low-Wage Labor • Informal economy operates outside of governmental processes • Regular and irregular labor market • Regular labor market - operates according to the principles of the conventional labor market
 • Stability, wages, health insurance and pension… • Irregular or hidden economy operates outside the boundaries of the regular economy as it relates to job stability, wages, working conditions or benefits
• Stability, wages, health insurance and pension… • Irregular or hidden economy operates outside the boundaries of the regular economy as it relates to job stability, wages, working conditions or benefits
 Informal Economy and Discrimination continued • Subordinate groups have often been used as an elastic part of the labor force and relegated to the irregular economy • In the irregular labor market entrance to better jobs is a function of past discrimination that effects entrance into the primary labor market • The irregular economy discrimination and low-wage labor
Informal Economy and Discrimination continued • Subordinate groups have often been used as an elastic part of the labor force and relegated to the irregular economy • In the irregular labor market entrance to better jobs is a function of past discrimination that effects entrance into the primary labor market • The irregular economy discrimination and low-wage labor
 Discrimination Today • Measuring discrimination • How much discrimination is there? 1. Identifying the different treatment 2. Determining the cost of discrimination • Distribution of income as a measure of discrimination
Discrimination Today • Measuring discrimination • How much discrimination is there? 1. Identifying the different treatment 2. Determining the cost of discrimination • Distribution of income as a measure of discrimination
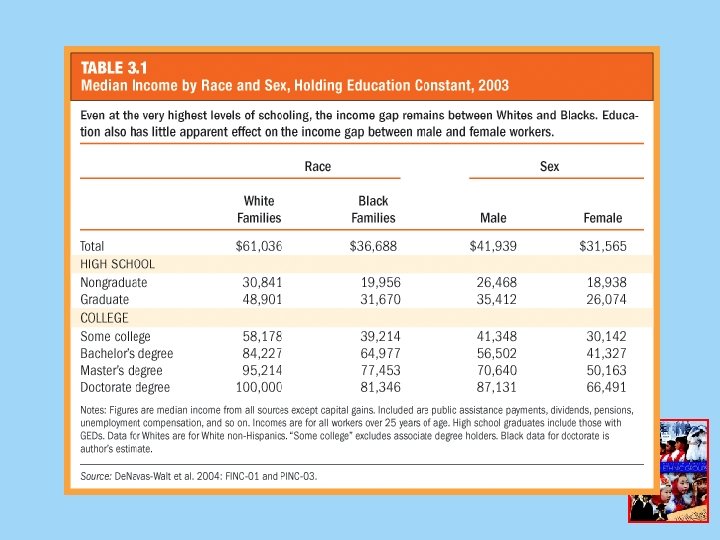
 Income Differences • Difference in White and Black male income • Double jeopardy and gender, race and the distribution of income – Direct discrimination in hiring – Promotion – Past discrimination
Income Differences • Difference in White and Black male income • Double jeopardy and gender, race and the distribution of income – Direct discrimination in hiring – Promotion – Past discrimination
 Eliminating Discrimination • Two major sources for the elimination of discrimination: – Voluntary associations – Governmental agencies and policies • Roosevelt’s 1943 and the Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC) • Supreme court decision - 1954 Brown v. Board of Education
Eliminating Discrimination • Two major sources for the elimination of discrimination: – Voluntary associations – Governmental agencies and policies • Roosevelt’s 1943 and the Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC) • Supreme court decision - 1954 Brown v. Board of Education
 Eliminating Discrimination • Affirmative Action - Executive order issued by President Kennedy in 1961 • Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the establishment of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
Eliminating Discrimination • Affirmative Action - Executive order issued by President Kennedy in 1961 • Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the establishment of the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC)
 • However, redlining (the process of discrimination against people trying to buy homes in minority and racially changing neighborhoods) still exists.
• However, redlining (the process of discrimination against people trying to buy homes in minority and racially changing neighborhoods) still exists.
 Environmental Justice • Environmental racism • Race and the exposure to environmental pollutants • Executive order (1994) and environmental justice for the poor and minorities
Environmental Justice • Environmental racism • Race and the exposure to environmental pollutants • Executive order (1994) and environmental justice for the poor and minorities
 Affirmative action • Affirmative action - refers to positive policies and efforts to recruit and promote minority group members for educational and job opportunities • Affirmative action and addressing the problem of institutional discrimination
Affirmative action • Affirmative action - refers to positive policies and efforts to recruit and promote minority group members for educational and job opportunities • Affirmative action and addressing the problem of institutional discrimination
 Examples of Affirmative Action and Institutional Discrimination • Height and weight requirements that are unnecessarily geared to the physical proportions of White males • Seniority rules, when applied to jobs historically held only by white males • Nepotism-based membership policies
Examples of Affirmative Action and Institutional Discrimination • Height and weight requirements that are unnecessarily geared to the physical proportions of White males • Seniority rules, when applied to jobs historically held only by white males • Nepotism-based membership policies
 • Restrictive employment leave policies • Rules requiring only English be spoken at the workplace • Standardized academic tests or criteria • Preferences shown by law and medical schools
• Restrictive employment leave policies • Rules requiring only English be spoken at the workplace • Standardized academic tests or criteria • Preferences shown by law and medical schools
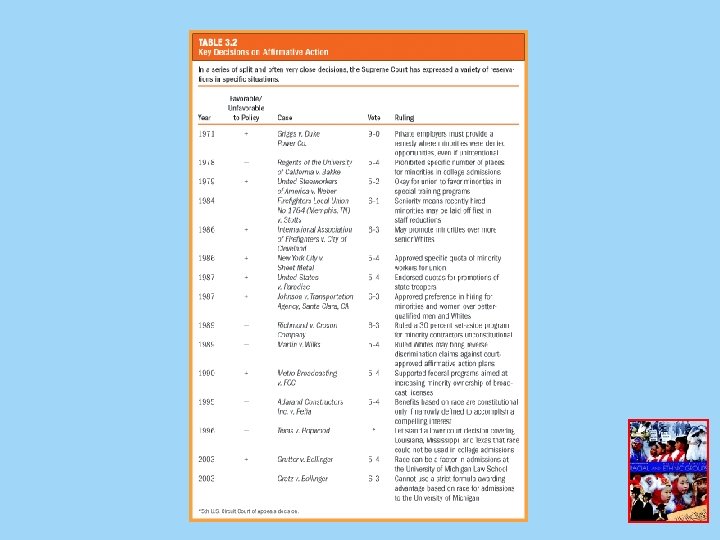
 Reverse Discrimination • Reverse discrimination - the view that more qualified white males are bypassed for less qualified minority candidates – Affirmative action and reverse discrimination • Issues have focused on quotas • The myth of quotas
Reverse Discrimination • Reverse discrimination - the view that more qualified white males are bypassed for less qualified minority candidates – Affirmative action and reverse discrimination • Issues have focused on quotas • The myth of quotas
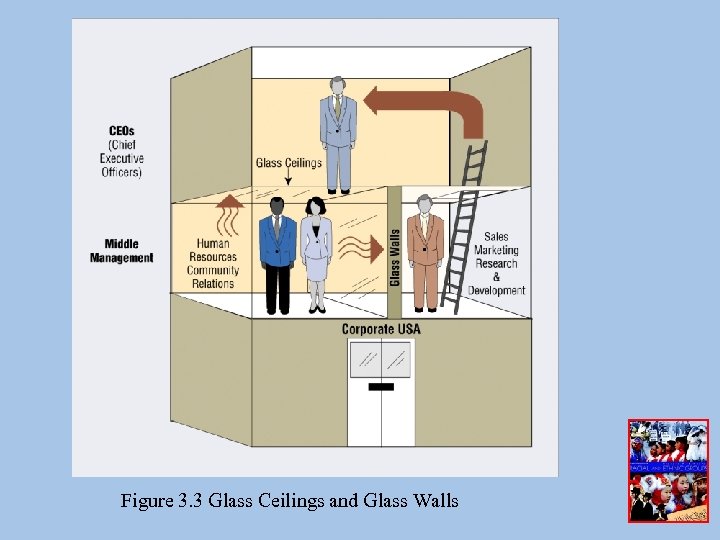 Figure 3. 3 Glass Ceilings and Glass Walls
Figure 3. 3 Glass Ceilings and Glass Walls
 Determinants of Glass Ceilings • Lack of management commitment to establishing system, policies, and practices for achieving workplace diversity and upward mobility • Pay inequities for work of equal or comparable value • Sex, race, and ethnic-based stereotyping and harassment
Determinants of Glass Ceilings • Lack of management commitment to establishing system, policies, and practices for achieving workplace diversity and upward mobility • Pay inequities for work of equal or comparable value • Sex, race, and ethnic-based stereotyping and harassment
 • Unfair recruitment practices • Lack of family-friendly workplace policies • “Parent-track” policies • Limited opportunities for advancement to decision-making positions
• Unfair recruitment practices • Lack of family-friendly workplace policies • “Parent-track” policies • Limited opportunities for advancement to decision-making positions


