03e1b0aa8566f8d10b5701c7953845d5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 CHAPTER 3 DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS
CHAPTER 3 DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS
 DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS • Depository Inst. in U. S. A • Commercial Banks • Savings and Loan Associations • Savings Banks • Credit Unions • Sources of income; • Interest from the loans made and securities invested in. • Non-Interest Income (Fees)
DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS • Depository Inst. in U. S. A • Commercial Banks • Savings and Loan Associations • Savings Banks • Credit Unions • Sources of income; • Interest from the loans made and securities invested in. • Non-Interest Income (Fees)
 THE ASSET/LIABILITY PROBLEM OF DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS • Spread income, margin. • The risks that a depository institution faces include: • Credit Risk (Default Risk) • Regulatory Risk • Funding (Interest rate) Risk • Liquidity Risk
THE ASSET/LIABILITY PROBLEM OF DEPOSITORY INSTITUTIONS • Spread income, margin. • The risks that a depository institution faces include: • Credit Risk (Default Risk) • Regulatory Risk • Funding (Interest rate) Risk • Liquidity Risk
 CREDIT RISK (DEFAULT RISK) • The risk that a borrower may default on a loan abligation or that the issuer of a security that they held may default on its obligation.
CREDIT RISK (DEFAULT RISK) • The risk that a borrower may default on a loan abligation or that the issuer of a security that they held may default on its obligation.
 REGULATORY RISK • Regulaters will change the rules and affect earnings of institutions unfavorably.
REGULATORY RISK • Regulaters will change the rules and affect earnings of institutions unfavorably.
 FUNDING RISK • Borrowing short-Lending long: This policy benefits from a decline in interest rates however if interest rates rise, it will loose.
FUNDING RISK • Borrowing short-Lending long: This policy benefits from a decline in interest rates however if interest rates rise, it will loose.
 LIQUIDITY RISK • Com. Banks must be prepared to satisfy withdrawals and to provide loans. • Options available to manage the liquidity involve; • attracting additional deposits • using securities owned as collateral for borrowing from central bank and other financial institutions • liquidating securities that it currently holds in its portfolio • raising short-term funds in the money market (Repos). • Com. Banks hold liquid assets not only for operational purposes but also for regulatory requirements.
LIQUIDITY RISK • Com. Banks must be prepared to satisfy withdrawals and to provide loans. • Options available to manage the liquidity involve; • attracting additional deposits • using securities owned as collateral for borrowing from central bank and other financial institutions • liquidating securities that it currently holds in its portfolio • raising short-term funds in the money market (Repos). • Com. Banks hold liquid assets not only for operational purposes but also for regulatory requirements.
 COMMERCIAL BANKS The main role of the commercial banks is taking deposits and making loans. Others; • Carrying out currency exchanges • Providing credits by discounting commercial loans • Safekeeping of customer valuables such as gold, securities etc. • Supporting government activities with credit • Purchasing government securities
COMMERCIAL BANKS The main role of the commercial banks is taking deposits and making loans. Others; • Carrying out currency exchanges • Providing credits by discounting commercial loans • Safekeeping of customer valuables such as gold, securities etc. • Supporting government activities with credit • Purchasing government securities
 COMMERCIAL BANKS In today’s world, banks increase their services and activities, such as providing; • financial advising to customers who use credits and have savings. • equipment leasing services though which the bank buys the equipment and rent it to customers • selling insurance policies such as life and non-life • security brokerage services to their customers though buying bonds and other securities • mutual funds, which usually provide higher returns than that on bank deposits.
COMMERCIAL BANKS In today’s world, banks increase their services and activities, such as providing; • financial advising to customers who use credits and have savings. • equipment leasing services though which the bank buys the equipment and rent it to customers • selling insurance policies such as life and non-life • security brokerage services to their customers though buying bonds and other securities • mutual funds, which usually provide higher returns than that on bank deposits.
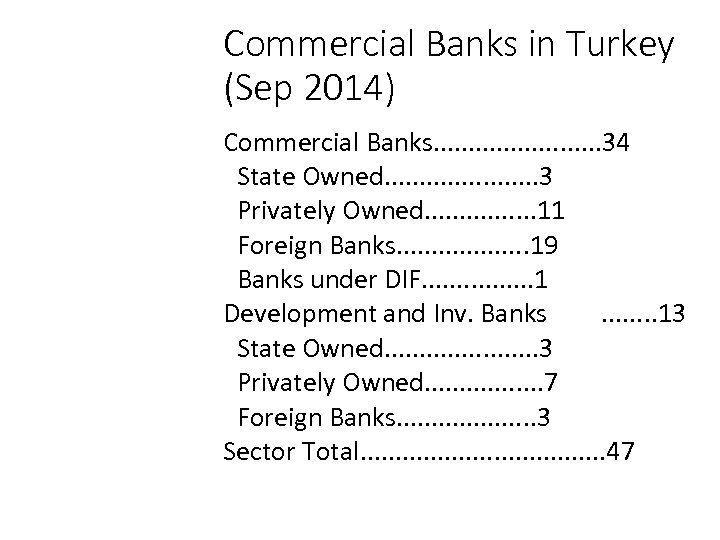 Commercial Banks in Turkey (Sep 2014) Commercial Banks. . . 34 State Owned. . . . . 3 Privately Owned. . . . 11 Foreign Banks. . . . . 19 Banks under DIF. . . . 1 Development and Inv. Banks. . . . 13 State Owned. . . . . 3 Privately Owned. . . . 7 Foreign Banks. . . . . 3 Sector Total. . . . . 47
Commercial Banks in Turkey (Sep 2014) Commercial Banks. . . 34 State Owned. . . . . 3 Privately Owned. . . . 11 Foreign Banks. . . . . 19 Banks under DIF. . . . 1 Development and Inv. Banks. . . . 13 State Owned. . . . . 3 Privately Owned. . . . 7 Foreign Banks. . . . . 3 Sector Total. . . . . 47
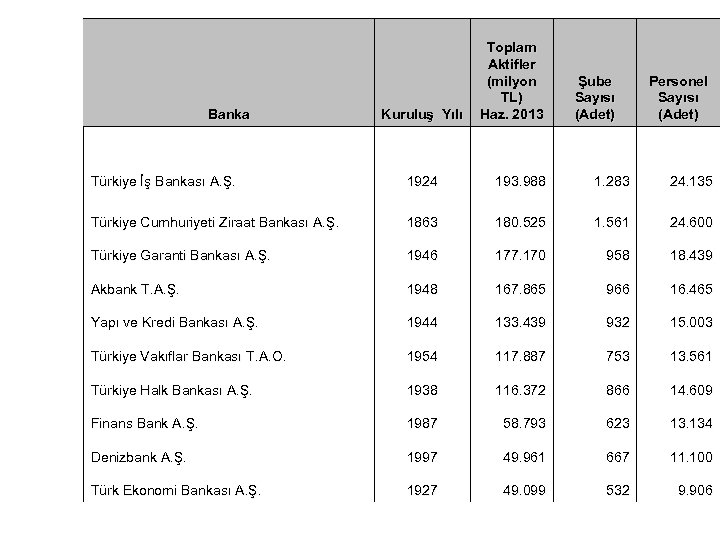 Banka Kuruluş Yılı Toplam Aktifler (milyon TL) Haz. 2013 Şube Sayısı (Adet) Personel Sayısı (Adet) Türkiye İş Bankası A. Ş. 1924 193. 988 1. 283 24. 135 Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Ziraat Bankası A. Ş. 1863 180. 525 1. 561 24. 600 Türkiye Garanti Bankası A. Ş. 1946 177. 170 958 18. 439 Akbank T. A. Ş. 1948 167. 865 966 16. 465 Yapı ve Kredi Bankası A. Ş. 1944 133. 439 932 15. 003 Türkiye Vakıflar Bankası T. A. O. 1954 117. 887 753 13. 561 Türkiye Halk Bankası A. Ş. 1938 116. 372 866 14. 609 Finans Bank A. Ş. 1987 58. 793 623 13. 134 Denizbank A. Ş. 1997 49. 961 667 11. 100 Türk Ekonomi Bankası A. Ş. 1927 49. 099 532 9. 906
Banka Kuruluş Yılı Toplam Aktifler (milyon TL) Haz. 2013 Şube Sayısı (Adet) Personel Sayısı (Adet) Türkiye İş Bankası A. Ş. 1924 193. 988 1. 283 24. 135 Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Ziraat Bankası A. Ş. 1863 180. 525 1. 561 24. 600 Türkiye Garanti Bankası A. Ş. 1946 177. 170 958 18. 439 Akbank T. A. Ş. 1948 167. 865 966 16. 465 Yapı ve Kredi Bankası A. Ş. 1944 133. 439 932 15. 003 Türkiye Vakıflar Bankası T. A. O. 1954 117. 887 753 13. 561 Türkiye Halk Bankası A. Ş. 1938 116. 372 866 14. 609 Finans Bank A. Ş. 1987 58. 793 623 13. 134 Denizbank A. Ş. 1997 49. 961 667 11. 100 Türk Ekonomi Bankası A. Ş. 1927 49. 099 532 9. 906
 THE NATURE OF BANKING SERVICES • Broad classification of services: • Individual banking • Institutional banking • Global banking
THE NATURE OF BANKING SERVICES • Broad classification of services: • Individual banking • Institutional banking • Global banking
 INDIVIDUAL BANKING • Consumer loans, mortgage loans, credit cards, brokerage services. . etc.
INDIVIDUAL BANKING • Consumer loans, mortgage loans, credit cards, brokerage services. . etc.
 INSTITUTIONAL BANKING • Loans to non-financial institutions, government entities. Commercial real estate financing, leasing, factoring. • Management of assets (mutual funds), check clearing and electronic transfers.
INSTITUTIONAL BANKING • Loans to non-financial institutions, government entities. Commercial real estate financing, leasing, factoring. • Management of assets (mutual funds), check clearing and electronic transfers.
 GLOBAL BANKING • Covers corporate finance, capital markets and foreign exchage services, investment banking firms. • Corporate financing; • Underwriting of securities, Banker’s acceptances, L/C. • Advices on obtaining funds, corp. restructuring, divestitures&acquisitions. • Interest rate swaps, currency swaps, forward contracts, interest rate options etc. . .
GLOBAL BANKING • Covers corporate finance, capital markets and foreign exchage services, investment banking firms. • Corporate financing; • Underwriting of securities, Banker’s acceptances, L/C. • Advices on obtaining funds, corp. restructuring, divestitures&acquisitions. • Interest rate swaps, currency swaps, forward contracts, interest rate options etc. . .
 BALANCE SHEET STRUCTURE OF COMMERCIAL BANKS
BALANCE SHEET STRUCTURE OF COMMERCIAL BANKS
 ASSETS • Liquid Assets • Cash • Central Bank • Due from Banks • Investment Securities (T-bills, Repos, Debt ad Equity securites and etc) • Bank Loans (Working Cap. Loan- Term Loan) (Leases and Foctoring reveivables) • Commercial Loans • Consumer Loans • Real Estate Loans etc. • Fixed Assets
ASSETS • Liquid Assets • Cash • Central Bank • Due from Banks • Investment Securities (T-bills, Repos, Debt ad Equity securites and etc) • Bank Loans (Working Cap. Loan- Term Loan) (Leases and Foctoring reveivables) • Commercial Loans • Consumer Loans • Real Estate Loans etc. • Fixed Assets
 LIABILITIES AND EQUITY CAPITAL • Deposits • Borrowed Funds • Equity Capital
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY CAPITAL • Deposits • Borrowed Funds • Equity Capital
 DEPOSITS • Deposits are the main source of funding. They can be categorized based on; • Maturity • Depositors • Negotiability
DEPOSITS • Deposits are the main source of funding. They can be categorized based on; • Maturity • Depositors • Negotiability
 DEPOSITS Accoring to maturity, bank deposits are categorized as; • Demand deposits (Checking Account): • Time deposits • One month • Three-month • Six-month • One year
DEPOSITS Accoring to maturity, bank deposits are categorized as; • Demand deposits (Checking Account): • Time deposits • One month • Three-month • Six-month • One year
 DEPOSITS According to depositors; • Saving deposits • Commercial deposits • Interbank deposits • Official deposits
DEPOSITS According to depositors; • Saving deposits • Commercial deposits • Interbank deposits • Official deposits
 DEPOSITS • According to negotiability; • Negotiable deposits (Certificate of Deposits, CDs) • Non-negotiable deposits (All others)
DEPOSITS • According to negotiability; • Negotiable deposits (Certificate of Deposits, CDs) • Non-negotiable deposits (All others)
 BORROWED FUNDS • Borrowed Funds (Non Depository Funds ): • Interbank funds borrowed • Borrowing from; • Central bank • Other banks • Abroad. • Debentures
BORROWED FUNDS • Borrowed Funds (Non Depository Funds ): • Interbank funds borrowed • Borrowing from; • Central bank • Other banks • Abroad. • Debentures
 EQUITY CAPITAL • Common stock • Paid in Capital • Retained Earnings
EQUITY CAPITAL • Common stock • Paid in Capital • Retained Earnings
 B/S OF TURKISH BANKS • Assets • Liquid Assets • Cash and Central Bank • Due from banks • Receivables from money market • Financial assets ready to sell • Bank Loans • Loan Reveivables • Factoring receivables • Assets holding up-to maturity • Subsidiaries • Leasing receivables • Derivatives for hedging • Fixed Assets
B/S OF TURKISH BANKS • Assets • Liquid Assets • Cash and Central Bank • Due from banks • Receivables from money market • Financial assets ready to sell • Bank Loans • Loan Reveivables • Factoring receivables • Assets holding up-to maturity • Subsidiaries • Leasing receivables • Derivatives for hedging • Fixed Assets
 • Liabilities • Deposits • Financial derivative liab. for buying and selling purposes • Issued securities • Funds • Foreign liabilities • Financial derivative liab. for hedging • Reserves • Tax liabilies • Loans on fixed assets for buying and selling purposes
• Liabilities • Deposits • Financial derivative liab. for buying and selling purposes • Issued securities • Funds • Foreign liabilities • Financial derivative liab. for hedging • Reserves • Tax liabilies • Loans on fixed assets for buying and selling purposes
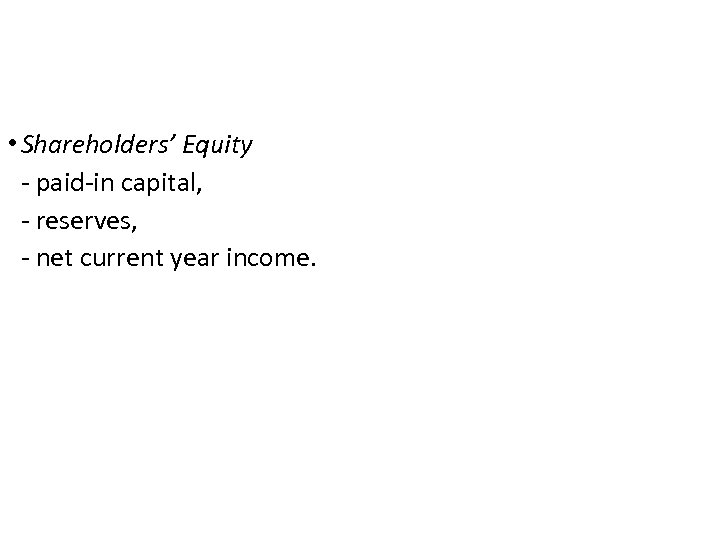 • Shareholders’ Equity - paid-in capital, - reserves, - net current year income.
• Shareholders’ Equity - paid-in capital, - reserves, - net current year income.
 OFF B/S ASSETS AND LIABILITIES Off- Balance-Sheet Items • Guarantee letters • Loan Commitments (Taahhütler): Contractural commitment by a bank to loan to a customer a certain maximum amount at given interest rate terms • Financial Derivatives • Custody accounts (securities) (emenat kıymetler)
OFF B/S ASSETS AND LIABILITIES Off- Balance-Sheet Items • Guarantee letters • Loan Commitments (Taahhütler): Contractural commitment by a bank to loan to a customer a certain maximum amount at given interest rate terms • Financial Derivatives • Custody accounts (securities) (emenat kıymetler)
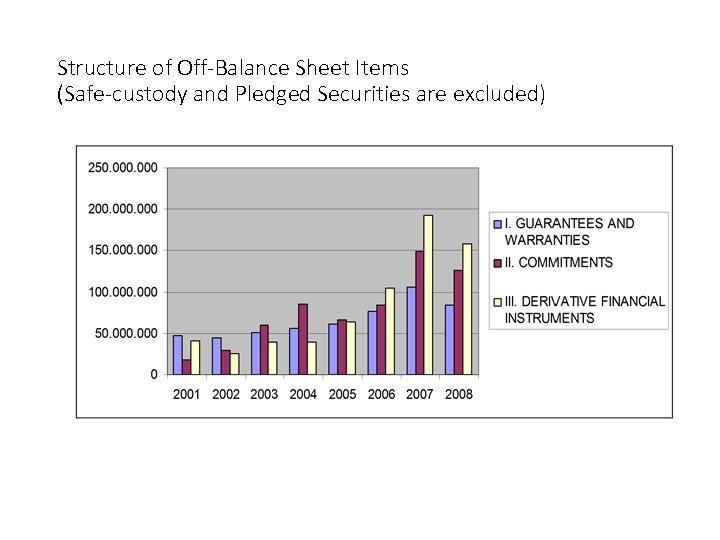 Structure of Off-Balance Sheet Items (Safe-custody and Pledged Securities are excluded)
Structure of Off-Balance Sheet Items (Safe-custody and Pledged Securities are excluded)
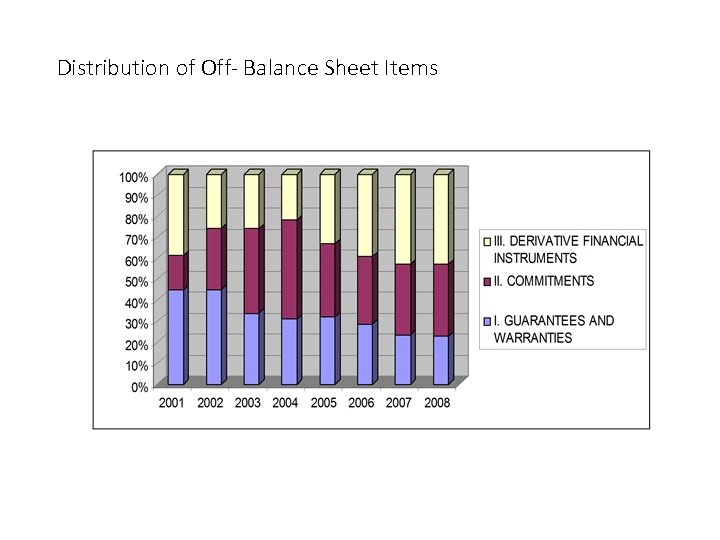 Distribution of Off- Balance Sheet Items
Distribution of Off- Balance Sheet Items
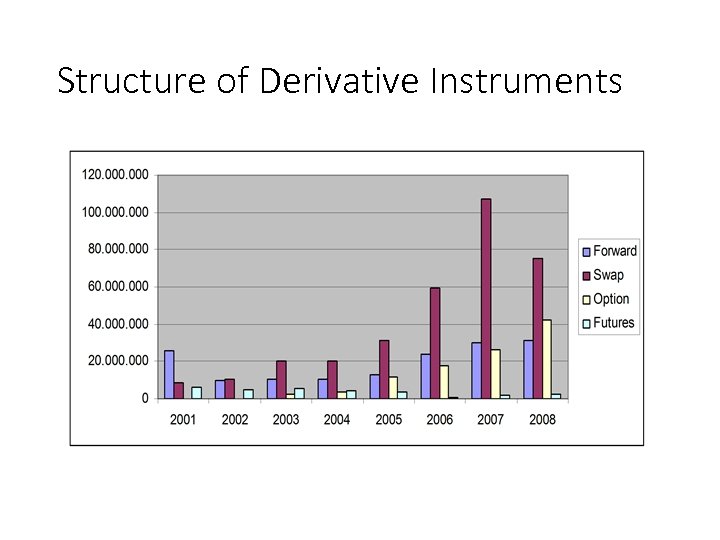 Structure of Derivative Instruments
Structure of Derivative Instruments
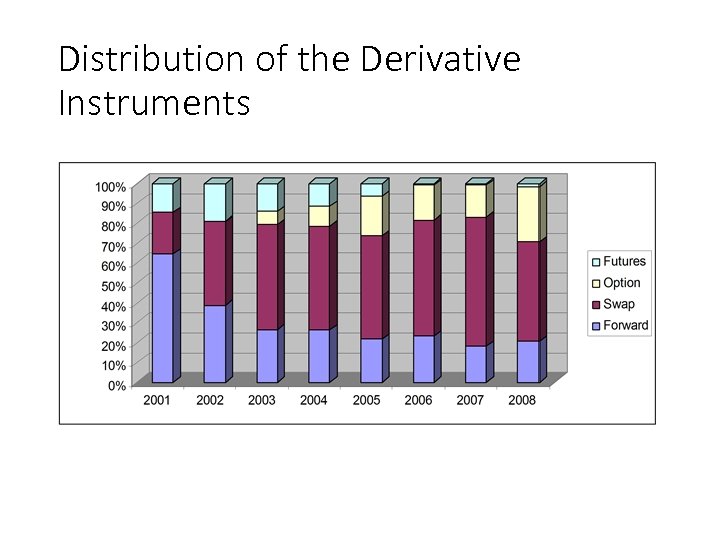 Distribution of the Derivative Instruments
Distribution of the Derivative Instruments
 INCOME STATEMENT • Interest Income on Loans • Interest on Leases • Interest on Deposits at other Institutions • Interest on Investment Securities • Interest Expenses • Interest on Deposits • Interest on Borrowed Funds • Interest on debentures
INCOME STATEMENT • Interest Income on Loans • Interest on Leases • Interest on Deposits at other Institutions • Interest on Investment Securities • Interest Expenses • Interest on Deposits • Interest on Borrowed Funds • Interest on debentures
 INCOME STATEMENT • Non-Interest Income • Income from fiduaciary activities • Service charges on deposit accounts • Gains from trading assets and liabilities • Non-Interest Expenses • Salaries and Employee Benefits • Expenses on fixed assets • Total Operating Income (Total Revenue) = Interest Income +Non-Interest Income
INCOME STATEMENT • Non-Interest Income • Income from fiduaciary activities • Service charges on deposit accounts • Gains from trading assets and liabilities • Non-Interest Expenses • Salaries and Employee Benefits • Expenses on fixed assets • Total Operating Income (Total Revenue) = Interest Income +Non-Interest Income
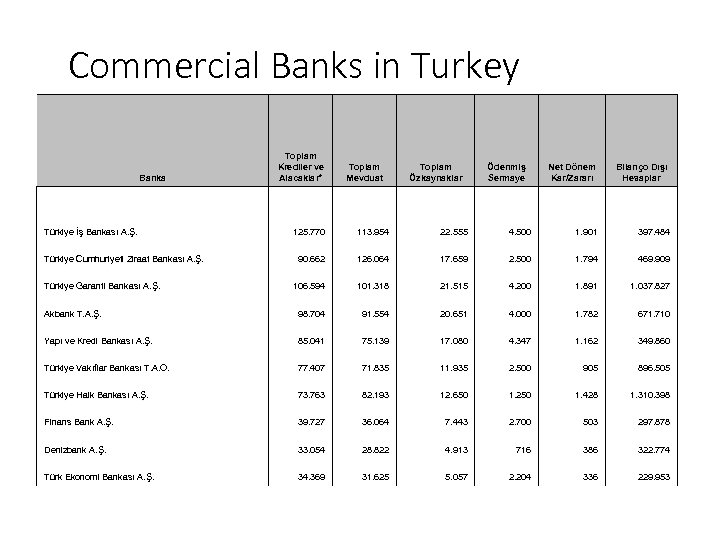 Commercial Banks in Turkey Banka Türkiye İş Bankası A. Ş. Toplam Krediler ve Alacaklar* Toplam Mevduat Toplam Özkaynaklar Ödenmiş Sermaye Net Dönem Kar/Zararı Bilanço Dışı Hesaplar 125. 770 113. 954 22. 555 4. 500 1. 901 397. 484 90. 662 126. 064 17. 659 2. 500 1. 794 469. 909 106. 594 101. 318 21. 515 4. 200 1. 891 1. 037. 827 Akbank T. A. Ş. 98. 704 91. 554 20. 651 4. 000 1. 782 671. 710 Yapı ve Kredi Bankası A. Ş. 85. 041 75. 139 17. 080 4. 347 1. 162 349. 860 Türkiye Vakıflar Bankası T. A. O. 77. 407 71. 835 11. 935 2. 500 905 896. 505 Türkiye Halk Bankası A. Ş. 73. 763 82. 193 12. 650 1. 250 1. 428 1. 310. 398 Finans Bank A. Ş. 39. 727 36. 064 7. 443 2. 700 503 297. 878 Denizbank A. Ş. 33. 054 28. 822 4. 913 716 386 322. 774 Türk Ekonomi Bankası A. Ş. 34. 369 31. 625 5. 057 2. 204 336 229. 953 Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Ziraat Bankası A. Ş. Türkiye Garanti Bankası A. Ş.
Commercial Banks in Turkey Banka Türkiye İş Bankası A. Ş. Toplam Krediler ve Alacaklar* Toplam Mevduat Toplam Özkaynaklar Ödenmiş Sermaye Net Dönem Kar/Zararı Bilanço Dışı Hesaplar 125. 770 113. 954 22. 555 4. 500 1. 901 397. 484 90. 662 126. 064 17. 659 2. 500 1. 794 469. 909 106. 594 101. 318 21. 515 4. 200 1. 891 1. 037. 827 Akbank T. A. Ş. 98. 704 91. 554 20. 651 4. 000 1. 782 671. 710 Yapı ve Kredi Bankası A. Ş. 85. 041 75. 139 17. 080 4. 347 1. 162 349. 860 Türkiye Vakıflar Bankası T. A. O. 77. 407 71. 835 11. 935 2. 500 905 896. 505 Türkiye Halk Bankası A. Ş. 73. 763 82. 193 12. 650 1. 250 1. 428 1. 310. 398 Finans Bank A. Ş. 39. 727 36. 064 7. 443 2. 700 503 297. 878 Denizbank A. Ş. 33. 054 28. 822 4. 913 716 386 322. 774 Türk Ekonomi Bankası A. Ş. 34. 369 31. 625 5. 057 2. 204 336 229. 953 Türkiye Cumhuriyeti Ziraat Bankası A. Ş. Türkiye Garanti Bankası A. Ş.
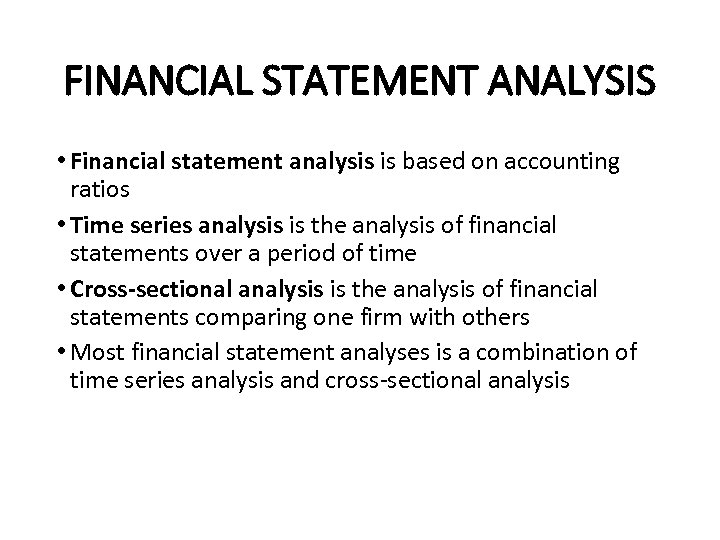 FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS • Financial statement analysis is based on accounting ratios • Time series analysis is the analysis of financial statements over a period of time • Cross-sectional analysis is the analysis of financial statements comparing one firm with others • Most financial statement analyses is a combination of time series analysis and cross-sectional analysis
FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS • Financial statement analysis is based on accounting ratios • Time series analysis is the analysis of financial statements over a period of time • Cross-sectional analysis is the analysis of financial statements comparing one firm with others • Most financial statement analyses is a combination of time series analysis and cross-sectional analysis
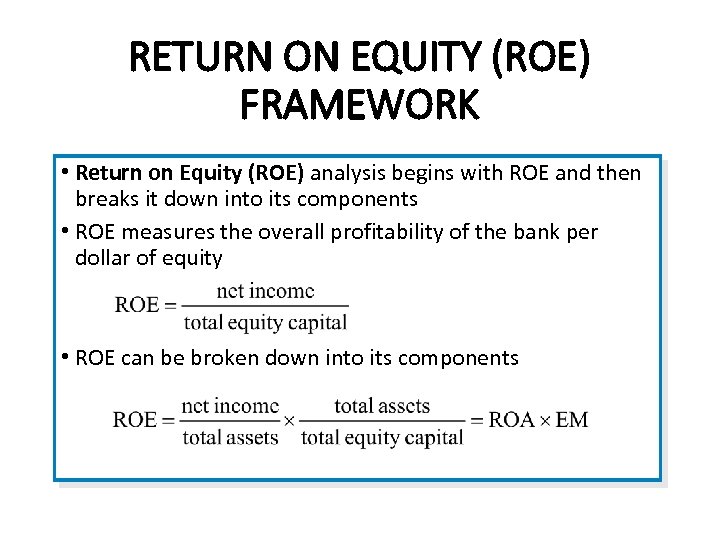 RETURN ON EQUITY (ROE) FRAMEWORK • Return on Equity (ROE) analysis begins with ROE and then breaks it down into its components • ROE measures the overall profitability of the bank per dollar of equity • ROE can be broken down into its components
RETURN ON EQUITY (ROE) FRAMEWORK • Return on Equity (ROE) analysis begins with ROE and then breaks it down into its components • ROE measures the overall profitability of the bank per dollar of equity • ROE can be broken down into its components
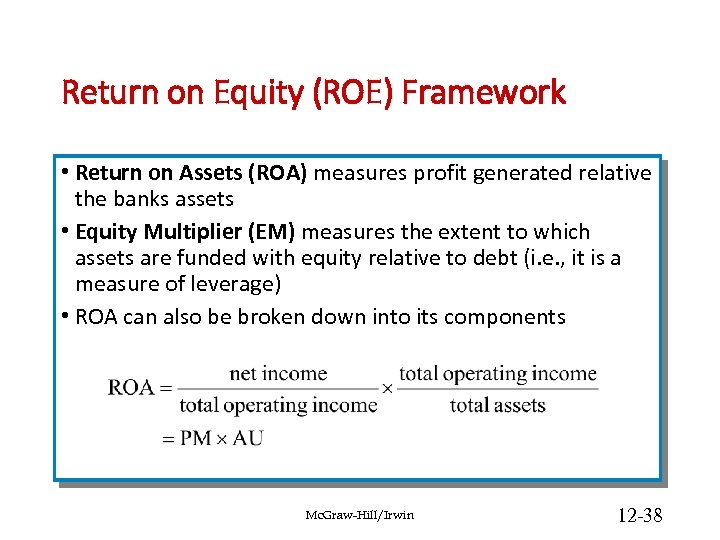 Return on Equity (ROE) Framework • Return on Assets (ROA) measures profit generated relative the banks assets • Equity Multiplier (EM) measures the extent to which assets are funded with equity relative to debt (i. e. , it is a measure of leverage) • ROA can also be broken down into its components Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -38
Return on Equity (ROE) Framework • Return on Assets (ROA) measures profit generated relative the banks assets • Equity Multiplier (EM) measures the extent to which assets are funded with equity relative to debt (i. e. , it is a measure of leverage) • ROA can also be broken down into its components Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -38
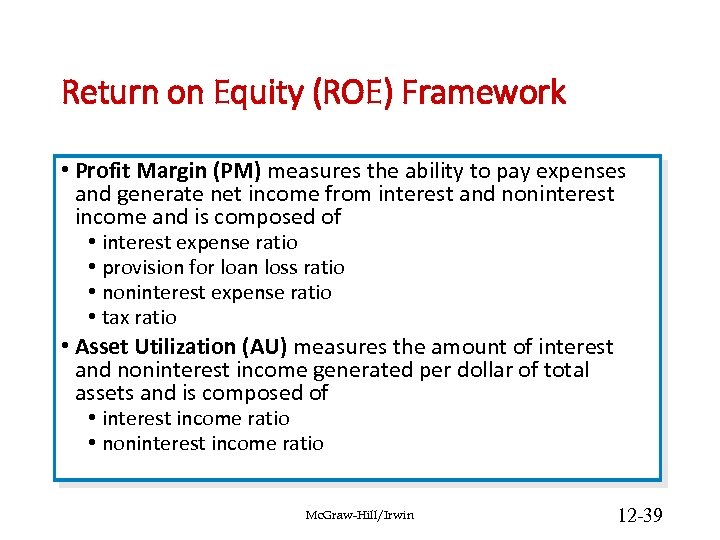 Return on Equity (ROE) Framework • Profit Margin (PM) measures the ability to pay expenses and generate net income from interest and noninterest income and is composed of • interest expense ratio • provision for loan loss ratio • noninterest expense ratio • tax ratio • Asset Utilization (AU) measures the amount of interest and noninterest income generated per dollar of total assets and is composed of • interest income ratio • noninterest income ratio Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -39
Return on Equity (ROE) Framework • Profit Margin (PM) measures the ability to pay expenses and generate net income from interest and noninterest income and is composed of • interest expense ratio • provision for loan loss ratio • noninterest expense ratio • tax ratio • Asset Utilization (AU) measures the amount of interest and noninterest income generated per dollar of total assets and is composed of • interest income ratio • noninterest income ratio Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -39
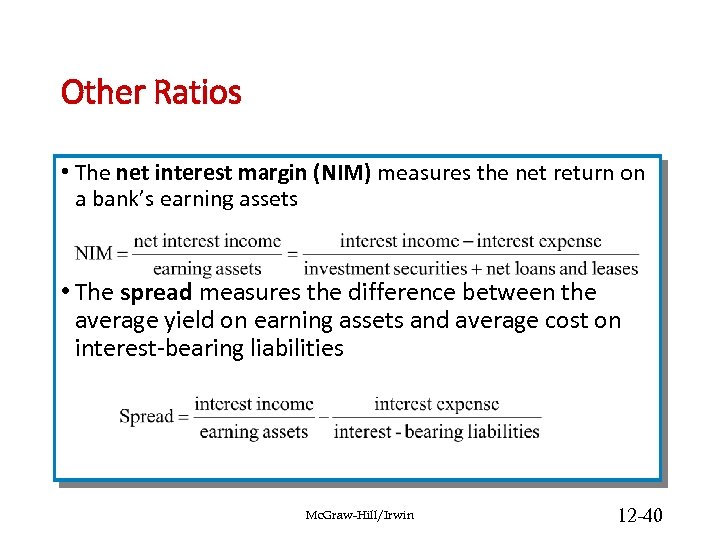 Other Ratios • The net interest margin (NIM) measures the net return on a bank’s earning assets • The spread measures the difference between the average yield on earning assets and average cost on interest-bearing liabilities Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -40
Other Ratios • The net interest margin (NIM) measures the net return on a bank’s earning assets • The spread measures the difference between the average yield on earning assets and average cost on interest-bearing liabilities Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -40
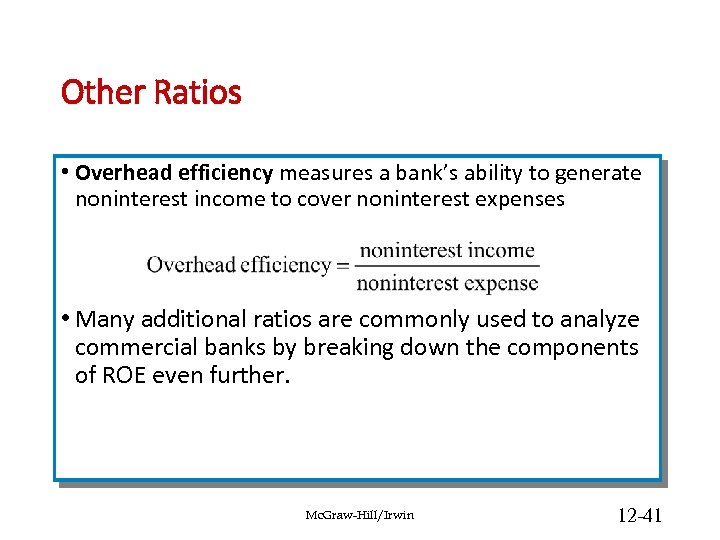 Other Ratios • Overhead efficiency measures a bank’s ability to generate noninterest income to cover noninterest expenses • Many additional ratios are commonly used to analyze commercial banks by breaking down the components of ROE even further. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -41
Other Ratios • Overhead efficiency measures a bank’s ability to generate noninterest income to cover noninterest expenses • Many additional ratios are commonly used to analyze commercial banks by breaking down the components of ROE even further. Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin 12 -41


