9d3f2e755b3edd0a3ad402add41472d4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Chapter 3 Demand Supply
Chapter 3 Demand Supply
 The Law of Demand ¡ Demand l How much of a good or service people will purchase at any price during a specified time period, other things being constant. l Simply stated: How much people are willing and able to buy 2
The Law of Demand ¡ Demand l How much of a good or service people will purchase at any price during a specified time period, other things being constant. l Simply stated: How much people are willing and able to buy 2
 The Law of Demand ¡ Law of Demand l Quantity demanded is inversely related to price, holding other factors constant. ¡Price # Qd $ ¡Price $ Qd # 3
The Law of Demand ¡ Law of Demand l Quantity demanded is inversely related to price, holding other factors constant. ¡Price # Qd $ ¡Price $ Qd # 3
 The Demand Schedule ¡ The demand schedule l Table relating prices to quantity demanded Demand Curve l Negatively sloped line showing inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, all else equal 4
The Demand Schedule ¡ The demand schedule l Table relating prices to quantity demanded Demand Curve l Negatively sloped line showing inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, all else equal 4
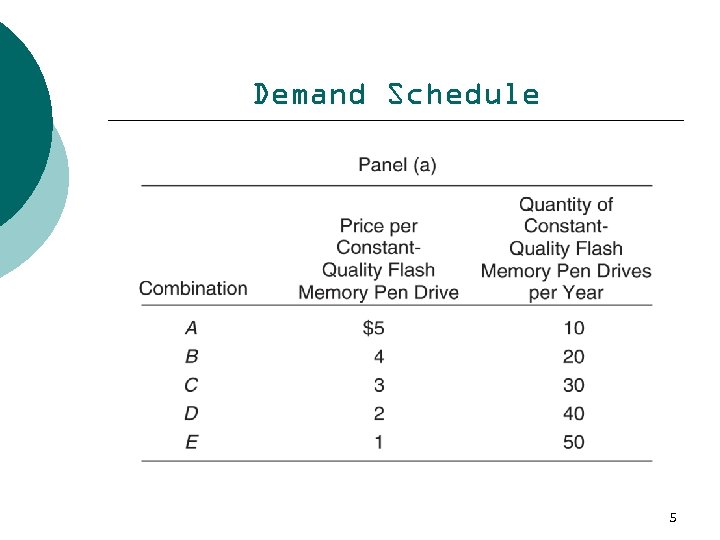 Demand Schedule 5
Demand Schedule 5
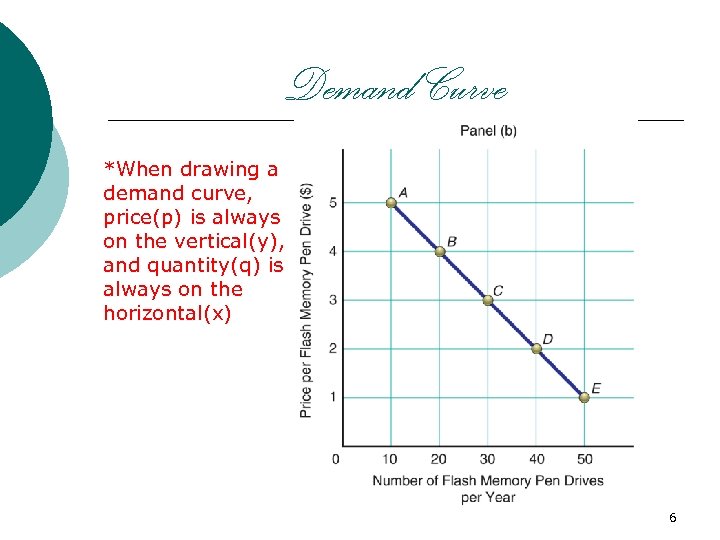 Demand Curve *When drawing a demand curve, price(p) is always on the vertical(y), and quantity(q) is always on the horizontal(x) 6
Demand Curve *When drawing a demand curve, price(p) is always on the vertical(y), and quantity(q) is always on the horizontal(x) 6
 The Demand Schedule ¡ ¡ Individual versus market demand curves Market Demand l The demand of all consumers in the marketplace for a particular good or service l Summation at each price of the quantity demanded by each individual 7
The Demand Schedule ¡ ¡ Individual versus market demand curves Market Demand l The demand of all consumers in the marketplace for a particular good or service l Summation at each price of the quantity demanded by each individual 7
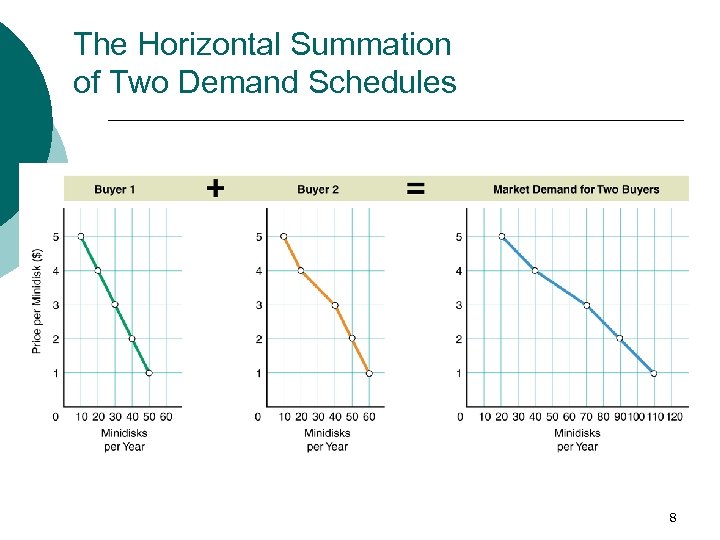 The Horizontal Summation of Two Demand Schedules 8
The Horizontal Summation of Two Demand Schedules 8
 normal and inferior goods ¡ Normal Goods l ¡ Goods for which demand rises as income rises, most goods are normal goods (DVDs, shoes, computers, etc…) Inferior Goods l Goods for which demand falls as income rises (beans, top ramen) ¡ Now you can afford better goods 9
normal and inferior goods ¡ Normal Goods l ¡ Goods for which demand rises as income rises, most goods are normal goods (DVDs, shoes, computers, etc…) Inferior Goods l Goods for which demand falls as income rises (beans, top ramen) ¡ Now you can afford better goods 9
 Shifts in Demand ¡ Determinants of demand l Income l Tastes and preferences l The prices of related goods ¡ Substitutes l ¡ butter/margarine Complements l Computers/printers 10
Shifts in Demand ¡ Determinants of demand l Income l Tastes and preferences l The prices of related goods ¡ Substitutes l ¡ butter/margarine Complements l Computers/printers 10
 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Substitutes l Two goods are substitutes when a change in the price of one causes a shift in demand for the other in the same direction as the price change. *If the price of butter goes up, the demand for margarine will increase 11
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Substitutes l Two goods are substitutes when a change in the price of one causes a shift in demand for the other in the same direction as the price change. *If the price of butter goes up, the demand for margarine will increase 11
 Example: Kids Give Barbie Dolls and Legos the Boot ¡ Barbie dolls and Lego building blocks were among the most popular toys for many years. ¡ Since the early 2000 s, annual purchases of such toys have fallen by as much as 25%. The demand for all toys has decreased ¡ At the same time, prices of substitute forms of entertainment, such as video games and computer software, have declined. 12
Example: Kids Give Barbie Dolls and Legos the Boot ¡ Barbie dolls and Lego building blocks were among the most popular toys for many years. ¡ Since the early 2000 s, annual purchases of such toys have fallen by as much as 25%. The demand for all toys has decreased ¡ At the same time, prices of substitute forms of entertainment, such as video games and computer software, have declined. 12
 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Complements l Two goods are complements when a change in the price of one causes an opposite shift in the demand curve for the other. *If the price of computers go down, more people will now be able to afford a printer and the demand will increase. 13
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Complements l Two goods are complements when a change in the price of one causes an opposite shift in the demand curve for the other. *If the price of computers go down, more people will now be able to afford a printer and the demand will increase. 13
 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Determinants of demand l Expectations ¡ Future prices l What if you know it will cost more in a month? ¡ ¡ l Income – raise? Product availability– shortage? Market size (number of buyers) More people means what? ? ? 14
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Determinants of demand l Expectations ¡ Future prices l What if you know it will cost more in a month? ¡ ¡ l Income – raise? Product availability– shortage? Market size (number of buyers) More people means what? ? ? 14
 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Changes in demand versus changes in quantity demanded l A change in one or more of the nonprice determinants (income, tastes, etc. ) will lead to a change in demand. ¡ This is a shift of the whole curve. 15
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Changes in demand versus changes in quantity demanded l A change in one or more of the nonprice determinants (income, tastes, etc. ) will lead to a change in demand. ¡ This is a shift of the whole curve. 15
 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Changes in demand versus changes in quantity demanded l A change in a good’s own price leads to a change in quantity demanded. ¡ This is a movement along the same curve. l ∆D is not the same as ∆Qd. 16
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) ¡ Changes in demand versus changes in quantity demanded l A change in a good’s own price leads to a change in quantity demanded. ¡ This is a movement along the same curve. l ∆D is not the same as ∆Qd. 16
 Question? ? ? When people realize that Soulja Boy can’t really rap, and that he isn’t that good, will this lead to a change in Demand or a change in Quantity Demanded for his CD? 17
Question? ? ? When people realize that Soulja Boy can’t really rap, and that he isn’t that good, will this lead to a change in Demand or a change in Quantity Demanded for his CD? 17
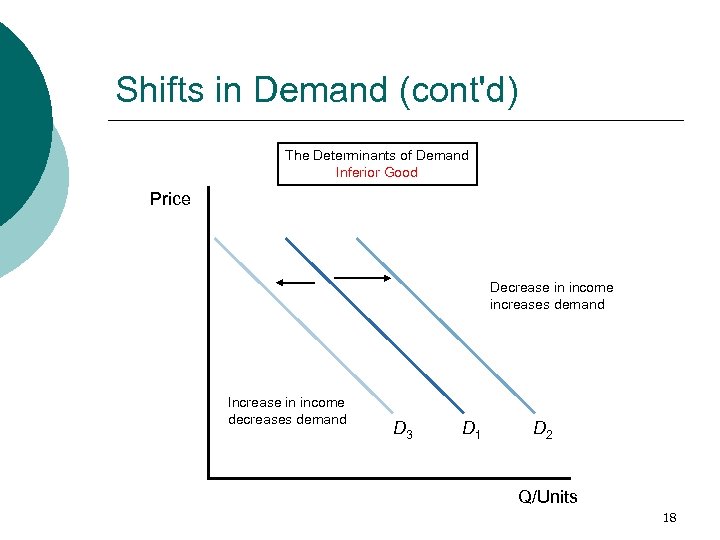 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Inferior Good Price Decrease in income increases demand Increase in income decreases demand D 3 D 1 D 2 Q/Units 18
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Inferior Good Price Decrease in income increases demand Increase in income decreases demand D 3 D 1 D 2 Q/Units 18
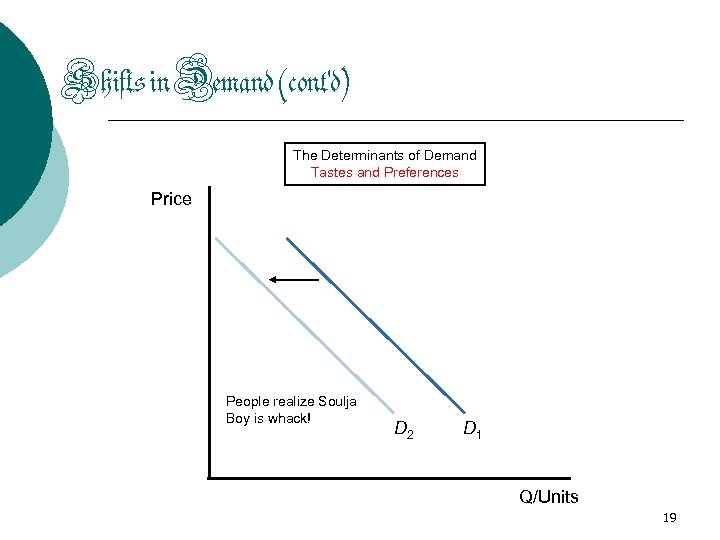 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Tastes and Preferences Price People realize Soulja Boy is whack! D 2 D 1 Q/Units 19
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Tastes and Preferences Price People realize Soulja Boy is whack! D 2 D 1 Q/Units 19
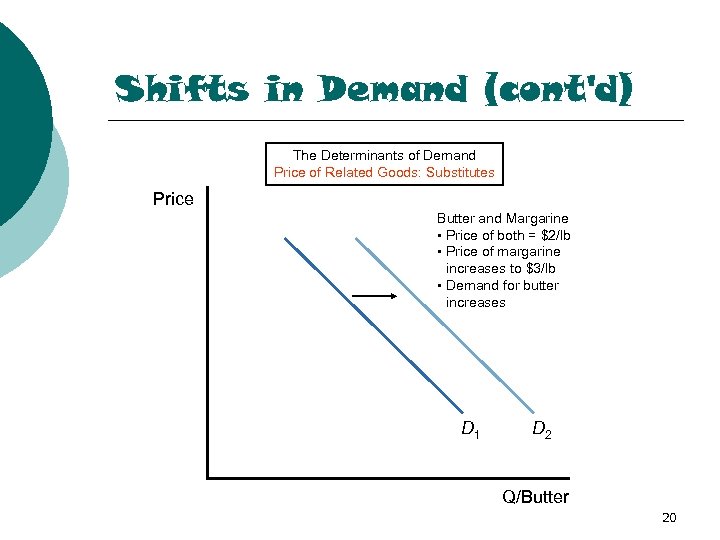 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Price of Related Goods: Substitutes Price Butter and Margarine • Price of both = $2/lb • Price of margarine increases to $3/lb • Demand for butter increases D 1 D 2 Q/Butter 20
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Price of Related Goods: Substitutes Price Butter and Margarine • Price of both = $2/lb • Price of margarine increases to $3/lb • Demand for butter increases D 1 D 2 Q/Butter 20
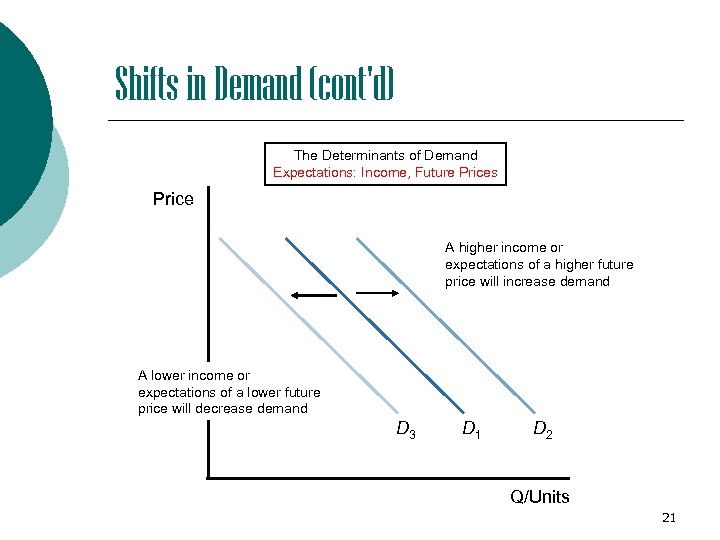 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Expectations: Income, Future Prices Price A higher income or expectations of a higher future price will increase demand A lower income or expectations of a lower future price will decrease demand D 3 D 1 D 2 Q/Units 21
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Expectations: Income, Future Prices Price A higher income or expectations of a higher future price will increase demand A lower income or expectations of a lower future price will decrease demand D 3 D 1 D 2 Q/Units 21
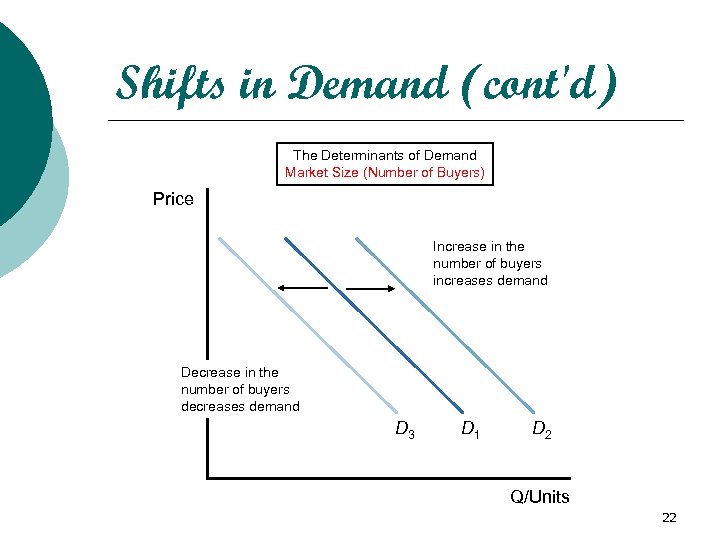 Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Market Size (Number of Buyers) Price Increase in the number of buyers increases demand Decrease in the number of buyers decreases demand D 3 D 1 D 2 Q/Units 22
Shifts in Demand (cont'd) The Determinants of Demand Market Size (Number of Buyers) Price Increase in the number of buyers increases demand Decrease in the number of buyers decreases demand D 3 D 1 D 2 Q/Units 22
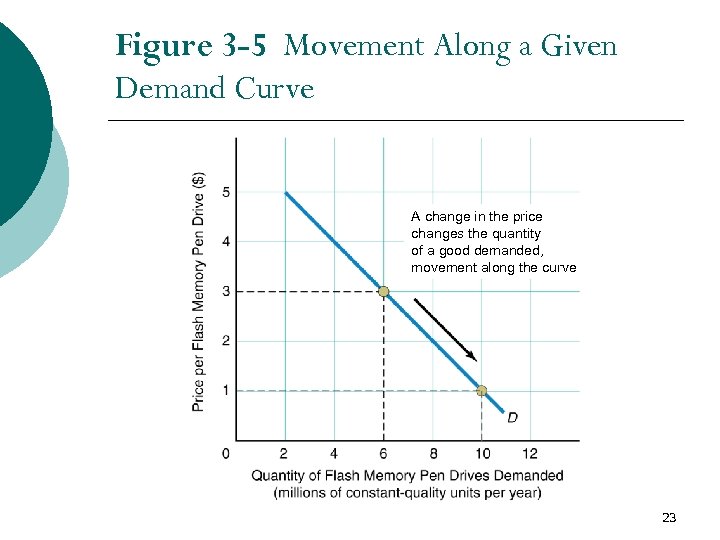 Figure 3 -5 Movement Along a Given Demand Curve A change in the price changes the quantity of a good demanded, movement along the curve 23
Figure 3 -5 Movement Along a Given Demand Curve A change in the price changes the quantity of a good demanded, movement along the curve 23
 The Law of Supply ¡ Supply l Schedule showing relationship between price and quantity supplied for a specified time period, other things being equal l The amount of a product or service that firms are willing to sell at alternative prices 24
The Law of Supply ¡ Supply l Schedule showing relationship between price and quantity supplied for a specified time period, other things being equal l The amount of a product or service that firms are willing to sell at alternative prices 24
 The Law of Supply (cont'd) ¡ Law of Supply l The price of a product or service and the quantity supplied are directly related. ¡ P # Qs # ¡ P $ Qs $ Confusing, right? It will make sense when we look at supply and demand combined 25
The Law of Supply (cont'd) ¡ Law of Supply l The price of a product or service and the quantity supplied are directly related. ¡ P # Qs # ¡ P $ Qs $ Confusing, right? It will make sense when we look at supply and demand combined 25
 The Supply Schedule ¡ ¡ The supply schedule is a table relating prices to quantity supplied at each price. Supply Curve l A graphical representation of the supply schedule l Positively sloped line showing direct relationship between price and quantity supplied, all else equal 26
The Supply Schedule ¡ ¡ The supply schedule is a table relating prices to quantity supplied at each price. Supply Curve l A graphical representation of the supply schedule l Positively sloped line showing direct relationship between price and quantity supplied, all else equal 26
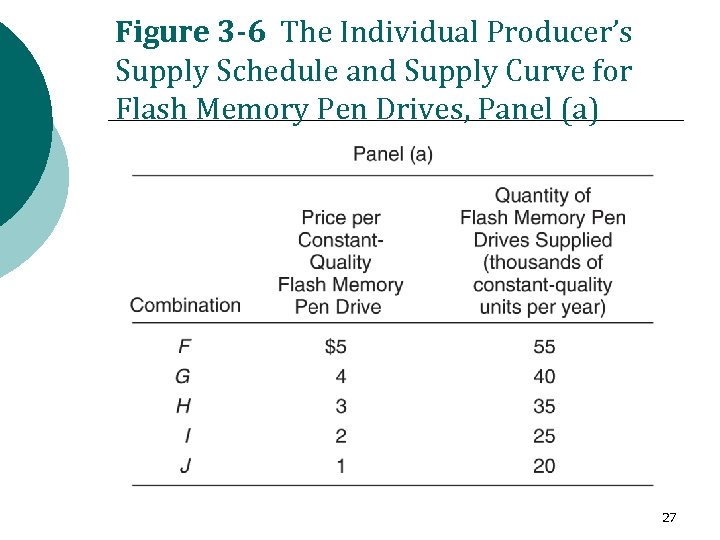 Figure 3 -6 The Individual Producer’s Supply Schedule and Supply Curve for Flash Memory Pen Drives, Panel (a) 27
Figure 3 -6 The Individual Producer’s Supply Schedule and Supply Curve for Flash Memory Pen Drives, Panel (a) 27
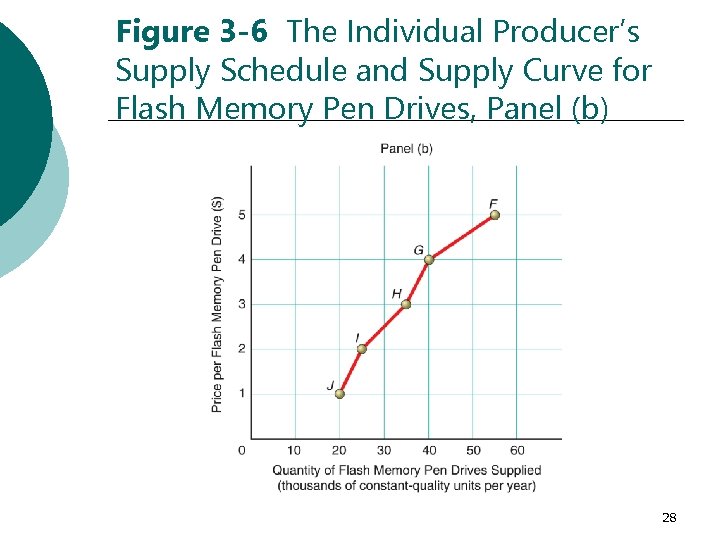 Figure 3 -6 The Individual Producer’s Supply Schedule and Supply Curve for Flash Memory Pen Drives, Panel (b) 28
Figure 3 -6 The Individual Producer’s Supply Schedule and Supply Curve for Flash Memory Pen Drives, Panel (b) 28
 Shifts in Supply ¡ Scenario l A new method of manufacturing flash memory pen drives reduces the cost of production dramatically. 29
Shifts in Supply ¡ Scenario l A new method of manufacturing flash memory pen drives reduces the cost of production dramatically. 29
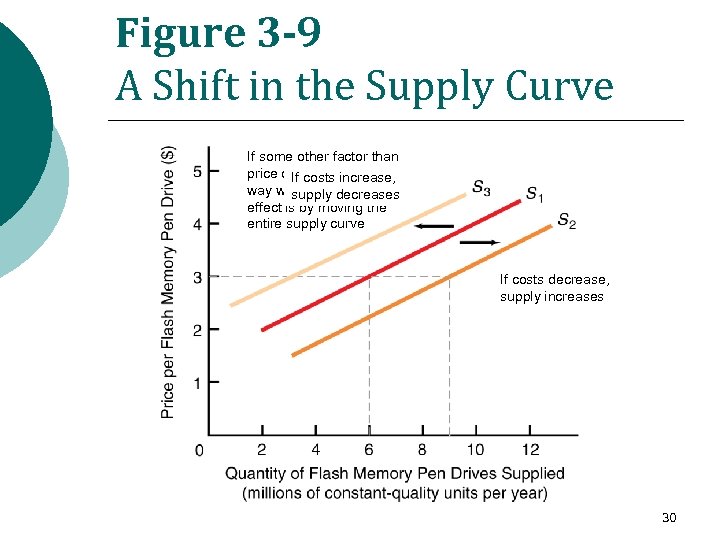 Figure 3 -9 A Shift in the Supply Curve If some other factor than price changes, increase, If costs the only way wesupply decreases can show its effect is by moving the entire supply curve If costs decrease, supply increases 30
Figure 3 -9 A Shift in the Supply Curve If some other factor than price changes, increase, If costs the only way wesupply decreases can show its effect is by moving the entire supply curve If costs decrease, supply increases 30
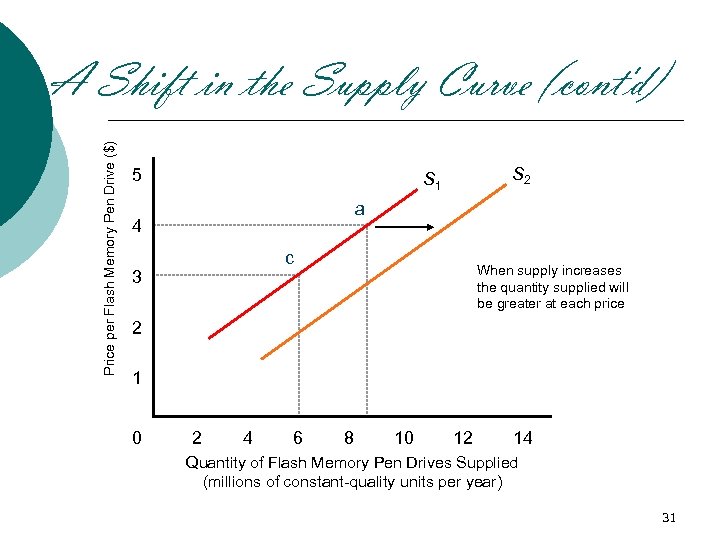 Price per Flash Memory Pen Drive ($) A Shift in the Supply Curve (cont'd) 5 S 2 S 1 a 4 c 3 When supply increases the quantity supplied will be greater at each price 2 1 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Quantity of Flash Memory Pen Drives Supplied (millions of constant-quality units per year) 31
Price per Flash Memory Pen Drive ($) A Shift in the Supply Curve (cont'd) 5 S 2 S 1 a 4 c 3 When supply increases the quantity supplied will be greater at each price 2 1 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Quantity of Flash Memory Pen Drives Supplied (millions of constant-quality units per year) 31
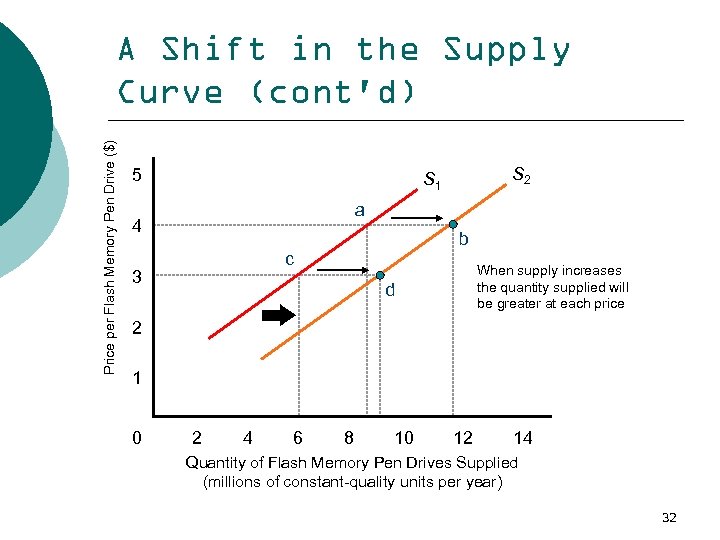 Price per Flash Memory Pen Drive ($) A Shift in the Supply Curve (cont'd) 5 S 2 S 1 a 4 b c 3 When supply increases the quantity supplied will be greater at each price d 2 1 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Quantity of Flash Memory Pen Drives Supplied (millions of constant-quality units per year) 32
Price per Flash Memory Pen Drive ($) A Shift in the Supply Curve (cont'd) 5 S 2 S 1 a 4 b c 3 When supply increases the quantity supplied will be greater at each price d 2 1 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Quantity of Flash Memory Pen Drives Supplied (millions of constant-quality units per year) 32
 Shifts in Supply (cont'd) ¡ Determinants of supply l Cost of inputs l Technology and productivity l Taxes and subsidies l Price expectations l Number of firms in industry 33
Shifts in Supply (cont'd) ¡ Determinants of supply l Cost of inputs l Technology and productivity l Taxes and subsidies l Price expectations l Number of firms in industry 33
 Shifts in Supply (cont'd) ¡ Changes in supply versus changes in quantity supplied l A change in one or more of the nonprice determinants will lead to a change in supply. ¡ This is a shift of the whole curve. 34
Shifts in Supply (cont'd) ¡ Changes in supply versus changes in quantity supplied l A change in one or more of the nonprice determinants will lead to a change in supply. ¡ This is a shift of the whole curve. 34
 Shifts in Supply (cont'd) ¡ Changes in supply versus changes in quantity supplied l A change in a good’s own price leads to a change in quantity supplied. ¡ This is a movement along the same curve. l ∆S is not the same as ∆Qs. 35
Shifts in Supply (cont'd) ¡ Changes in supply versus changes in quantity supplied l A change in a good’s own price leads to a change in quantity supplied. ¡ This is a movement along the same curve. l ∆S is not the same as ∆Qs. 35
 putting demand supply together Equilibrium (Market Clearing) Price l The price that clears the market l The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied l The price where the demand curve intersects the supply curve 36
putting demand supply together Equilibrium (Market Clearing) Price l The price that clears the market l The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied l The price where the demand curve intersects the supply curve 36
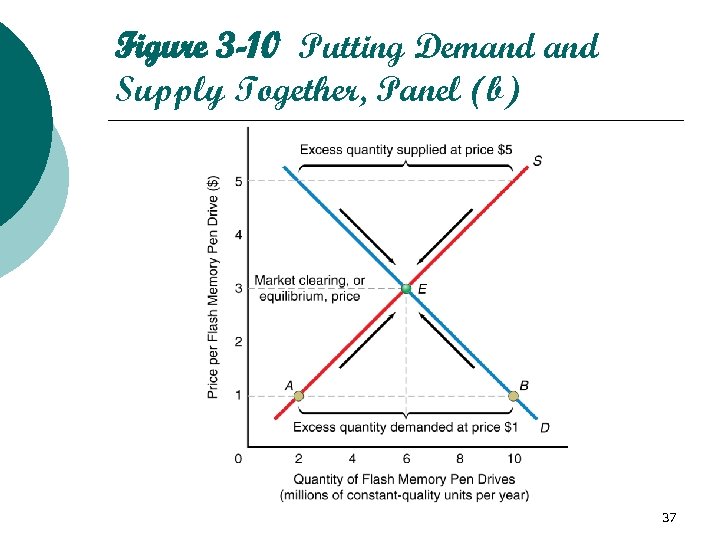 Figure 3 -10 Putting Demand Supply Together, Panel (b) 37
Figure 3 -10 Putting Demand Supply Together, Panel (b) 37
 Putting Demand Supply Together (cont'd) ¡ Shortages l The situation when quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied ¡ Qd > Qs l Exist at any price below the market clearing price 38
Putting Demand Supply Together (cont'd) ¡ Shortages l The situation when quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied ¡ Qd > Qs l Exist at any price below the market clearing price 38
 Putting Demand Supply Together (cont'd) ¡ Surpluses l The situation when quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded ¡ Qd < Qs l Exist at any price above the market clearing price 39
Putting Demand Supply Together (cont'd) ¡ Surpluses l The situation when quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded ¡ Qd < Qs l Exist at any price above the market clearing price 39
 Policy Example: Should Shortages in the Ticket Market Be Solved by Scalpers? ¡ ¡ ¡ If you’ve ever tried to get tickets to the big game you know all about “shortages. ” Since the quantity of tickets is fixed, the price can go pretty high. Enter the scalper. 40
Policy Example: Should Shortages in the Ticket Market Be Solved by Scalpers? ¡ ¡ ¡ If you’ve ever tried to get tickets to the big game you know all about “shortages. ” Since the quantity of tickets is fixed, the price can go pretty high. Enter the scalper. 40
 Issues and Applications: The Market Clearing Prices of Baseball Cards ¡ Various companies, such as Topps and Upper Deck, print sports trading cards that provide photos and stats on pro athletes. ¡ Why are some of the market clearing prices so high? ¡ The answer has to do with demand supply. (A relatively low supply helps explain the relatively high market clearing price. ) ¡ You can buy a “Shoeless” Joe Jackson card for up to $9, 000! 41
Issues and Applications: The Market Clearing Prices of Baseball Cards ¡ Various companies, such as Topps and Upper Deck, print sports trading cards that provide photos and stats on pro athletes. ¡ Why are some of the market clearing prices so high? ¡ The answer has to do with demand supply. (A relatively low supply helps explain the relatively high market clearing price. ) ¡ You can buy a “Shoeless” Joe Jackson card for up to $9, 000! 41
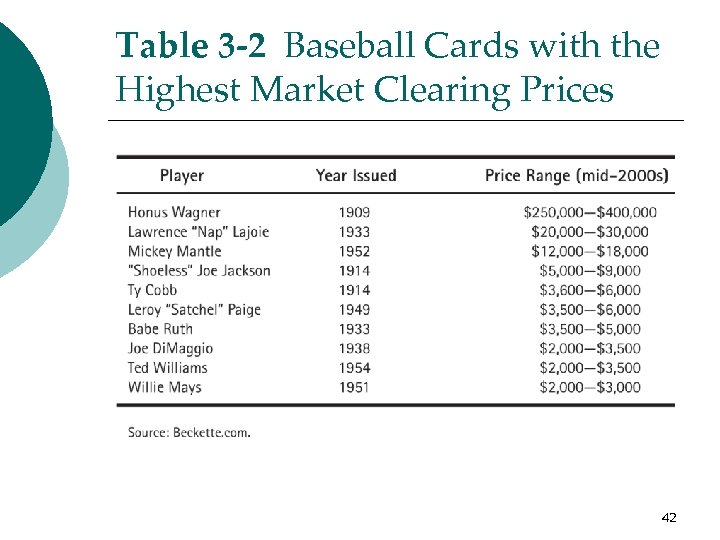 Table 3 -2 Baseball Cards with the Highest Market Clearing Prices 42
Table 3 -2 Baseball Cards with the Highest Market Clearing Prices 42
 Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives ¡ The law of demand says that prices and quantity demanded are inversely related. l ¡ At a higher price people buy less, at a lower price people buy more. Relative prices must be distinguished from money prices, since people respond to changes in relative prices. 43
Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives ¡ The law of demand says that prices and quantity demanded are inversely related. l ¡ At a higher price people buy less, at a lower price people buy more. Relative prices must be distinguished from money prices, since people respond to changes in relative prices. 43
 Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives (cont'd) ¡ A change in quantity demanded versus a change in demand l A change in quantity demanded is a movement along the same demand curve. l A change in demand is a shift of the whole demand curve. 44
Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives (cont'd) ¡ A change in quantity demanded versus a change in demand l A change in quantity demanded is a movement along the same demand curve. l A change in demand is a shift of the whole demand curve. 44
 Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives (cont'd) ¡ The law of supply states that price and quantity supplied are directly related. l ¡ At a high price firms offer more; at a low price firms offer less. A change in quantity supplied versus a change in supply l l A change in quantity supplied is a movement along the same supply curve. A change in supply is a shift of the whole supply curve. 45
Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives (cont'd) ¡ The law of supply states that price and quantity supplied are directly related. l ¡ At a high price firms offer more; at a low price firms offer less. A change in quantity supplied versus a change in supply l l A change in quantity supplied is a movement along the same supply curve. A change in supply is a shift of the whole supply curve. 45
 Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives (cont'd) ¡ Determining market price and equilibrium quantity l The demand supply curves intersect at the market clearing, or equilibrium point. l Surpluses exist if the price of the good is greater than the market price. l Shortages exist when the price of a good is below the market price. 46
Summary Discussion of Learning Objectives (cont'd) ¡ Determining market price and equilibrium quantity l The demand supply curves intersect at the market clearing, or equilibrium point. l Surpluses exist if the price of the good is greater than the market price. l Shortages exist when the price of a good is below the market price. 46
 End of Chapter 3 Demand Supply
End of Chapter 3 Demand Supply


