da9d929c2a16f46669475ff1031c421d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

Chapter 3 Databases and Data Warehouses Building Business Intelligence Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 1

What is the chapter all about This chapter deals with the different elements of creating knowledge in an organization and having the right tools to work with this knowledge to gain Business Intelligence. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 2

What is the chapter all about Having the right tools to create/build Business Intelligence revolves around the capturing, use and management of information, hence Information Resource Management gains importance. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 3
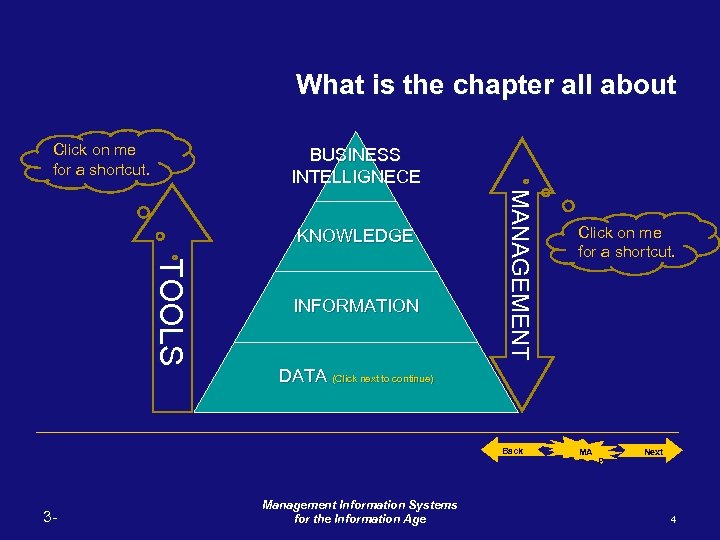
What is the chapter all about Click on me for a shortcut. BUSINESS INTELLIGNECE T O O LS INFORMATION MA N A G E ME N T KNOWLEDGE DATA (Click next to continue) Back 3 - Click on me for a shortcut. Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 4
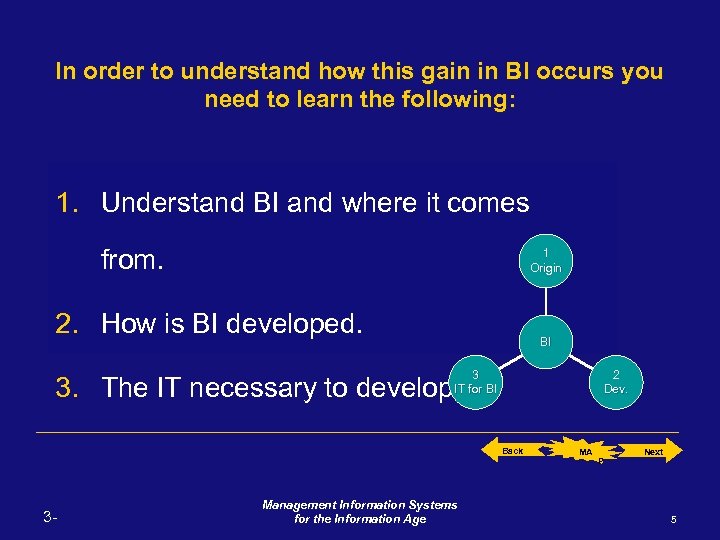
In order to understand how this gain in BI occurs you need to learn the following: 1. Understand BI and where it comes from. 1 Origin 2. How is BI developed. BI 3 IT for BI 2 Dev. 3. The IT necessary to develop BI. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 5
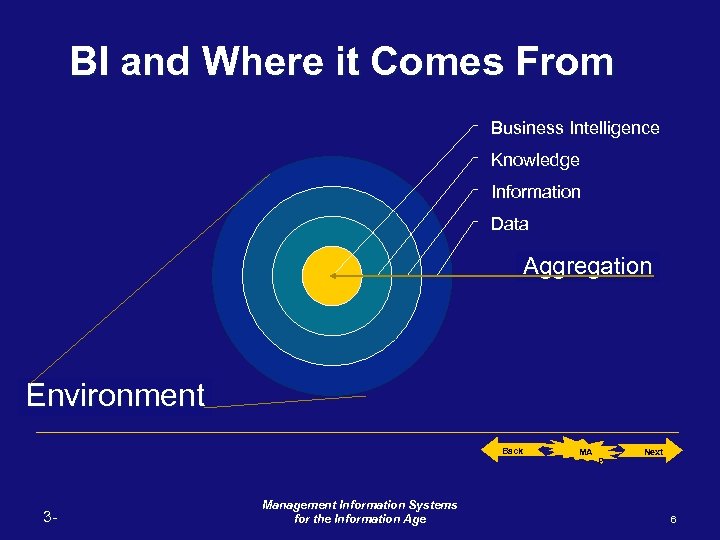
BI and Where it Comes From Business Intelligence Knowledge Information Data Aggregation Environment Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 6
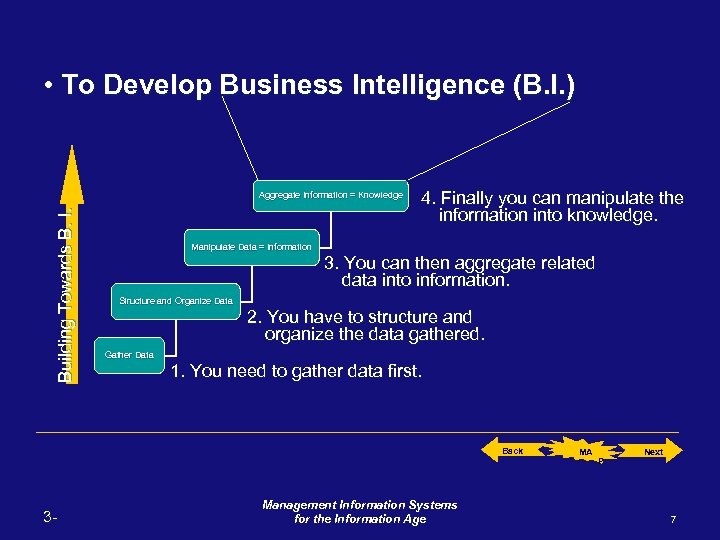
• To Develop Business Intelligence (B. I. ) Building Towards B. I. Aggregate Information = Knowledge 4. Finally you can manipulate the information into knowledge. Manipulate Data = Information 3. You can then aggregate related data into information. Structure and Organize Data 2. You have to structure and organize the data gathered. Gather Data 1. You need to gather data first. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 7
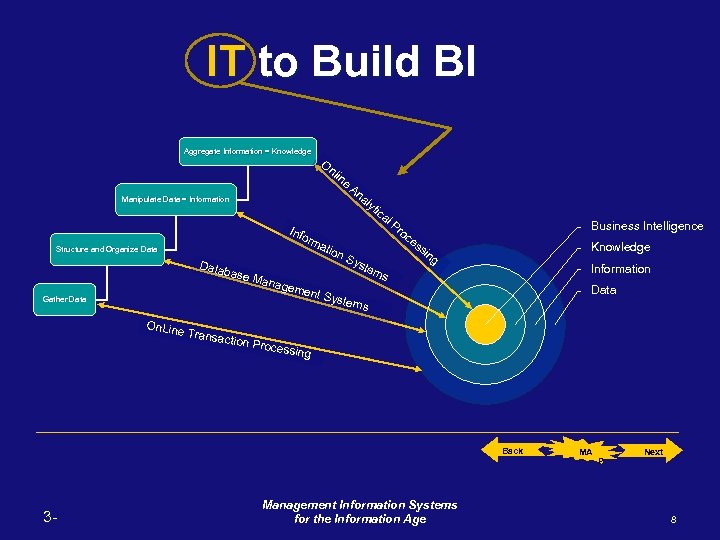
IT to Build BI Aggregate Information = Knowledge O nl in e An al yt ica l. P ro Info ce rm ss atio in n. S g yst Data em base s Mana geme nt Sy stem s Manipulate Data = Information Structure and Organize Data Gather Data Business Intelligence Knowledge Information Data On. Line Transa ction P rocess ing Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 8
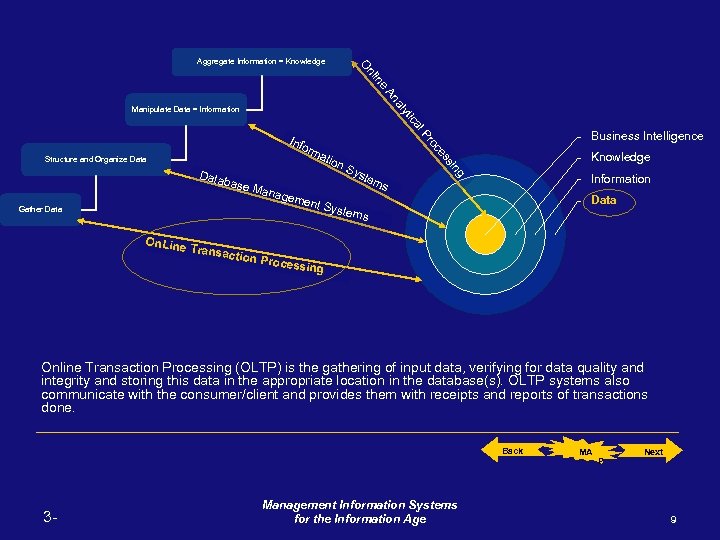
g siin s es es oc oc Prr ll P ca ica ytt y al An An Manipulate Data = Information Structure and Organize Data Gather Data ne iin nl n O O Aggregate Information = Knowledge Business Intelligence Info rm atio n. S yst Data em base s Mana geme nt Sy stem s Knowledge Information Data On. Line Transa ction P rocess ing Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) is the gathering of input data, verifying for data quality and integrity and storing this data in the appropriate location in the database(s). OLTP systems also communicate with the consumer/client and provides them with receipts and reports of transactions done. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 9
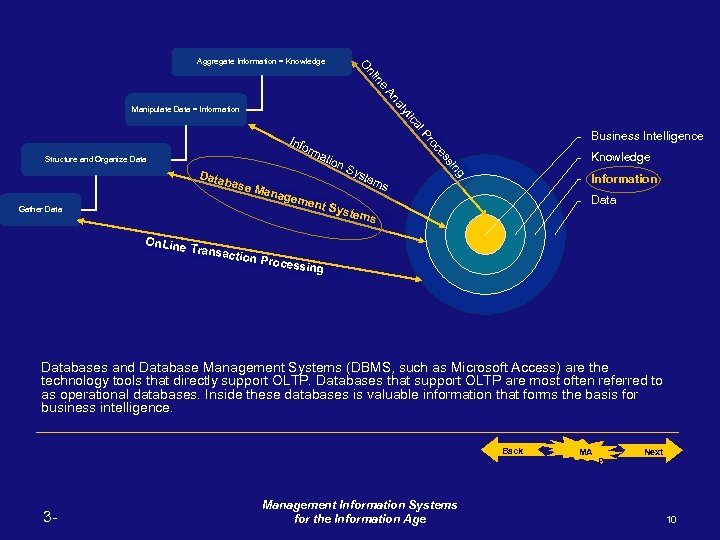
g siin s es es oc oc Prr ll P ca ica ytt y al An An Manipulate Data = Information Structure and Organize Data Gather Data ne iin nl n O O Aggregate Information = Knowledge Business Intelligence Info rm atio n. S yst Data em base s Mana geme nt Sy stem s Knowledge Information Data On. Line Transa ction P rocess ing Databases and Database Management Systems (DBMS, such as Microsoft Access) are the technology tools that directly support OLTP. Databases that support OLTP are most often referred to as operational databases. Inside these databases is valuable information that forms the basis for business intelligence. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 10
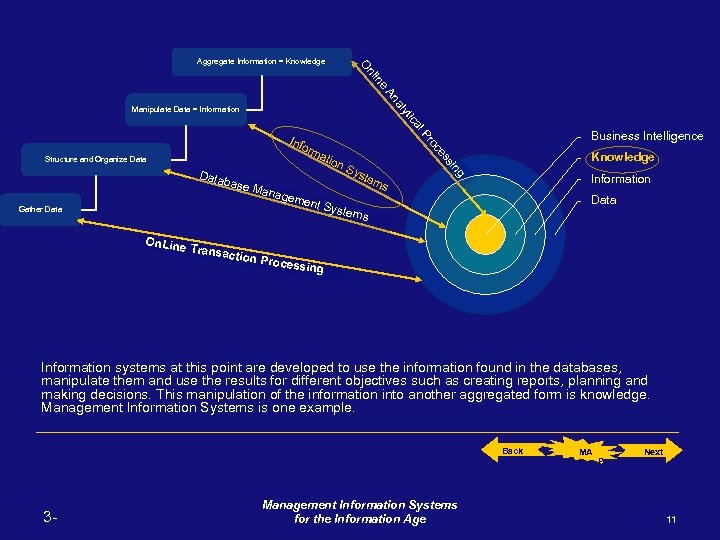
g siin s es es oc oc Prr ll P ca ica ytt y al An An Manipulate Data = Information Structure and Organize Data Gather Data ne iin nl n O O Aggregate Information = Knowledge Business Intelligence Info rm atio n. S yst Data em base s Mana geme nt Sy stem s Knowledge Information Data On. Line Transa ction P rocess ing Information systems at this point are developed to use the information found in the databases, manipulate them and use the results for different objectives such as creating reports, planning and making decisions. This manipulation of the information into another aggregated form is knowledge. Management Information Systems is one example. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 11
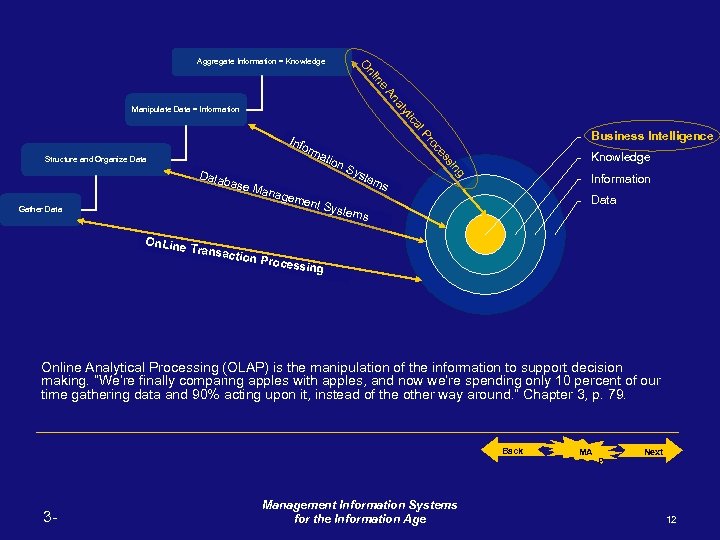
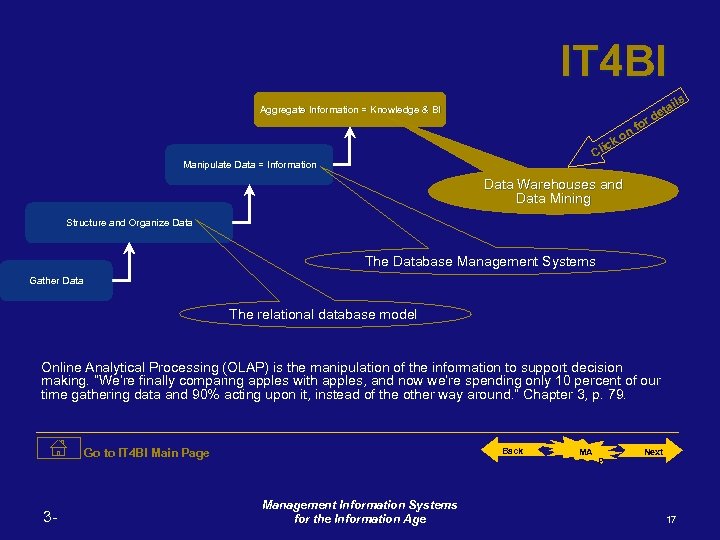
g siin s es es oc oc Prr ll P ca ica ytt y al An An Manipulate Data = Information Structure and Organize Data Gather Data ne iin nl n O O Aggregate Information = Knowledge Business Intelligence Info rm atio n. S yst Data em base s Mana geme nt Sy stem s Knowledge Information Data On. Line Transa ction P rocess ing Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is the manipulation of the information to support decision making. “We’re finally comparing apples with apples, and now we’re spending only 10 percent of our time gathering data and 90% acting upon it, instead of the other way around. ” Chapter 3, p. 79. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 12
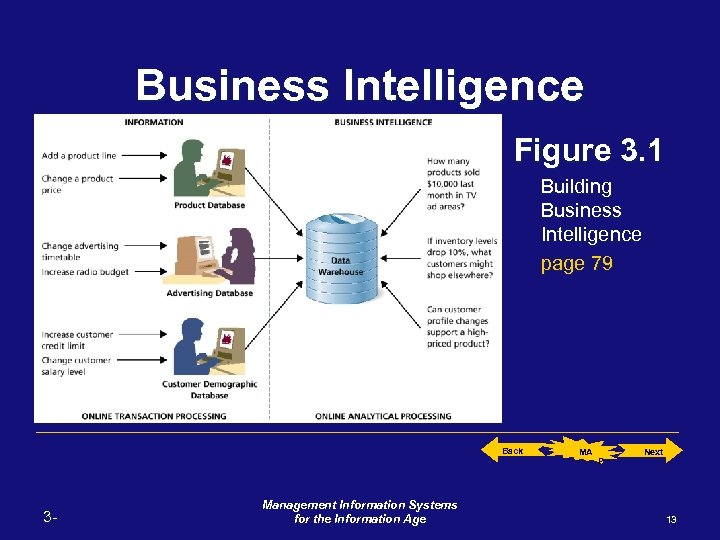
Business Intelligence Figure 3. 1 Building Business Intelligence page 79 Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 13
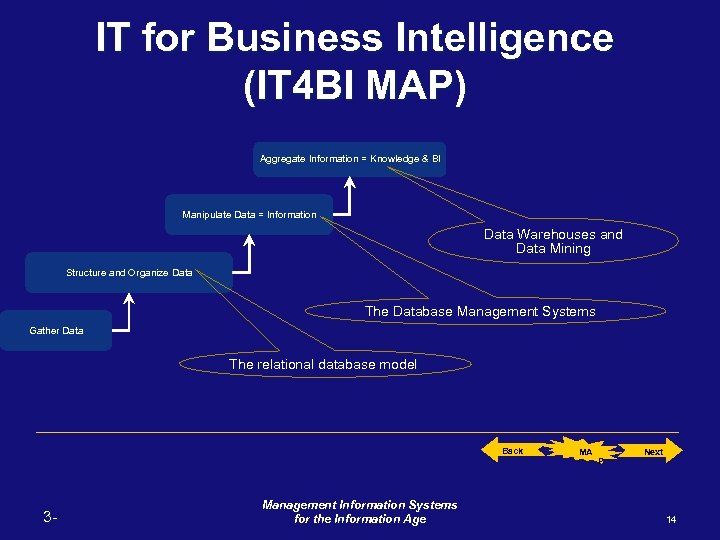
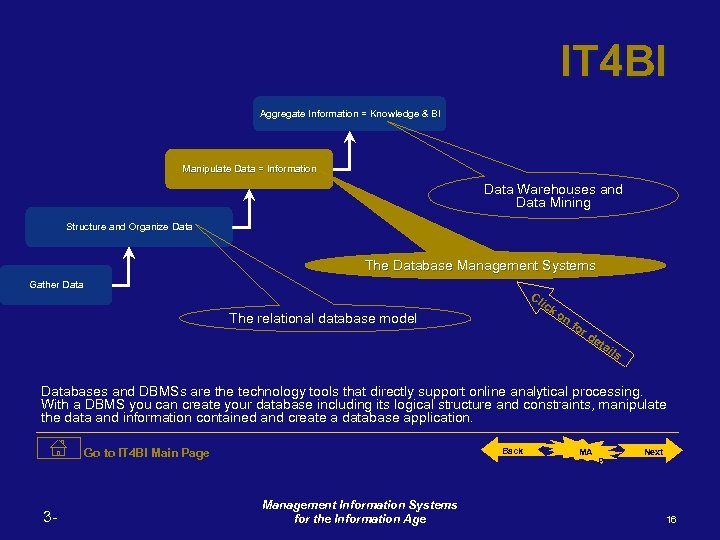
IT for Business Intelligence (IT 4 BI MAP) Aggregate Information = Knowledge & BI Manipulate Data = Information Data Warehouses and Data Mining Structure and Organize Data The Database Management Systems Gather Data The relational database model Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 14
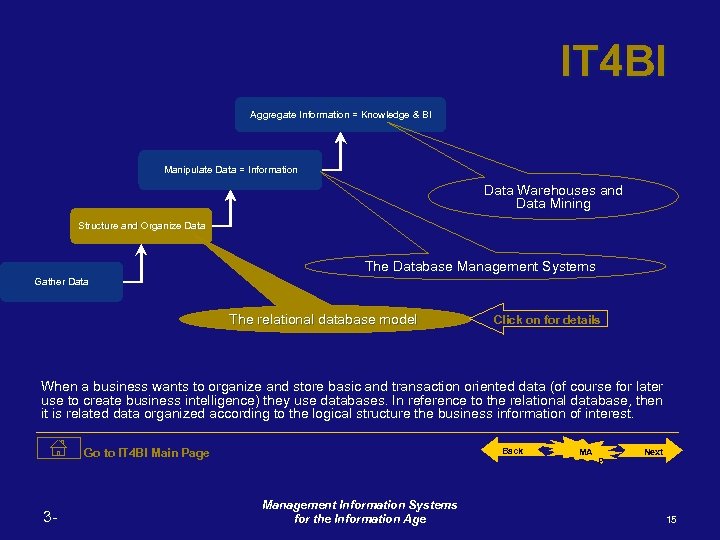
IT 4 BI Aggregate Information = Knowledge & BI Manipulate Data = Information Data Warehouses and Data Mining Structure and Organize Data The Database Management Systems Gather Data The relational database model Click on for details When a business wants to organize and store basic and transaction oriented data (of course for later use to create business intelligence) they use databases. In reference to the relational database, then it is related data organized according to the logical structure the business information of interest. Go to IT 4 BI Main Page 3 - Back Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 15
IT 4 BI Aggregate Information = Knowledge & BI Manipulate Data = Information Data Warehouses and Data Mining Structure and Organize Data The Database Management Systems Gather Data Cl ick on fo rd et ail s The relational database model Databases and DBMSs are the technology tools that directly support online analytical processing. With a DBMS you can create your database including its logical structure and constraints, manipulate the data and information contained and create a database application. Go to IT 4 BI Main Page 3 - Back Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 16
IT 4 BI Aggregate Information = Knowledge & BI on ick Cl Manipulate Data = Information ils eta d for Data Warehouses and Data Mining Structure and Organize Data The Database Management Systems Gather Data The relational database model Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) is the manipulation of the information to support decision making. “We’re finally comparing apples with apples, and now we’re spending only 10 percent of our time gathering data and 90% acting upon it, instead of the other way around. ” Chapter 3, p. 79. Go to IT 4 BI Main Page 3 - Back Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 17

MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE The success of an organization strongly depends on the proper organization and management of the information as it relates to the organizations’ short and long term objectives. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 18

MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE Some of the issues that are important when it comes to the management of the information in the organization are: n n Information officers. The influence of changes in technology on the organizations information. Information ownership. Ethical issues. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 19

MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE Who Should Oversee the Organization’s Information? n Chief information officer (CIO) - responsible for overseeing an organization’s information resource. n Data administration - plans for, oversees the development of, and monitors the information resource. n Database administration - responsible for the more technical and operational aspects of managing the information contained in organizational databases. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 20

MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE How Will Changes in Technology Affect Organizing and Managing Information? n n As new technologies become available, you should ask yourself whether those technologies will help you organize and manage your information better. One of the greatest technological changes that will occur over the coming years is a convergence of different tools that will help you better organize and manage information. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 21

MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE Is Information Ownership a Consideration? On Your Own n n Information ownership is a key consideration in today’s informationbased business environment. Ownership refers to who is responsible for information quality. CRUD – Defining Information Ownership (p. 102) Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 22

MANAGING THE INFORMATION RESOURCE What Are the Ethics Involved in Managing and Organizing Information? n n Databases, data warehouses, DBMSs, and data mining tools make it possible for people to easily access all kinds of organizational information. How does an organization safeguard against the unethical use of information within the organization? Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 23

Closing Case Study One We’ve Got OLTP Covered; Let’s Go on to OLAP n What is the single most important factor that hinders all organizations in general from providing good online analytical processing (OLAP) support? n Why is it so much easier for organizations to provide good online transaction processing (OLTP) support? Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 24

Closing Case Study Two Mining Data n Consider the issue of timely information with respect to the businesses discussed in the case. n Which of the businesses must have the most up-to-date information in its data warehouse? Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 25

Summary Student Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe business intelligence and its role in an organization. Differentiate between databases and data warehouses with respect to their focus on online transaction processing and online analytical processing. List and describe the key characteristics of a relational database. Define the five software components of a database management system. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 26

Summary Student Learning Outcomes 5. 6. 7. List and describe the key characteristics of a data warehouse. Define the four major types of data mining tools in a data warehouse environment. List key considerations in managing the information resource in an organization. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 27

Summary Assignments & Exercises 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Finding “hacked” databases Defining queries for a video rental store Creating a query Career opportunities in your major Salaries for database administrators Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 28

Real Hot Electronic Commerce Searching Online Databases and Information Repositories n n n Financial aid resources Libraries Consumer information Demographics Real estate Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 29

Visit the Web to Learn More www. mhhe. com/haag n n n Financial aid resources Libraries Consumer information Demographics Real estate Data warehouses and data mining tools Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 30

Appendix Beyond this point the slides are not in any order. They are part of the interactivity. Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 31
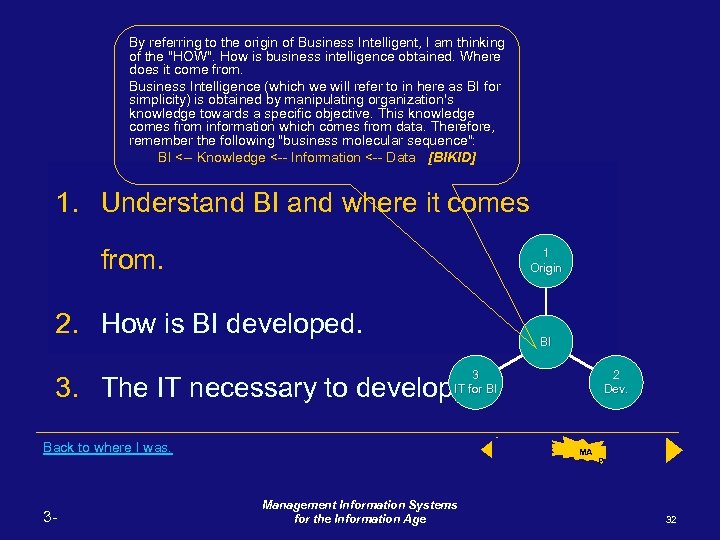
By referring to the origin of Business Intelligent, I am thinking of the "HOW". How is business intelligence obtained. Where does it come from. Business Intelligence (which we will refer to in here as BI for simplicity) is obtained by manipulating organization's knowledge towards a specific objective. This knowledge comes from information which comes from data. Therefore, remember the following "business molecular sequence": BI <-- Knowledge <-- Information <-- Data [BIKID] 1. Understand BI and where it comes from. 1 Origin 2. How is BI developed. BI 3 IT for BI 2 Dev. 3. The IT necessary to develop BI. Back to where I was. 3 - Back Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 32
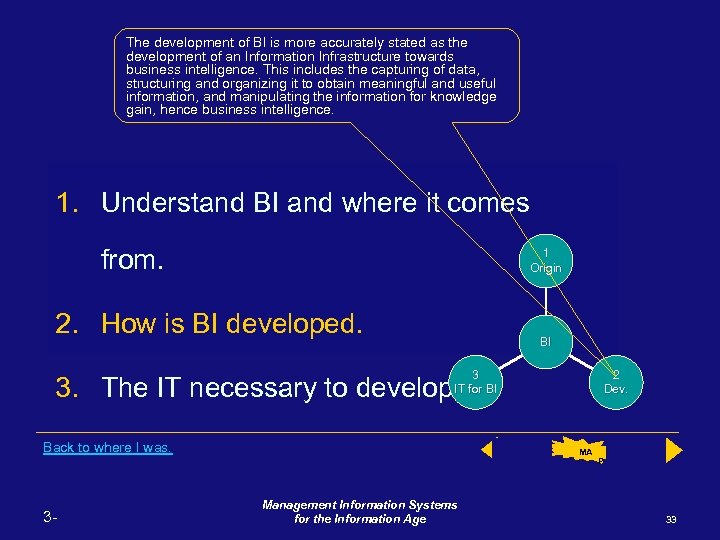
The development of BI is more accurately stated as the development of an Information Infrastructure towards business intelligence. This includes the capturing of data, structuring and organizing it to obtain meaningful and useful information, and manipulating the information for knowledge gain, hence business intelligence. 1. Understand BI and where it comes from. 1 Origin 2. How is BI developed. BI 3 IT for BI 2 Dev. 3. The IT necessary to develop BI. Back to where I was. 3 - Back Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 33
This information infrastructure does not occur on its own. You cannot buy an information infrastructure of the shelf. You need to acquire, use and maintain the IT to develop and build this information infrastructure. This includes database design, database management systems, data warehouses and data mining tools. 1. Understand BI and where it comes from. 1 Origin 2. How is BI developed. BI 3 IT for BI 2 Dev. 3. The IT necessary to develop BI. Back to where I was. 3 - Back Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 34
Chapter 3 What is the chapter all about? Understanding Business Intelligence Where BI comes from To develop BI IT to build BI Data Information Knowledge BI IT 4 BI - MAP The Relational Data Model The DBMS Data Warehouses and Data Mining Managing Information Resources Who should oversee the org. information? How will changes in tech. affect org. and managing information? Is information ownership a consideration? What are the ethical issues Back 3 - Management Information Systems for the Information Age MA P Next 35
da9d929c2a16f46669475ff1031c421d.ppt