767dca8cd7aa2c22fb8c0e679b9fff11.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 Chapter 3 Applications of Data Communications Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 1
Chapter 3 Applications of Data Communications Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 1
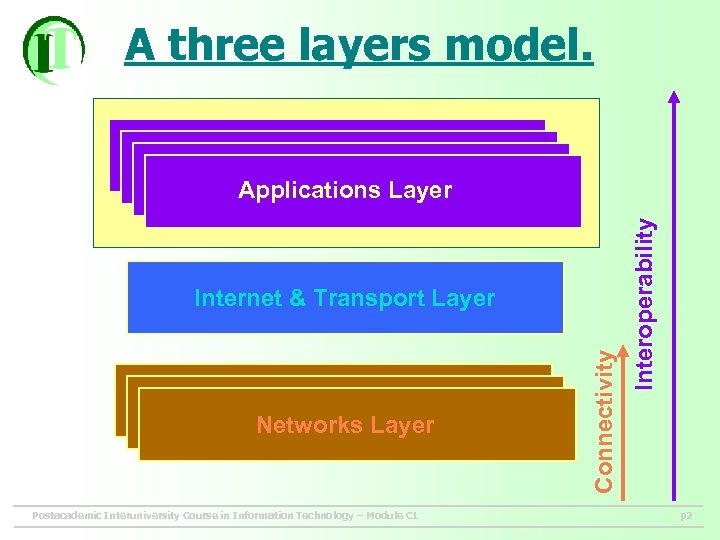 A three layers model. Networks Layer Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 Connectivity Internet & Transport Layer Interoperability Applications Layer p 2
A three layers model. Networks Layer Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 Connectivity Internet & Transport Layer Interoperability Applications Layer p 2
 Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 3
Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 3
 Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 4
Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 4
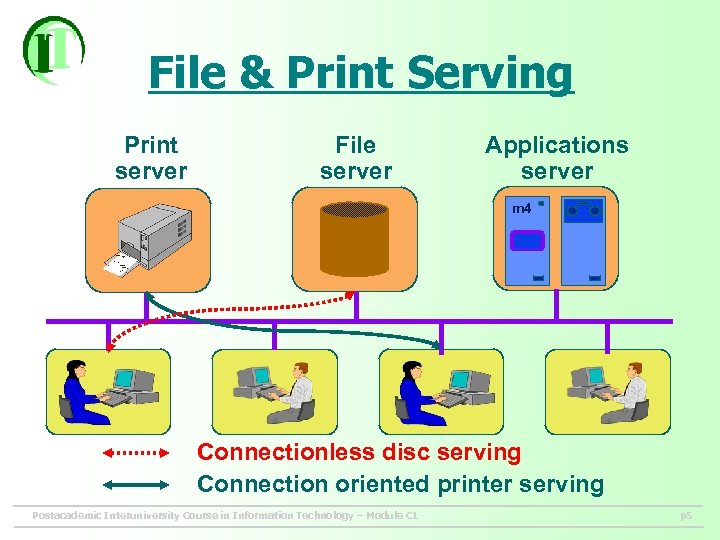 File & Print Serving Print server File server Applications server m 4 Connectionless disc serving Connection oriented printer serving Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 5
File & Print Serving Print server File server Applications server m 4 Connectionless disc serving Connection oriented printer serving Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 5
 Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 6
Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 6
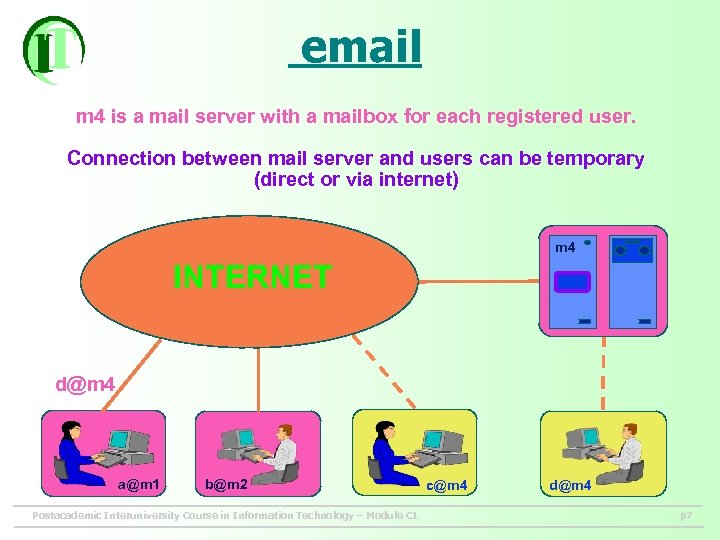 email m 4 is a mail server with a mailbox for each registered user. Connection between mail server and users can be temporary (direct or via internet) m 4 INTERNET d@m 4 a@m 1 b@m 2 Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 c@m 4 d@m 4 p 7
email m 4 is a mail server with a mailbox for each registered user. Connection between mail server and users can be temporary (direct or via internet) m 4 INTERNET d@m 4 a@m 1 b@m 2 Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 c@m 4 d@m 4 p 7
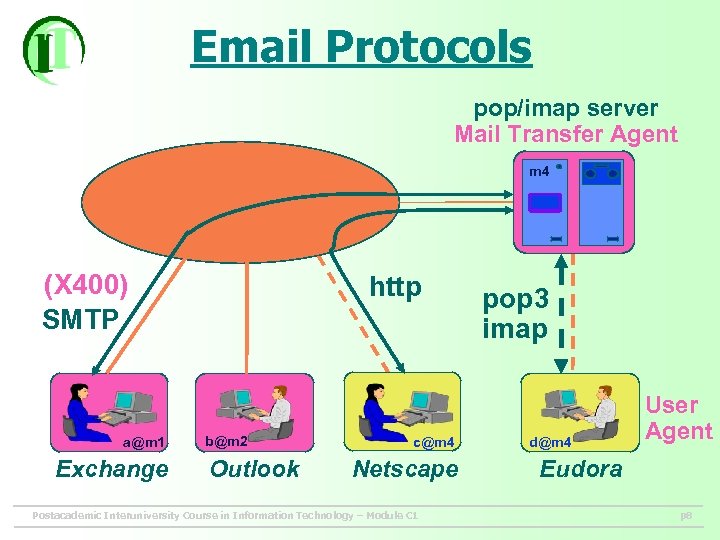 Email Protocols pop/imap server Mail Transfer Agent m 4 (X 400) SMTP a@m 1 Exchange http b@m 2 Outlook c@m 4 Netscape Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 pop 3 imap d@m 4 User Agent Eudora p 8
Email Protocols pop/imap server Mail Transfer Agent m 4 (X 400) SMTP a@m 1 Exchange http b@m 2 Outlook c@m 4 Netscape Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 pop 3 imap d@m 4 User Agent Eudora p 8
 Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 9
Contents • Data Communications Applications – File & print serving – Mail – Domain Name Server – Telnet – File Transfer Protocol – World Wide Web • Multi-media Applications – Voice – Images Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 9
 Hierarchical Addresses • Addresses composed of meaningful fields • Address = hierarchical list of domain names • A domain is an organizational and/or geographic entity regrouping lower level domains or hosts. • Addresses belonging to a given domain are maintained by the authority of that domain. • Example : classical telephone numbers – 32 2 629 2905, 32 475 819327 – hierarchy jeopardized by number portability! Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 10
Hierarchical Addresses • Addresses composed of meaningful fields • Address = hierarchical list of domain names • A domain is an organizational and/or geographic entity regrouping lower level domains or hosts. • Addresses belonging to a given domain are maintained by the authority of that domain. • Example : classical telephone numbers – 32 2 629 2905, 32 475 819327 – hierarchy jeopardized by number portability! Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 10
 Flat Addresses • Organizational and geographic hierarchy do not necessarily match • Address values contain no useful information • Example : Internet network ID’s – VUB = 134. 184 ULB = 164. 015 – KUL = 134. 058 KULAK = 193. 190 – RUG = 157. 193 • Using large set of flat addresses user-unfriendly • Solution : Assign a flat and an hierarchical address to every user and maintain a database linking both Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 11
Flat Addresses • Organizational and geographic hierarchy do not necessarily match • Address values contain no useful information • Example : Internet network ID’s – VUB = 134. 184 ULB = 164. 015 – KUL = 134. 058 KULAK = 193. 190 – RUG = 157. 193 • Using large set of flat addresses user-unfriendly • Solution : Assign a flat and an hierarchical address to every user and maintain a database linking both Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 11
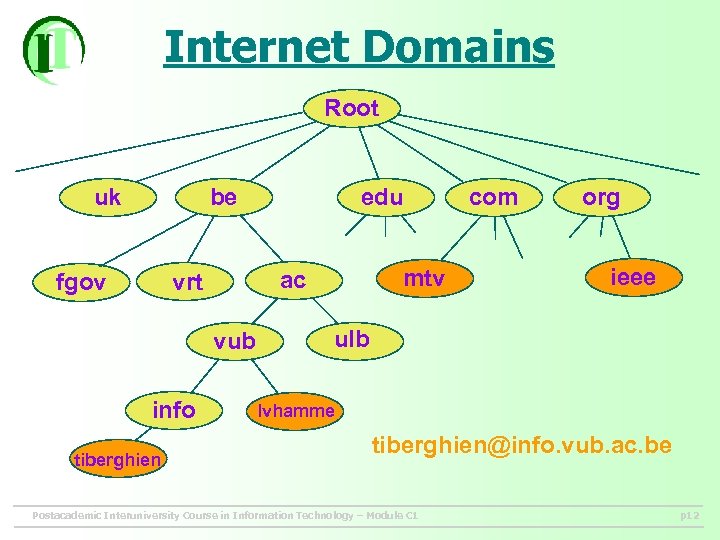 Internet Domains Root uk be fgov vub tiberghien mtv ac vrt info edu com org ieee ulb lvhamme tiberghien@info. vub. ac. be Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 12
Internet Domains Root uk be fgov vub tiberghien mtv ac vrt info edu com org ieee ulb lvhamme tiberghien@info. vub. ac. be Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 12
 Domain Name Servers • In Each domain, there is at least one DNS – Name & DNS Address of all subdomains – Name & address of all hosts in the domain – DNS address of, at least, root of DNS system – Names & DNS addresses of frequently used domains • Each host must know the address of one DNS • Local DNS is locally maintained • Caching greatly improves performance of DNS by keeping the translations of most recently accessed domains and hosts Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 13
Domain Name Servers • In Each domain, there is at least one DNS – Name & DNS Address of all subdomains – Name & address of all hosts in the domain – DNS address of, at least, root of DNS system – Names & DNS addresses of frequently used domains • Each host must know the address of one DNS • Local DNS is locally maintained • Caching greatly improves performance of DNS by keeping the translations of most recently accessed domains and hosts Postacademic Interuniversity Course in Information Technology – Module C 1 p 13


