af5757697dbe38849be41245669b648c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Chapter 3&4 Getting the Job © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning

Contents of an Application Letter n The application letter, or cover letter, introduces you to a potential employer. n The application letter is a sales letter. n “Sell” your qualifications. n Create interest in the enclosed resume. n Purpose is to get an interview. Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 2

Preparing for an Application Letter n Use 81/2 x 11 –inch paper n Resume paper (can buy at office max or staples) n A standard 12 point for the type n Font: Arial, Times New Roman Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 3
![[Your Name] [Street Address] [City, ST ZIP Code] January 2, 2009 [Recipient Name] [Title] [Your Name] [Street Address] [City, ST ZIP Code] January 2, 2009 [Recipient Name] [Title]](https://present5.com/presentation/af5757697dbe38849be41245669b648c/image-4.jpg)
[Your Name] [Street Address] [City, ST ZIP Code] January 2, 2009 [Recipient Name] [Title] [Company Name] [Street Address] [City, ST ZIP Code] Return address Letter address Salutation Dear [Recipient Name]: Sincerely, [Your Name] [type signature] Closing Enclosure: Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 4

Body of Application Letter In this very first paragraph explain why you are contacting the person (state job title), also mention your connection with that person or someone who knows that person. Describe where you heard about the current job opening. You will also briefly state who you are. In this second paragraph communicate more about yourself. Explain with detailed examples, that you are the best and most suitable candidate for this position. Then end this paragraph with detailed qualifications you have that make you exactly what they are looking for in an employee. This ending paragraph will be you thanking the person reading this letter, for their time. Also include, you will be looking forward in the future, hearing from them or a representative of their company, with their reply. Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 5

Preparing an E-Mail Application Letter n Set your e-mail to plain text n Place everything at the left margin. n Use no special formatting or tabs. n Prepare your application letter in your -mail message window. e Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 6

The Resume n A resume shows information that may be of interest to an employer. n Aka: n Personal data sheet n Biographical summary n Professional profile Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 7

Parts of the Resume What would you want to read? What main sections? Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 8

General Guidelines for a Resume n Keep resume to one page. n Include all information pertinent to the job for which you are applying. n Choose a format that is attractive, professional looking, and easy to read. n Proofread thoroughly. n Use a high-resolution printer and good quality paper. Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 9

References n References people who are 18 years of age or older who have known you for at least a year and can provide information about your skills, character, and achievements. n Who would you ask? Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 10

Purpose of the Resume n. Get the interview!!! Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 11

The Application Form n An employment application, or job application, is a form that asks questions of people who apply for a job. n Ways to complete an application form n Use pen to fill out paper form n Complete form online at company web site n Download form and submit electronically Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 12

The Job Interview n A job interview is a face-to-face meeting with a potential employer to discuss a job opening. n You should spend at least as much time preparing for the interview as you did getting the interview. Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 13

Preparing for the interview n What research should I do before a job interview? n Answer n What should I bring to an interview? n Answer Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 14

Making a Good First Impression n Arrive on time n Dress appropriately n Go alone n Be prepared n Appear-self confident n Be courteous n Think before you speak n Be enthusiastic n Emphasize your strong points n Look for cues © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning Chapter 3 SLIDE 15

Job Interview questions? n How do I know what the interviewer is going to ask me? n Answer n How should I handle questions I don't want to be asked? n Answer Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 16

The Follow-Up/Thank you n Follow-up is contact with the employer after the interview but before hiring occurs. n Thank you - It reminds the employer of who you are and could improve your chance of getting the job because you are showing appreciation to the employer for taking time to speak with you. Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 17

Brie Bella and Daniel Bryan go on a mock job interview n Mock Interview How do you think they did? Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 18

Other---TESTING n What kind of tests can they ask you to take before they offer you the job? n Which test are many people finding the hardest to pass? ? Chapter 3 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 19
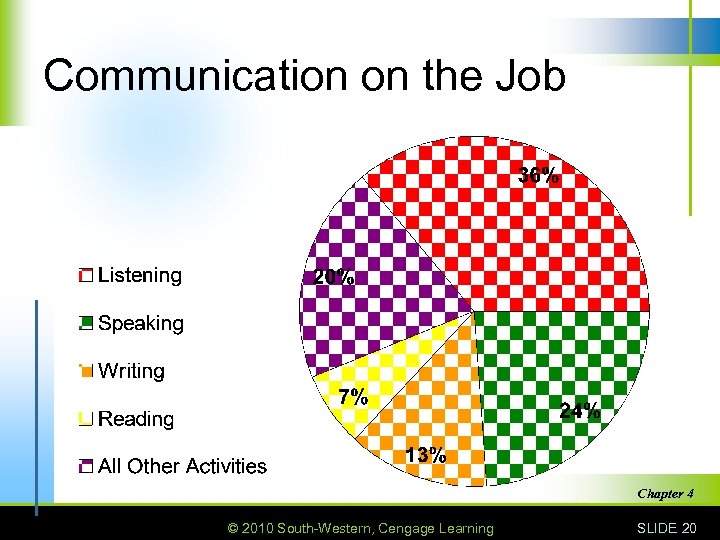
Communication on the Job Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 20

Effective Communication at Work n Success on the job depends on good communication skills. n Of all the job activities you perform in a day, 80 percent involve communication in one form or another. n More than half of all job communication involves listening and speaking. n Many job ads list good communication skills as a must. Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 21

Hearing vs. Listening n Hearing is the process of perceiving sound. n Listening is an active hearing process that requires concentration and effort. Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 22

Informal Speaking n Making contact with others n Exchanging information n Influencing others n Solving problems Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 23

Formal Speaking n To inform n To entertain n To persuade Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 24

E-mail Communication n E-mail is the most common form of communication in business today. n Rules of good writing apply. n Be concise. n Use correct grammar. n Proofread. n Review for clarity before sending. Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 25

E-mail Communication n Advantages n Fast n Inexpensive n Simultaneous n Easy to learn and use n Disadvantages n Overuse n No cues from reaction n Lack of privacy n Temptation to use inappropriately Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 26

Human Relations at Work n Human relations is the art of getting along with others. n To be truly competent in human relations, you need to have a good understanding of yourself and of others and a genuine concern for their needs and feelings. n YOU worked hard to get the job now know how to keep it!! Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 27

Work Rules n Work rules are the do’s and don’ts of fitting in successfully and having a positive work experience. n Unwritten work rules n Not documented n Not verbally communicated n Written work rules n Posted n Include in an employee manual Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 28

Leave a Favorable Impression n Remember customers’ names and preferences. n Make an extra effort to be helpful. n Demonstrate knowledge, enthusiasm, and interest in customers. n Display genuine concern for the quality of products and services. n Care about people and meeting their needs. n Listen sympathetically to customer complaints. n Take pride in yourself and your work. Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 29

Absenteeism n Absenteeism is the record and pattern of absence rates for workers. n Businesses must deal with the causes and effects of absenteeism. n Types of absentees n Consequences of absenteeism n Costs of absenteeism Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 30

Motivation and Needs n All human beings have some needs that are basic to survival and other needs that go beyond mere physical existence. n Unfulfilled needs motivate people to work toward satisfying those needs. n Anyone seen Tom Hanks in Cast Away? ? ? Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 31

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs n The model has five levels of need: n Level 1: Food, Clothing, and Shelter n Level 2: Safety and Security n Level 3: Love and Belonging n Level 4: Self-Esteem n Self-esteem is self-respect and recognition from others. n Level 5: Self-Actualization n Self-actualization is the need to reach one’s full potential, to grow, and to be creative. Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 32

(continued) Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs n Employment can help satisfy all five levels of needs. n According to Maslow, in general, lowerlevel needs must be satisfied first. n Once a need is met, the next higher one in the hierarchy begins to motivate the person’s behavior. Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 33

Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Level 5 Self- actualization Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 1 Self-esteem Love and Belonging Safety and Security Food, Clothing, and Shelter Chapter 4 © 2010 South-Western, Cengage Learning SLIDE 34
af5757697dbe38849be41245669b648c.ppt