df1439b833b27576c916f9c031929e60.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Chapter 29, Section 3: Protest, Reform, and Doubt Main Idea: The 1960 s was a decade filled with problems: political assassinations, scandals, political crises, and protest movements.

A. Kennedy in the White House Election of 1960 w John F. Kennedy defeated Richard M. Nixon by a very narrow margin in 1960. n n The 1 st televised debates favored Kennedy, who appeared youthful & confident (Nixon looked tired & nervous). Kennedy became the youngest elected President @ 43: “Ask not what your country can do for you – ask what you can do for your country. ” (& the only Catholic so far) Kennedy’s Policies w The “New Frontier” described JFK’s domestic programs, including the Peace Corps & more space exploration. n n The Peace Corps sent volunteers to developing nations to teach and provide technical help Alan Shepard became the 1 st American in space in 1961. Tragedy in Dallas w JFK was assassinated on November 22, 1963 in Dallas, TX while riding in a convertible near Dealey Plaza. n n Lee Harvey Oswald was arrested for the crime. However, he was killed shortly after, by Jack Ruby, on live television. The Warren Commission later concluded that Oswald was the lone gunman, but many believe the assassination was part of a conspiracy that was covered up by the government. l n “Magic Bullet” & “Grassy Knoll” theories (Seinfeld – “Magic Loogie”) Lyndon Johnson became President after he was sworn in on board Air Force One, while JFK’s widow, Jackie, looked on.

President John F. Kennedy JFK – Election and Assassination: View the debate, the · Democrat John F. Kennedy defeated first televised the Republican Richard Nixon in the presidential debate presidential election of 1960. in U. S. history. President -elect John F. Kennedy, left, shakes hands with Vice President Richard M. Nixon after a postelection conferen ce in Miami.
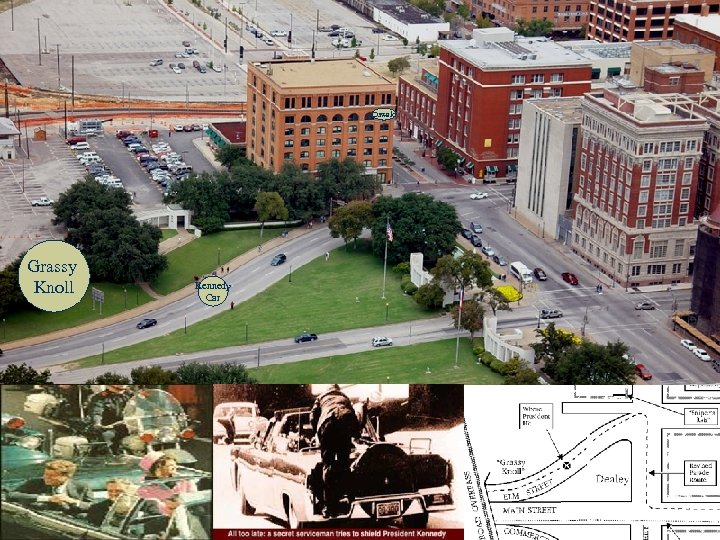

Oswald Grassy Knoll Kennedy Car

In 1963, Pres. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald in Dallas, TX. Jack Ruby, shot Lee Harvey Oswald on November 24 th, 1963, as the Dallas Police was transferring Oswald to the county jail.

B. Johnson’s Great Society w After finishing Kennedy’s term, Lyndon Johnson defeated Barry Goldwater in 1964. w With his “Great Society, ” LBJ planned to improve the standard of living for all Americans by declaring a “war on poverty. ” n n n In just two years, he persuaded Congress to pass 50 new laws, including Medicare (health care for the elderly) & Medicaid (health care for the poor). The Office of Economic Opportunity set up jobtraining programs for the unemployed, and gave loans to needy farmers & businesses in poor sections of cities. HUD (Department of Housing & Urban Development) built housing for low-income families. l n Robert Weaver - the 1 st black Presidential cabinet member Reviews of these programs are mixed. They aided the poor, but at great taxpayer expense. w The Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed race discrimination in public places, at work, & when voting (greatest achievement of the CRM). n This was mostly Kennedy’s work that Johnson pushed through after his death.

“Kindly Move Over A Little, Gentlemen”

C. Protest Movements The Counterculture Movement w Young people rejected the “American values” of their parents’ generation. Instead of college, many “dropped out, ” living in communes & experimenting with illegal drugs (Hippies). n w w w Woodstock concert in Upstate NY in August 1969 The Antiwar Movement Vietnam War protests grew after Tet in 1968, resulting in college campus rallies, burning draft cards, marching on Washington, etc. LBJ announced he wouldn’t seek re-election in 1968, because Vietnam was too much to take. The Election of 1968 Bobby Kennedy (JFK’s brother) was killed while campaigning in LA by Sirhan. n RFK had good chance to be Democratic candidate for President in the 1968 election. Democratic Convention in Chicago erupted in violence outside (police v. antiwar protesters). Richard Nixon (R) defeated Hubert Humphry (D) & George Wallace in the 1968 election. n He promised “peace with honor” in Vietnam & “law & order” at home.

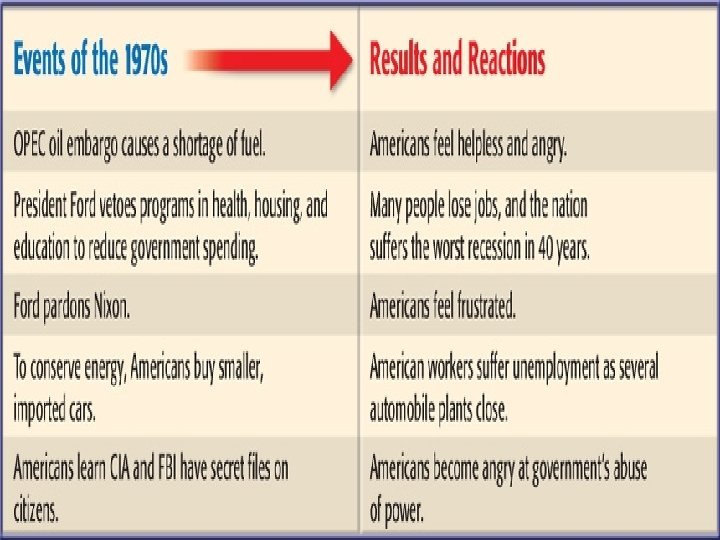
D. The Nixon/Ford Years Law and Order w Nixon saw himself as leader of the “silent majority” (those bothered by the unrest of the 1960 s, but did not want to speak out). He believed most Americans felt this way. w He looked to re-establish “law & order, ” cutting many of Johnson’s Great Society programs (too costly), increasing spending for law enforcement, & naming 4 conservative SC Justices. w The economy suffered from “stagflation” = inflation, high unemployment, & slow growth. The Space Program w In the summer of 1969, the US put the 1 st man on the moon. Neil Armstrong said, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind, ” as millions watched on TV around the world The Watergate Scandal w The Break-In - 5 men were caught breaking into the Democratic headquarters (the Watergate building in Washington, DC) during the 1972 campaign to plant “bugs” to spy on Democrats. Evidence linked the break-in to Nixon’s reelection committee, but he denied any involvement w The Cover-Up - Hearings revealed that Nixon had secret recordings of all conversations in the Oval Office. When he was ordered to turn them over, the tapes showed that he had been involved in trying to cover up the truth about the break-in (parts of the tapes had been erased). w The Result – Nixon resigned in August 1974, rather than go through an impeachment trial that probably would have resulted in a conviction (only President ever to resign from office). Ford Pardons Nixon w Gerald Ford became Vice President in 1973 (during the Watergate Affair) when then-Vice President Spiro Agnew was forced to resign for taking bribes & for tax evasion. w Ford then became President when Nixon resigned in 1974. He granted Nixon a “full, free and absolute pardon” a month later, hoping to put the scandal behind the nation & allow the country to move on (he lost a lot of support, as many felt Nixon should have been punished).


E. Carter in the White House w In the Election of 1976, Jimmy Carter (D), a former governor of Georgia, narrowly defeated Gerald Ford (R). w Carter was a Washington “outsider, ” which was good in some ways (he brought new ideas) & bad in others (it was difficult to work with Congress to get things passed). w High inflation made it difficult for many families to make ends meet. w In foreign affairs, Carter was a strong defender of human rights. n n The Helsinki Agreement – 35 nations pledged to respect basic human rights (freedom of religion, speech, thought, etc. ) Camp David Accords – Carter negotiated a peace treaty between Egypt & Israel w Carter lost to Ronald Reagan in the 1980 election, serving only one term.

Meeting at Camp David · In 1977, President Jimmy Carter met with Egyptian President Anwar el-Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin at Camp · The leaders signed the Camp David, Maryland. Accords in 1979, bringing peace between Egypt and Israel.
df1439b833b27576c916f9c031929e60.ppt