92c320eaa8e450a1d4450d66c67ae758.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 49

Chapter 28 Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901– 1912

p 636

p 637

I. Progressive Roots • Progressive ideas and theories – Against “let-alone” (laissez-faire) policy / philosophy – The people, through government, must act / help • Politicians and writers began to pinpoint targets – “Bloated trusts” attacked as corrupt – Jacob A. Riis’s How the Other Half Lives (1890) – Socialists gained support in elections – Social gospel movement • Promoted progressivism based on Christian teachings

p 639

II. Raking Muck with the Muckrakers • Muckraking magazines – Mc. Clure’s, Cosmopolitan, Collier’s and Everybody’s • Reporters (muckrakers) dug for ‘dirt’ about… – Corrupt big businesses (Oil, insurance, railroad) – Corrupt municipal government officials
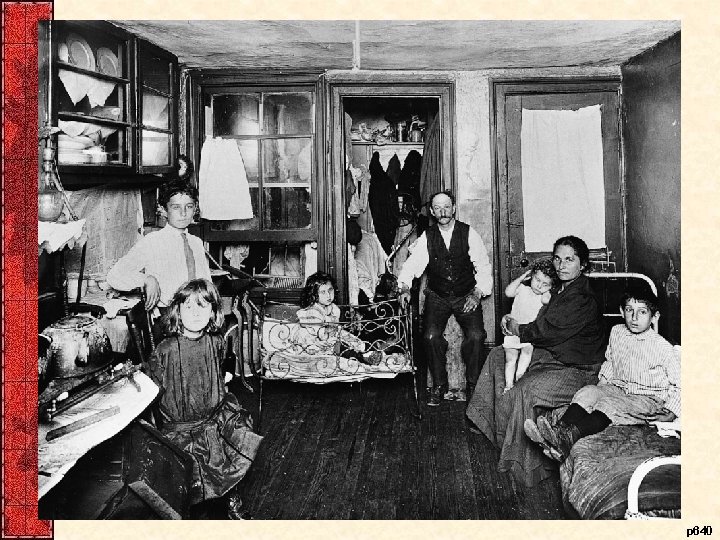

p 640

p 641

III. Political Progressivism • The progressives – Included both political parties, at all levels of gov’t • They sought to modernize American institutions – Curb trust / monopoly power – To improve the common person’s life and labor • What they achieved – Primary elections, initiative , referendum , recall – Introduced the secret Australian ballot – Direct election of senators (17 th Amendment - 1913) – Also Income Tax (16 th Amendment – 1909) • Indirectly Prohibition (18 th) and Women’s suffrage (19 th)

p 642

p 643

p 644

IV. Progressivism in the Cities and States • Progressives impressive gains in the cities – Reorganized city government (city-manager system) – “slumlords, ” juvenile delinquency, prostitution issues – Improved water supplies, streetlights, mass transit • They bubbled up to states – Elected ‘Progressive’ candidates – Biggest success - regulating public utilities
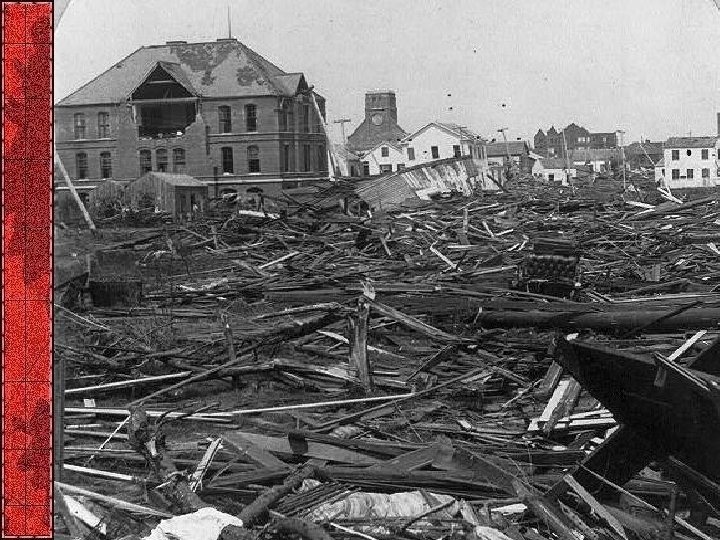
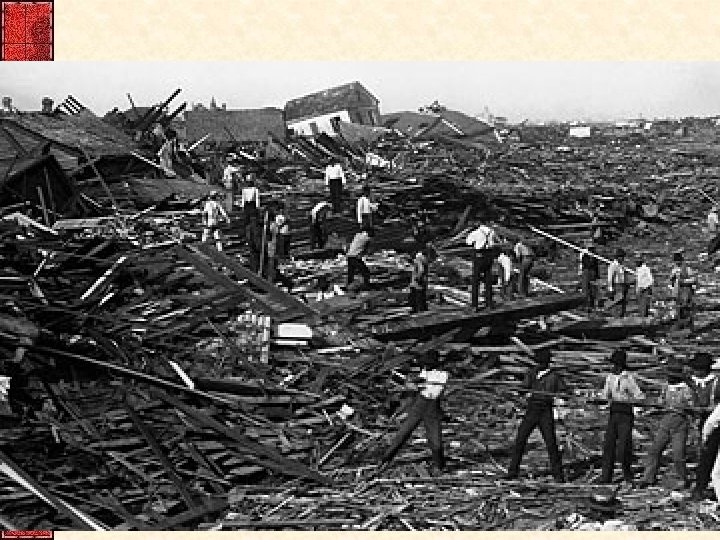



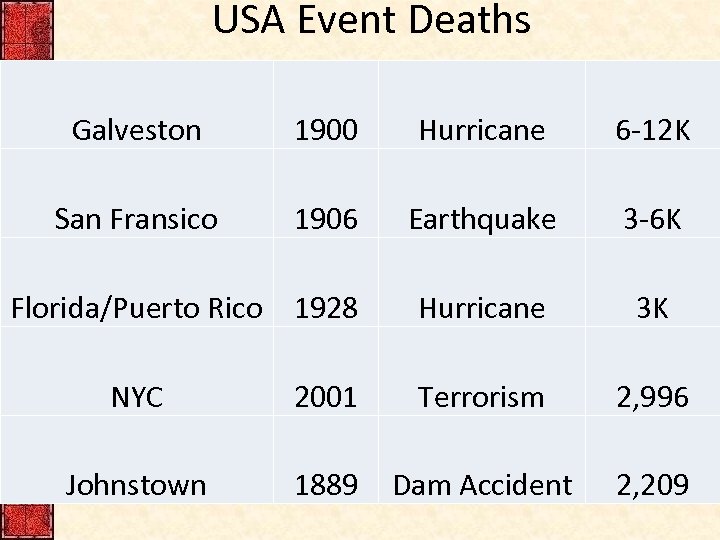
USA Event Deaths Galveston 1900 Hurricane 6 -12 K San Fransico 1906 Earthquake 3 -6 K Hurricane 3 K Florida/Puerto Rico 1928 NYC 2001 Terrorism 2, 996 Johnstown 1889 Dam Accident 2, 209

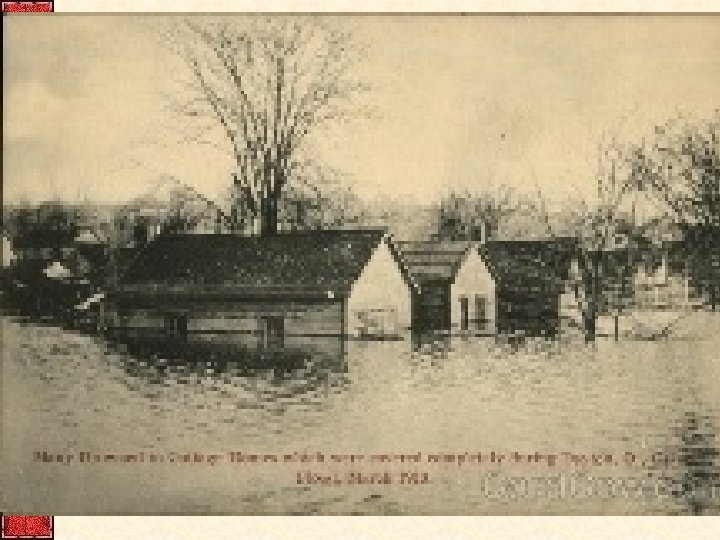
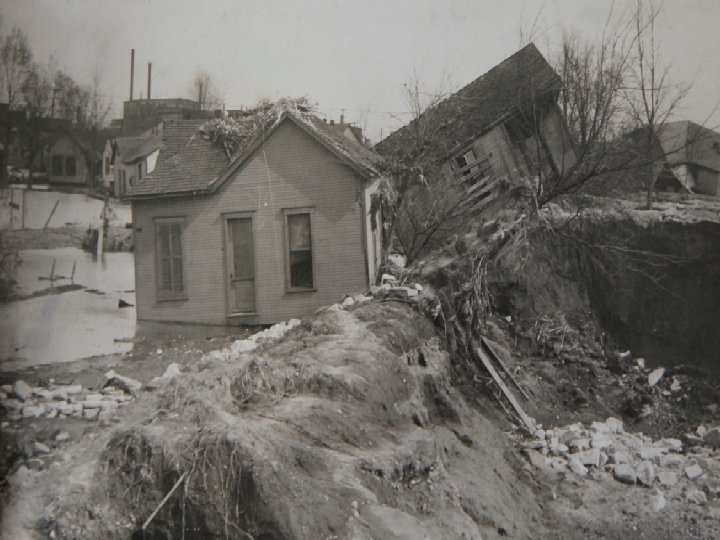
1913 Dayton Flood



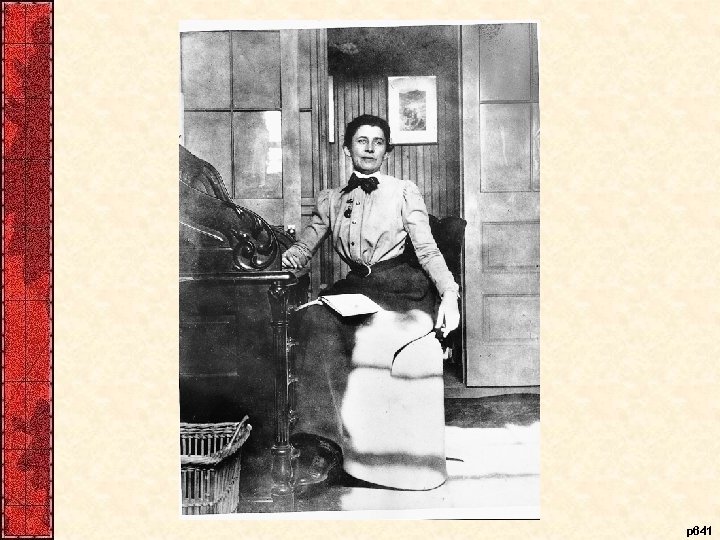
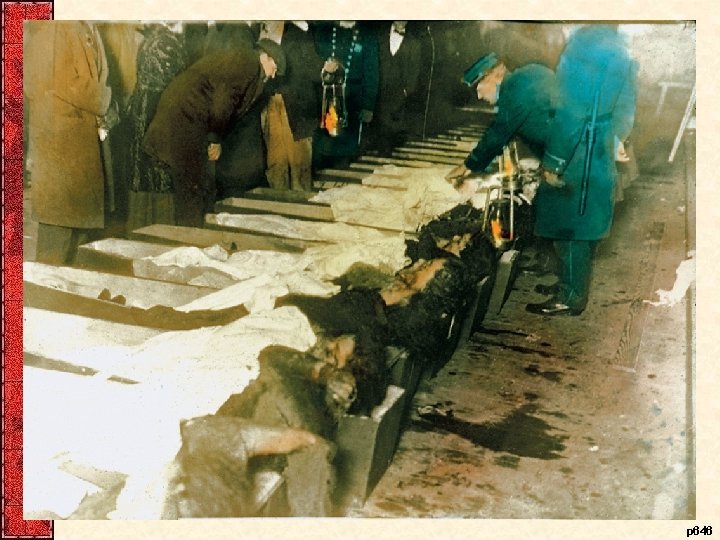
V. Progressive Women • Women ran the settlement house movement – Exposed middle-class women to urban problems – Increased women’s skill, confidence, connections • Campaigns for factory reform and temperance – Muller v. Oregon (1908), Lochner v. N. Y. (1905) – Laws not enforced (EG: Triangle Shirtwaist fire - 1911) • American welfare focused on women & children • Woman’s Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) – Concern over the cause of social problems

p 646

p 647

VI. TR’s Square Deal for Labor • His program embraced three C’s – Control of the corporations – Consumer protection – Conservation of natural resources • Administrative practice – Created Department of Commerce and Labor (1903) – The Bureau of Corporations was authorized • Cleared the road for the era of “trust-busting. ”

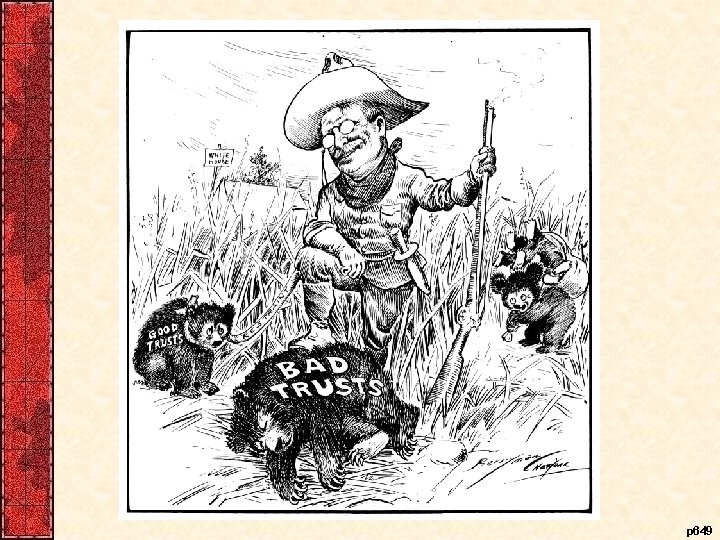
VII. TR Corrals the Corporations • Theodore Roosevelt’s belief system – Government, not private business, ruled the country – Believed in “good trusts” and “bad trusts” • His first focus - The Railroads – Hatch Act (1903) & Hepburn Act (1906) • TR initiated 40 + anti-trust lawsuits (Taft filed more)

p 649

VIII. Caring for the Consumer • Roosevelt induced Congress to pass – The Meat Inspection Act (1906) – The Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) – Motivated by Upton Sinclair’s The Jungle (1906)


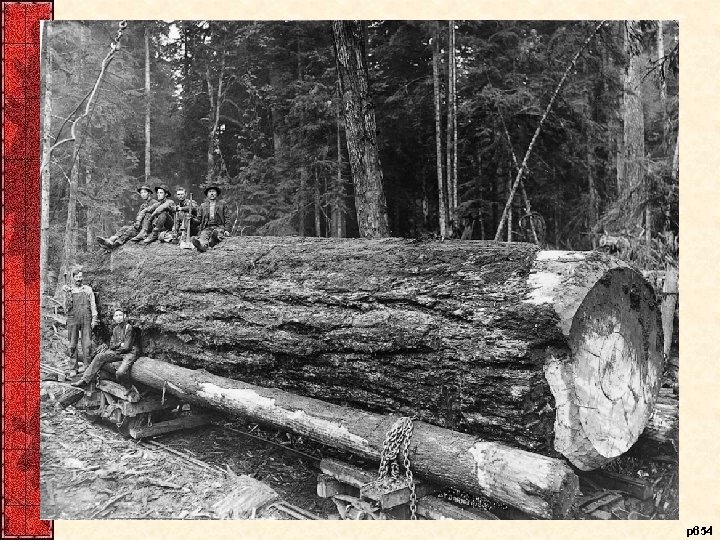
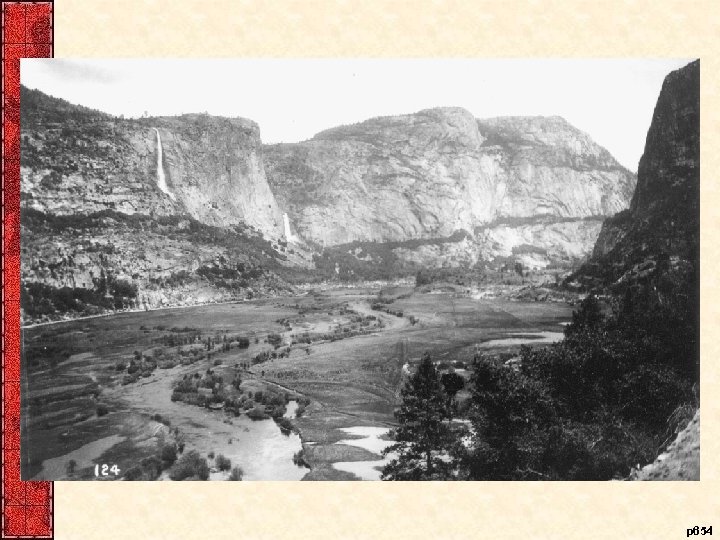
IX. Earth Control • Steps to conservation of US natural resources – Forest Reserve Act (1891)-Set aside parks / reserves • Roosevelt expanded on these previous laws – Preservation of the nation’s shrinking forests – Promoted reclamation of land (deserts / swamps) • Private organizations and societies created – Boy Scouts, Audubon Society, Sierra Club

p 650

p 651

p 652

p 653

p 653

p 654

p 654

p 655

X. The “Roosevelt Panic” of 1907 • The goals of Roosevelt’s second term – Regulate corporations, tax incomes, protect workers • 1907 Wall St. panic (Recession) – Causes “Runs” on banks, speculators arrested – Conservatives blamed “Theodore the Meddler” • Results of the 1907 panic – Paved the way for long-overdue fiscal reforms – Congress (1908) passed the Aldrich-Vreeland Act • Authorized national banks to issue emergency currency

XI. The Rough Rider Thunders Out • Republican select was William Henry Taft – TR’s successor would carry out “my policies” • Democrats nominated William Jennings Bryan – Had lost twice in previous elections • The results of campaign of 1908 – Taft polled 321 electoral votes to 162 for Bryan – High # of votes for Socialist Party (Debs)

p 656

XII. Taft: A Round Peg in a Square Hole • President William Howard Taft – Previously a lawyer, judge, cabinet administrator – Non-confrontational, candid, liked status quo – Selected a ‘conservative’ cabinet

p 657

XIII. The Dollar Goes Abroad as a Diplomat • Taft’s foreign policy – “dollar diplomacy” – U. S. investments boosted U. S. political interests • China’s Manchuria • Caribbean-especially Cuba • Nicaragua - 2500 marines (1912), stayed for 30 years

XIV. Taft the Trustbuster • Taft brought 90 suits against trusts • SCOTUS dissolution of Standard Oil (1911) – violation of the Sherman Anti-Trust Act of 1890 • “Rule of reason” doctrine – Trusts that “unreasonably” restrained trade illegal • U. S. Steel anti-trust lawsuit (1911) – This initiative infuriated Roosevelt

XV. Taft Splits the Republican Party • Republican progressives wanted lower tariffs – Taft signed Payne-Aldrich Bill, which raised tariffs • Taft also upset progressive conservationists – Allowed mining on ‘protected’ lands • Reformist Republican wing upset – TR promoted, “New Nationalism” doctrine • Increase gov’t to improve society • Congressional elections (1910) – Democrats control House (228 -161) – Republican ‘holdovers’ control Senate (51 -41)

XVI. The Taft-Roosevelt Rupture • Taft-TR fight at the Republican convention – Fight over seating delegates • Taft (conservatives) win – Fight over nomination • Taft (conservatives) win • Roosevelt refused to quit – Lead a third-party crusade

p 660
92c320eaa8e450a1d4450d66c67ae758.ppt