c9d83ae1da174b585bb5e6cf0d43a593.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 77
 Chapter 25
Chapter 25
 Section 1
Section 1
 Egypt n Three factors make it a world power n n n Strategic location Size Population
Egypt n Three factors make it a world power n n n Strategic location Size Population
 Egypt n World power n n One of the most populous in Africa – 68 million Vital location in NE Africa Goods and people travel between continents Large - 1 ½ times size of Texas
Egypt n World power n n One of the most populous in Africa – 68 million Vital location in NE Africa Goods and people travel between continents Large - 1 ½ times size of Texas
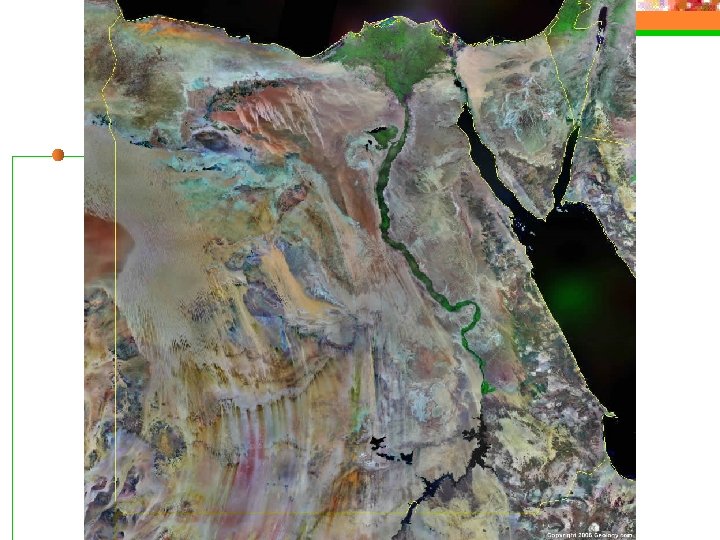
 The Nile River Desert divided by the world’s longest river, the Nile n Flows S to N 4160 miles into the Mediterranean Sea n Forks into two branches – Nile Delta – extremely fertile area n Fellaheen are Egyptian peasant farmers who farm with human labor instead of modern machinery n
The Nile River Desert divided by the world’s longest river, the Nile n Flows S to N 4160 miles into the Mediterranean Sea n Forks into two branches – Nile Delta – extremely fertile area n Fellaheen are Egyptian peasant farmers who farm with human labor instead of modern machinery n
 Egyptian people 99% people live in Nile Valley or delta region n Population density - 2700 people per square mile n Cairo straddles the Nile n Alexandria is a major seaport on the Mediterranean n
Egyptian people 99% people live in Nile Valley or delta region n Population density - 2700 people per square mile n Cairo straddles the Nile n Alexandria is a major seaport on the Mediterranean n
 Desert Regions West – Libyan Desert n East – Arabian Desert n East - The Sinai Peninsula located in SE Asia – east of the Suez Canal n
Desert Regions West – Libyan Desert n East – Arabian Desert n East - The Sinai Peninsula located in SE Asia – east of the Suez Canal n
 Deserts Strong winds blow constantly across the Sahara n Early summer a wind called khamsin create huge sandstorms n Oases only arable land n Some minerals (phosphates) and some oil n
Deserts Strong winds blow constantly across the Sahara n Early summer a wind called khamsin create huge sandstorms n Oases only arable land n Some minerals (phosphates) and some oil n

 Patterns of Rural Settlement 50% live in rural areas n Village life remains unchanged n Fellaheen live small low houses made of mud bricks - formed around small courtyard n Often keep animals in courtyard n
Patterns of Rural Settlement 50% live in rural areas n Village life remains unchanged n Fellaheen live small low houses made of mud bricks - formed around small courtyard n Often keep animals in courtyard n
 Pattern of urban settlement More people are moving to urban areas n Cairo and Alexandria n Lure of jobs leads to unemployment, increases slums n New arrivals often live in tents or shelters n Contrast of modern life of modern stores and traditional bazaars n
Pattern of urban settlement More people are moving to urban areas n Cairo and Alexandria n Lure of jobs leads to unemployment, increases slums n New arrivals often live in tents or shelters n Contrast of modern life of modern stores and traditional bazaars n

 Ancient Egypt Civilization goes back 5000 years n First to have: n n organized government organized religion written language
Ancient Egypt Civilization goes back 5000 years n First to have: n n organized government organized religion written language
 Ancient Egypt n Major accomplishment - pyramids n n south of Cairo tombs for pharaohs mummification preserved bodies for a return to life after death belief that spirit needed assistance in the afterlife – food, money
Ancient Egypt n Major accomplishment - pyramids n n south of Cairo tombs for pharaohs mummification preserved bodies for a return to life after death belief that spirit needed assistance in the afterlife – food, money
 Pyramids of Giza – west of Cairo
Pyramids of Giza – west of Cairo
 Cultural Change n n Egypt’s location – open to invaders Greeks n n Romans n n Alexander the Great brought Greek language Under Caesar’s rule brought laws and Roman customs Arabs – 1000 years of rule n n n First invaded in 642 AD Brought Arabic and Islam (90%) Ottoman Turks last to invade
Cultural Change n n Egypt’s location – open to invaders Greeks n n Romans n n Alexander the Great brought Greek language Under Caesar’s rule brought laws and Roman customs Arabs – 1000 years of rule n n n First invaded in 642 AD Brought Arabic and Islam (90%) Ottoman Turks last to invade
 Culture Today Arabic is the official language n 90% are Muslim (Islam) n Remaining minority – Copts a very old Christian sect n
Culture Today Arabic is the official language n 90% are Muslim (Islam) n Remaining minority – Copts a very old Christian sect n
 European Interventions Late 1700 s Turks’ power was in decline n Europeans started to intervene in Egypt n The Suez Canal n World War II n
European Interventions Late 1700 s Turks’ power was in decline n Europeans started to intervene in Egypt n The Suez Canal n World War II n
 The Suez Canal was dug as early as 1850 BC n Pharaohs had slave labor dig n Proof of existence Ramses II in 1300 BC n King Darius I of Persia – ordered repairs n Said Pasha –Viceroy n n n In 1854 – began larger excavation using forced labor Ran up huge debts
The Suez Canal was dug as early as 1850 BC n Pharaohs had slave labor dig n Proof of existence Ramses II in 1300 BC n King Darius I of Persia – ordered repairs n Said Pasha –Viceroy n n n In 1854 – began larger excavation using forced labor Ran up huge debts
 The Suez Canal 1882 drawing Satellite photograph
The Suez Canal 1882 drawing Satellite photograph
 British control n 1875 n n 1879 n n n Egyptian nationalists revolted to gain back the canal Britain responded by invading Egypt 1822 n n Great Britain purchased Egypt’s shares of the canal Britain takes control of government 1922 n n Egyptian nationalists pushed for independence Britain allowed Egyptians to self-rule but had little power
British control n 1875 n n 1879 n n n Egyptian nationalists revolted to gain back the canal Britain responded by invading Egypt 1822 n n Great Britain purchased Egypt’s shares of the canal Britain takes control of government 1922 n n Egyptian nationalists pushed for independence Britain allowed Egyptians to self-rule but had little power
 Independent Egypt n 1952 n n Colonel Gamal Abdel Nasser emerged as a new ruler and tried to modernize and advance world power 1956 n n n Nasser seized control of the Suez Canal International crisis Israel, France and Britain jointly invaded US and Russia favored a UN resolution - cease fire Nasser held the canal – forced others to call off attack
Independent Egypt n 1952 n n Colonel Gamal Abdel Nasser emerged as a new ruler and tried to modernize and advance world power 1956 n n n Nasser seized control of the Suez Canal International crisis Israel, France and Britain jointly invaded US and Russia favored a UN resolution - cease fire Nasser held the canal – forced others to call off attack
 Independent Egypt n 1957 n n Britain withdrew Egypt ruled itself for the first time in 2000 years
Independent Egypt n 1957 n n Britain withdrew Egypt ruled itself for the first time in 2000 years
 Egypt Under Nasser n Formed close ties with Communist Soviet Union n n Used their money and experts Began modernization projects Developed industry Dependence on cotton (major export) was reduced Nasser died in 1970
Egypt Under Nasser n Formed close ties with Communist Soviet Union n n Used their money and experts Began modernization projects Developed industry Dependence on cotton (major export) was reduced Nasser died in 1970
 Anwar Sadat n Sadat became new president of Egypt n n n Ended ties with Soviet Union New alliances with the West Became closer to Arab nations because of the creation of Israel Major wars with Israel 1948, 1967, 1978 Suffered worst defeat in 1967 - losing the Sinai Peninsula to Israel
Anwar Sadat n Sadat became new president of Egypt n n n Ended ties with Soviet Union New alliances with the West Became closer to Arab nations because of the creation of Israel Major wars with Israel 1948, 1967, 1978 Suffered worst defeat in 1967 - losing the Sinai Peninsula to Israel
 Egypt and Israel n 1978 n n After defeat, Sadat decided to seek a permanent peace with Israel 1979 n n n Egypt became to 1 st Arab nation to recognize Israel’s existence - in return, Israel returned the Sinai to Egypt Anwar Sadat, Menachem Began, and President Jimmy Carter signed the historic Camp David Peace Accord Shared the Nobel Peace Prize
Egypt and Israel n 1978 n n After defeat, Sadat decided to seek a permanent peace with Israel 1979 n n n Egypt became to 1 st Arab nation to recognize Israel’s existence - in return, Israel returned the Sinai to Egypt Anwar Sadat, Menachem Began, and President Jimmy Carter signed the historic Camp David Peace Accord Shared the Nobel Peace Prize
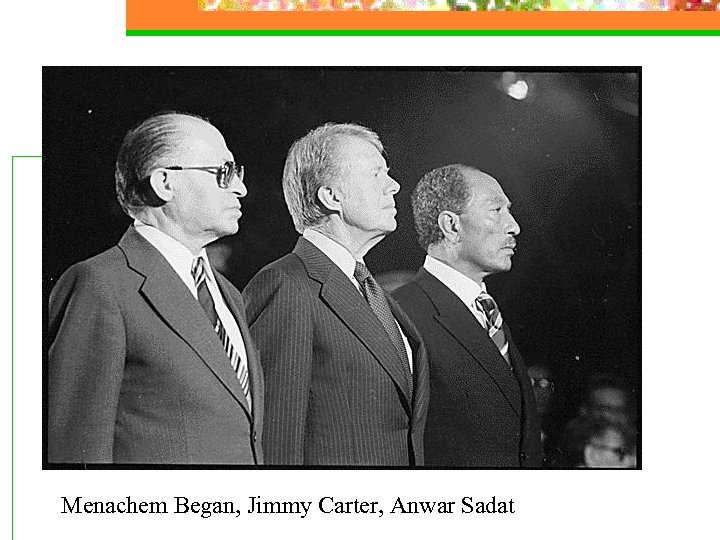 Menachem Began, Jimmy Carter, Anwar Sadat
Menachem Began, Jimmy Carter, Anwar Sadat
 Arab Fallout n Sadat’s Egypt – Israel peace treaty n n Harshly criticized by the Arab nations Called a traitor Assassinated in 1981 Successor - Hosni Mubarak n n n Has honored the peace treaty to this day Still member of OPEC Important ties to the Arab nations
Arab Fallout n Sadat’s Egypt – Israel peace treaty n n Harshly criticized by the Arab nations Called a traitor Assassinated in 1981 Successor - Hosni Mubarak n n n Has honored the peace treaty to this day Still member of OPEC Important ties to the Arab nations
 Egypt Today President Hosni Mubarak Currently the cause of protests in Cairo regarding poverty, unemployment, and a government not of the people
Egypt Today President Hosni Mubarak Currently the cause of protests in Cairo regarding poverty, unemployment, and a government not of the people

 Nile flooding n Nile flooded every year n n n Farmers built walls around their fields to trap the water and silt Called basin irrigation Good for growing crops Hard to control heavy flooding Didn’t work year round
Nile flooding n Nile flooded every year n n n Farmers built walls around their fields to trap the water and silt Called basin irrigation Good for growing crops Hard to control heavy flooding Didn’t work year round
 Controlling the Nile n 1960 Nasser took on the problem of flooding n n n Completed the Aswan High Dam in 1970 Created Lake Nasser, a reservoir - a natural or artificial lake used to store water Control flood waters Created perennial irrigation - a system providing water year round Farmers were able to grow 2 -3 crops a year Provided extra water for Cairo and electricity for industries
Controlling the Nile n 1960 Nasser took on the problem of flooding n n n Completed the Aswan High Dam in 1970 Created Lake Nasser, a reservoir - a natural or artificial lake used to store water Control flood waters Created perennial irrigation - a system providing water year round Farmers were able to grow 2 -3 crops a year Provided extra water for Cairo and electricity for industries
 Solution or Problem? n Perennial Irrigation n n Floodwaters no longer bring rich silt Farmers have to add chemical fertilizers Constant irrigation has built up salt content 35% land too high in salt content Need to build expensive drainage systems
Solution or Problem? n Perennial Irrigation n n Floodwaters no longer bring rich silt Farmers have to add chemical fertilizers Constant irrigation has built up salt content 35% land too high in salt content Need to build expensive drainage systems

 Key trends and problems n Urbanization n n Problems of enough food, housing, education and services Population Growth n n n Main problem is producing enough food Trying to increase amount of farming People resist limiting family size
Key trends and problems n Urbanization n n Problems of enough food, housing, education and services Population Growth n n n Main problem is producing enough food Trying to increase amount of farming People resist limiting family size
 Global Trade Patterns Past economy relied on cotton n Discovery of oil has taken over as the #1 export n Not enough manufacturing to improve the economy n Depend on imports of raw materials n Need an industrial base to provide jobs and make goods to export n
Global Trade Patterns Past economy relied on cotton n Discovery of oil has taken over as the #1 export n Not enough manufacturing to improve the economy n Depend on imports of raw materials n Need an industrial base to provide jobs and make goods to export n
 Obstacles to Development n Labor n n n Limited number of skilled workers Educated people go elsewhere for better salaries Lack of capital n n Capital – money that is invested into new industries Depends on money from the West or Arab countries
Obstacles to Development n Labor n n n Limited number of skilled workers Educated people go elsewhere for better salaries Lack of capital n n Capital – money that is invested into new industries Depends on money from the West or Arab countries
 Egypt Today n n n n n Important political country - Arab world Moderate Arab leadership – under fire Ally of United States Extremes of wealth and poverty Economy - tourism, cotton, oil Relies on imports of natural resources Relies on government aid from US Most populous country in Africa Vital location - the Suez Canal
Egypt Today n n n n n Important political country - Arab world Moderate Arab leadership – under fire Ally of United States Extremes of wealth and poverty Economy - tourism, cotton, oil Relies on imports of natural resources Relies on government aid from US Most populous country in Africa Vital location - the Suez Canal



 Section 2 Libya and the Maghreb Countries west of Egypt n Libya n Maghreb Nations n Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco n Term means ”Land Furthest West” n
Section 2 Libya and the Maghreb Countries west of Egypt n Libya n Maghreb Nations n Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco n Term means ”Land Furthest West” n
 Similarities of Four Countries Majority -Arab-speaking Muslims n Close ties - Islamic countries n Most live - Mediterranean coast n Away from the coast – n n n Northern Sahara Desert Similar histories/cultures
Similarities of Four Countries Majority -Arab-speaking Muslims n Close ties - Islamic countries n Most live - Mediterranean coast n Away from the coast – n n n Northern Sahara Desert Similar histories/cultures
 Differences n Libya n n Large country Oil Little arable land Tunisia n n n Small country No oil Arable lands
Differences n Libya n n Large country Oil Little arable land Tunisia n n n Small country No oil Arable lands

 Coastal areas Mediterranean climate n Early settlers n n Stayed along coast Contact with Spain, France, Italy Influenced n cultures of Europe, Africa, Asia
Coastal areas Mediterranean climate n Early settlers n n Stayed along coast Contact with Spain, France, Italy Influenced n cultures of Europe, Africa, Asia
 Interior n n Extremely dry climate Landscape varies n n n wadis -dry riverbeds, sharp gullies catch and hold water from sudden downpours Low basin rise to meet high windy plateaus Mountains No navigable rivers limits contact Mountains and deserts n n barriers to travel and communication People - maintained traditional ways
Interior n n Extremely dry climate Landscape varies n n n wadis -dry riverbeds, sharp gullies catch and hold water from sudden downpours Low basin rise to meet high windy plateaus Mountains No navigable rivers limits contact Mountains and deserts n n barriers to travel and communication People - maintained traditional ways

 Blend of Cultures Early people - Berbers n n Original inhabitants of N. Africa Gave up nomadic life - farmers and herders Settled in villages on coast /north slopes of mountains Coastal areas n contact with Rome and Carthage (Tunis)
Blend of Cultures Early people - Berbers n n Original inhabitants of N. Africa Gave up nomadic life - farmers and herders Settled in villages on coast /north slopes of mountains Coastal areas n contact with Rome and Carthage (Tunis)
 Camels –Ships of the Desert n n n n Brought from Asia by Romans Allowed trade - people south of the Sahara Crossed the desert in caravans Traded salt (north) - gold, ivory, wild animals (south) Transported elephants and hippos to Rome Important to culture of Africa Physically adapted to desert
Camels –Ships of the Desert n n n n Brought from Asia by Romans Allowed trade - people south of the Sahara Crossed the desert in caravans Traded salt (north) - gold, ivory, wild animals (south) Transported elephants and hippos to Rome Important to culture of Africa Physically adapted to desert

 Spread of Islam n Mid 600 s – Arab armies invaded n n n Brought Arabic and Islam Golden age of Northern Africa Vital trade center n between Europe, Africa and Asia Center of learning - Timbukto n Arab majority; Berbers minority (17%) n
Spread of Islam n Mid 600 s – Arab armies invaded n n n Brought Arabic and Islam Golden age of Northern Africa Vital trade center n between Europe, Africa and Asia Center of learning - Timbukto n Arab majority; Berbers minority (17%) n
 European Influence n n 1800 s Europe sought control 1830 France invaded n n Italy conquered Libya in 1912 n n Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco After WW II UN declared Libya independent Algeria (1962), Tunisia (1956) and Morocco (1956) n Had to fight for freedom
European Influence n n 1800 s Europe sought control 1830 France invaded n n Italy conquered Libya in 1912 n n Algeria, Tunisia, and Morocco After WW II UN declared Libya independent Algeria (1962), Tunisia (1956) and Morocco (1956) n Had to fight for freedom

 Rural vs Urban n Rural life n n n Small villages, mud or stone houses Windows face away from street to courtyard Village well supplies water Work in the early morning – rest in the heat of the day (3 hour siesta) Farm small plots - wheat, barley – use livestock Some villagers hire out to large farms
Rural vs Urban n Rural life n n n Small villages, mud or stone houses Windows face away from street to courtyard Village well supplies water Work in the early morning – rest in the heat of the day (3 hour siesta) Farm small plots - wheat, barley – use livestock Some villagers hire out to large farms
 Desert Nomads n Tuareg (TWAR ehg) n n Means “free men” Have their own language n n n Only written Berber language Live in small groups Practice a unique form of Islam Resisted change Severe droughts n n forced them to settle in villages work on farms to survive
Desert Nomads n Tuareg (TWAR ehg) n n Means “free men” Have their own language n n n Only written Berber language Live in small groups Practice a unique form of Islam Resisted change Severe droughts n n forced them to settle in villages work on farms to survive
 Urban Life n n n Urbanization - 50% population moving to cities Modern sections of cities look like modern cities Medinas n n n Older areas of cities Centered around a mosque Souks (market areas) n wind out from mosque in narrow streets and alleys
Urban Life n n n Urbanization - 50% population moving to cities Modern sections of cities look like modern cities Medinas n n n Older areas of cities Centered around a mosque Souks (market areas) n wind out from mosque in narrow streets and alleys
 Major cities n Cairo, Tripoli, Algiers, Tunis, Casablanca n n n Attracting more people than they can handle Unskilled laborers High unemployment Not enough housing Discovery of oil n n n Fueled modernization Skyscrapers, highways International name-brand stores
Major cities n Cairo, Tripoli, Algiers, Tunis, Casablanca n n n Attracting more people than they can handle Unskilled laborers High unemployment Not enough housing Discovery of oil n n n Fueled modernization Skyscrapers, highways International name-brand stores

 North Africa today - Libya n 1951 independence from Italy n n n Poor nation Relied - foreign aid and rent (military bases) 1961 – discovered oil n n 99% of exports Provided housing, schools, hospitals, electricity, water wells and jobs
North Africa today - Libya n 1951 independence from Italy n n n Poor nation Relied - foreign aid and rent (military bases) 1961 – discovered oil n n 99% of exports Provided housing, schools, hospitals, electricity, water wells and jobs
 Libya’s government n 1969 military coup n n n Colonel Muammar Qaddafi Abolished pro-Western monarchy Established new socialism n n Equal distribution of wealth n n combined a strict Islam with economic reform Gov’t seized property No one could have more than $3400 Get rid of Western influence Established Islamic Law
Libya’s government n 1969 military coup n n n Colonel Muammar Qaddafi Abolished pro-Western monarchy Established new socialism n n Equal distribution of wealth n n combined a strict Islam with economic reform Gov’t seized property No one could have more than $3400 Get rid of Western influence Established Islamic Law
 Government & Foreign Policy n Qaddafi clashed with West & neighbors n n Brief wars with Chad and Egypt Bought weapons from Soviets Supported terrorist groups 1986 n n n Reagan launched air strike in response to a terrorist bombing of Pan Am Flight 103 UN imposed sanctions hiding terrorists Fear of creation of chemical weapons
Government & Foreign Policy n Qaddafi clashed with West & neighbors n n Brief wars with Chad and Egypt Bought weapons from Soviets Supported terrorist groups 1986 n n n Reagan launched air strike in response to a terrorist bombing of Pan Am Flight 103 UN imposed sanctions hiding terrorists Fear of creation of chemical weapons
 Libya Today n Qaddafi trying to mend fences n n n Paid 3 billion in compensation to families of Pan Am 103 Relations are normalizing with EU Poor human rights record Qaddafi is still in power Britain allowed terrorist to go home based on terminal illness
Libya Today n Qaddafi trying to mend fences n n n Paid 3 billion in compensation to families of Pan Am 103 Relations are normalizing with EU Poor human rights record Qaddafi is still in power Britain allowed terrorist to go home based on terminal illness

 Algeria n 1962 independence from France n n Immediately 1 million Frenchmen left Had no education on self-rule Depended on French to help them self-rule Discovered oil and natural gas– 96% exports
Algeria n 1962 independence from France n n Immediately 1 million Frenchmen left Had no education on self-rule Depended on French to help them self-rule Discovered oil and natural gas– 96% exports
 Algerian economy n Oil has raised the standard of living n n Provided few jobs Population growing Many move to France Encourage people to farm n n n Jobs Feed themselves (1/3 food imported) Ease overcrowding in cities
Algerian economy n Oil has raised the standard of living n n Provided few jobs Population growing Many move to France Encourage people to farm n n n Jobs Feed themselves (1/3 food imported) Ease overcrowding in cities
 Economic and Government Problems 1988 Economic discontent led to riots n End to one party government n 1992 Islamic government nearly won n Frightened people - who feared rule similar to Iran n Army took over elections n Radical Islamists responded with terrorist attacks and assassinations n
Economic and Government Problems 1988 Economic discontent led to riots n End to one party government n 1992 Islamic government nearly won n Frightened people - who feared rule similar to Iran n Army took over elections n Radical Islamists responded with terrorist attacks and assassinations n
 Algeria Today Relies on oil n 8% world reserves of natural gas n Trying to pay off foreign debt n n Russia has forgiven debt Stable government n Still has a French influence n n Yves Saint Lauent
Algeria Today Relies on oil n 8% world reserves of natural gas n Trying to pay off foreign debt n n Russia has forgiven debt Stable government n Still has a French influence n n Yves Saint Lauent

 Tunisia and Morocco n Do not have large oil reserves n Developed human resources Begun to develop clothing manufacturing n Have minerals – phosphates n n Mine and process before exporting
Tunisia and Morocco n Do not have large oil reserves n Developed human resources Begun to develop clothing manufacturing n Have minerals – phosphates n n Mine and process before exporting
 Tunesia Spends 15% of its money on education n Ruling power is in charge n Authoritarian government n Riots in 2011 forced leader out n Currently trying to get government ready for real elections n
Tunesia Spends 15% of its money on education n Ruling power is in charge n Authoritarian government n Riots in 2011 forced leader out n Currently trying to get government ready for real elections n
 Morocco Today n Constitutional monarchy n n n Mohammed VI - ruler Has absolute power Can dissolve government Mixture of Arabs and Berbers n Non- NATO ally n n n Member of the Arab League Rides the fence/friend and enemy of the US
Morocco Today n Constitutional monarchy n n n Mohammed VI - ruler Has absolute power Can dissolve government Mixture of Arabs and Berbers n Non- NATO ally n n n Member of the Arab League Rides the fence/friend and enemy of the US
 Vocabulary from Section 1 n n n n Basin irrigation Bazaar Capital Fellaheen medina Perennial irrigation Reservoir Pharaoh
Vocabulary from Section 1 n n n n Basin irrigation Bazaar Capital Fellaheen medina Perennial irrigation Reservoir Pharaoh
 Main ideas from Egypt n n n What is the importance of the Nile? Where do most of the people live and why do they live there? What caused Europe to desire control of Egypt? What is a problem as a result of overpopulation and growth? Why are industries limited in their growth?
Main ideas from Egypt n n n What is the importance of the Nile? Where do most of the people live and why do they live there? What caused Europe to desire control of Egypt? What is a problem as a result of overpopulation and growth? Why are industries limited in their growth?
 Vocabulary from Libya and the Maghreb Berbers n Maghreb n Medina n Souk n Tuareg n wadis n
Vocabulary from Libya and the Maghreb Berbers n Maghreb n Medina n Souk n Tuareg n wadis n
 Main ideas from Libya and the Maghreb n n n What areas influence the countries of north Africa? What are the major cultural divisions in Libya and the Maghreb? What makes Libya and Algeria alike? What is the economic key to Morocco and Tunisia? What is Libya’s government based on? What are the major Arab contributions to N. Africa?
Main ideas from Libya and the Maghreb n n n What areas influence the countries of north Africa? What are the major cultural divisions in Libya and the Maghreb? What makes Libya and Algeria alike? What is the economic key to Morocco and Tunisia? What is Libya’s government based on? What are the major Arab contributions to N. Africa?


