0f2547a997a0bb455d3bb40dcbc220ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Chapter 25: Politics and a Thin Prosperity n n n Americans Confront Postwar Controversy The Nation Returns to Normalcy and Isolation Coolidge Conducts the Nation’s Business Problems Threaten Economic Prosperity A Slipping Economy Signals the End of an Era
Chapter 25: Politics and a Thin Prosperity n n n Americans Confront Postwar Controversy The Nation Returns to Normalcy and Isolation Coolidge Conducts the Nation’s Business Problems Threaten Economic Prosperity A Slipping Economy Signals the End of an Era
 Americans Confront Postwar Controversy n Threat of Communism q q q n Bolshevik Revolution Communism Comintern Palmer Raids Anarchists Ku Klux Klan q q q W. A. S. P. Xenophobia Red Scare
Americans Confront Postwar Controversy n Threat of Communism q q q n Bolshevik Revolution Communism Comintern Palmer Raids Anarchists Ku Klux Klan q q q W. A. S. P. Xenophobia Red Scare
 Red Scare n n n Americans were afraid of Communists called for a worldwide revolution against capitalism. Sacco and Vanzetti were Italian immigrants and anarchists. Charged with robbery and murder of two men. Witnesses said the killers were Italian.
Red Scare n n n Americans were afraid of Communists called for a worldwide revolution against capitalism. Sacco and Vanzetti were Italian immigrants and anarchists. Charged with robbery and murder of two men. Witnesses said the killers were Italian.
 Americans Confront Postwar Controversy - continued n Labor Unrest q q Steelworkers Strike Coal Miners n n John L. Lewis Sacco and Vanzetti
Americans Confront Postwar Controversy - continued n Labor Unrest q q Steelworkers Strike Coal Miners n n John L. Lewis Sacco and Vanzetti
 Sacco & Vanzetti (con’t) n n n Sacco & Vanzetti had alibis. Circumstantial evidence provided at the trial. Judge made racist remarks and the jury sentenced them to death.
Sacco & Vanzetti (con’t) n n n Sacco & Vanzetti had alibis. Circumstantial evidence provided at the trial. Judge made racist remarks and the jury sentenced them to death.
 The Nation Returns to Normalcy and Isolation n Warren G. Harding q q n Return to Normalcy Ohio Gang Working for Peace q q Kellogg-Briand Pact Naval Holiday Washington Naval Conference Arms Race
The Nation Returns to Normalcy and Isolation n Warren G. Harding q q n Return to Normalcy Ohio Gang Working for Peace q q Kellogg-Briand Pact Naval Holiday Washington Naval Conference Arms Race
 Warren G. Harding President in 1921 n Wanted U. S. , Great Britain, France, Japan, & Italy to scrap large warships n They all did. n
Warren G. Harding President in 1921 n Wanted U. S. , Great Britain, France, Japan, & Italy to scrap large warships n They all did. n
 The Nation Returns to Normalcy and Isolation - continued n Isolationism q q n Limiting Immigration q q n High Tariffs Fordney-Mc. Cumber Tariff Dawes Plan Reparations Nativism Quota System Harding Scandal q Teapot Dome
The Nation Returns to Normalcy and Isolation - continued n Isolationism q q n Limiting Immigration q q n High Tariffs Fordney-Mc. Cumber Tariff Dawes Plan Reparations Nativism Quota System Harding Scandal q Teapot Dome
 Fordney-Mc. Cumber Tariff Raised taxes over 60% on imports. n Because Great Britain and France could not pay back loans from WWI. n Great Britain and France could not pay us because Germany could not pay the $33 billion in reparations. n
Fordney-Mc. Cumber Tariff Raised taxes over 60% on imports. n Because Great Britain and France could not pay back loans from WWI. n Great Britain and France could not pay us because Germany could not pay the $33 billion in reparations. n
 Teapot Dome Scandal Secretary of the Interior, Albert Fall, did a secret leasing of oil-rich public land to private companies in return for $ and land. n Fall received over $400, 000 of illegal $ n First government/company scandal. n
Teapot Dome Scandal Secretary of the Interior, Albert Fall, did a secret leasing of oil-rich public land to private companies in return for $ and land. n Fall received over $400, 000 of illegal $ n First government/company scandal. n
 Coolidge Conducts the Nation’s Business n Calvin Coolidge q n Election of 1924 Prosperous Times q q Standard of Living Soars Modern Conveniences n n q Retailers n n q Electricity Automobile Urban Sprawl Airplane Installment payments Planned obsolescence Modern Advertising
Coolidge Conducts the Nation’s Business n Calvin Coolidge q n Election of 1924 Prosperous Times q q Standard of Living Soars Modern Conveniences n n q Retailers n n q Electricity Automobile Urban Sprawl Airplane Installment payments Planned obsolescence Modern Advertising
 Calvin Coolidge n President from 1923 -1929. n Was a probusiness president.
Calvin Coolidge n President from 1923 -1929. n Was a probusiness president.
 Buying on Credit n Installment Plan q Buy goods with out putting $ down q Pay interest with payments q Will cause HUGE problems in 1929 & the 1930’s
Buying on Credit n Installment Plan q Buy goods with out putting $ down q Pay interest with payments q Will cause HUGE problems in 1929 & the 1930’s
 Modern Conveniences
Modern Conveniences
 THE GREAT DEPRESSION BEGINS Photos by photographer Dorothea Lange
THE GREAT DEPRESSION BEGINS Photos by photographer Dorothea Lange
 Problems threaten Economic Prosperity n Economic Competition q q q n Farmers Suffer q q n Railroads Textiles Coal Mining Overproduction Price Supports Consumers q q q Less money to spend Buying on margin Uneven distribution of income
Problems threaten Economic Prosperity n Economic Competition q q q n Farmers Suffer q q n Railroads Textiles Coal Mining Overproduction Price Supports Consumers q q q Less money to spend Buying on margin Uneven distribution of income
 SECTION 4: THE NATION’S SICK ECONOMY As the 1920 s advanced, serious problems threatened the economy while Important industries struggled, including: n n n n n Agriculture Railroads Textiles Steel Mining Lumber Automobiles Housing Consumer goods
SECTION 4: THE NATION’S SICK ECONOMY As the 1920 s advanced, serious problems threatened the economy while Important industries struggled, including: n n n n n Agriculture Railroads Textiles Steel Mining Lumber Automobiles Housing Consumer goods
 FARMERS STRUGGLE n n Photo by Dorothea Lange No industry suffered as much as agriculture During World War I European demand for American crops soared After the war demand plummeted Farmers increased production sending prices further downward
FARMERS STRUGGLE n n Photo by Dorothea Lange No industry suffered as much as agriculture During World War I European demand for American crops soared After the war demand plummeted Farmers increased production sending prices further downward
 CONSUMER SPENDING DOWN n n n By the late 1920 s, American consumers were buying less Rising prices, stagnant wages and overbuying on credit were to blame Most people did not have the money to buy the flood of goods factories produced
CONSUMER SPENDING DOWN n n n By the late 1920 s, American consumers were buying less Rising prices, stagnant wages and overbuying on credit were to blame Most people did not have the money to buy the flood of goods factories produced
 GAP BETWEEN RICH & POOR n n Photo by Dorothea Lange The gap between rich and poor widened The wealthiest 1% saw their income rise 75% The rest of the population saw an increase of only 9% More than 70% of American families earned less than $2500 per year
GAP BETWEEN RICH & POOR n n Photo by Dorothea Lange The gap between rich and poor widened The wealthiest 1% saw their income rise 75% The rest of the population saw an increase of only 9% More than 70% of American families earned less than $2500 per year
 SEEDS OF TROUBLE n n n The Stock Market’s bubble was about to break By the late 1920 s, problems with the economy emerged Speculation: Too many Americans were engaged in speculation – buying stocks & bonds hoping for a quick profit Margin: Americans were Margin buying “on margin” – paying a small percentage of a stock’s price as a down payment and borrowing the rest
SEEDS OF TROUBLE n n n The Stock Market’s bubble was about to break By the late 1920 s, problems with the economy emerged Speculation: Too many Americans were engaged in speculation – buying stocks & bonds hoping for a quick profit Margin: Americans were Margin buying “on margin” – paying a small percentage of a stock’s price as a down payment and borrowing the rest
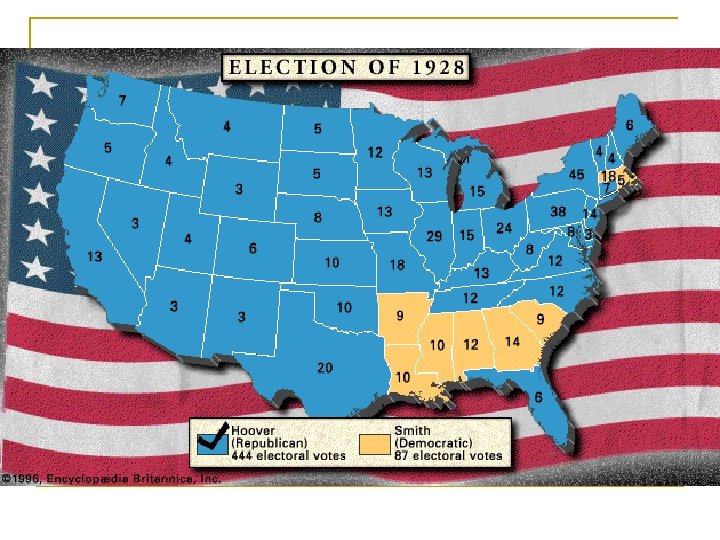
 HOOVER WINS 1928 ELECTION n n n Republican Herbert Hoover ran against Democrat Alfred E. Smith in the 1928 election Hoover emphasized years of prosperity under Republican administrations Hoover won an overwhelming victory
HOOVER WINS 1928 ELECTION n n n Republican Herbert Hoover ran against Democrat Alfred E. Smith in the 1928 election Hoover emphasized years of prosperity under Republican administrations Hoover won an overwhelming victory
 Young Hoover supporter in 1928
Young Hoover supporter in 1928
 A Slipping Economy n Herbert Hoover q q n Election of 1928 “America’s business is business” Laissez-faire economics Good Neighbor Policy Stock Market Crashes q q Speculation Buying on margin Black Tuesday Great Depression
A Slipping Economy n Herbert Hoover q q n Election of 1928 “America’s business is business” Laissez-faire economics Good Neighbor Policy Stock Market Crashes q q Speculation Buying on margin Black Tuesday Great Depression
 THE STOCK MARKET n n By 1929, many Americans were invested in the Stock Market The Stock Market had become the most visible symbol of a prosperous American economy The Dow Jones Industrial Average was the barometer of the Stock Market’s worth The Dow is a measure based on the price of 30 large firms
THE STOCK MARKET n n By 1929, many Americans were invested in the Stock Market The Stock Market had become the most visible symbol of a prosperous American economy The Dow Jones Industrial Average was the barometer of the Stock Market’s worth The Dow is a measure based on the price of 30 large firms
 STOCK PRICES RISE THROUGH THE 1920 s n n n Through most of the 1920 s, stock prices rose steadily The Dow reached a high in 1929 of 381 points (300 points higher than 1924) By 1929, 4 million Americans owned stocks New York Stock Exchange
STOCK PRICES RISE THROUGH THE 1920 s n n n Through most of the 1920 s, stock prices rose steadily The Dow reached a high in 1929 of 381 points (300 points higher than 1924) By 1929, 4 million Americans owned stocks New York Stock Exchange
 Black Tuesday
Black Tuesday
 Stock Market Crashes n The market went down on October 24 th, panicked investors sold their shares. n Black Tuesday – October 29, 1929, the bottom fell out of the market. n Those who tried to sell after Black Tuesday made stocks worth less money.
Stock Market Crashes n The market went down on October 24 th, panicked investors sold their shares. n Black Tuesday – October 29, 1929, the bottom fell out of the market. n Those who tried to sell after Black Tuesday made stocks worth less money.
 THE 1929 CRASH n n n In September the Stock Market had some unusual up & down movements On October 24, the market took a plunge. . . the worst was yet to come On October 29, now known as Black Tuesday, the bottom fell out 16. 4 million shares were sold that day – prices plummeted People who had bought on margin (credit) were stuck with huge debts
THE 1929 CRASH n n n In September the Stock Market had some unusual up & down movements On October 24, the market took a plunge. . . the worst was yet to come On October 29, now known as Black Tuesday, the bottom fell out 16. 4 million shares were sold that day – prices plummeted People who had bought on margin (credit) were stuck with huge debts
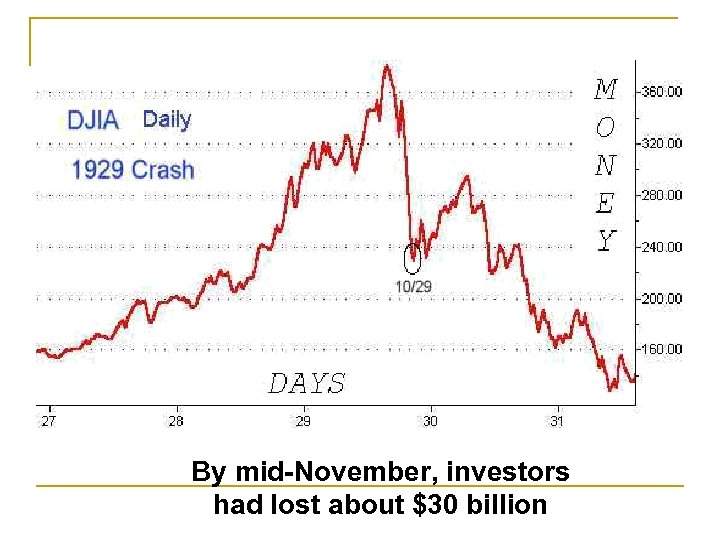 By mid-November, investors had lost about $30 billion
By mid-November, investors had lost about $30 billion

 A Slipping Economy - continued n Four major causes of the Great Depression q q n Old and decaying industrial base Crisis in the farm sector Availability of easy credit Unequal distribution of income End of pure capitalism q q q Capitalism – Private Enterprise Socialism – Public Ownership Communism – Command Economy Mixed Economy Traditional Economy
A Slipping Economy - continued n Four major causes of the Great Depression q q n Old and decaying industrial base Crisis in the farm sector Availability of easy credit Unequal distribution of income End of pure capitalism q q q Capitalism – Private Enterprise Socialism – Public Ownership Communism – Command Economy Mixed Economy Traditional Economy


