3387dfca395d4365405529658d80a72e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Chapter 22, Section 5: Other Americans Seek Justice Main Idea: African Americans and other Americans created their own communities and struggled for equality during the Progressive Era.
Chapter 22, Section 5: Other Americans Seek Justice Main Idea: African Americans and other Americans created their own communities and struggled for equality during the Progressive Era.
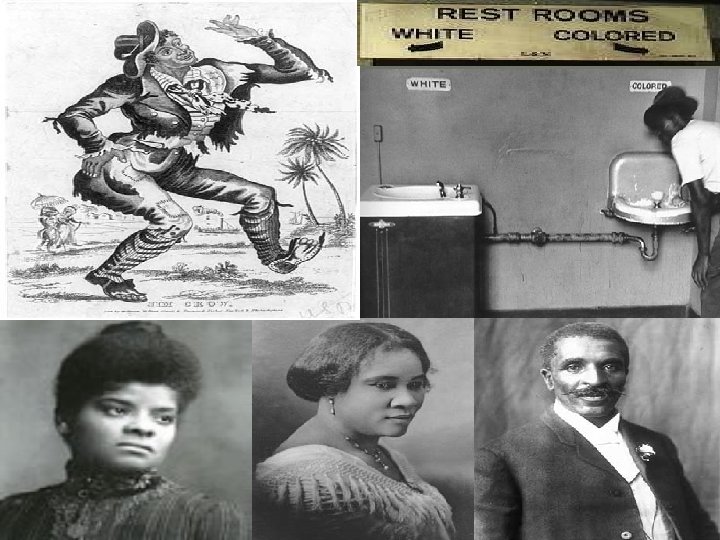
 A. African Americans u u u u Progressives didn’t give much attention to black problems. Reformers did little to help minorities. South: Jim Crow laws segregation North: prejudice & discrimination (more hidden) for housing & jobs (racist landlords/bosses) Ida Wells fought to end lynchings – blacks murdered by white mobs (over 1000 in 1890 s) GW Carver – black scientist (peanuts, crop rotation) Madame CJ Walker – 1 st female millionaire (hair care products for black women) Black-owned businesses, colleges & churches existed to serve needs of black people that weren’t being met by white society due to racism
A. African Americans u u u u Progressives didn’t give much attention to black problems. Reformers did little to help minorities. South: Jim Crow laws segregation North: prejudice & discrimination (more hidden) for housing & jobs (racist landlords/bosses) Ida Wells fought to end lynchings – blacks murdered by white mobs (over 1000 in 1890 s) GW Carver – black scientist (peanuts, crop rotation) Madame CJ Walker – 1 st female millionaire (hair care products for black women) Black-owned businesses, colleges & churches existed to serve needs of black people that weren’t being met by white society due to racism

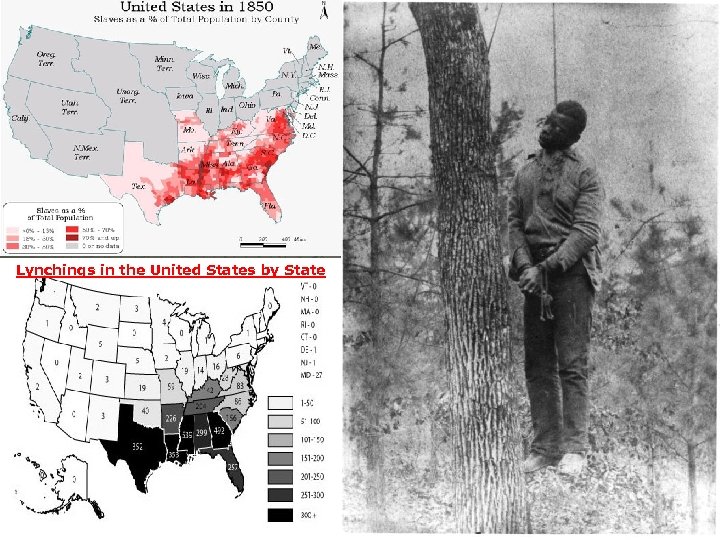 Lynchings in the United States by State
Lynchings in the United States by State
 George Washington Carver · scientist and teacher at the Tuskegee Institute · discovered hundreds of new uses for Southern crops Example: peanut butter List of By-Products From Peanuts By George Washington Carver
George Washington Carver · scientist and teacher at the Tuskegee Institute · discovered hundreds of new uses for Southern crops Example: peanut butter List of By-Products From Peanuts By George Washington Carver
 Booker T. Washington u Called on blacks & whites to live in harmony; taught that African Americans should work patiently to move up in society; learn trades & earn $, then work for equality (“boot straps”) • Founded Tuskegee Institute (black college in AL)
Booker T. Washington u Called on blacks & whites to live in harmony; taught that African Americans should work patiently to move up in society; learn trades & earn $, then work for equality (“boot straps”) • Founded Tuskegee Institute (black college in AL)
 Booker T. Washington · wrote about his success in his autobiography Up From Slavery. * He stressed living in harmony with whites. * He believed that African Americans needed to learn trades and earn a decent income in order to achieve political and social equality. · a former slave that taught himself how to read · founded the Tuskegee Institute, still a leading black college today
Booker T. Washington · wrote about his success in his autobiography Up From Slavery. * He stressed living in harmony with whites. * He believed that African Americans needed to learn trades and earn a decent income in order to achieve political and social equality. · a former slave that taught himself how to read · founded the Tuskegee Institute, still a leading black college today
 v W. E. B. Du. Bois Argued that instead of patiently accepting discrimination, blacks should fight it actively & demand equal rights • Organized NAACP (National Association for the Advancement of Colored People) in 1909 to work for equal rights for African Americans
v W. E. B. Du. Bois Argued that instead of patiently accepting discrimination, blacks should fight it actively & demand equal rights • Organized NAACP (National Association for the Advancement of Colored People) in 1909 to work for equal rights for African Americans
 W. E. B. Du. Bois · African American professor, author and public speaker * Du. Bois disagreed with Booker T. Washington’s acceptance of segregation. · Du. Bois formed the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909 with Jane Addams and Lincoln Steffens.
W. E. B. Du. Bois · African American professor, author and public speaker * Du. Bois disagreed with Booker T. Washington’s acceptance of segregation. · Du. Bois formed the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) in 1909 with Jane Addams and Lincoln Steffens.
 Washington v. Du. Bois “The wisest among my race understand that the agitation of questions of social equality is the extremist folly, and that progress in the enjoyment of all the privileges that will come to us must be the result of severe and constant struggle rather than of artificial forcing. ” - Booker T. Washington “When Mr. Washington apologizes for injustice, he does not rightly value the privilege and duty of voting, belittles the emasculating effects of caste distinctions, and opposes the higher training and ambition of our brighter minds…we must unceasingly and firmly oppose him. ” – W. E. B. Du. Bois
Washington v. Du. Bois “The wisest among my race understand that the agitation of questions of social equality is the extremist folly, and that progress in the enjoyment of all the privileges that will come to us must be the result of severe and constant struggle rather than of artificial forcing. ” - Booker T. Washington “When Mr. Washington apologizes for injustice, he does not rightly value the privilege and duty of voting, belittles the emasculating effects of caste distinctions, and opposes the higher training and ambition of our brighter minds…we must unceasingly and firmly oppose him. ” – W. E. B. Du. Bois
 u B. Mexican Americans Many lived in Southwest US (CA, TX, AZ, NM) due to already being there when US acquired land, as well as immigration (revolution & famine) Daily Life u u Many provided cheap manual labor in construction & farming Barrios – Mexican neighborhoods that promoted Mexican culture & traditions (Los Angeles) Mutual Aid u Mutualistas – mutual aid groups that worked to help Mexican immigrants & Mexican-Americans by pooling $ to buy insurance, legal advice & assist sick & needy
u B. Mexican Americans Many lived in Southwest US (CA, TX, AZ, NM) due to already being there when US acquired land, as well as immigration (revolution & famine) Daily Life u u Many provided cheap manual labor in construction & farming Barrios – Mexican neighborhoods that promoted Mexican culture & traditions (Los Angeles) Mutual Aid u Mutualistas – mutual aid groups that worked to help Mexican immigrants & Mexican-Americans by pooling $ to buy insurance, legal advice & assist sick & needy
 C. Asian Americans u u Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) – banned Chinese immigrants from coming to US Newcomers from Japan This increased Japanese immigration to US (cheap labor). Settled mostly in Hawaii & on West Coast (CA, OR, WA) & became successful fruit & vegetable farmers A “Gentleman’s Agreement” • prejudice & jealousy by white farmers & workers led to discrimination against Asian students & workers. • In 1907, President Roosevelt agreed to let Japanese women join their husbands who were already in the US, but only if Japan agreed to stop sending more workers to the US. • Unfortunately, this did little to reduce anti-Japanese feelings on West Coast & more steps to stop Asian immigration would follow
C. Asian Americans u u Chinese Exclusion Act (1882) – banned Chinese immigrants from coming to US Newcomers from Japan This increased Japanese immigration to US (cheap labor). Settled mostly in Hawaii & on West Coast (CA, OR, WA) & became successful fruit & vegetable farmers A “Gentleman’s Agreement” • prejudice & jealousy by white farmers & workers led to discrimination against Asian students & workers. • In 1907, President Roosevelt agreed to let Japanese women join their husbands who were already in the US, but only if Japan agreed to stop sending more workers to the US. • Unfortunately, this did little to reduce anti-Japanese feelings on West Coast & more steps to stop Asian immigration would follow

 D. Native Americans u The Dawes Act • divided reservations into family plots so that Native Americans would learn to farm & become more like white settlers. • This ended up being a disaster, because the land they were given was so bad & because their culture emphasized hunting on open land (not farming in separate plots), which made it hard to adjust. • In the end, many ended up selling their plot to white settlers for practically nothing. Before long, Native Americans were cheated out of millions of acres of reservation land The Society of American Indians worked for social justice & tried to educate white Americans about Indian life. But because it supported policies that forced Indians off of reservations and into mainstream life, many Native Americans opposed the Society and it ended shortly after.
D. Native Americans u The Dawes Act • divided reservations into family plots so that Native Americans would learn to farm & become more like white settlers. • This ended up being a disaster, because the land they were given was so bad & because their culture emphasized hunting on open land (not farming in separate plots), which made it hard to adjust. • In the end, many ended up selling their plot to white settlers for practically nothing. Before long, Native Americans were cheated out of millions of acres of reservation land The Society of American Indians worked for social justice & tried to educate white Americans about Indian life. But because it supported policies that forced Indians off of reservations and into mainstream life, many Native Americans opposed the Society and it ended shortly after.
 Before After
Before After


