fb0caacae5ba7a7084b58fa5b16953c5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Chapter 20: The Atlantic World 1492 - 1800 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Nj. EGncrido. Q
Chapter 20: The Atlantic World 1492 - 1800 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Nj. EGncrido. Q
 Chapter 20 Overview Chapter 20: The Atlantic World Section 1: Spain Builds an American Empire Section 2: European Nations Settle North America Section 3: The Atlantic Slave Trade Section 4: The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
Chapter 20 Overview Chapter 20: The Atlantic World Section 1: Spain Builds an American Empire Section 2: European Nations Settle North America Section 3: The Atlantic Slave Trade Section 4: The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade
 Section 1: Spain Builds an American Empire § Background: Competition for wealth among Europeans + Exposure to “cool stuff” from the “East” via Silk Roads and Crusades + improvements in sailing + Arabic inventions (astrolabe) + Prince Henry the Navigator’s School for Sailors + interest in cartography + wealth + new thinking from Renaissance = Era of Exploration http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=rjh. Izem. Ldos
Section 1: Spain Builds an American Empire § Background: Competition for wealth among Europeans + Exposure to “cool stuff” from the “East” via Silk Roads and Crusades + improvements in sailing + Arabic inventions (astrolabe) + Prince Henry the Navigator’s School for Sailors + interest in cartography + wealth + new thinking from Renaissance = Era of Exploration http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=rjh. Izem. Ldos
 Christopher Columbus § Approach Isabella and Ferdinand (of Spain) shortly after Moors had been kicked out by the Reconquesta – Perfect timing! – Isabella provided backing for initial voyages, and the 3 voyages afterwards – “I’ll sail to Asia and open up trade with the Indies. ” § Well…got to the Caribbean instead. § “In 1492 Columbus sailed the ocean blue…”.
Christopher Columbus § Approach Isabella and Ferdinand (of Spain) shortly after Moors had been kicked out by the Reconquesta – Perfect timing! – Isabella provided backing for initial voyages, and the 3 voyages afterwards – “I’ll sail to Asia and open up trade with the Indies. ” § Well…got to the Caribbean instead. § “In 1492 Columbus sailed the ocean blue…”.
 The Three G’s § Early explorers and conquistadors interested in just 3 things: – Gold – Glory – God – (In that order!) § Columbus’s 2 nd voyage provided a means to establish an empire – Abused local natives – Established colonies throughout Caribbean – Later conquistadors came with Columbus on these voyages
The Three G’s § Early explorers and conquistadors interested in just 3 things: – Gold – Glory – God – (In that order!) § Columbus’s 2 nd voyage provided a means to establish an empire – Abused local natives – Established colonies throughout Caribbean – Later conquistadors came with Columbus on these voyages
 Other Explorers § Pedro Alvares Cabral (Portugal): Brazil and claimed it for Portugal in 1500 – Treaty of Tordesillas: 1494, Spain and Portugal divide new world § Ferdinand Magellan – Circumnavigated the globe, proving: § It could be done (sailing around the world) § You could get “East” by sailing West § The natives on the Philippines are nasty § This trading thing is very, very profitable!
Other Explorers § Pedro Alvares Cabral (Portugal): Brazil and claimed it for Portugal in 1500 – Treaty of Tordesillas: 1494, Spain and Portugal divide new world § Ferdinand Magellan – Circumnavigated the globe, proving: § It could be done (sailing around the world) § You could get “East” by sailing West § The natives on the Philippines are nasty § This trading thing is very, very profitable!
 Hernando Cortez and the Aztecs § Became a conquistador – Heard of Aztecs – Landed on Carib. shore – Found locals to help him § Arrived in year 1 Reed—pale faced and with a beard! § How able to conquer an empire of millions with about 600 men and some native allies? !? ! – “Luck”, diseases, superior weapons, legend, horses, native allies
Hernando Cortez and the Aztecs § Became a conquistador – Heard of Aztecs – Landed on Carib. shore – Found locals to help him § Arrived in year 1 Reed—pale faced and with a beard! § How able to conquer an empire of millions with about 600 men and some native allies? !? ! – “Luck”, diseases, superior weapons, legend, horses, native allies
 Francisco Pizarro and the Inca § Pizarro and 200 men ambushed Atahualpa and 30, 000 men! – Again, superior weapons, disease (small pox had already come prior to Spaniards even showing up), horses, etc. – Kidnapped Atahualpa, held him for ransom—then killed him anyway
Francisco Pizarro and the Inca § Pizarro and 200 men ambushed Atahualpa and 30, 000 men! – Again, superior weapons, disease (small pox had already come prior to Spaniards even showing up), horses, etc. – Kidnapped Atahualpa, held him for ransom—then killed him anyway
 Spain’s Empire in the Americas § By mid 16 th C. , had “New Spain” in Mexico, etc. , and “Peru” in Ctrl/So. America – Regional capitals – Local governors § Imposed culture among natives – Intermarried mestizo population – Converted to Catholicism § Encomienda system—forced labor from Native Americans – Natives resisted, ran away, etc. (And many just died!) Worked on plantations, mines, etc.
Spain’s Empire in the Americas § By mid 16 th C. , had “New Spain” in Mexico, etc. , and “Peru” in Ctrl/So. America – Regional capitals – Local governors § Imposed culture among natives – Intermarried mestizo population – Converted to Catholicism § Encomienda system—forced labor from Native Americans – Natives resisted, ran away, etc. (And many just died!) Worked on plantations, mines, etc.
 Spain’s Influence Expands § Spain becoming very rich – Built a huge navy (or armada) to protect ships § Expand to (modern) United States – Send explorers throughout SW, southern Plains – Coronado explored 9 different states § Looking for the “Cities of Cibola” § Found the Grand Canyon instead § Priests went everywhere – Established colonies, churches, etc. – Priests did much of the colonizing in New Mexico, which became HQ for Church in New World
Spain’s Influence Expands § Spain becoming very rich – Built a huge navy (or armada) to protect ships § Expand to (modern) United States – Send explorers throughout SW, southern Plains – Coronado explored 9 different states § Looking for the “Cities of Cibola” § Found the Grand Canyon instead § Priests went everywhere – Established colonies, churches, etc. – Priests did much of the colonizing in New Mexico, which became HQ for Church in New World
 Opposition to Spanish Rule § Harsh rule, many abuses of natives (and even mestizos) – Harsh, rigid social system—if you weren’t born in Europe, you were “nothing” – Some natives rebelled; objecting to harsh rule and culture being destroyed § Priests started to be concerned – Bartolomé de Las Casas suggested using Africans for labor instead – Why Africans? New to area (won’t run away), “stronger”, and have “some immunity” to Old World diseases; plus, just running out of natives! – Importation of African slaves began
Opposition to Spanish Rule § Harsh rule, many abuses of natives (and even mestizos) – Harsh, rigid social system—if you weren’t born in Europe, you were “nothing” – Some natives rebelled; objecting to harsh rule and culture being destroyed § Priests started to be concerned – Bartolomé de Las Casas suggested using Africans for labor instead – Why Africans? New to area (won’t run away), “stronger”, and have “some immunity” to Old World diseases; plus, just running out of natives! – Importation of African slaves began
 In Brazil… § Cabral claimed land for Portugal in 1500 § 1530’s…colonial period began – Little minerals, so grew sugar instead – Made Portugal very rich § Also fell into slavery, and imported more slaves than all other areas in the New World combined § Rigid social class system like Spanish areas
In Brazil… § Cabral claimed land for Portugal in 1500 § 1530’s…colonial period began – Little minerals, so grew sugar instead – Made Portugal very rich § Also fell into slavery, and imported more slaves than all other areas in the New World combined § Rigid social class system like Spanish areas
 Section 2: European Nations Settle North Amer. § New France: – Who? Jacques Cartier, Samuel de Champlain, Sieur de la Salle – Why? Establish trade, esp. providing furs; not necessarily inhabiting the lands, but just “using” – Where? Originally up the St. Lawrence River – Important dates: 1534: Cartier (St. Law Ri) § 1608: Champlain founded Quebec, claimed “New France” § 1673: Marquette and Joliet: Upper Mississippi Ri.
Section 2: European Nations Settle North Amer. § New France: – Who? Jacques Cartier, Samuel de Champlain, Sieur de la Salle – Why? Establish trade, esp. providing furs; not necessarily inhabiting the lands, but just “using” – Where? Originally up the St. Lawrence River – Important dates: 1534: Cartier (St. Law Ri) § 1608: Champlain founded Quebec, claimed “New France” § 1673: Marquette and Joliet: Upper Mississippi Ri.
 English Arrive § § Who? Male settlers, Pilgrims, Puritans Why? Religious freedom; start a new life Where? “New England”, VA, MA Important dates: – 1607: Jamestown: $ $ $ All men. By 1620, women and slaves have arrived. Tobacco. – 1620: Plymouth: Pilgrims and “Strangers” – 1630: Mass. Bay Colony: Puritans – 1763: French and Indian War open way for English to inhabit most of North America
English Arrive § § Who? Male settlers, Pilgrims, Puritans Why? Religious freedom; start a new life Where? “New England”, VA, MA Important dates: – 1607: Jamestown: $ $ $ All men. By 1620, women and slaves have arrived. Tobacco. – 1620: Plymouth: Pilgrims and “Strangers” – 1630: Mass. Bay Colony: Puritans – 1763: French and Indian War open way for English to inhabit most of North America
 Dutch Are Next § § Who? Henry Hudson, others Why? Trade; searching for NW Passage Where? Hudson River; Manhattan Island Important dates: – 1609: Hudson River – 1621: New Netherlands established – Kicked out by English between 1664 - 1750
Dutch Are Next § § Who? Henry Hudson, others Why? Trade; searching for NW Passage Where? Hudson River; Manhattan Island Important dates: – 1609: Hudson River – 1621: New Netherlands established – Kicked out by English between 1664 - 1750
 Native Americans React and Revolt § French and Dutch had decent relationships, but English did not § Various “Indian Wars” throughout 13 English Colonies § Many fall to disease, loss of resources, kicked farther west – Small pox, others
Native Americans React and Revolt § French and Dutch had decent relationships, but English did not § Various “Indian Wars” throughout 13 English Colonies § Many fall to disease, loss of resources, kicked farther west – Small pox, others
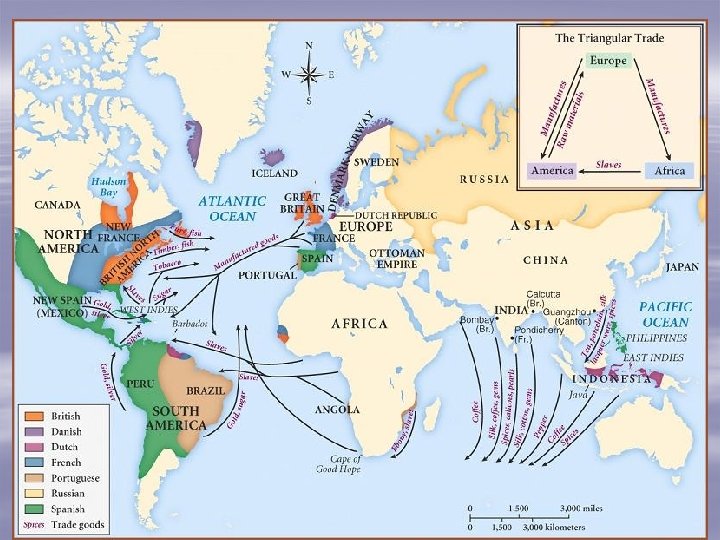
 Section 3: The Atlantic Slave Trade Was already an established business in Africa 650 Muslims transport about 17 mil. Africans to No. Africa and SW Asia 1400 -1500 Portuguese explore Africa 1500 -1600 Spain and Portugal colonize Americas; began enslaving Africans *300, 000 Africans 1600 -1700 Atlantic slave trade grows dramatically under Spain and Portugal *1. 3 million! 1690 England increases Atlantic slave trade 1870 Atlantic slave trade ends
Section 3: The Atlantic Slave Trade Was already an established business in Africa 650 Muslims transport about 17 mil. Africans to No. Africa and SW Asia 1400 -1500 Portuguese explore Africa 1500 -1600 Spain and Portugal colonize Americas; began enslaving Africans *300, 000 Africans 1600 -1700 Atlantic slave trade grows dramatically under Spain and Portugal *1. 3 million! 1690 England increases Atlantic slave trade 1870 Atlantic slave trade ends
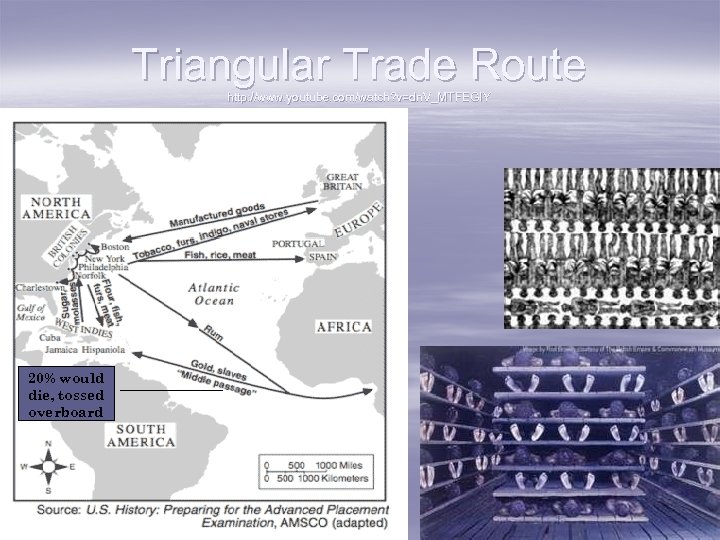 Triangular Trade Route http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=dn. V_MTFEGIY 20% would die, tossed overboard
Triangular Trade Route http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=dn. V_MTFEGIY 20% would die, tossed overboard
 Slavery in the Americas § Conditions – Horrible! – Field, forests, rice paddies, mines, houses – Beatings, starvation – Lifelong and hereditary – Some masters okay, but others were ruthless § Resistance, Rebellion, and How to Cope – Keep African culture alive – Stories, music – Would be less productive; sabotage efforts – Ran away – Armed revolts/Uprisings
Slavery in the Americas § Conditions – Horrible! – Field, forests, rice paddies, mines, houses – Beatings, starvation – Lifelong and hereditary – Some masters okay, but others were ruthless § Resistance, Rebellion, and How to Cope – Keep African culture alive – Stories, music – Would be less productive; sabotage efforts – Ran away – Armed revolts/Uprisings
 Consequences of Slave Trade § In Africa – Lost generations of people – Families torn apart – Introduced guns, encouraged violence among African peoples § In America (all) – Contributed labor – Assured some colonies would succeed and prosper – Brought culture, which mixed with natives + Euros – Many nations today are predominantly African. American
Consequences of Slave Trade § In Africa – Lost generations of people – Families torn apart – Introduced guns, encouraged violence among African peoples § In America (all) – Contributed labor – Assured some colonies would succeed and prosper – Brought culture, which mixed with natives + Euros – Many nations today are predominantly African. American
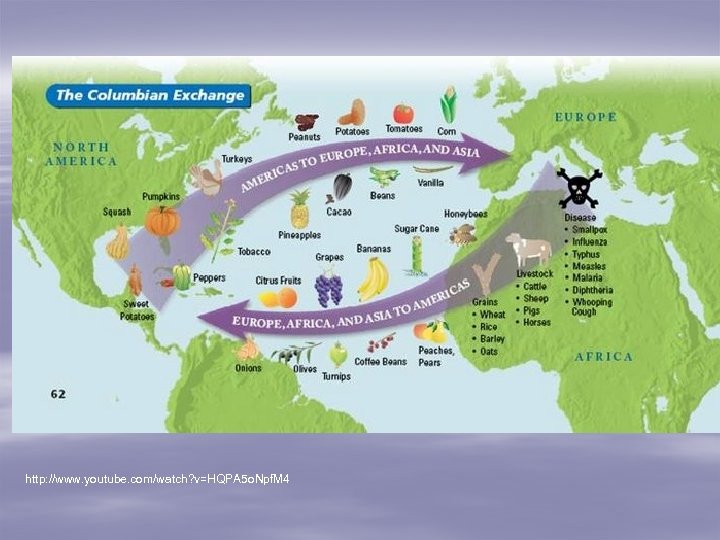
 Section 4: The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade § Exchange of plants, animals, diseases, etc. from Old World (Europe, Asia, Africa) to New World (Americas) – Not all good…not all bad. – Forever changed life for almost everyone on the whole planet! – Brought the extinction of many cultural groups of Native Americans. § Most important (positive) exchanges? – From East to West: livestock, bananas, wheat – From West to East: potato, corn
Section 4: The Columbian Exchange and Global Trade § Exchange of plants, animals, diseases, etc. from Old World (Europe, Asia, Africa) to New World (Americas) – Not all good…not all bad. – Forever changed life for almost everyone on the whole planet! – Brought the extinction of many cultural groups of Native Americans. § Most important (positive) exchanges? – From East to West: livestock, bananas, wheat – From West to East: potato, corn
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=HQPA 5 o. Npf. M 4
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=HQPA 5 o. Npf. M 4
 Global trade § New sources of wealth § Rise of capitalism – Economic system based on private ownership and investment as a way to make money – Profits! Reinvestment! Etc. Increase in money supply Inflation § Joint-Stock Companies – Like a corporation—investors pool money (buy shares) in hopes of getting a profit – Reduces individual financial risk – Popular way to “pay” for colonization
Global trade § New sources of wealth § Rise of capitalism – Economic system based on private ownership and investment as a way to make money – Profits! Reinvestment! Etc. Increase in money supply Inflation § Joint-Stock Companies – Like a corporation—investors pool money (buy shares) in hopes of getting a profit – Reduces individual financial risk – Popular way to “pay” for colonization
 Mercantilism (boo! hiss!) § “Colonies exist for the sole purpose of making money for the mother country. ” – Provides raw materials – Forced to buy finished products (but from factories in mother country) § It’s good for the mother country, if: – There’s lots of gold and silver, or – There’s a favorable balance of trade. Spain England § Goal: Become self-sufficient (off of your colonies) to eliminate need for trade with other “imperial powers”
Mercantilism (boo! hiss!) § “Colonies exist for the sole purpose of making money for the mother country. ” – Provides raw materials – Forced to buy finished products (but from factories in mother country) § It’s good for the mother country, if: – There’s lots of gold and silver, or – There’s a favorable balance of trade. Spain England § Goal: Become self-sufficient (off of your colonies) to eliminate need for trade with other “imperial powers”