d1dd2d22b560e83b86f1cc4901c4b5cc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Chapter 20 Option Valuation and Strategies
Chapter 20 Option Valuation and Strategies
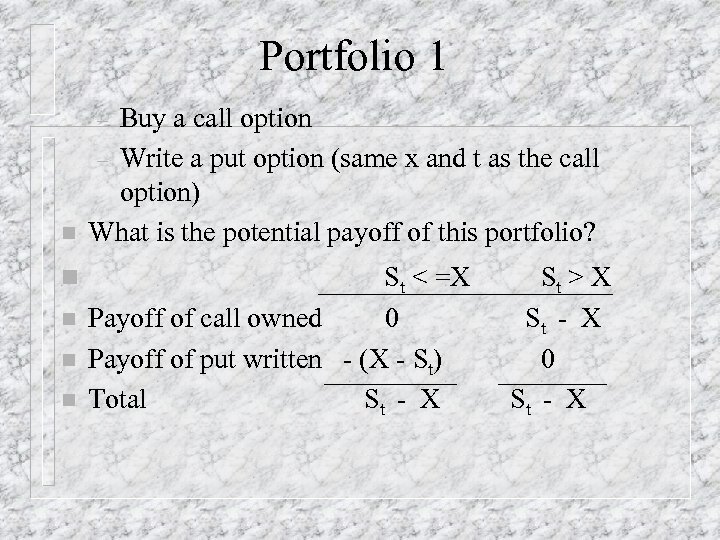 Portfolio 1 Buy a call option – Write a put option (same x and t as the call option) What is the potential payoff of this portfolio? – n n n St < =X Payoff of call owned 0 Payoff of put written - (X - St) Total St - X St > X St - X 0 St - X
Portfolio 1 Buy a call option – Write a put option (same x and t as the call option) What is the potential payoff of this portfolio? – n n n St < =X Payoff of call owned 0 Payoff of put written - (X - St) Total St - X St > X St - X 0 St - X
 Portfolio 2 Buy the stock – Borrow the present value x What is the potential payoff of this portfolio? St <= X St > X Payoff of stock St St Payoff of put written -X -X Total St - X – n n n
Portfolio 2 Buy the stock – Borrow the present value x What is the potential payoff of this portfolio? St <= X St > X Payoff of stock St St Payoff of put written -X -X Total St - X – n n n
 Portfolio 1 and 2 have identical payoffs so they must be worth the same amount or else there would be an arbitrage opportunity. n C - P = S - X / (1 + rf)t n This is the put-call parity relationship n
Portfolio 1 and 2 have identical payoffs so they must be worth the same amount or else there would be an arbitrage opportunity. n C - P = S - X / (1 + rf)t n This is the put-call parity relationship n
 Put-Call Parity Arbitrage n n n Stock price = 110 Call price = $17 (T = 6 months, and X = 105) Put Price = $? (T = 6 months, and X =$105) rf = 5% for a six-month period What is the equilibrium value of the put option? Suppose the WSJ states that the above put is selling for $5, is there an arbitrage opportunity? If so, then create a pure arbitrage.
Put-Call Parity Arbitrage n n n Stock price = 110 Call price = $17 (T = 6 months, and X = 105) Put Price = $? (T = 6 months, and X =$105) rf = 5% for a six-month period What is the equilibrium value of the put option? Suppose the WSJ states that the above put is selling for $5, is there an arbitrage opportunity? If so, then create a pure arbitrage.
 n The equilibrium value of the put is C - P = S - X / (1 + rf)t n 17 - P = 110 - 105 / 1. 05 n P = $7 n
n The equilibrium value of the put is C - P = S - X / (1 + rf)t n 17 - P = 110 - 105 / 1. 05 n P = $7 n
 n If the put is selling for $5 then an arbitrage opportunity exists. C - P = S - X / (1 + rf)t n 17 - 5 = 110 - 105 / 1. 05 n 12 > 10 n Buy low sell high. n So you would buy the right hand side of the equation and sell the left hand side. n
n If the put is selling for $5 then an arbitrage opportunity exists. C - P = S - X / (1 + rf)t n 17 - 5 = 110 - 105 / 1. 05 n 12 > 10 n Buy low sell high. n So you would buy the right hand side of the equation and sell the left hand side. n
 Buy the Stock and borrow the present value of the exercise price n Sell the call and buy the put option n To be a pure arbitrage you must show that there was zero net investment and that there is a guaranteed profit. n
Buy the Stock and borrow the present value of the exercise price n Sell the call and buy the put option n To be a pure arbitrage you must show that there was zero net investment and that there is a guaranteed profit. n
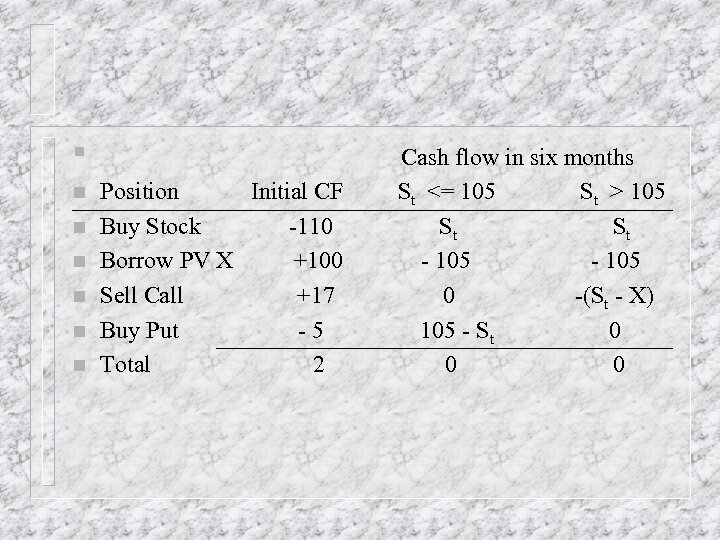 n n n n Position Initial CF Buy Stock -110 Borrow PV X +100 Sell Call +17 Buy Put -5 Total 2 Cash flow in six months St <= 105 St > 105 St St - 105 0 -(St - X) 105 - St 0 0 0
n n n n Position Initial CF Buy Stock -110 Borrow PV X +100 Sell Call +17 Buy Put -5 Total 2 Cash flow in six months St <= 105 St > 105 St St - 105 0 -(St - X) 105 - St 0 0 0
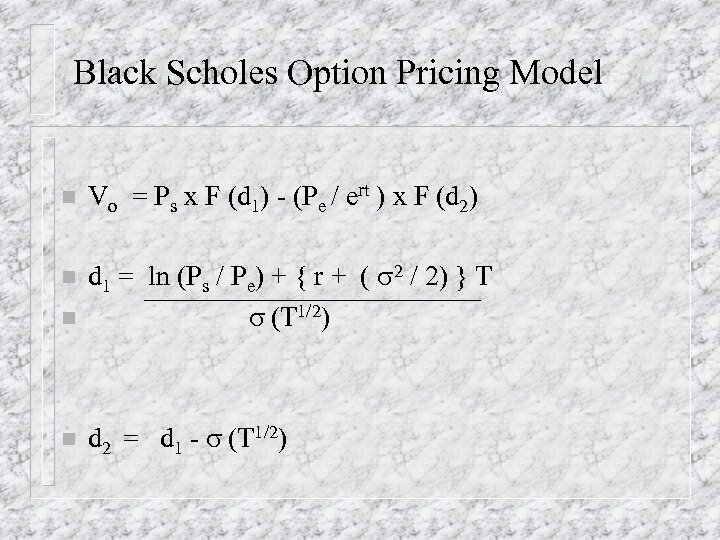 Black Scholes Option Pricing Model n Vo = Ps x F (d 1) - (Pe / ert ) x F (d 2) n n d 1 = ln (Ps / Pe) + { r + ( s 2 / 2) } T s (T 1/2) n d 2 = d 1 - s (T 1/2)
Black Scholes Option Pricing Model n Vo = Ps x F (d 1) - (Pe / ert ) x F (d 2) n n d 1 = ln (Ps / Pe) + { r + ( s 2 / 2) } T s (T 1/2) n d 2 = d 1 - s (T 1/2)
 Example of Black Scholes Model n Stock Price Exercise Price Time to expiration Standard deviation Interest Rate (risk free) n Calculate the intrinsic value of IBM’s call option. n n = = = 102 11/16 105 2 months 25% 6% annually
Example of Black Scholes Model n Stock Price Exercise Price Time to expiration Standard deviation Interest Rate (risk free) n Calculate the intrinsic value of IBM’s call option. n n = = = 102 11/16 105 2 months 25% 6% annually
 Solution to B-S Problem n n d 1 = ln (102. 69 / 105) + {. 06 + (. 252 / 2) }. 17. 25 (. 171/2) d 1 = -. 065 d 2 = -. 065 -. 25 (. 171/2) d 2 = -. 1681 Vo = 102. 69 x F (-. 07) - (105 / e(. 06)(. 17) ) x F (-. 17) V 0 = 102. 69 x. 4721 - 103. 93 x. 4325 V 0 = $3. 53
Solution to B-S Problem n n d 1 = ln (102. 69 / 105) + {. 06 + (. 252 / 2) }. 17. 25 (. 171/2) d 1 = -. 065 d 2 = -. 065 -. 25 (. 171/2) d 2 = -. 1681 Vo = 102. 69 x F (-. 07) - (105 / e(. 06)(. 17) ) x F (-. 17) V 0 = 102. 69 x. 4721 - 103. 93 x. 4325 V 0 = $3. 53
 The Hedge Ratio n n The ratio of the change in the price of a call option to the change in the price of the stock. The hedge ratio is also called the options delta. Is the delta positive or negative for a call option? Is the delta positive or negative for a put option?
The Hedge Ratio n n The ratio of the change in the price of a call option to the change in the price of the stock. The hedge ratio is also called the options delta. Is the delta positive or negative for a call option? Is the delta positive or negative for a put option?
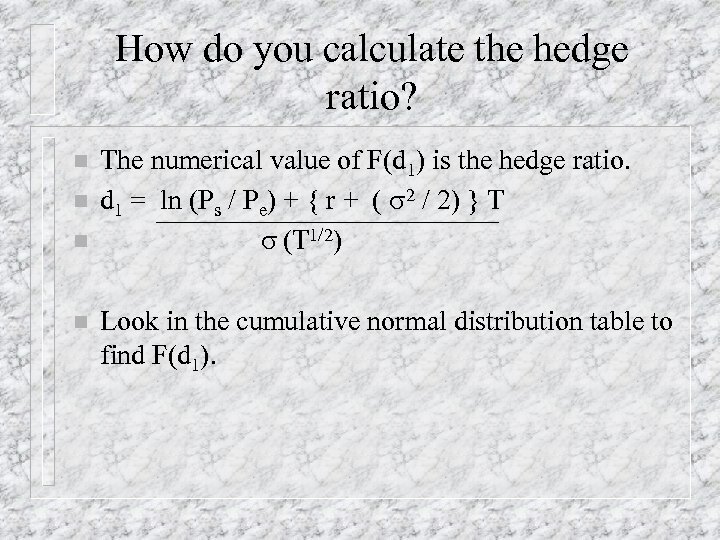 How do you calculate the hedge ratio? n n The numerical value of F(d 1) is the hedge ratio. d 1 = ln (Ps / Pe) + { r + ( s 2 / 2) } T s (T 1/2) Look in the cumulative normal distribution table to find F(d 1).
How do you calculate the hedge ratio? n n The numerical value of F(d 1) is the hedge ratio. d 1 = ln (Ps / Pe) + { r + ( s 2 / 2) } T s (T 1/2) Look in the cumulative normal distribution table to find F(d 1).
 Example of Hedge n In our example F(d 1) =. 4721, this means that the price of the option will rise $. 47 for every $1 increase in the price of the stock. Thus if the investor owns 100 shares of stock and has written 2. 12 calls, a $1 increase in the stock will generate a $1 decrease in the option. The gain in one position is exactly offset by the loss in the other position.
Example of Hedge n In our example F(d 1) =. 4721, this means that the price of the option will rise $. 47 for every $1 increase in the price of the stock. Thus if the investor owns 100 shares of stock and has written 2. 12 calls, a $1 increase in the stock will generate a $1 decrease in the option. The gain in one position is exactly offset by the loss in the other position.
 Example of Hedge (cont. ) n n n Number of call options to hedge 100 shares 1 / Hedge ratio Defines the number of call options that must be sold for each 100 shares purchased. Our example: 1 /. 4721 = 2. 118195 The hedge ratio may also be viewed as the number of shares that must be purchased for each option sold. In our example, the hedge ratio of. 4721 implies that 47. 21 shares purchased for every call option sold is a hedged position.
Example of Hedge (cont. ) n n n Number of call options to hedge 100 shares 1 / Hedge ratio Defines the number of call options that must be sold for each 100 shares purchased. Our example: 1 /. 4721 = 2. 118195 The hedge ratio may also be viewed as the number of shares that must be purchased for each option sold. In our example, the hedge ratio of. 4721 implies that 47. 21 shares purchased for every call option sold is a hedged position.
 Additional Option Strategies Covered Put n Protective Put n Straddle n Bull Spread n Bear Spread n Butterfly Spread n
Additional Option Strategies Covered Put n Protective Put n Straddle n Bull Spread n Bear Spread n Butterfly Spread n
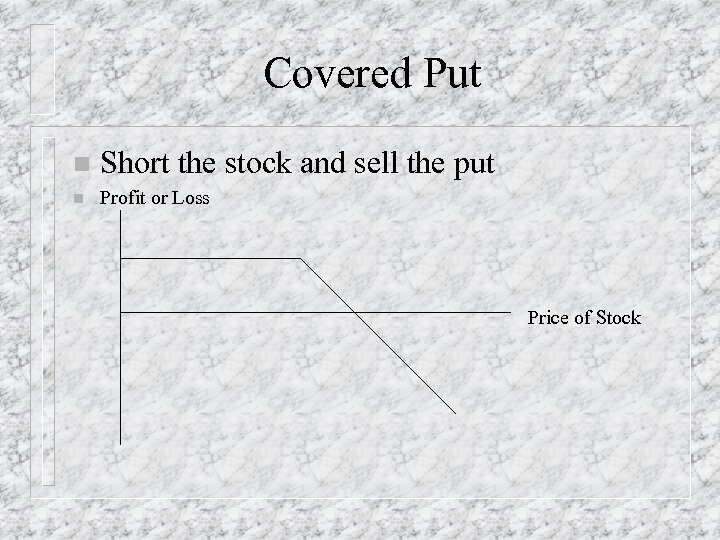 Covered Put n Short the stock and sell the put n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
Covered Put n Short the stock and sell the put n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
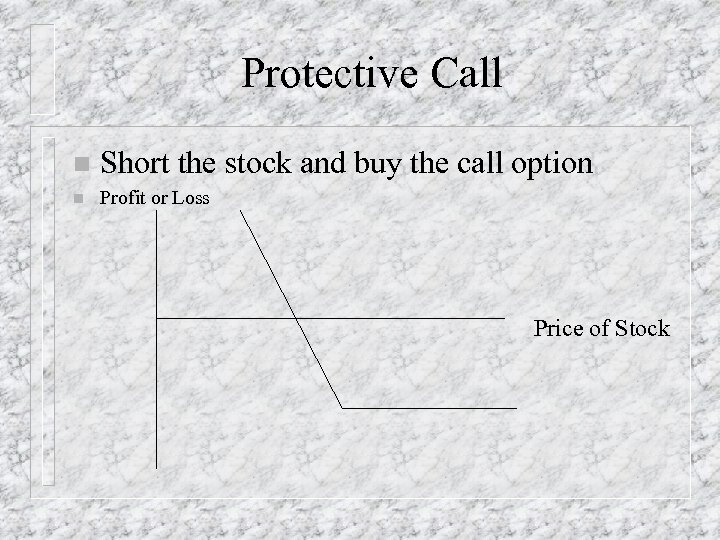 Protective Call n Short the stock and buy the call option n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
Protective Call n Short the stock and buy the call option n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
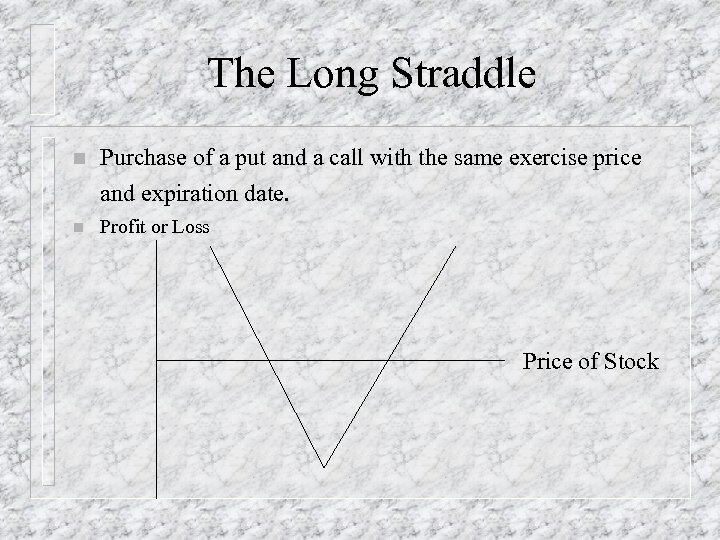 The Long Straddle n Purchase of a put and a call with the same exercise price and expiration date. n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
The Long Straddle n Purchase of a put and a call with the same exercise price and expiration date. n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
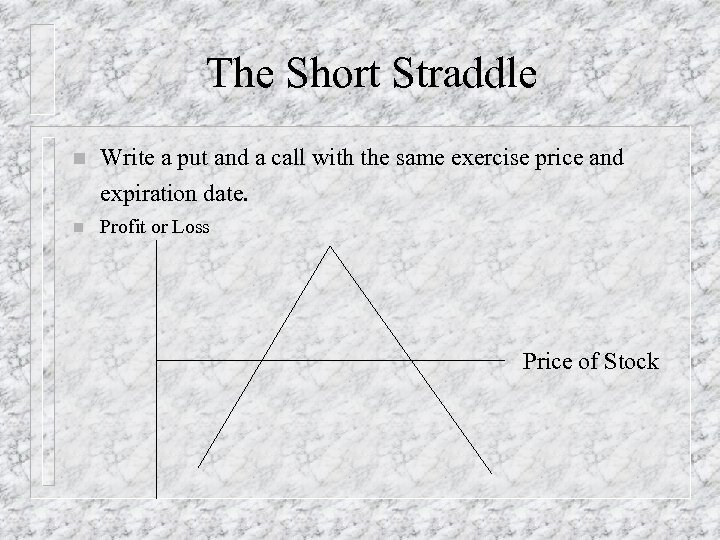 The Short Straddle n Write a put and a call with the same exercise price and expiration date. n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
The Short Straddle n Write a put and a call with the same exercise price and expiration date. n Profit or Loss Price of Stock
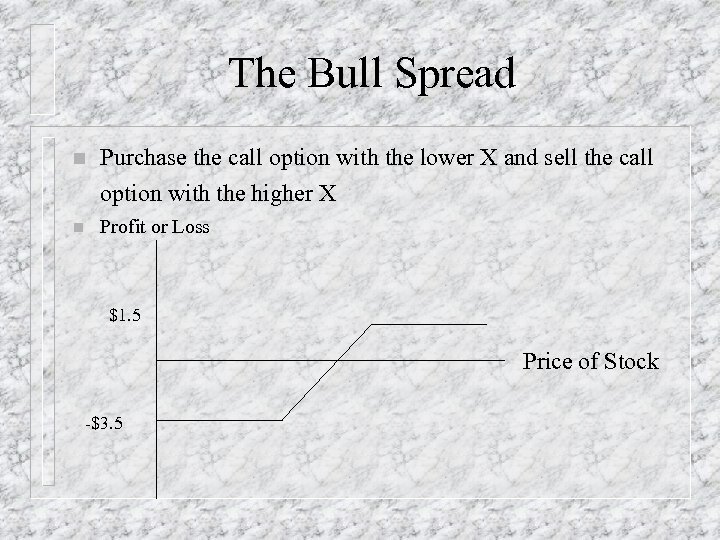 The Bull Spread n Purchase the call option with the lower X and sell the call option with the higher X n Profit or Loss $1. 5 Price of Stock -$3. 5
The Bull Spread n Purchase the call option with the lower X and sell the call option with the higher X n Profit or Loss $1. 5 Price of Stock -$3. 5
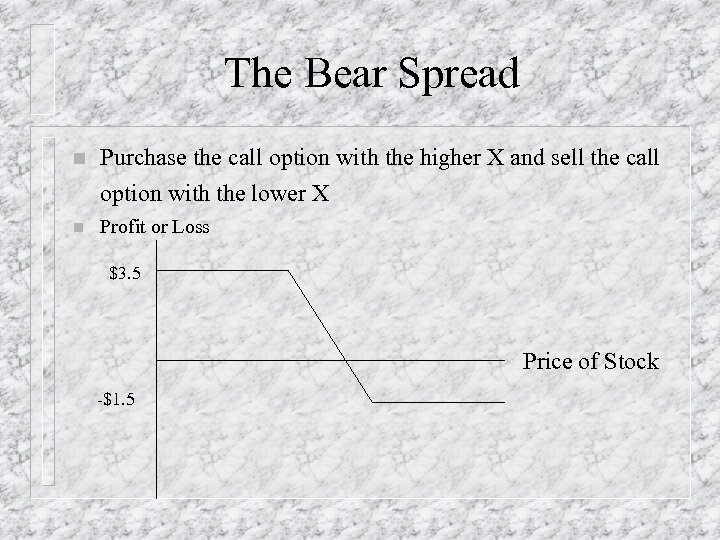 The Bear Spread n Purchase the call option with the higher X and sell the call option with the lower X n Profit or Loss $3. 5 Price of Stock -$1. 5
The Bear Spread n Purchase the call option with the higher X and sell the call option with the lower X n Profit or Loss $3. 5 Price of Stock -$1. 5
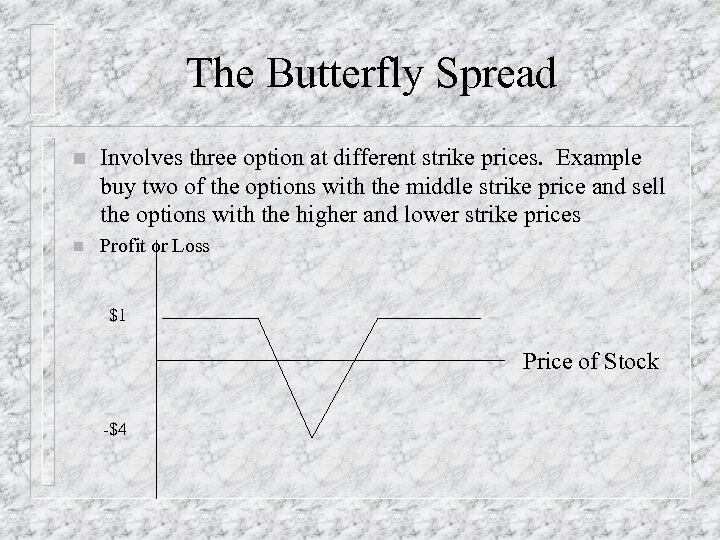 The Butterfly Spread n Involves three option at different strike prices. Example buy two of the options with the middle strike price and sell the options with the higher and lower strike prices n Profit or Loss $1 Price of Stock -$4
The Butterfly Spread n Involves three option at different strike prices. Example buy two of the options with the middle strike price and sell the options with the higher and lower strike prices n Profit or Loss $1 Price of Stock -$4
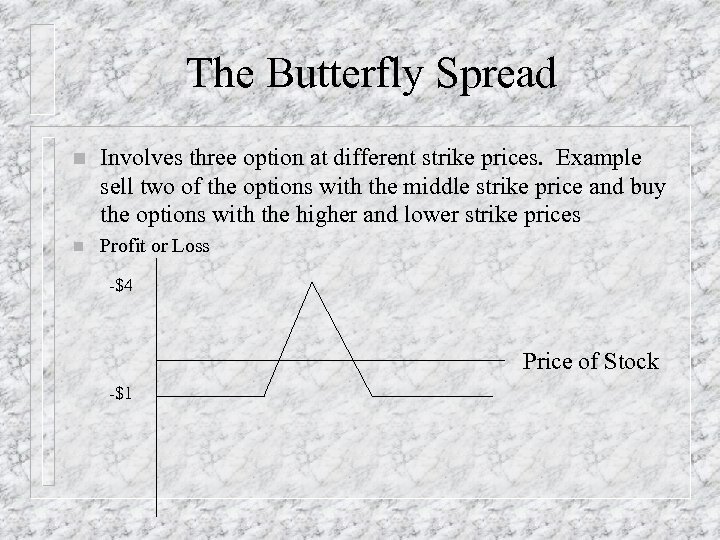 The Butterfly Spread n Involves three option at different strike prices. Example sell two of the options with the middle strike price and buy the options with the higher and lower strike prices n Profit or Loss -$4 Price of Stock -$1
The Butterfly Spread n Involves three option at different strike prices. Example sell two of the options with the middle strike price and buy the options with the higher and lower strike prices n Profit or Loss -$4 Price of Stock -$1


