7aa4496ba81a8f4ab0d5ad88db525bc4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 63
 Chapter 20 Genetics and Human Inheritance Lecture Presentation Betty Mc. Guire Cornell University Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 20 Genetics and Human Inheritance Lecture Presentation Betty Mc. Guire Cornell University Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Genetics and Human Inheritance § Principles of inheritance § Breaks in chromosomes § Detecting genetic disorders Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Genetics and Human Inheritance § Principles of inheritance § Breaks in chromosomes § Detecting genetic disorders Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Genetic information § Carried on chromosomes that are carried in the egg and sperm in equal numbers Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Genetic information § Carried on chromosomes that are carried in the egg and sperm in equal numbers Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
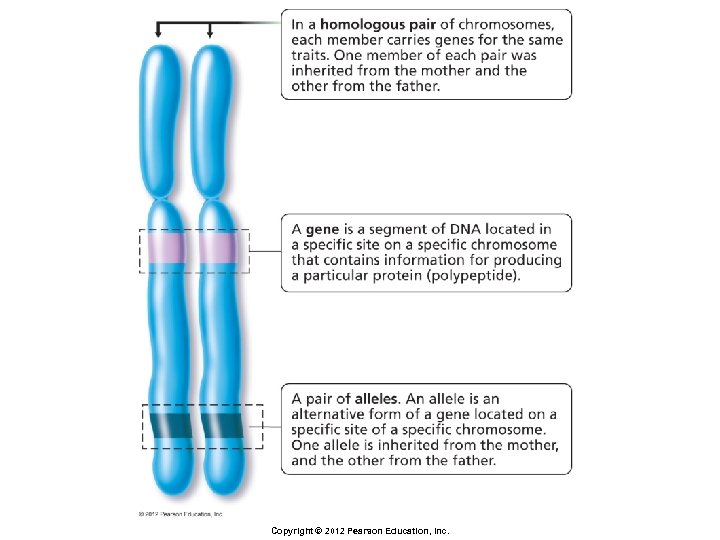
 Principles of Inheritance § Homologous pairs of chromosomes § 23 chromosomes received from one parent pair with 23 chromosomes from the other parent § Each member of a homologous pair carries genes for the same traits Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Homologous pairs of chromosomes § 23 chromosomes received from one parent pair with 23 chromosomes from the other parent § Each member of a homologous pair carries genes for the same traits Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Genes § Segments of DNA § Code for a specific protein that will play a structural or functional role in the cell Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Genes § Segments of DNA § Code for a specific protein that will play a structural or functional role in the cell Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Trait § Characteristic § Produced by the actions of one or more gene -directed proteins Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Trait § Characteristic § Produced by the actions of one or more gene -directed proteins Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Alleles § Different forms of a gene § Produce different versions of the trait they determine § Example: gene for freckles § One allele causes freckles to form § Other allele does not Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Alleles § Different forms of a gene § Produce different versions of the trait they determine § Example: gene for freckles § One allele causes freckles to form § Other allele does not Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
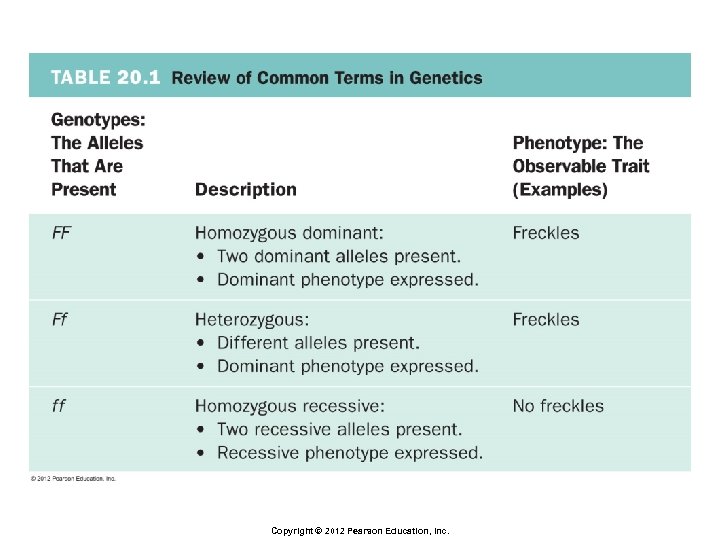
 Principles of Inheritance § Homozygous § Individuals with two copies of the same allele § Heterozygous § Individuals with different alleles of a given gene Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Homozygous § Individuals with two copies of the same allele § Heterozygous § Individuals with different alleles of a given gene Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Dominant § When the effects of an allele can be detected regardless of the alternative allele § Recessive § When the effects of an allele are masked in the heterozygous condition Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Dominant § When the effects of an allele can be detected regardless of the alternative allele § Recessive § When the effects of an allele are masked in the heterozygous condition Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Genotype § Alleles that are present § Genetic composition of an individual § Phenotype § Observable physical traits of an individual Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Genotype § Alleles that are present § Genetic composition of an individual § Phenotype § Observable physical traits of an individual Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
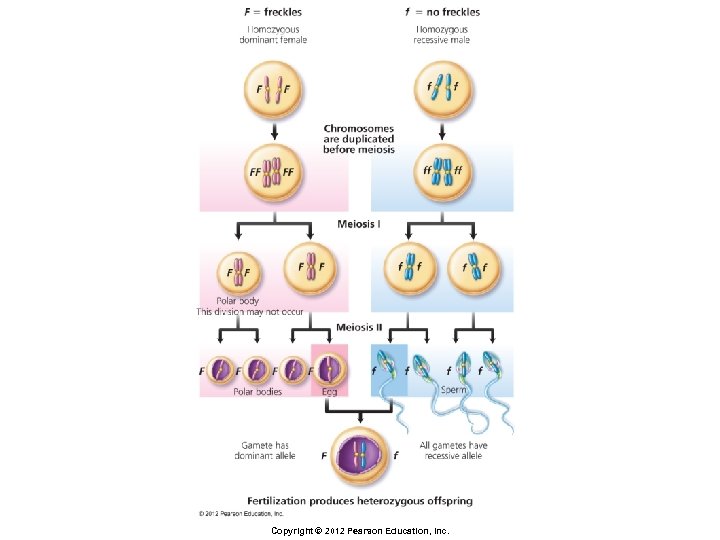
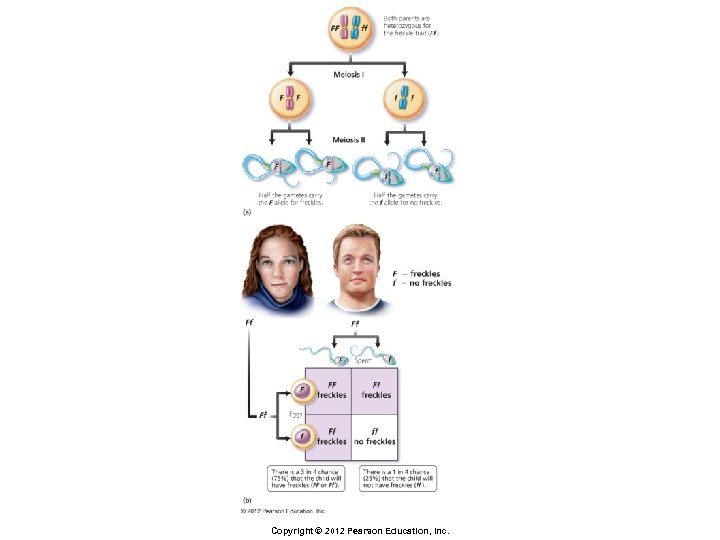
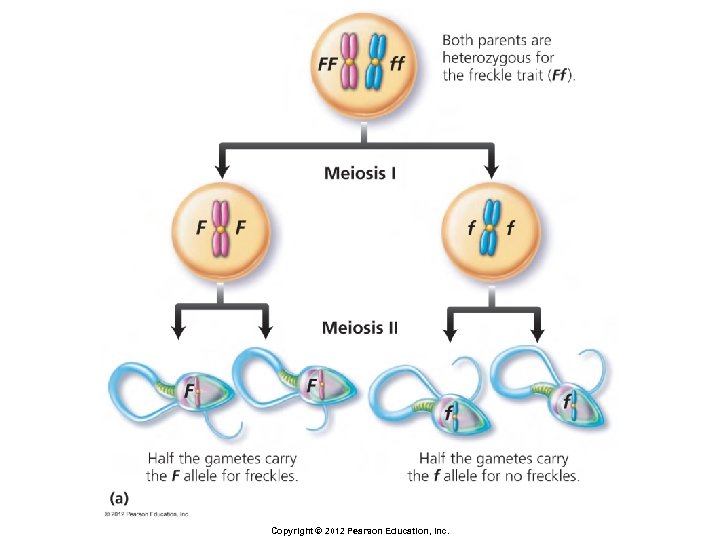
 Principles of Inheritance § Law of Segregation § During gamete formation, the two alleles for each gene separate as the homologous chromosomes move toward opposite ends of the cell during meiosis § Each chromosome is inherited independent of the other chromosomes, following the Law of Independent Assortment Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Law of Segregation § During gamete formation, the two alleles for each gene separate as the homologous chromosomes move toward opposite ends of the cell during meiosis § Each chromosome is inherited independent of the other chromosomes, following the Law of Independent Assortment Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Gregor Mendel § Studied how single genes are inherited from parent to offspring § First used one-trait crosses § Then used two-trait (dihybrid) crosses Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Gregor Mendel § Studied how single genes are inherited from parent to offspring § First used one-trait crosses § Then used two-trait (dihybrid) crosses Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
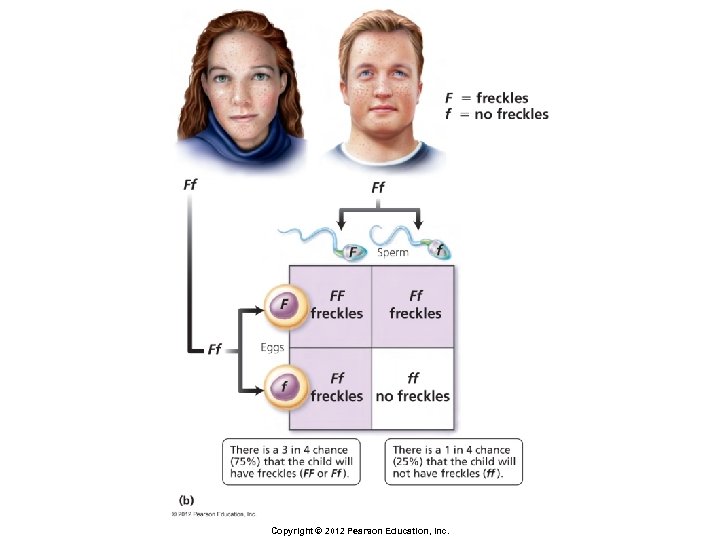
 Principles of Inheritance § Punnett square § Matrix used to predict genetic makeup of offspring of individuals of particular genotypes § Rows represent possible gametes of one parent § Columns represent possible gametes of the other parent § Boxes represent possible combinations of gametes Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Punnett square § Matrix used to predict genetic makeup of offspring of individuals of particular genotypes § Rows represent possible gametes of one parent § Columns represent possible gametes of the other parent § Boxes represent possible combinations of gametes Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
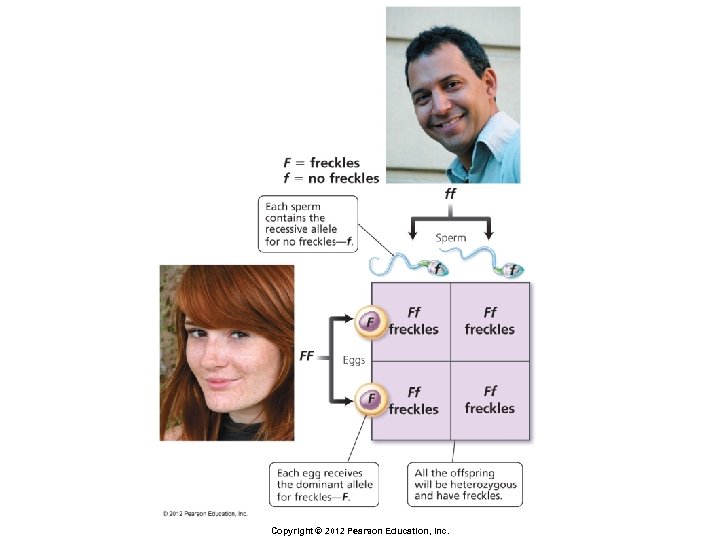
 Principles of Inheritance § Monohybrid cross § Cross in which both parents are heterozygous for one trait of interest § Genotypic ratio of offspring § 1 FF : 2 Ff : 1 ff § Phenotypic ratio of offspring § 3 with freckles (FF and Ff) : 1 without (ff) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Monohybrid cross § Cross in which both parents are heterozygous for one trait of interest § Genotypic ratio of offspring § 1 FF : 2 Ff : 1 ff § Phenotypic ratio of offspring § 3 with freckles (FF and Ff) : 1 without (ff) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
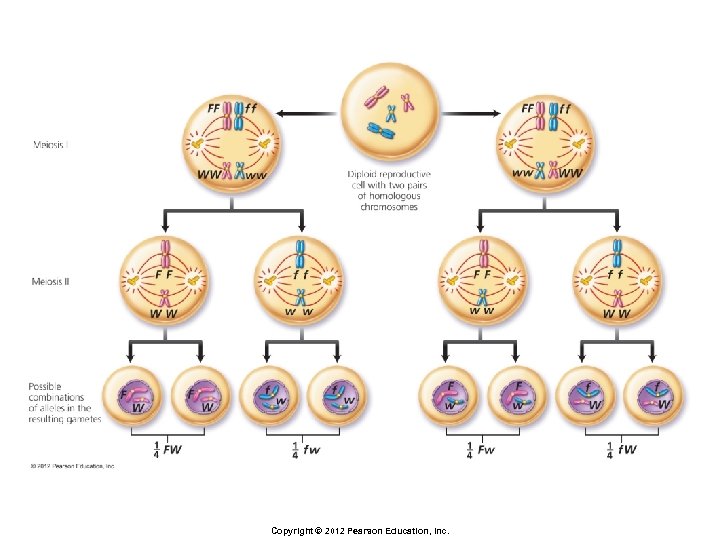
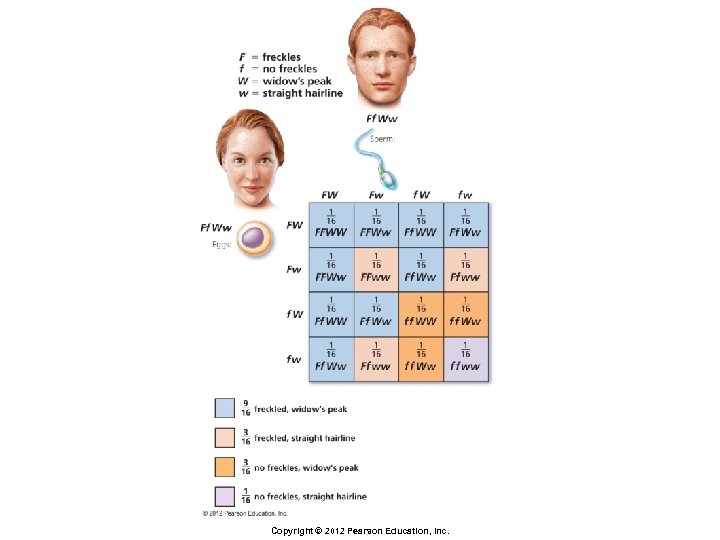
 Principles of Inheritance § Dihybrid cross § Cross in which both parents are heterozygous for two traits of interest § Phenotypic ratio of offspring § 9 : 3 : 1 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Dihybrid cross § Cross in which both parents are heterozygous for two traits of interest § Phenotypic ratio of offspring § 9 : 3 : 1 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance Web Activity: One- and Two-Trait Crosses Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance Web Activity: One- and Two-Trait Crosses Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
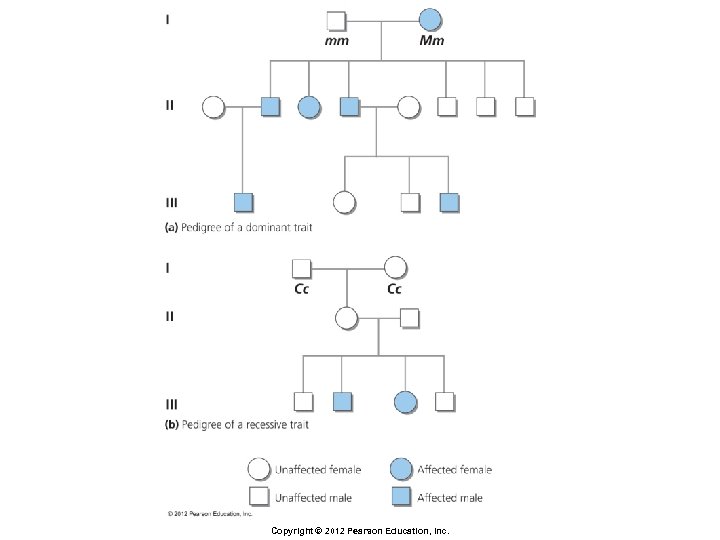
 Principles of Inheritance § Pedigree § Chart showing the genetic connections among individuals in a family § Especially useful in following recessive alleles that are not visible in the heterozygote Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Pedigree § Chart showing the genetic connections among individuals in a family § Especially useful in following recessive alleles that are not visible in the heterozygote Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
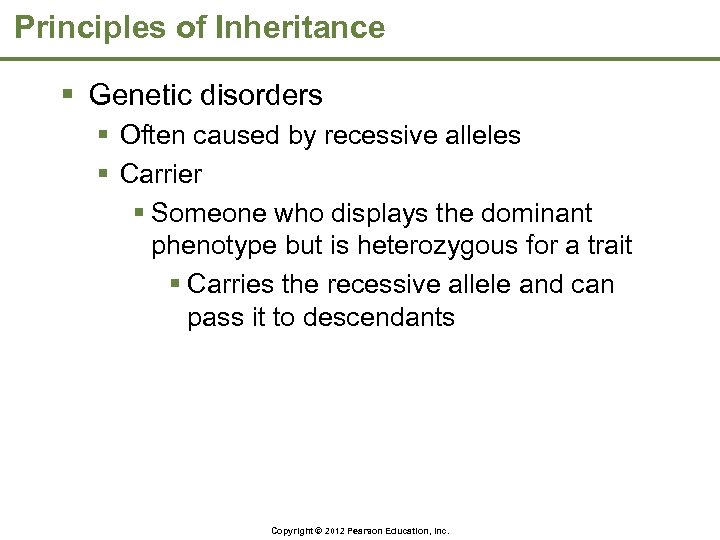 Principles of Inheritance § Genetic disorders § Often caused by recessive alleles § Carrier § Someone who displays the dominant phenotype but is heterozygous for a trait § Carries the recessive allele and can pass it to descendants Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Genetic disorders § Often caused by recessive alleles § Carrier § Someone who displays the dominant phenotype but is heterozygous for a trait § Carries the recessive allele and can pass it to descendants Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Dominant allele § Often produces a functional protein that the recessive allele does not Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Dominant allele § Often produces a functional protein that the recessive allele does not Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
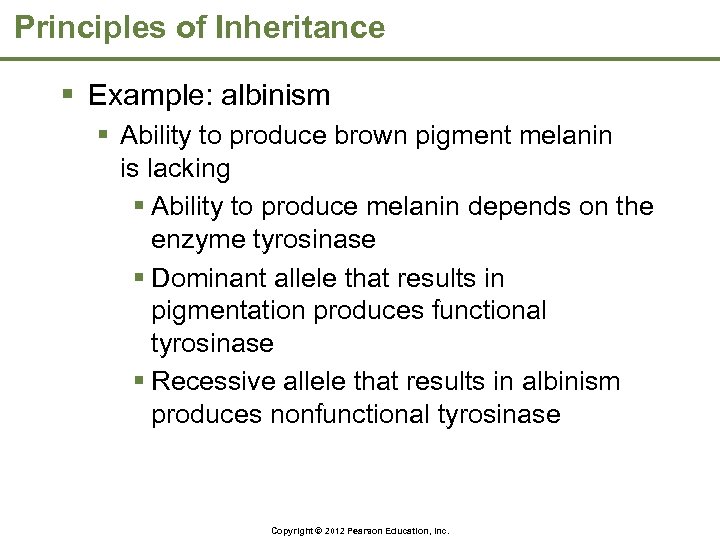 Principles of Inheritance § Example: albinism § Ability to produce brown pigment melanin is lacking § Ability to produce melanin depends on the enzyme tyrosinase § Dominant allele that results in pigmentation produces functional tyrosinase § Recessive allele that results in albinism produces nonfunctional tyrosinase Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Example: albinism § Ability to produce brown pigment melanin is lacking § Ability to produce melanin depends on the enzyme tyrosinase § Dominant allele that results in pigmentation produces functional tyrosinase § Recessive allele that results in albinism produces nonfunctional tyrosinase Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Complete dominance § Heterozygote exhibits the trait associated with the dominant allele but not that of the recessive allele Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Complete dominance § Heterozygote exhibits the trait associated with the dominant allele but not that of the recessive allele Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Codominance § Effects of both alleles are apparent in a heterozygote § Example: blood type AB § The protein products of both the A and B alleles are expressed on the surface of the red blood cell Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Codominance § Effects of both alleles are apparent in a heterozygote § Example: blood type AB § The protein products of both the A and B alleles are expressed on the surface of the red blood cell Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
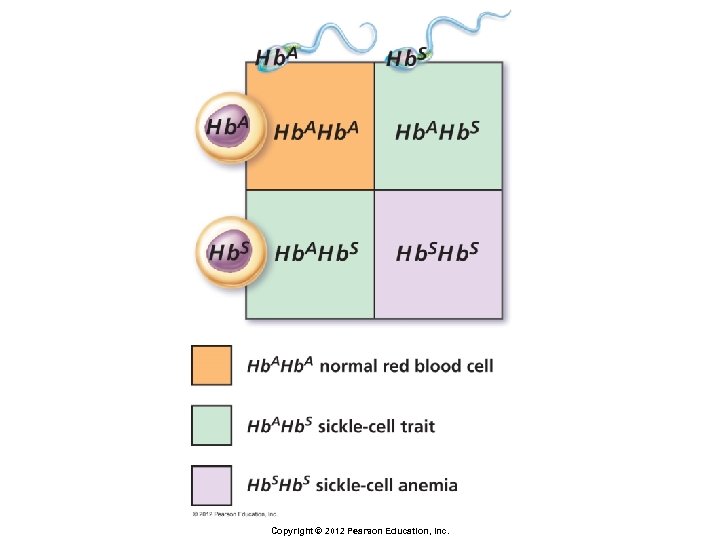
 Principles of Inheritance § Incomplete dominance § Expression of the trait in a heterozygous individual is in between the way the trait is expressed in a homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive person § Example: sickle-cell allele § Heterozygote has sickle-cell trait (Hb. AHb. S) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Incomplete dominance § Expression of the trait in a heterozygous individual is in between the way the trait is expressed in a homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive person § Example: sickle-cell allele § Heterozygote has sickle-cell trait (Hb. AHb. S) Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance Web Activity: Codominance and Incomplete Dominance Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance Web Activity: Codominance and Incomplete Dominance Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
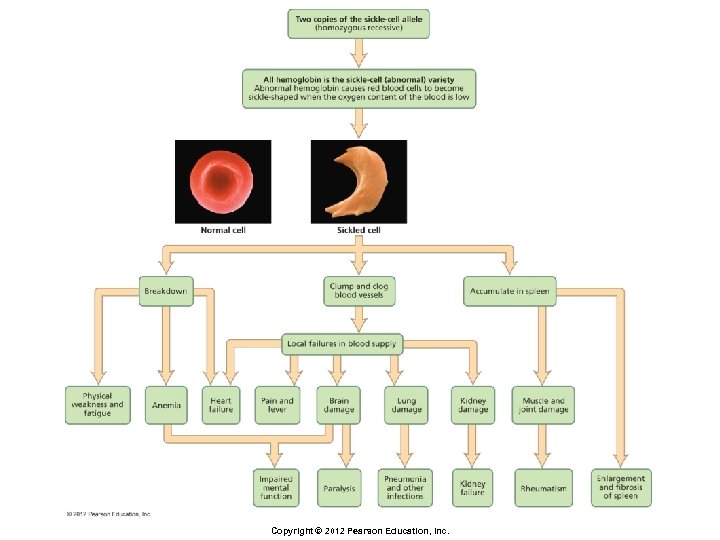
 Principles of Inheritance § Pleiotropy § One gene having many effects § Sickling of red blood cells caused by abnormal hemoglobin affects many areas of the body Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Pleiotropy § One gene having many effects § Sickling of red blood cells caused by abnormal hemoglobin affects many areas of the body Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
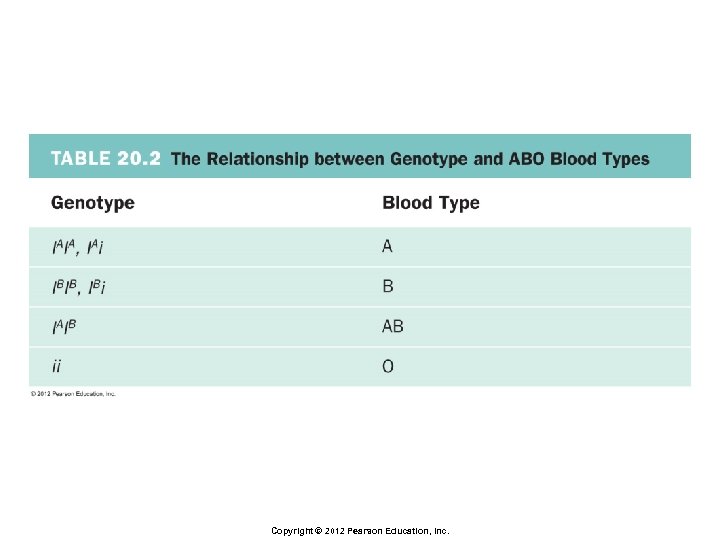
 Principles of Inheritance § Multiple alleles § When three or more forms of a given gene exist across many people in the population § Example: ABO blood types § Gene has three alleles: IA, IB, i Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Multiple alleles § When three or more forms of a given gene exist across many people in the population § Example: ABO blood types § Gene has three alleles: IA, IB, i Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
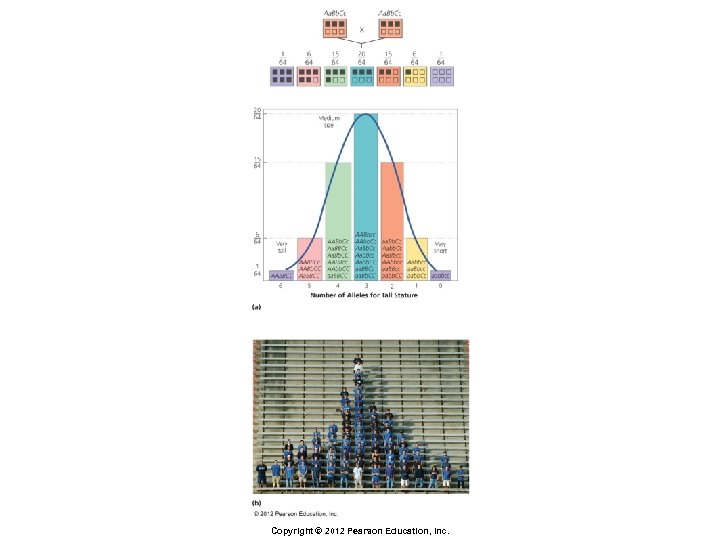
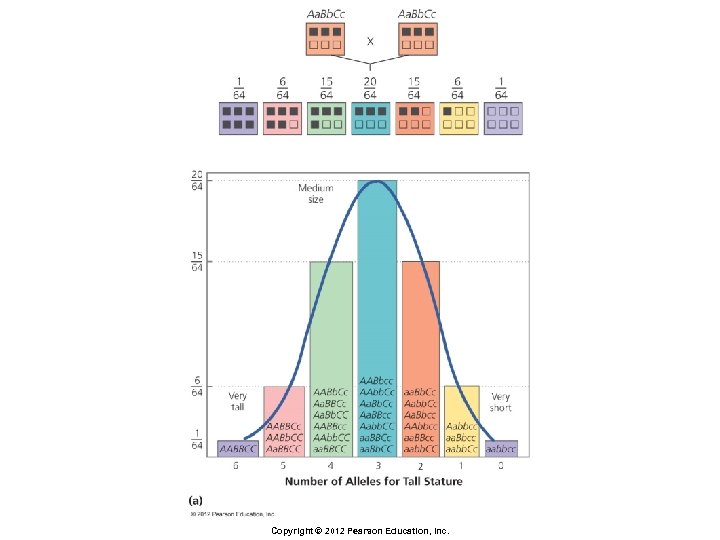
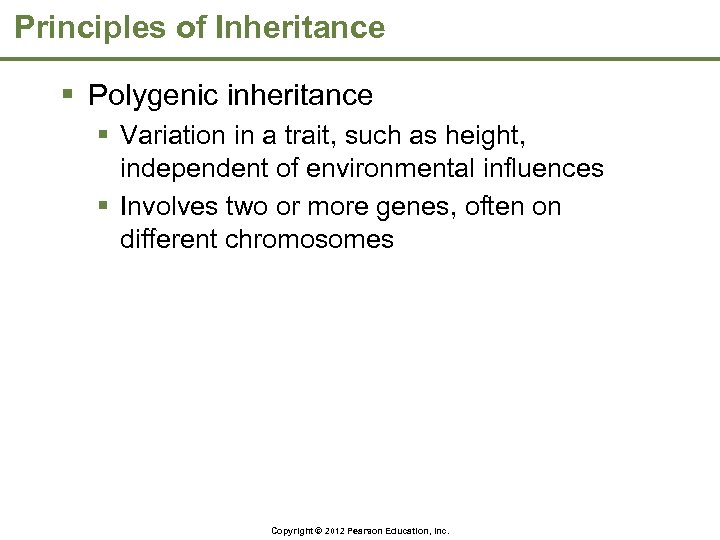 Principles of Inheritance § Polygenic inheritance § Variation in a trait, such as height, independent of environmental influences § Involves two or more genes, often on different chromosomes Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Polygenic inheritance § Variation in a trait, such as height, independent of environmental influences § Involves two or more genes, often on different chromosomes Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Genes on the same chromosome § Usually inherited together § Described as being linked Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Genes on the same chromosome § Usually inherited together § Described as being linked Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
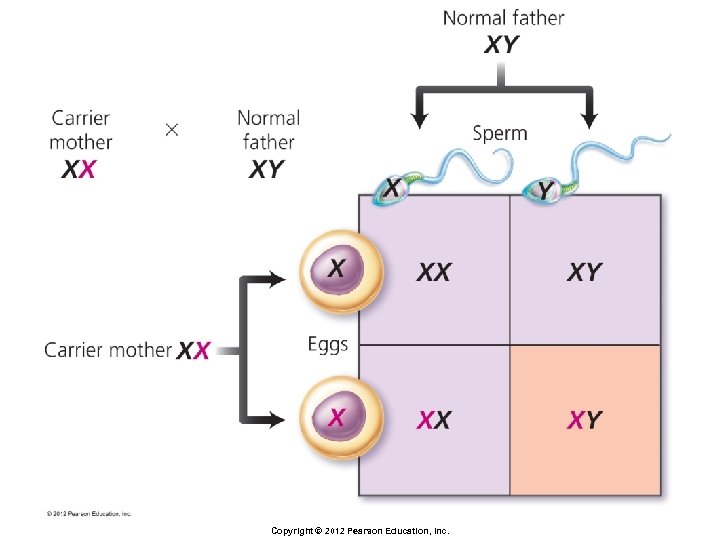
 Principles of Inheritance § Sex-linked genes § Y chromosome is much smaller than X chromosome § Y carries fewer genes § Most genes on the X chromosome have no corresponding alleles on the Y chromosome § Known as X-linked genes § Different pattern of inheritance § Recessive phenotype of X-linked genes more common in males § Son can inherit X-linked recessive only from mother Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Sex-linked genes § Y chromosome is much smaller than X chromosome § Y carries fewer genes § Most genes on the X chromosome have no corresponding alleles on the Y chromosome § Known as X-linked genes § Different pattern of inheritance § Recessive phenotype of X-linked genes more common in males § Son can inherit X-linked recessive only from mother Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Examples of disorders caused by X-linked recessive alleles § Red-green color blindness § Two forms of hemophilia § Duchenne muscular dystrophy Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Examples of disorders caused by X-linked recessive alleles § Red-green color blindness § Two forms of hemophilia § Duchenne muscular dystrophy Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance Web Activity: Sex-Linked Traits Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance Web Activity: Sex-Linked Traits Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Inheritance § Sex-influenced genes § Autosomal genes whose expression is influenced by sex hormones § Example: male pattern baldness § More common in men than in women because its expression depends on both the presence of the allele for baldness and the presence of testosterone Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Principles of Inheritance § Sex-influenced genes § Autosomal genes whose expression is influenced by sex hormones § Example: male pattern baldness § More common in men than in women because its expression depends on both the presence of the allele for baldness and the presence of testosterone Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Breaks in Chromosomes § Chromosome breakage § Usually caused by § Chemicals § Radiation § Viruses § Results in changes in the structure and function of the chromosome Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Breaks in Chromosomes § Chromosome breakage § Usually caused by § Chemicals § Radiation § Viruses § Results in changes in the structure and function of the chromosome Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
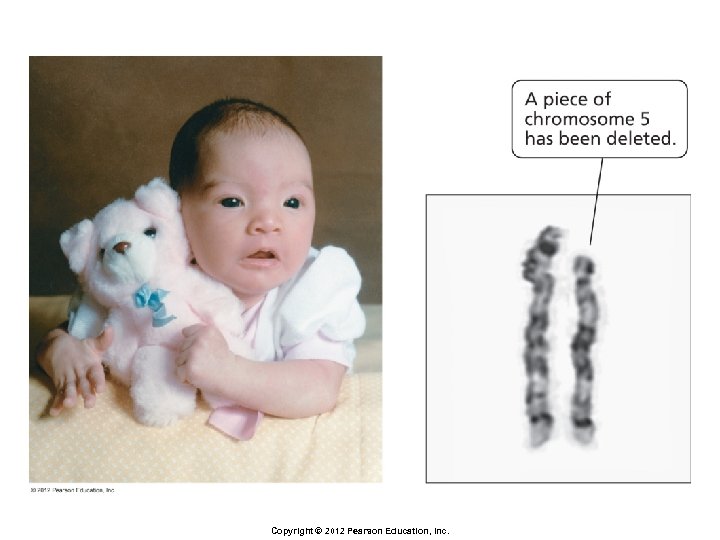
 Breaks in Chromosomes § Deletion § Loss of a piece of chromosome § Most common deletion occurs when the tip of a chromosome breaks off § Example: cri-du-chat syndrome § Loss of tip of chromosome 5 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Breaks in Chromosomes § Deletion § Loss of a piece of chromosome § Most common deletion occurs when the tip of a chromosome breaks off § Example: cri-du-chat syndrome § Loss of tip of chromosome 5 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
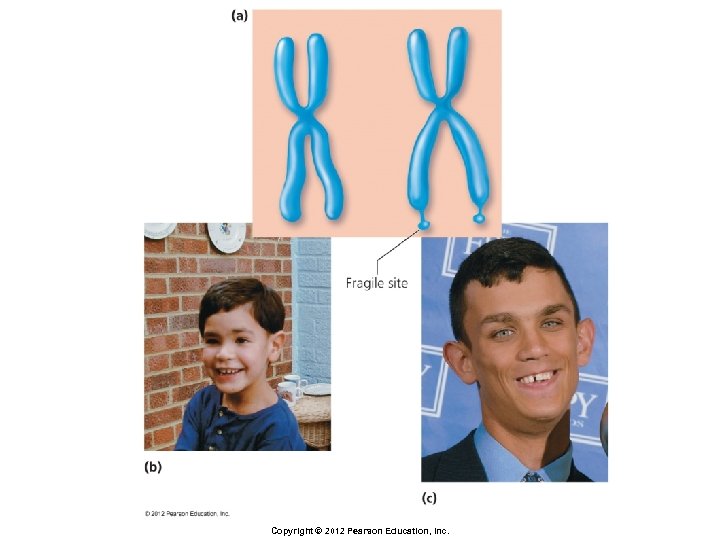
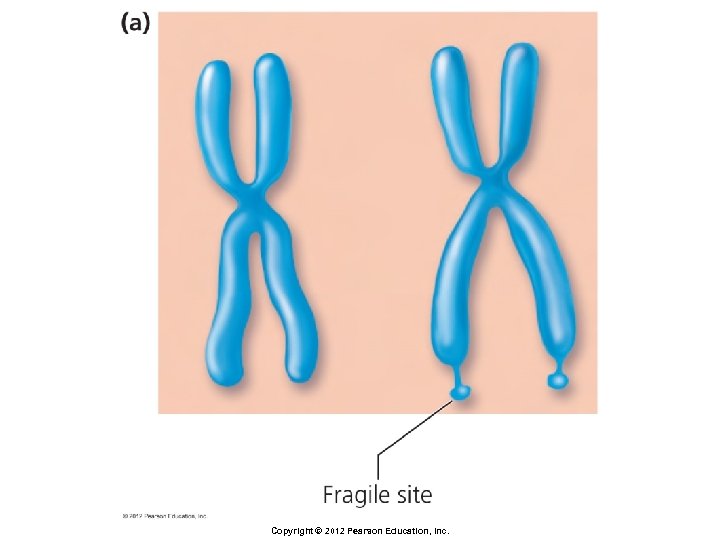
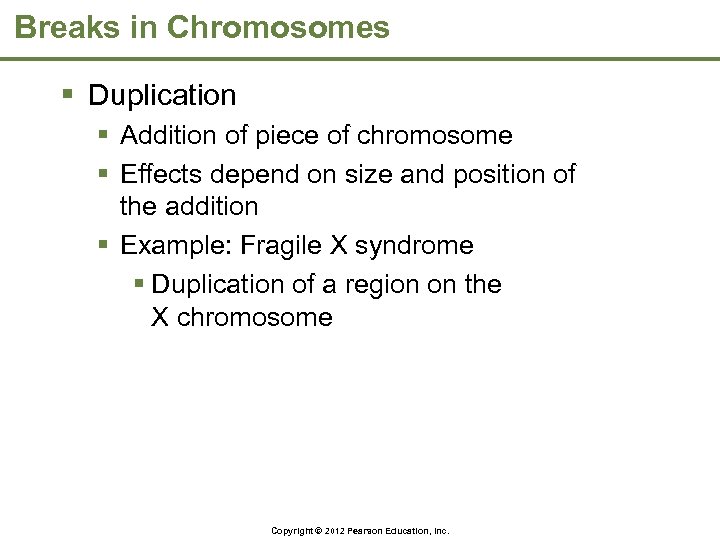 Breaks in Chromosomes § Duplication § Addition of piece of chromosome § Effects depend on size and position of the addition § Example: Fragile X syndrome § Duplication of a region on the X chromosome Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Breaks in Chromosomes § Duplication § Addition of piece of chromosome § Effects depend on size and position of the addition § Example: Fragile X syndrome § Duplication of a region on the X chromosome Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Detecting Genetic Disorders § Prenatal genetic testing is recommended § If a defective gene runs in the family § When the mother is older than 35 § Due to increased risks of nondisjunction Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Detecting Genetic Disorders § Prenatal genetic testing is recommended § If a defective gene runs in the family § When the mother is older than 35 § Due to increased risks of nondisjunction Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
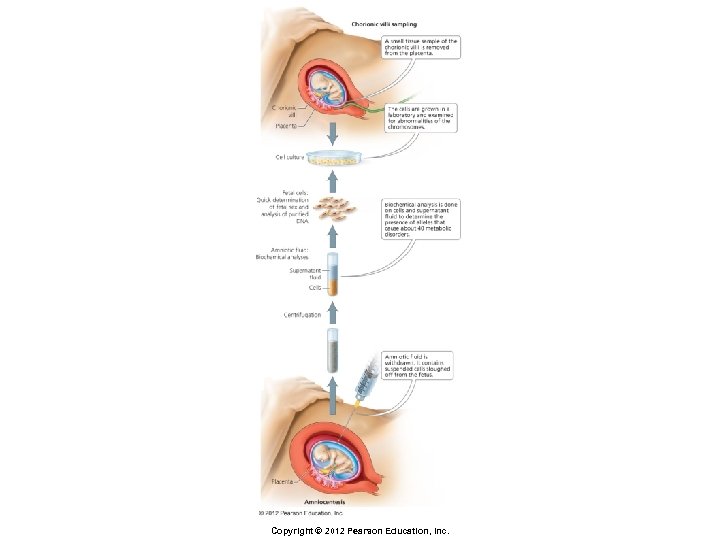
 Detecting Genetic Disorders § Amniocentesis § 10– 20 ml of amniotic fluid is withdrawn, which contain epithelial cells of the fetus § Cells are cultured and then examined § Abnormalities in the number of chromosomes § Presence of certain alleles that are likely to cause specific diseases Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Detecting Genetic Disorders § Amniocentesis § 10– 20 ml of amniotic fluid is withdrawn, which contain epithelial cells of the fetus § Cells are cultured and then examined § Abnormalities in the number of chromosomes § Presence of certain alleles that are likely to cause specific diseases Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Detecting Genetic Disorders § Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) § Involves taking a small piece of chorionic villi § Fingerlike projections of the chorion § Cells of chorion have same genetic makeup as fetus § Cells are cultured and then chromosomes examined Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Detecting Genetic Disorders § Chorionic villi sampling (CVS) § Involves taking a small piece of chorionic villi § Fingerlike projections of the chorion § Cells of chorion have same genetic makeup as fetus § Cells are cultured and then chromosomes examined Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Detecting Genetic Disorders § Newborn genetic testing § Blood test screens for phenylketonuria (PKU) § Adult genetic testing § Many predictive genetic tests are now available or being developed § Some identify people who are at risk or predisposed for a specific disease before symptoms appear Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.
Detecting Genetic Disorders § Newborn genetic testing § Blood test screens for phenylketonuria (PKU) § Adult genetic testing § Many predictive genetic tests are now available or being developed § Some identify people who are at risk or predisposed for a specific disease before symptoms appear Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.


