bbbe189731a36516b02bb38babeb8ebc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 103
 Chapter 2 The first Civilizations—Egypt—The Gift of the Nile
Chapter 2 The first Civilizations—Egypt—The Gift of the Nile
 Egypt
Egypt
 Nile River Valley o o Narrow strip of land about 10 miles wide Early people learned to control river – canals, dikes, reservoirs, irrigation ditches
Nile River Valley o o Narrow strip of land about 10 miles wide Early people learned to control river – canals, dikes, reservoirs, irrigation ditches
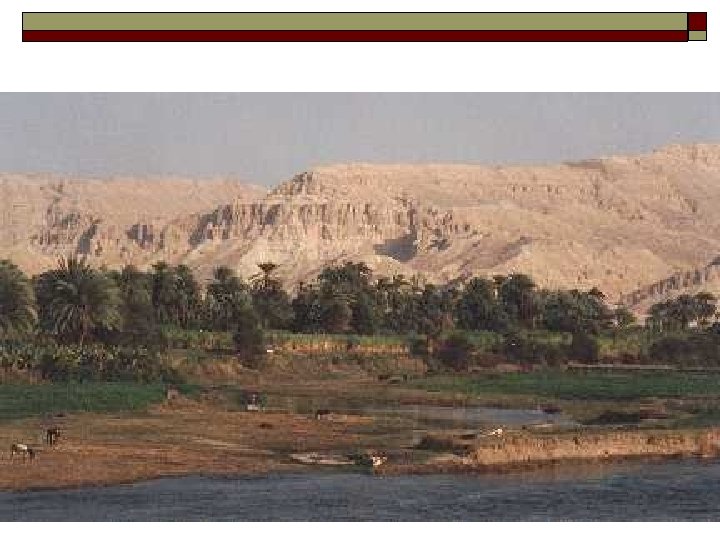

 Nile River o River n n n Flows north Originates in the highlands of Ethiopia (Blue Nile) White Nile comes from lakes of central Africa-main source is Lake Victoria Ends in the Mediterranean Sea Longest river in the world at 4, 160 miles
Nile River o River n n n Flows north Originates in the highlands of Ethiopia (Blue Nile) White Nile comes from lakes of central Africa-main source is Lake Victoria Ends in the Mediterranean Sea Longest river in the world at 4, 160 miles
 Nile River o Floods n n n Until recently, flooded annually in July. Sept Floods predictable Added moisture to the soil Deposited silt, replenishing the soil with nutrients-food, water and transportation delta to form at the mouth of the river Provided papyrus-reed that grows along the banks of the Nile
Nile River o Floods n n n Until recently, flooded annually in July. Sept Floods predictable Added moisture to the soil Deposited silt, replenishing the soil with nutrients-food, water and transportation delta to form at the mouth of the river Provided papyrus-reed that grows along the banks of the Nile
 First People o o 5, 000 to 4, 000 B. C. E. Divided into two regions Upper Egypt – first cataract to 100 miles of the sea Lower Egypt – from delta inland 100 miles
First People o o 5, 000 to 4, 000 B. C. E. Divided into two regions Upper Egypt – first cataract to 100 miles of the sea Lower Egypt – from delta inland 100 miles
 Natural Barriers o o Deserts- Lybian, Nubian, Arabian Seas- Mediterranean and Red Cataracts- waterfalls and rapids which interrupt Nile six times Only real access into Egypt was across the Sinai Peninsula- invaders and traders used this route into Egypt
Natural Barriers o o Deserts- Lybian, Nubian, Arabian Seas- Mediterranean and Red Cataracts- waterfalls and rapids which interrupt Nile six times Only real access into Egypt was across the Sinai Peninsula- invaders and traders used this route into Egypt
 The Nile River Valley
The Nile River Valley
 King Menes 3100 B. C. E. Unites the two kingdoms o First Egyptian dynasty o
King Menes 3100 B. C. E. Unites the two kingdoms o First Egyptian dynasty o
 Ruling Dynasties o Approximately 31 dynasties (ruling families) from 2700 B. C. E. to 1090 B. C. E. Dynasties ruled Egypt for a total of ~ 2700 years o Years between kingdoms without ruling dynasty usually marked by civil wars and/or invasion o
Ruling Dynasties o Approximately 31 dynasties (ruling families) from 2700 B. C. E. to 1090 B. C. E. Dynasties ruled Egypt for a total of ~ 2700 years o Years between kingdoms without ruling dynasty usually marked by civil wars and/or invasion o
 Egyptian Historical Periods o Ancient Egyptian history divided into three periods n n n Old Kingdom Middle Kingdom New Kingdom
Egyptian Historical Periods o Ancient Egyptian history divided into three periods n n n Old Kingdom Middle Kingdom New Kingdom
 Old Kingdom 2700 B. C. E. to 2200 B. C. E. AKA - The Pyramid Age Rulers called Pharaohs (great house) - claimed to be divine and worshiped as gods on Earth Chief god – Amon-Re (pharaohs sons of Sun god) Pharaohs had absolute power ( owned all land water) Viziers – supervisors that ran the government o o o
Old Kingdom 2700 B. C. E. to 2200 B. C. E. AKA - The Pyramid Age Rulers called Pharaohs (great house) - claimed to be divine and worshiped as gods on Earth Chief god – Amon-Re (pharaohs sons of Sun god) Pharaohs had absolute power ( owned all land water) Viziers – supervisors that ran the government o o o
 OLD KINGDOM o o o Era was remarkable for prosperity, artistic flowering, and the evolution of religious beliefs Pharaoh commanded the wealth, resources, and people of all Egypt Pharaoh cared for his people
OLD KINGDOM o o o Era was remarkable for prosperity, artistic flowering, and the evolution of religious beliefs Pharaoh commanded the wealth, resources, and people of all Egypt Pharaoh cared for his people
 The Great Pyramid of Khufu About 2560 B. C. E.
The Great Pyramid of Khufu About 2560 B. C. E.
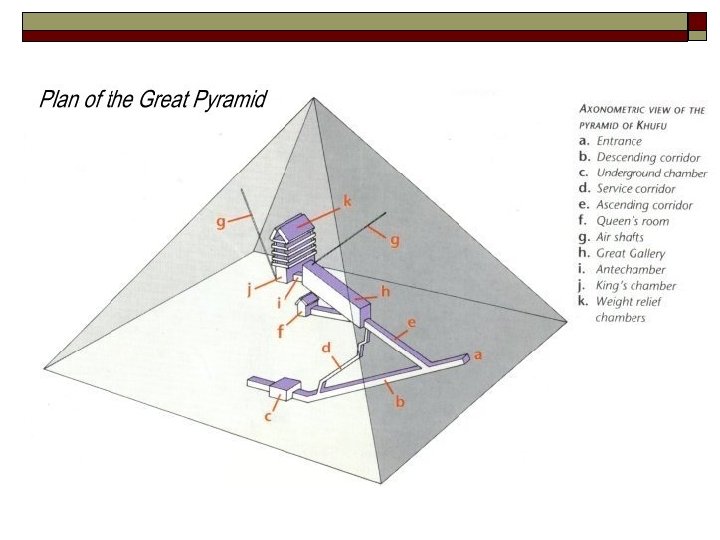
 The Great Pyramid of Khufu o o Egypt had great enormous quantities of stone for building Took 20 years to build 481 feet tall- tallest structure in the world for 43 centuries Each side perfectly aligned North, South, East, & West
The Great Pyramid of Khufu o o Egypt had great enormous quantities of stone for building Took 20 years to build 481 feet tall- tallest structure in the world for 43 centuries Each side perfectly aligned North, South, East, & West
 The Great Pyramid of Khufu o o o Each side 751 feet long – error of less than 9 inches per side Covers 13 acres Used more than 2 million stones – each more than 2 tons some more than 15 tons
The Great Pyramid of Khufu o o o Each side 751 feet long – error of less than 9 inches per side Covers 13 acres Used more than 2 million stones – each more than 2 tons some more than 15 tons
 The Great Sphinx o o o Located in Giza Body of a lion and face of a man (the pharaoh Khafre) Faces the rising sun—tall as a six-story building
The Great Sphinx o o o Located in Giza Body of a lion and face of a man (the pharaoh Khafre) Faces the rising sun—tall as a six-story building

 Step Pyramid at Sakkara is oldest stone building in the world which was built for the pharaoh Zoser
Step Pyramid at Sakkara is oldest stone building in the world which was built for the pharaoh Zoser
 Old Kingdom ended about 2200 B. C. E. o Reasons: n n n o o Cost of Pyramids Crop failure Power struggle Results: over 100 years of chaos Princes from the city of Thebes reunited Egypt
Old Kingdom ended about 2200 B. C. E. o Reasons: n n n o o Cost of Pyramids Crop failure Power struggle Results: over 100 years of chaos Princes from the city of Thebes reunited Egypt
 Middle Kingdom 2050 B. C. E. to 1800 B. C. E. o Marked by troubles – n o corruption, rebellions, Nile failed to flood regularly Accomplishment: n n n Drainage projects Canal from Red Sea to Mediterranean Sea Pharaohs more concerned with common people-allowed mummification
Middle Kingdom 2050 B. C. E. to 1800 B. C. E. o Marked by troubles – n o corruption, rebellions, Nile failed to flood regularly Accomplishment: n n n Drainage projects Canal from Red Sea to Mediterranean Sea Pharaohs more concerned with common people-allowed mummification
 Middle Kingdom o o Increased trade Egyptian Army invades Nubia and occupied rich gold lands
Middle Kingdom o o Increased trade Egyptian Army invades Nubia and occupied rich gold lands
 End of Middle Kingdom o o About 1700 B. C. E. invaded by the Hyksos had advance military technologythe horse drawn chariot
End of Middle Kingdom o o About 1700 B. C. E. invaded by the Hyksos had advance military technologythe horse drawn chariot
 Hyksos o o Adopted Egyptian customs, language & beliefs Fully introduced bronze age to Egypt Ruled for about 100 years About 1600 B. C. E. overthrown by the Egyptians
Hyksos o o Adopted Egyptian customs, language & beliefs Fully introduced bronze age to Egypt Ruled for about 100 years About 1600 B. C. E. overthrown by the Egyptians
 New Kingdom 1550 B. C. E. to 1100 B. C. E. o o o Powerful Pharaohs created a new larger empire – all the way to the Euphrates River Egypt at the height of wealth and power— widespread slavery became a feature of Egyptian life for the first time Hordes of slaves brought home
New Kingdom 1550 B. C. E. to 1100 B. C. E. o o o Powerful Pharaohs created a new larger empire – all the way to the Euphrates River Egypt at the height of wealth and power— widespread slavery became a feature of Egyptian life for the first time Hordes of slaves brought home
 Important rulers of the New Kingdom o o Hatshepsut- first female ruler known in history 1501 B. C. E. - 1482 B. C. E. o Increased trade
Important rulers of the New Kingdom o o Hatshepsut- first female ruler known in history 1501 B. C. E. - 1482 B. C. E. o Increased trade
 Thutmose III o o Known as the Napoleon of Egypt because of his military victories Not allowed to rule in his own right because of his age Ruled Egyptian Empire at its greatest size Tried to wipe out the memory of Hatshepsut
Thutmose III o o Known as the Napoleon of Egypt because of his military victories Not allowed to rule in his own right because of his age Ruled Egyptian Empire at its greatest size Tried to wipe out the memory of Hatshepsut
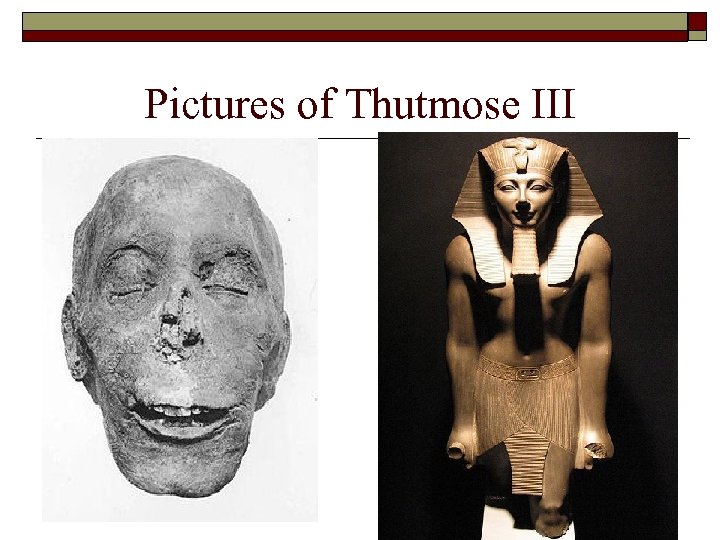 Pictures of Thutmose III
Pictures of Thutmose III
 Ramses II o o Last great ruler of the New Kingdom Signed first known treaty in history with the Hittites Ruled for 67 years—he was in his nineties when he died It is believed he fathered more than 150 children
Ramses II o o Last great ruler of the New Kingdom Signed first known treaty in history with the Hittites Ruled for 67 years—he was in his nineties when he died It is believed he fathered more than 150 children
 Mummy of Ramses II
Mummy of Ramses II
 Foreign Invaders o o o Nubia – 750 B. C. E. 650 B. C. E. Assyrians Persians Later the Greeks & Romans All wanted the Nile Valley for its food
Foreign Invaders o o o Nubia – 750 B. C. E. 650 B. C. E. Assyrians Persians Later the Greeks & Romans All wanted the Nile Valley for its food
 Religion (polytheism) o Amon-Re – Sun god- Chief god
Religion (polytheism) o Amon-Re – Sun god- Chief god
 Osiris and Isis
Osiris and Isis
 Osiris and Isis o o God of the Under World-ruler of the Nile Judges the dead Rise & Fall the Nile believed to be the death & rebirth of Osiris Father of Horus o o o Wife of Osiris Brought him back to life after Set killed him -symbol is the ankhmother of Horus Taught women how to grind corn, spin flax, care for children
Osiris and Isis o o God of the Under World-ruler of the Nile Judges the dead Rise & Fall the Nile believed to be the death & rebirth of Osiris Father of Horus o o o Wife of Osiris Brought him back to life after Set killed him -symbol is the ankhmother of Horus Taught women how to grind corn, spin flax, care for children
 Horus o Son of Osiris – kills Set – god of the sky
Horus o Son of Osiris – kills Set – god of the sky
 Bastet and Anubis o o Goddess of fertility, sensuality and fire prevention Symbolized by cats o o god of mummy wrapping/embalm ing Holds the scales of justice while your heart is weighed
Bastet and Anubis o o Goddess of fertility, sensuality and fire prevention Symbolized by cats o o god of mummy wrapping/embalm ing Holds the scales of justice while your heart is weighed
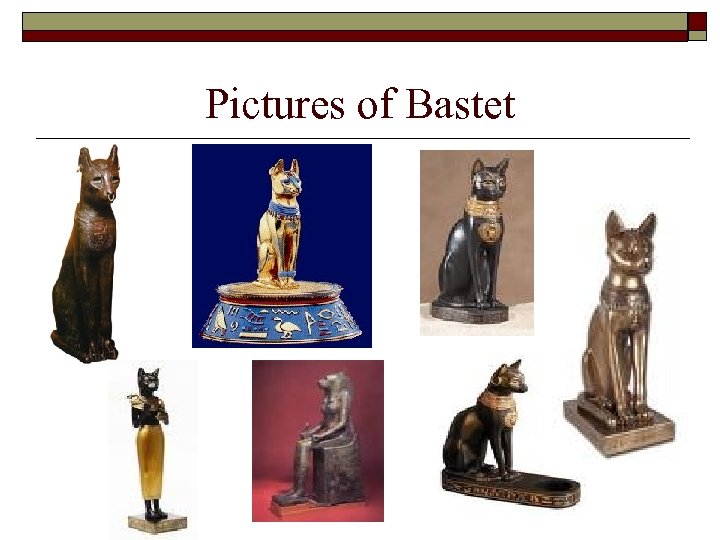 Pictures of Bastet
Pictures of Bastet
 Pictures of Anubis
Pictures of Anubis
 Egyptian Afterlife o o o Believed in a life after death Each soul needed to pass a test Weighed the heart against the feather of truth Sinners were fed to the Eater of the Dead Worthy souls entered the “Happy Field of Food”
Egyptian Afterlife o o o Believed in a life after death Each soul needed to pass a test Weighed the heart against the feather of truth Sinners were fed to the Eater of the Dead Worthy souls entered the “Happy Field of Food”
 Mummification—presevation of the body after death o o At first just for Pharaohs Process took 70 days Removed all organs and preserved them in jars Needed body in afterlife-home for the Ka-eternal spirit
Mummification—presevation of the body after death o o At first just for Pharaohs Process took 70 days Removed all organs and preserved them in jars Needed body in afterlife-home for the Ka-eternal spirit
 Valley of the Kings
Valley of the Kings
 Amenhotep IV o o Religious rebel Akhenaton Tried to outlaw all gods except Aton Introduced monotheism
Amenhotep IV o o Religious rebel Akhenaton Tried to outlaw all gods except Aton Introduced monotheism
 Nefertiti o o o Wife of Amenhotep IV Helps her husband Husbands rule started the downfall of the New Kingdom
Nefertiti o o o Wife of Amenhotep IV Helps her husband Husbands rule started the downfall of the New Kingdom
 Tutankhamen o o o Reestablished Amon -Re “Boy King” Howard Carter
Tutankhamen o o o Reestablished Amon -Re “Boy King” Howard Carter
 Pharaohs organized centralized state Corrupt government suffered frequent rebellions Pharaohs created a large empire Built enormous tombs, the pyramids Land drained for farming Traded with lands along eastern Mediterranean and Red Sea Power struggles, crop failures and cost of pyramids caused collapse Hyksos invaded and conquered Nubians, then others invaded
Pharaohs organized centralized state Corrupt government suffered frequent rebellions Pharaohs created a large empire Built enormous tombs, the pyramids Land drained for farming Traded with lands along eastern Mediterranean and Red Sea Power struggles, crop failures and cost of pyramids caused collapse Hyksos invaded and conquered Nubians, then others invaded
 Egyptian Society o Social Class n n A persons social position and occupation determined at birth Parents taught their children their own trade
Egyptian Society o Social Class n n A persons social position and occupation determined at birth Parents taught their children their own trade
 Egyptian Society o Social Structure n Top = Pharaoh (royal family) o o Ruling class of vizier, priests and nobles Scribes and soldiers Middle class of merchants, artisans, doctors Peasant farmers were majority of population and slaves
Egyptian Society o Social Structure n Top = Pharaoh (royal family) o o Ruling class of vizier, priests and nobles Scribes and soldiers Middle class of merchants, artisans, doctors Peasant farmers were majority of population and slaves
 Egyptian Social Stucture
Egyptian Social Stucture
 o Ruling Class n n n Egyptian life revolved around religion Priests and nobles had highest status after pharaoh Only priests knew how to please gods Gods controlled nature Priests performed rituals to obtain fertile land etc.
o Ruling Class n n n Egyptian life revolved around religion Priests and nobles had highest status after pharaoh Only priests knew how to please gods Gods controlled nature Priests performed rituals to obtain fertile land etc.
 n People paid tax to the temples o n n n Grain, gold, linen, etc nobles mainly held government positions Generals in armies, governors of provinces, tax collectors and court officials Had many luxuries
n People paid tax to the temples o n n n Grain, gold, linen, etc nobles mainly held government positions Generals in armies, governors of provinces, tax collectors and court officials Had many luxuries
 o Middle Class n n n Small group Settled in cities Provided goods & services to the ruling class
o Middle Class n n n Small group Settled in cities Provided goods & services to the ruling class
 o Peasants n n n Majority of Egyptians Lifestyle unchanged for thousands of years Pharaoh owned all the land o n 60% of the crops had to be paid as taxes Usually had to work on palace or government project-serve in army, up keep and repair of irrigations systems
o Peasants n n n Majority of Egyptians Lifestyle unchanged for thousands of years Pharaoh owned all the land o n 60% of the crops had to be paid as taxes Usually had to work on palace or government project-serve in army, up keep and repair of irrigations systems
 o Slaves n n n Brought to Egypt as POW’s or were descendents of POW’s Some slaves lived comfortable lives Some became trusted officials (Joseph) Some earned their freedom Life was tough for most- Average 36 at death
o Slaves n n n Brought to Egypt as POW’s or were descendents of POW’s Some slaves lived comfortable lives Some became trusted officials (Joseph) Some earned their freedom Life was tough for most- Average 36 at death
 Status of Women n n n Relatively high status for that time in history—more independence Could buy and sell property Could seek divorce (although rare) Property inherited through female line Role of wife and mother important A woman’s status increased when she had children
Status of Women n n n Relatively high status for that time in history—more independence Could buy and sell property Could seek divorce (although rare) Property inherited through female line Role of wife and mother important A woman’s status increased when she had children
 Status of Women n n Sometimes women considered property, but were treated kindly Wore make-up/wigs etc. (lice always an issue) Queen might rule with pharaoh If pharaoh had more than one wife, the first wife was most important o Her son would be the next pharaoh
Status of Women n n Sometimes women considered property, but were treated kindly Wore make-up/wigs etc. (lice always an issue) Queen might rule with pharaoh If pharaoh had more than one wife, the first wife was most important o Her son would be the next pharaoh
 Egyptian Writing o o o ~3100 B. C. E. Hieroglyphics Developed by priests
Egyptian Writing o o o ~3100 B. C. E. Hieroglyphics Developed by priests
 Scribes o o Scribes were very important Kept records, recorded history Could possibly become rich About the only social mobility of the era
Scribes o o Scribes were very important Kept records, recorded history Could possibly become rich About the only social mobility of the era
 The Rosetta Stone - 1799 o Slab of black rock carved in three languages n n n o Hieroglyphics Demotic (everyday language) Greek Jean Champollion deciphered the Rosetta Stone
The Rosetta Stone - 1799 o Slab of black rock carved in three languages n n n o Hieroglyphics Demotic (everyday language) Greek Jean Champollion deciphered the Rosetta Stone
 Egyptian Achievements o In areas of math and science n n Developed system of surveying land Important due to annual floods Surveying land led to Geometry n n Area & volume Did not develop the concept of zero
Egyptian Achievements o In areas of math and science n n Developed system of surveying land Important due to annual floods Surveying land led to Geometry n n Area & volume Did not develop the concept of zero
 Egyptian Achievements o Development of astronomy n n To predict floods, eclipses Led to development of calendar based on Sirius o o 365 days, 12 months 3 seasons, 30 days for 11 months, 35 for the 12 th 6 hours short of a solar year Development of building techniques n engineering
Egyptian Achievements o Development of astronomy n n To predict floods, eclipses Led to development of calendar based on Sirius o o 365 days, 12 months 3 seasons, 30 days for 11 months, 35 for the 12 th 6 hours short of a solar year Development of building techniques n engineering
 Egyptian Achievements o Medical discoveries n n n Magic heavily used Developed surgery Greeks & Romans based much of their medical knowledge on that of the Egyptians
Egyptian Achievements o Medical discoveries n n n Magic heavily used Developed surgery Greeks & Romans based much of their medical knowledge on that of the Egyptians
 Egyptian Achievements o Literature n n Hymns Book of the Dead Love poems Folk tales o The Tale of Sinuhe
Egyptian Achievements o Literature n n Hymns Book of the Dead Love poems Folk tales o The Tale of Sinuhe
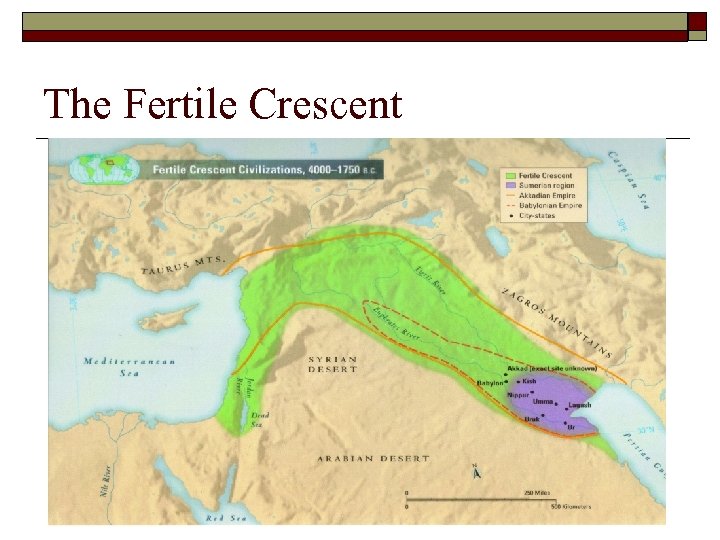 The Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent
 “Crossroads of Civilization” o o o It commands land routes to 3 continents Few natural barriers Constant exchange of ideas through invasions and migrations
“Crossroads of Civilization” o o o It commands land routes to 3 continents Few natural barriers Constant exchange of ideas through invasions and migrations
 Mesopotamia o o Tigris River & Euphrates River Floods almost every year (April –June) Periods of drought Rivers unpredictable and deadly
Mesopotamia o o Tigris River & Euphrates River Floods almost every year (April –June) Periods of drought Rivers unpredictable and deadly
 Sumerian Civilization – 3200 B. C. E. o City States—large towns and cities and the surrounding countryside n n n Ur Uruk Kish Cities are independent of each other Social classes set up in hierarchy-system of ranks
Sumerian Civilization – 3200 B. C. E. o City States—large towns and cities and the surrounding countryside n n n Ur Uruk Kish Cities are independent of each other Social classes set up in hierarchy-system of ranks
 Ziggurats Largest building in the city-state o Pyramid-temple
Ziggurats Largest building in the city-state o Pyramid-temple
 Economy o o First to use wheeled vehicles Trade with neighboring city-states was basis of the economy Sumerians fought for control of land water Cities protected by high walls
Economy o o First to use wheeled vehicles Trade with neighboring city-states was basis of the economy Sumerians fought for control of land water Cities protected by high walls
 Religion o Polytheism n n n Council of gods & goddesses rule the earth Each city-state had it specific god/goddess Natural events explained through actions of gods/goddesses-keep gods happy Gods & goddess behaved like ordinary people—kings were gods representatives Believed in an afterlife-gloomy underworld
Religion o Polytheism n n n Council of gods & goddesses rule the earth Each city-state had it specific god/goddess Natural events explained through actions of gods/goddesses-keep gods happy Gods & goddess behaved like ordinary people—kings were gods representatives Believed in an afterlife-gloomy underworld
 Writing – cuneiform means wedged-shaped o o Stylus Scribes
Writing – cuneiform means wedged-shaped o o Stylus Scribes
 Achievements o o Basic algebra & geometry Number system based on 6 n n o o Hour = 60 minutes Circle into 360 degrees Invented the plow & sail First to use columns, inclined walks & arch
Achievements o o Basic algebra & geometry Number system based on 6 n n o o Hour = 60 minutes Circle into 360 degrees Invented the plow & sail First to use columns, inclined walks & arch
 Empires of the Middle East o o Sargon – 2300 B. C. E. ruler of Akkad conquered the city-states of Sumer First empire in recorded history
Empires of the Middle East o o Sargon – 2300 B. C. E. ruler of Akkad conquered the city-states of Sumer First empire in recorded history
 Babylonian Empire o o o Amorites invade Sumer & locate their government in Babylon Became known as the Babylonian Empire Promoted chief Babylonian god called Marduk
Babylonian Empire o o o Amorites invade Sumer & locate their government in Babylon Became known as the Babylonian Empire Promoted chief Babylonian god called Marduk
 Hammurabi o o Code of Hammurabi 300 laws carved into stone pillars n n n Criminal law Civil Law “eye for an eye”
Hammurabi o o Code of Hammurabi 300 laws carved into stone pillars n n n Criminal law Civil Law “eye for an eye”
 Hittites – 1400 B. C. E. o o Conquered Mesopotamia because of their secret weapon – iron Introduced Iron Age in Europe, Africa, & Asia
Hittites – 1400 B. C. E. o o Conquered Mesopotamia because of their secret weapon – iron Introduced Iron Age in Europe, Africa, & Asia
 Assyrians – 1100 B. C. E. o o o o Most cruel & warlike First people to develop effective way of governing an empire Ruled by fear-uprooted people which spread ideas Well-ordered society-capital at Nineveh New military techniques-cavalry, siege weapons, disciplined army Assurbanipal established first library-helped preserve history of Middle East 612 B. C. E. crushed by their neighbors
Assyrians – 1100 B. C. E. o o o o Most cruel & warlike First people to develop effective way of governing an empire Ruled by fear-uprooted people which spread ideas Well-ordered society-capital at Nineveh New military techniques-cavalry, siege weapons, disciplined army Assurbanipal established first library-helped preserve history of Middle East 612 B. C. E. crushed by their neighbors

 Nebuchadnezzar (Chaldeans) o o o Ruled from Babylon-New Babylonians Enslaved the Jews- known as the Babylonian Captivity Built the Hanging Gardens of Babylon & Tower of Babel
Nebuchadnezzar (Chaldeans) o o o Ruled from Babylon-New Babylonians Enslaved the Jews- known as the Babylonian Captivity Built the Hanging Gardens of Babylon & Tower of Babel


 Accomplishments o o Astrology-stars determined human destiny Calendar – accurate to within 7 minutes
Accomplishments o o Astrology-stars determined human destiny Calendar – accurate to within 7 minutes
 Lydians o o o Introduced the use of coined money Created money economy which helped trade Did not eliminate barter system
Lydians o o o Introduced the use of coined money Created money economy which helped trade Did not eliminate barter system
 Persian Empire – 539 B. C. E. o o o Cyrus the Great began empire Created the largest empire yet seen in the world-Asia Minor to India to Egypt Treated conquered peoples with toleration and respected customs and traditions
Persian Empire – 539 B. C. E. o o o Cyrus the Great began empire Created the largest empire yet seen in the world-Asia Minor to India to Egypt Treated conquered peoples with toleration and respected customs and traditions
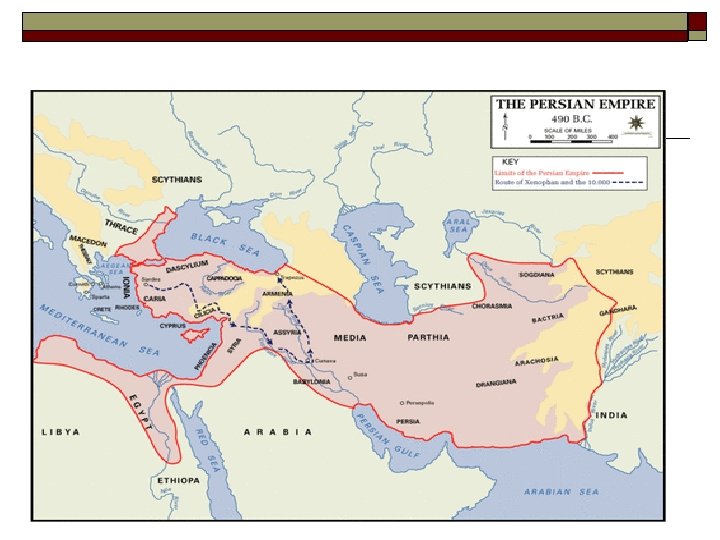
 Darius – 522 B. C. E. o o o Concerned for justice Divided empire into provinces called a Satrapy which was ruled by Satrap Sent spies “eyes and ears of the king” to check on satraps
Darius – 522 B. C. E. o o o Concerned for justice Divided empire into provinces called a Satrapy which was ruled by Satrap Sent spies “eyes and ears of the king” to check on satraps
 Accomplishments o o Linked empire with roads-Great Royal Road (1, 677 miles)--early pony express system Created set of common weights & measures First large empire to create uniform system of coinage Single code of laws for all
Accomplishments o o Linked empire with roads-Great Royal Road (1, 677 miles)--early pony express system Created set of common weights & measures First large empire to create uniform system of coinage Single code of laws for all
 Persian Religion o o o Created by Zoroaster – 600 B. C. E. Single wise god – Ahura Mazda-symbolized by light In a battle with evil prince of lies Ahrimansymbolized by darkness Sacred book called Zend Avesta Each individual chooses who to follow and there would be a Day of Judgment
Persian Religion o o o Created by Zoroaster – 600 B. C. E. Single wise god – Ahura Mazda-symbolized by light In a battle with evil prince of lies Ahrimansymbolized by darkness Sacred book called Zend Avesta Each individual chooses who to follow and there would be a Day of Judgment
 Phoenicians o o Greatest sailors/explorers of ancient times-established colonies “Carriers of Civilization”-spread Middle Eastern civilization around the Med. Region Made glass and had purple dye made from a tiny sea snail Gave us our alphabet
Phoenicians o o Greatest sailors/explorers of ancient times-established colonies “Carriers of Civilization”-spread Middle Eastern civilization around the Med. Region Made glass and had purple dye made from a tiny sea snail Gave us our alphabet
 Hebrews – 2000 B. C. E. o o o Nomads out of Ur in Mesopotamia Abraham – founder of Judaism Monotheism – single God – Yahweh Torah-first five books of the Old Testament which is their most sacred text Developed a code of ethical laws
Hebrews – 2000 B. C. E. o o o Nomads out of Ur in Mesopotamia Abraham – founder of Judaism Monotheism – single God – Yahweh Torah-first five books of the Old Testament which is their most sacred text Developed a code of ethical laws
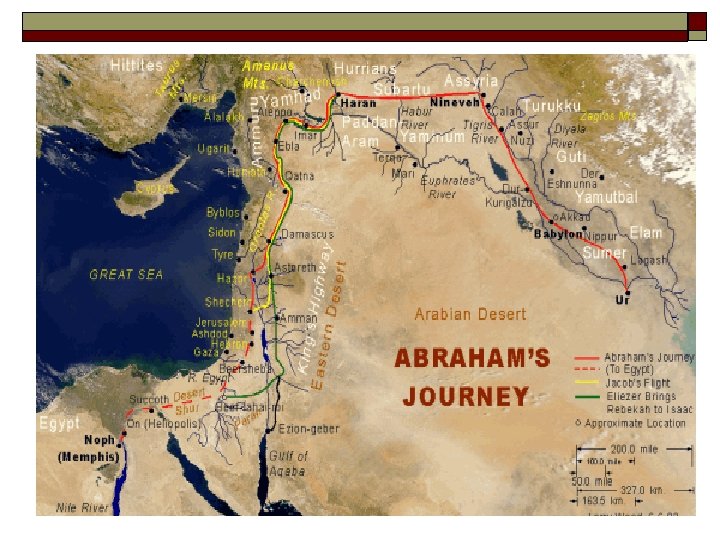
 Moved to Canaan then to Egypt o Enslaved by Egyptians
Moved to Canaan then to Egypt o Enslaved by Egyptians
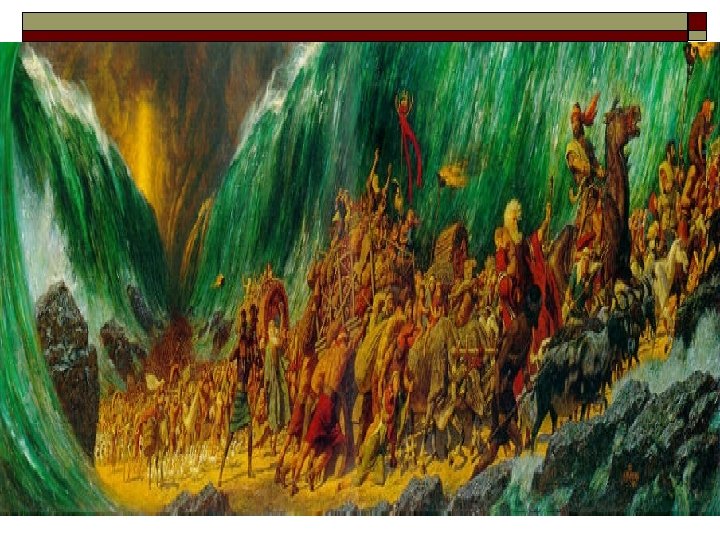
 Moses o o o Passover Freed Hebrews from bondage in Egypt Ten Commandments
Moses o o o Passover Freed Hebrews from bondage in Egypt Ten Commandments


 Religious The Covenant—binding agreement o Prophets— spiritual leaders who interpret God’s will o Ethics—moral standards of behavior o
Religious The Covenant—binding agreement o Prophets— spiritual leaders who interpret God’s will o Ethics—moral standards of behavior o
 Kingdom of Israel – 1000 BCE o o o Saul first king of Israel David – slew Goliath—ruled for 40 years Solomon was the son of David n n Built the Temple of Jerusalem Home of the Ark of the Covenant
Kingdom of Israel – 1000 BCE o o o Saul first king of Israel David – slew Goliath—ruled for 40 years Solomon was the son of David n n Built the Temple of Jerusalem Home of the Ark of the Covenant

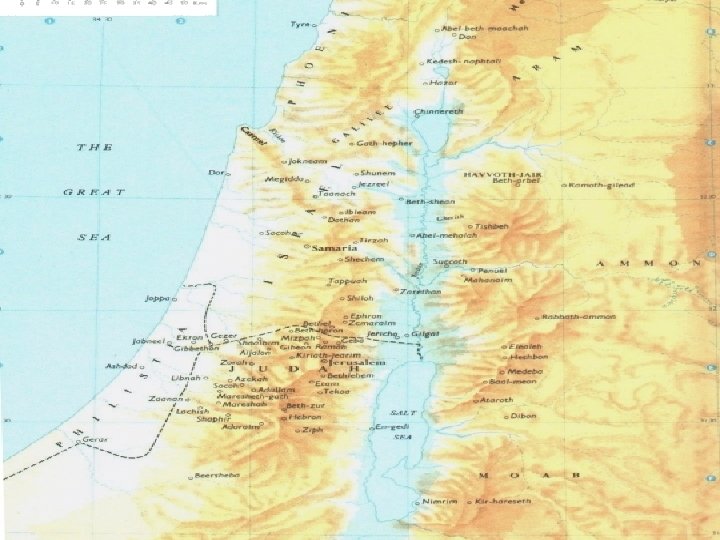
 Kingdom of Israel o o Kingdom split – Israel in north & Judah in the south Israel conquered by the Assyrians in 722 B. C. E. o Judah conquered by the Babylonians in 586 B. C. E.
Kingdom of Israel o o Kingdom split – Israel in north & Judah in the south Israel conquered by the Assyrians in 722 B. C. E. o Judah conquered by the Babylonians in 586 B. C. E.


