c4c1b37077295e2577a21fd4ee0180ec.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Chapter 2 The Constitution
Chapter 2 The Constitution
 2 Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
2 Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 § The Colonial Mind § Men will seek power because they are ambitious, greedy, and easily corrupted § Colonists sought “natural rights” § Unalienable rights Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Problem of Liberty 3
§ The Colonial Mind § Men will seek power because they are ambitious, greedy, and easily corrupted § Colonists sought “natural rights” § Unalienable rights Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Problem of Liberty 3
 LC-DIG-ppmsca-02949/Library of Congress Even before the Revolutionary War, many felt some form of union would be necessary if the rebellious colonies were to survive. In 1774, the Massachusetts Spy portrayed the colonies as segments of a snake that must “Join or Die. ” p. 20
LC-DIG-ppmsca-02949/Library of Congress Even before the Revolutionary War, many felt some form of union would be necessary if the rebellious colonies were to survive. In 1774, the Massachusetts Spy portrayed the colonies as segments of a snake that must “Join or Die. ” p. 20
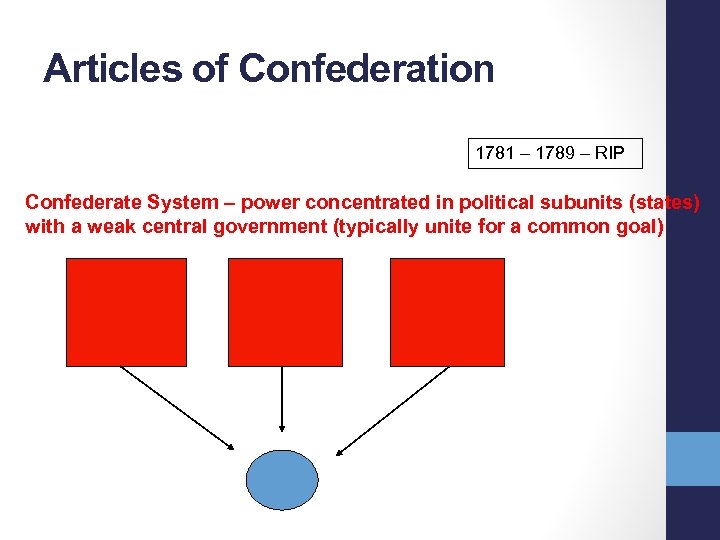 Articles of Confederation 1781 – 1789 – RIP Confederate System – power concentrated in political subunits (states) with a weak central government (typically unite for a common goal)
Articles of Confederation 1781 – 1789 – RIP Confederate System – power concentrated in political subunits (states) with a weak central government (typically unite for a common goal)
 § Weaknesses of the Confederation § Articles of Confederation 1781 § “League of Friendship” § No strong central government § No Executive (No President), no central authority § Unicameral Congress § No Federal Judiciary (No Supreme Court), no central law § No control of taxation, commerce between states or with foreign nations, money system Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Problem of Liberty 6
§ Weaknesses of the Confederation § Articles of Confederation 1781 § “League of Friendship” § No strong central government § No Executive (No President), no central authority § Unicameral Congress § No Federal Judiciary (No Supreme Court), no central law § No control of taxation, commerce between states or with foreign nations, money system Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Problem of Liberty 6
 § Article II – “Each state retains its sovereignty, freedom, and independence. ” Gov’t has no control § Unicameral Congress (one house) with one vote per state Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Weaknesses Cont. . 7
§ Article II – “Each state retains its sovereignty, freedom, and independence. ” Gov’t has no control § Unicameral Congress (one house) with one vote per state Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Weaknesses Cont. . 7
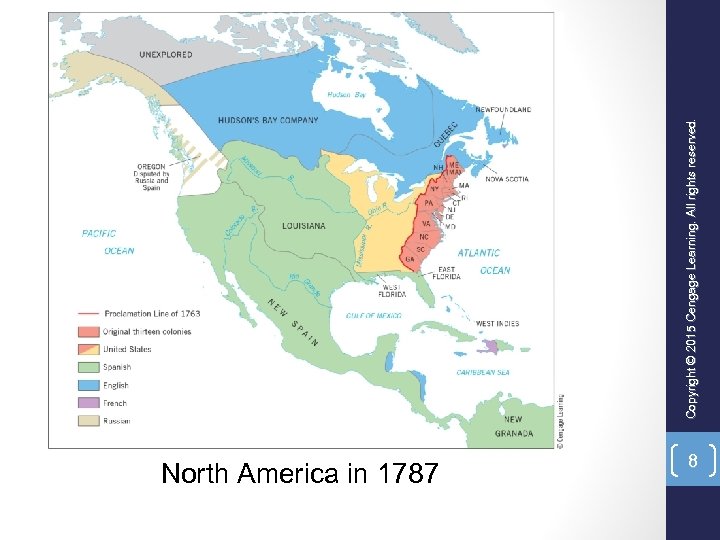 North America in 1787 8 reserved. Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
North America in 1787 8 reserved. Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved
 Shays’s Rebellion § Colonies were in debt after the war, central gov’t tried to raise taxes § Farmers in western Massachusetts rebelled against tax they could not afford § Rebelled against foreclosures, forced judges out of court, freed debtors from jail § Showed that national gov’t was weak, needed to seek a stronger national gov’t
Shays’s Rebellion § Colonies were in debt after the war, central gov’t tried to raise taxes § Farmers in western Massachusetts rebelled against tax they could not afford § Rebelled against foreclosures, forced judges out of court, freed debtors from jail § Showed that national gov’t was weak, needed to seek a stronger national gov’t
 § The Framers § 55 delegates, none from Rhode Island § Mostly young and educated § Produced new written constitution § Commitment to liberty and natural rights § Original desire was to revise the articles of confederation Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitutional Convention 10
§ The Framers § 55 delegates, none from Rhode Island § Mostly young and educated § Produced new written constitution § Commitment to liberty and natural rights § Original desire was to revise the articles of confederation Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitutional Convention 10
 § The Virginia Plan–proposal to create a strong national government § 3 branches of government § Executive (president) chose by congress (2 houses) § National legislature has power of states § The New Jersey Plan–proposal to create a weak national government Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Challenge § Left articles virtually unchanged 11
§ The Virginia Plan–proposal to create a strong national government § 3 branches of government § Executive (president) chose by congress (2 houses) § National legislature has power of states § The New Jersey Plan–proposal to create a weak national government Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Challenge § Left articles virtually unchanged 11
 § The Compromise § Popularly-elected house based on state population § State-elected senate, with two members for each state § Making Congress bicameral = 2 parts § Electoral college – would select the president Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Challenge 12
§ The Compromise § Popularly-elected house based on state population § State-elected senate, with two members for each state § Making Congress bicameral = 2 parts § Electoral college – would select the president Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Challenge 12
 § Created a republic § Representative democracy § Judicial review § Key principles § Federalism § Separation of powers § Enumerated powers § Reserved powers § Concurrent powers § –USE ALL 3 through the semester Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Democracy 13
§ Created a republic § Representative democracy § Judicial review § Key principles § Federalism § Separation of powers § Enumerated powers § Reserved powers § Concurrent powers § –USE ALL 3 through the semester Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Democracy 13
 § Government and Human Nature § Republican government “even in the absence of political virtue” = representative gov. § Checks and balances § Factions: a group with a distinct political interest, soon to be federalist/anti-fed. § Today Dem/Republican § In Federalist #10 Madison warns a need for a constitution to balance competing interests Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Democracy 14
§ Government and Human Nature § Republican government “even in the absence of political virtue” = representative gov. § Checks and balances § Factions: a group with a distinct political interest, soon to be federalist/anti-fed. § Today Dem/Republican § In Federalist #10 Madison warns a need for a constitution to balance competing interests Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Democracy 14
 Federalists Antifederalists §“Nationalists” §Strong national government §View liberty as protected by large republic §Moderate coalitions §States’ rights advocates §Prefer small republic or confederation §Need to limit central powers §Bill of rights Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Liberty 15
Federalists Antifederalists §“Nationalists” §Strong national government §View liberty as protected by large republic §Moderate coalitions §States’ rights advocates §Prefer small republic or confederation §Need to limit central powers §Bill of rights Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Liberty 15
 § Liberties guaranteed by Constitution (before Bill of Rights added) § Writ of habeas corpus protected § No bills of attainder § No ex post facto laws § Right of trial by jury § Citizens of each state entitled to same privileges/immunities § No religious qualifications for office Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Liberty 16
§ Liberties guaranteed by Constitution (before Bill of Rights added) § Writ of habeas corpus protected § No bills of attainder § No ex post facto laws § Right of trial by jury § Citizens of each state entitled to same privileges/immunities § No religious qualifications for office Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Liberty 16
 § Need for a Bill of Rights § The Constitution and Slavery § Needed southern states for ratification § “Greatest Compromise” (threefifths compromise) § Would help add to population for house of reps Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Liberty 17
§ Need for a Bill of Rights § The Constitution and Slavery § Needed southern states for ratification § “Greatest Compromise” (threefifths compromise) § Would help add to population for house of reps Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Constitution and Liberty 17
 Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Ratification of the Federal Constitution by State Constitutions, 1787– 1790 18
Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Ratification of the Federal Constitution by State Constitutions, 1787– 1790 18
 § Economic Interests § State interests dominate § The Constitution and Equality § Framers did not view liberty and political equality as in conflict § Saw political privilege as worst inequality Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Motives of the Framers 19
§ Economic Interests § State interests dominate § The Constitution and Equality § Framers did not view liberty and political equality as in conflict § Saw political privilege as worst inequality Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. The Motives of the Framers 19
 § Reducing the Separation of Powers § Increase presidential authority § Lengthen terms for members of House Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Constitutional Reform: Modern Views 20
§ Reducing the Separation of Powers § Increase presidential authority § Lengthen terms for members of House Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Constitutional Reform: Modern Views 20
 § Making the System Less Democratic § Balanced budget amendment § Line-item veto § Narrow authority of federal courts Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Constitutional Reform: Modern Views 21
§ Making the System Less Democratic § Balanced budget amendment § Line-item veto § Narrow authority of federal courts Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Constitutional Reform: Modern Views 21
 § Who is Right? § Study the government’s historical evolution § Study how the government works and why it has produced the policies you see § Study the practices of other nations Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Constitutional Reform: Modern Views 22
§ Who is Right? § Study the government’s historical evolution § Study how the government works and why it has produced the policies you see § Study the practices of other nations Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Constitutional Reform: Modern Views 22


