f416817533b540b6eb82ba8d1d5211ca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 chapter 2 the computer
chapter 2 the computer
 The Computer a computer system is made up of various elements each of these elements affects the interaction – input devices – text entry and pointing – output devices – screen (small&large), digital paper – virtual reality – special interaction and display devices – physical interaction – e. g. sound, haptic, bio-sensing – paper – as output (print) and input (scan) – memory – RAM & permanent media, capacity & access – processing – speed of processing, networks
The Computer a computer system is made up of various elements each of these elements affects the interaction – input devices – text entry and pointing – output devices – screen (small&large), digital paper – virtual reality – special interaction and display devices – physical interaction – e. g. sound, haptic, bio-sensing – paper – as output (print) and input (scan) – memory – RAM & permanent media, capacity & access – processing – speed of processing, networks
 Interacting with computers to understand human–computer interaction … need to understand computers! what goes in and out devices, paper, sensors, etc. what can it do? memory, processing, networks
Interacting with computers to understand human–computer interaction … need to understand computers! what goes in and out devices, paper, sensors, etc. what can it do? memory, processing, networks
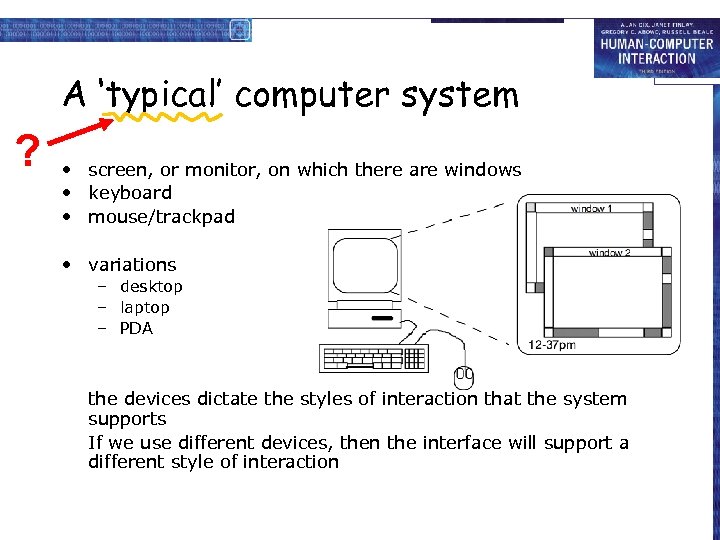 A ‘typical’ computer system ? • screen, or monitor, on which there are windows • keyboard • mouse/trackpad • variations – desktop – laptop – PDA the devices dictate the styles of interaction that the system supports If we use different devices, then the interface will support a different style of interaction
A ‘typical’ computer system ? • screen, or monitor, on which there are windows • keyboard • mouse/trackpad • variations – desktop – laptop – PDA the devices dictate the styles of interaction that the system supports If we use different devices, then the interface will support a different style of interaction
 How many … • computers in your house? – hands up, … … none, 1, 2 , 3, more!! • computers in your pockets? are you thinking … … PC, laptop, PDA ? ?
How many … • computers in your house? – hands up, … … none, 1, 2 , 3, more!! • computers in your pockets? are you thinking … … PC, laptop, PDA ? ?
 How many computers … in your house? – PC – TV, VCR, DVD, Hi. Fi, cable/satellite TV – microwave, cooker, washing machine – central heating – security system can you think of more? in your pockets? – PDA – phone, camera – smart card, card with magnetic strip? – electronic car key – USB memory try your pockets and bags
How many computers … in your house? – PC – TV, VCR, DVD, Hi. Fi, cable/satellite TV – microwave, cooker, washing machine – central heating – security system can you think of more? in your pockets? – PDA – phone, camera – smart card, card with magnetic strip? – electronic car key – USB memory try your pockets and bags
 Interactivity? Long ago in a galaxy far away … batch processing – punched card stacks or large data files prepared – long wait …. – line printer output … and if it is not right … Now most computing is interactive – rapid feedback – the user in control (most of the time) – doing rather than thinking … Is faster always better?
Interactivity? Long ago in a galaxy far away … batch processing – punched card stacks or large data files prepared – long wait …. – line printer output … and if it is not right … Now most computing is interactive – rapid feedback – the user in control (most of the time) – doing rather than thinking … Is faster always better?
 Richer interaction sensors and devices everywhere
Richer interaction sensors and devices everywhere
 text entry devices keyboards (QWERTY et al. ) chord keyboards, phone pads handwriting, speech
text entry devices keyboards (QWERTY et al. ) chord keyboards, phone pads handwriting, speech
 Keyboards • Most common text input device • Allows rapid entry of text by experienced users • Keypress closes connection, causing a character code to be sent • Usually connected by cable, but can be wireless
Keyboards • Most common text input device • Allows rapid entry of text by experienced users • Keypress closes connection, causing a character code to be sent • Usually connected by cable, but can be wireless
 layout – QWERTY • Standardised layout but … – non-alphanumeric keys are placed differently – accented symbols needed for different scripts – minor differences between UK and USA keyboards • QWERTY arrangement not optimal for typing – layout to prevent typewriters jamming! • Alternative designs allow faster typing but large social base of QWERTY typists produces reluctance to change.
layout – QWERTY • Standardised layout but … – non-alphanumeric keys are placed differently – accented symbols needed for different scripts – minor differences between UK and USA keyboards • QWERTY arrangement not optimal for typing – layout to prevent typewriters jamming! • Alternative designs allow faster typing but large social base of QWERTY typists produces reluctance to change.
 alternative keyboard layouts Alphabetic – keys arranged in alphabetic order – not faster for trained typists – not faster for beginners either! Dvorak – – – common letters under dominant fingers biased towards right hand common combinations of letters alternate between hands 10 -15% improvement in speed and reduction in fatigue But - large social base of QWERTY typists produce market pressures not to change
alternative keyboard layouts Alphabetic – keys arranged in alphabetic order – not faster for trained typists – not faster for beginners either! Dvorak – – – common letters under dominant fingers biased towards right hand common combinations of letters alternate between hands 10 -15% improvement in speed and reduction in fatigue But - large social base of QWERTY typists produce market pressures not to change
 phone pad and T 9 entry • use numeric keys with multiple presses 2 3 4 5 –abc -def -ghi -jkl 6 7 8 9 - mno pqrs tuv wxyz hello = 4433555[pause]555666 surprisingly fast! • T 9 predictive entry – – type as if single key for each letter use dictionary to ‘guess’ the right word hello = 43556 … but 26 -> menu ‘am’ or ‘an’
phone pad and T 9 entry • use numeric keys with multiple presses 2 3 4 5 –abc -def -ghi -jkl 6 7 8 9 - mno pqrs tuv wxyz hello = 4433555[pause]555666 surprisingly fast! • T 9 predictive entry – – type as if single key for each letter use dictionary to ‘guess’ the right word hello = 43556 … but 26 -> menu ‘am’ or ‘an’
 Handwriting recognition • Text can be input into the computer, using a pen and a digesting tablet – natural interaction • Technical problems: – capturing all useful information - stroke path, pressure, etc. in a natural manner – segmenting joined up writing into individual letters – interpreting individual letters – coping with different styles of handwriting • Used in PDAs, and tablet computers … … leave the keyboard on the desk!
Handwriting recognition • Text can be input into the computer, using a pen and a digesting tablet – natural interaction • Technical problems: – capturing all useful information - stroke path, pressure, etc. in a natural manner – segmenting joined up writing into individual letters – interpreting individual letters – coping with different styles of handwriting • Used in PDAs, and tablet computers … … leave the keyboard on the desk!
 Speech recognition • Improving rapidly • Most successful when: – single user – initial training and learns peculiarities – limited vocabulary systems • Problems with – – external noise interfering imprecision of pronunciation large vocabularies different speakers
Speech recognition • Improving rapidly • Most successful when: – single user – initial training and learns peculiarities – limited vocabulary systems • Problems with – – external noise interfering imprecision of pronunciation large vocabularies different speakers
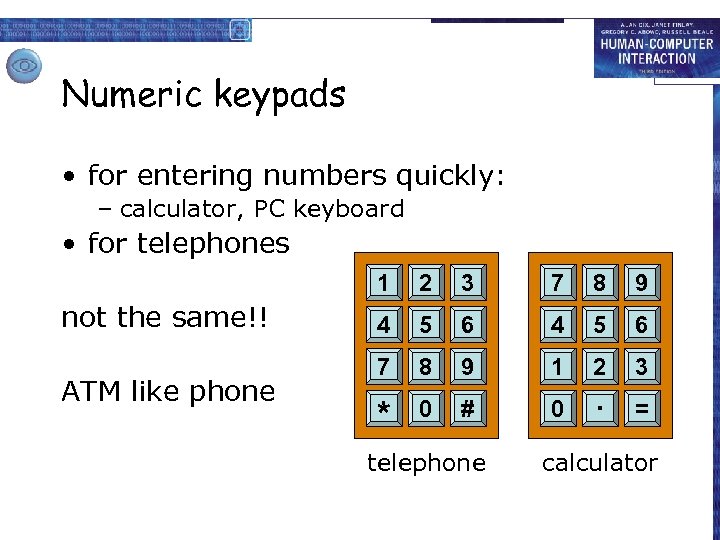 Numeric keypads • for entering numbers quickly: – calculator, PC keyboard • for telephones 1 not the same!! ATM like phone 2 3 7 8 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 * 0 # 0 . = telephone calculator
Numeric keypads • for entering numbers quickly: – calculator, PC keyboard • for telephones 1 not the same!! ATM like phone 2 3 7 8 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 3 * 0 # 0 . = telephone calculator
 positioning, pointing and drawing mouse, touchpad trackballs, joysticks etc. touch screens, tablets eyegaze
positioning, pointing and drawing mouse, touchpad trackballs, joysticks etc. touch screens, tablets eyegaze
 the Mouse • Handheld pointing device – very common – easy to use • Two characteristics – planar movement – buttons (usually from 1 to 3 buttons on top, used for making a selection, indicating an option, or to initiate drawing etc. )
the Mouse • Handheld pointing device – very common – easy to use • Two characteristics – planar movement – buttons (usually from 1 to 3 buttons on top, used for making a selection, indicating an option, or to initiate drawing etc. )
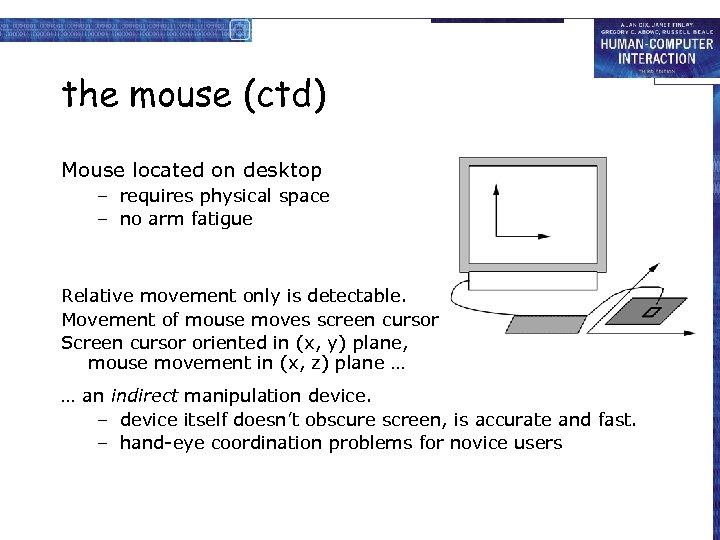 the mouse (ctd) Mouse located on desktop – requires physical space – no arm fatigue Relative movement only is detectable. Movement of mouse moves screen cursor Screen cursor oriented in (x, y) plane, mouse movement in (x, z) plane … … an indirect manipulation device. – device itself doesn’t obscure screen, is accurate and fast. – hand-eye coordination problems for novice users
the mouse (ctd) Mouse located on desktop – requires physical space – no arm fatigue Relative movement only is detectable. Movement of mouse moves screen cursor Screen cursor oriented in (x, y) plane, mouse movement in (x, z) plane … … an indirect manipulation device. – device itself doesn’t obscure screen, is accurate and fast. – hand-eye coordination problems for novice users
 How does it work? Two methods for detecting motion • Mechanical – Ball on underside of mouse turns as mouse is moved – Rotates orthogonal potentiometers – Can be used on almost any flat surface • Optical – – light emitting diode on underside of mouse may use special grid-like pad or just on desk less susceptible to dust and dirt detects fluctuating alterations in reflected light intensity to calculate relative motion in (x, z) plane
How does it work? Two methods for detecting motion • Mechanical – Ball on underside of mouse turns as mouse is moved – Rotates orthogonal potentiometers – Can be used on almost any flat surface • Optical – – light emitting diode on underside of mouse may use special grid-like pad or just on desk less susceptible to dust and dirt detects fluctuating alterations in reflected light intensity to calculate relative motion in (x, z) plane
 Even by foot … • some experiments with the footmouse – controlling mouse movement with feet … – not very common : -) • but foot controls are common elsewhere: – car pedals – sewing machine speed control – organ and piano pedals
Even by foot … • some experiments with the footmouse – controlling mouse movement with feet … – not very common : -) • but foot controls are common elsewhere: – car pedals – sewing machine speed control – organ and piano pedals
 Touchpad • small touch sensitive tablets • ‘stroke’ to move mouse pointer • used mainly in laptop computers • good ‘acceleration’ settings important – fast stroke • lots of pixels per inch moved • initial movement to the target – slow stroke • less pixels per inch • for accurate positioning
Touchpad • small touch sensitive tablets • ‘stroke’ to move mouse pointer • used mainly in laptop computers • good ‘acceleration’ settings important – fast stroke • lots of pixels per inch moved • initial movement to the target – slow stroke • less pixels per inch • for accurate positioning
 Trackball and thumbwheels Trackball – ball is rotated inside static housing • like an upsdie down mouse! – – – relative motion moves cursor indirect device, fairly accurate separate buttons for picking very fast for gaming used in some portable and notebook computers. Thumbwheels … – for accurate CAD – two dials for X-Y cursor position – for fast scrolling – single dial on mouse
Trackball and thumbwheels Trackball – ball is rotated inside static housing • like an upsdie down mouse! – – – relative motion moves cursor indirect device, fairly accurate separate buttons for picking very fast for gaming used in some portable and notebook computers. Thumbwheels … – for accurate CAD – two dials for X-Y cursor position – for fast scrolling – single dial on mouse
 Joystick – indirect pressure of stick = velocity of movement – buttons for selection on top or on front like a trigger – often used for computer games aircraft controls and 3 D navigation
Joystick – indirect pressure of stick = velocity of movement – buttons for selection on top or on front like a trigger – often used for computer games aircraft controls and 3 D navigation
 Touch-sensitive screen • Detect the presence of finger or stylus on the screen. – works by interrupting matrix of light beams, capacitance changes or ultrasonic reflections – direct pointing device • Advantages: – fast, and requires no specialised pointer – good for menu selection – suitable for use in hostile environment: clean and safe from damage. • Disadvantages: – finger can mark screen – imprecise (finger is a fairly blunt instrument!) • difficult to select small regions or perform accurate drawing – lifting arm can be tiring
Touch-sensitive screen • Detect the presence of finger or stylus on the screen. – works by interrupting matrix of light beams, capacitance changes or ultrasonic reflections – direct pointing device • Advantages: – fast, and requires no specialised pointer – good for menu selection – suitable for use in hostile environment: clean and safe from damage. • Disadvantages: – finger can mark screen – imprecise (finger is a fairly blunt instrument!) • difficult to select small regions or perform accurate drawing – lifting arm can be tiring
 Stylus and light pen Stylus – small pen-like pointer to draw directly on screen – may use touch sensitive surface or magnetic detection – used in PDA, tablets PCs and drawing tables Light Pen – now rarely used – uses light from screen to detect location BOTH … – very direct and obvious to use – but can obscure screen
Stylus and light pen Stylus – small pen-like pointer to draw directly on screen – may use touch sensitive surface or magnetic detection – used in PDA, tablets PCs and drawing tables Light Pen – now rarely used – uses light from screen to detect location BOTH … – very direct and obvious to use – but can obscure screen
 Digitizing tablet • Mouse like-device with cross hairs • used on special surface - rather like stylus • very accurate - used for digitizing maps
Digitizing tablet • Mouse like-device with cross hairs • used on special surface - rather like stylus • very accurate - used for digitizing maps
 Eyegaze • control interface by eye gaze direction – e. g. look at a menu item to select it • uses laser beam reflected off retina – … a very low power laser! • • mainly used for evaluation (ch x) potential for hands-free control high accuracy requires headset cheaper and lower accuracy devices available sit under the screen like a small webcam
Eyegaze • control interface by eye gaze direction – e. g. look at a menu item to select it • uses laser beam reflected off retina – … a very low power laser! • • mainly used for evaluation (ch x) potential for hands-free control high accuracy requires headset cheaper and lower accuracy devices available sit under the screen like a small webcam
 Multitouch, gestural • Good points? • Bad points?
Multitouch, gestural • Good points? • Bad points?


