Chapter 2 Personality. After studying this chapter, you














ch02_personality.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Chapter 2 Personality
Chapter 2 Personality
 After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the factors that determine an individual’s personality. Describe the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator model. Identify the key traits in the Big Five personality model. Explain how the major personality attributes predict behaviour at work. Contrast terminal and instrumental values. List today’s dominant values in today’s workforce. Identify Hofstede’s five value dimensions of national culture. Learning Objectives
After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the factors that determine an individual’s personality. Describe the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator model. Identify the key traits in the Big Five personality model. Explain how the major personality attributes predict behaviour at work. Contrast terminal and instrumental values. List today’s dominant values in today’s workforce. Identify Hofstede’s five value dimensions of national culture. Learning Objectives
 What Is Personality? Personality The sum total of ways in which an individual reacts and interacts with others, measurable traits a person exhibits Personality Traits Enduring characteristics that describe an individual’s behaviour Personality Determinants Heredity Environment Situation
What Is Personality? Personality The sum total of ways in which an individual reacts and interacts with others, measurable traits a person exhibits Personality Traits Enduring characteristics that describe an individual’s behaviour Personality Determinants Heredity Environment Situation
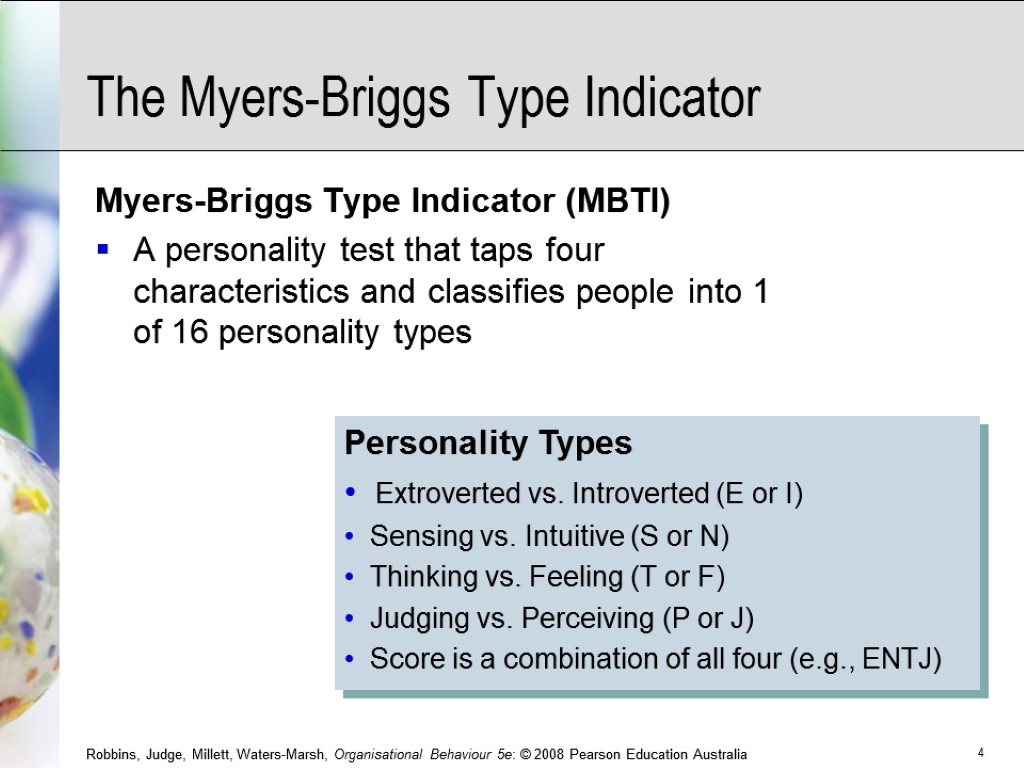
 Personality Types Extroverted vs. Introverted (E or I) Sensing vs. Intuitive (S or N) Thinking vs. Feeling (T or F) Judging vs. Perceiving (P or J) Score is a combination of all four (e.g., ENTJ) The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) A personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into 1 of 16 personality types
Personality Types Extroverted vs. Introverted (E or I) Sensing vs. Intuitive (S or N) Thinking vs. Feeling (T or F) Judging vs. Perceiving (P or J) Score is a combination of all four (e.g., ENTJ) The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) A personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into 1 of 16 personality types
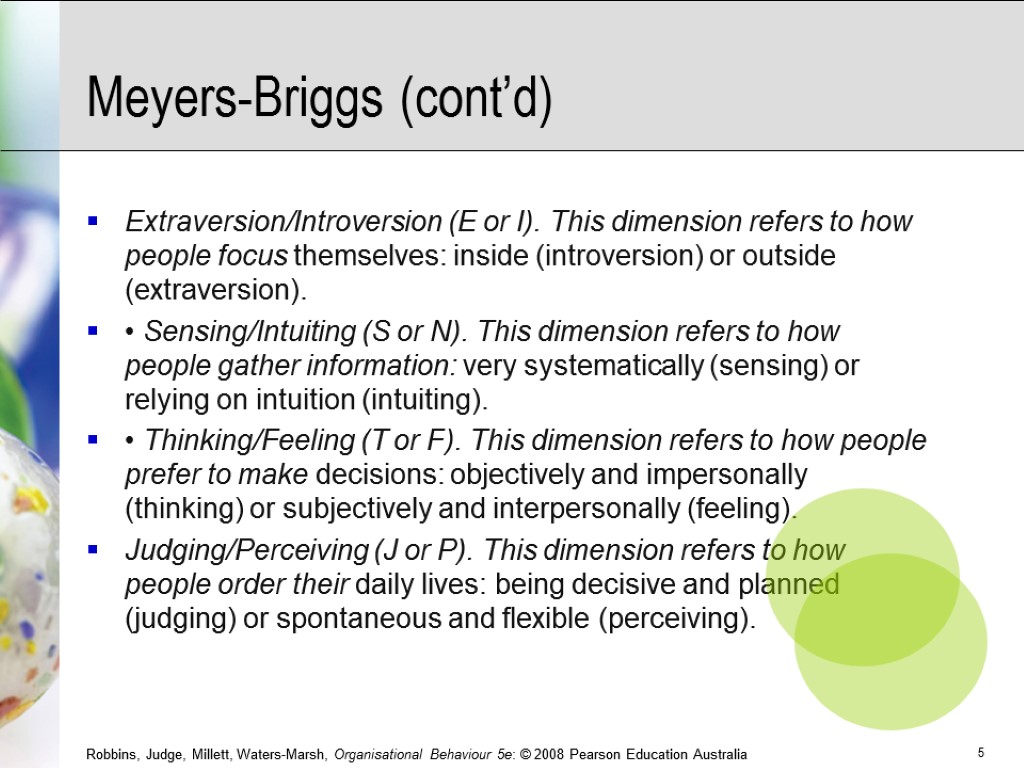
 Meyers-Briggs (cont’d) Extraversion/Introversion (E or I). This dimension refers to how people focus themselves: inside (introversion) or outside (extraversion). • Sensing/Intuiting (S or N). This dimension refers to how people gather information: very systematically (sensing) or relying on intuition (intuiting). • Thinking/Feeling (T or F). This dimension refers to how people prefer to make decisions: objectively and impersonally (thinking) or subjectively and interpersonally (feeling). Judging/Perceiving (J or P). This dimension refers to how people order their daily lives: being decisive and planned (judging) or spontaneous and flexible (perceiving).
Meyers-Briggs (cont’d) Extraversion/Introversion (E or I). This dimension refers to how people focus themselves: inside (introversion) or outside (extraversion). • Sensing/Intuiting (S or N). This dimension refers to how people gather information: very systematically (sensing) or relying on intuition (intuiting). • Thinking/Feeling (T or F). This dimension refers to how people prefer to make decisions: objectively and impersonally (thinking) or subjectively and interpersonally (feeling). Judging/Perceiving (J or P). This dimension refers to how people order their daily lives: being decisive and planned (judging) or spontaneous and flexible (perceiving).
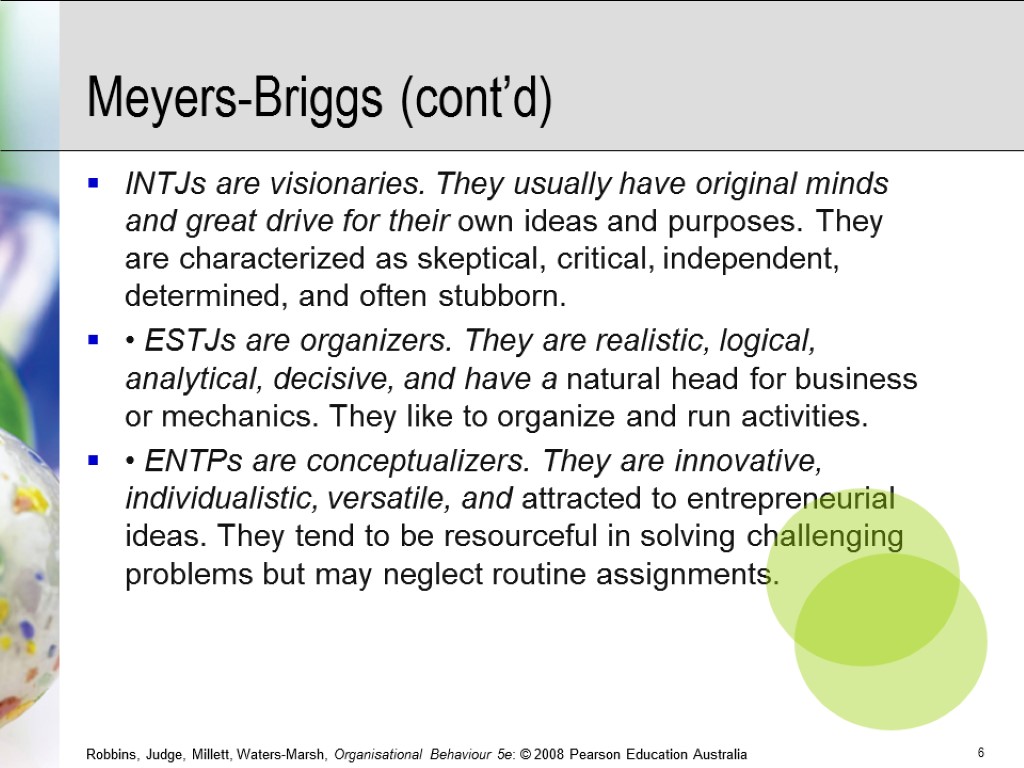
 Meyers-Briggs (cont’d) INTJs are visionaries. They usually have original minds and great drive for their own ideas and purposes. They are characterized as skeptical, critical, independent, determined, and often stubborn. • ESTJs are organizers. They are realistic, logical, analytical, decisive, and have a natural head for business or mechanics. They like to organize and run activities. • ENTPs are conceptualizers. They are innovative, individualistic, versatile, and attracted to entrepreneurial ideas. They tend to be resourceful in solving challenging problems but may neglect routine assignments.
Meyers-Briggs (cont’d) INTJs are visionaries. They usually have original minds and great drive for their own ideas and purposes. They are characterized as skeptical, critical, independent, determined, and often stubborn. • ESTJs are organizers. They are realistic, logical, analytical, decisive, and have a natural head for business or mechanics. They like to organize and run activities. • ENTPs are conceptualizers. They are innovative, individualistic, versatile, and attracted to entrepreneurial ideas. They tend to be resourceful in solving challenging problems but may neglect routine assignments.
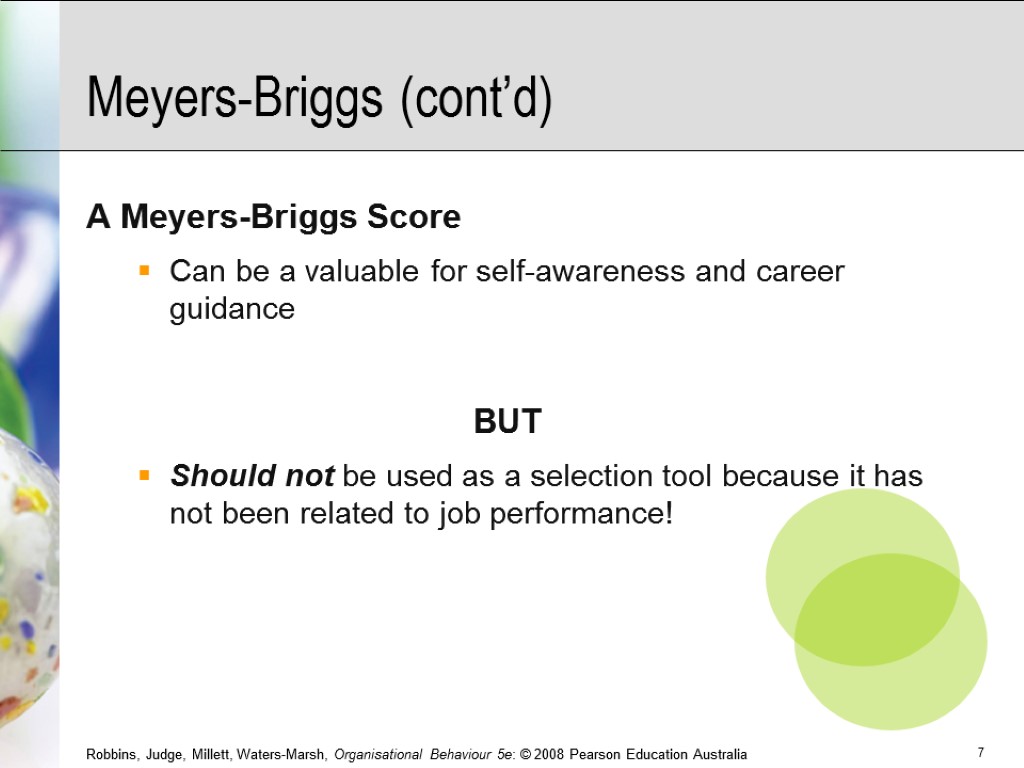
 Meyers-Briggs (cont’d) A Meyers-Briggs Score Can be a valuable for self-awareness and career guidance BUT Should not be used as a selection tool because it has not been related to job performance!
Meyers-Briggs (cont’d) A Meyers-Briggs Score Can be a valuable for self-awareness and career guidance BUT Should not be used as a selection tool because it has not been related to job performance!
 The Big Five Model of Personality Dimensions Extraversion. This dimension captures a person’s comfort level with relationships. Extraverted individuals are sociable, talkative, and assertive. Agreeableness. This dimension refers to how readily a person will go along with others. Highly agreeable people are good-natured, cooperative, warm, and trusting. Conscientiousness. This dimension is a measure of a person’s reliability. People who score high on conscientiousness are responsible, dependable, persistent, and achievement-oriented. Emotional stability. This dimension taps a person’s ability to withstand stress. People high on emotional stability are calm, self-confident, and secure. versus nervous, depressed, and insecure under stress (negative) Openness to experience. The final dimension addresses a person’s range of interests and fascination with novelty. People high on openness to experience are imaginative, artistically sensitive, and intellectual.
The Big Five Model of Personality Dimensions Extraversion. This dimension captures a person’s comfort level with relationships. Extraverted individuals are sociable, talkative, and assertive. Agreeableness. This dimension refers to how readily a person will go along with others. Highly agreeable people are good-natured, cooperative, warm, and trusting. Conscientiousness. This dimension is a measure of a person’s reliability. People who score high on conscientiousness are responsible, dependable, persistent, and achievement-oriented. Emotional stability. This dimension taps a person’s ability to withstand stress. People high on emotional stability are calm, self-confident, and secure. versus nervous, depressed, and insecure under stress (negative) Openness to experience. The final dimension addresses a person’s range of interests and fascination with novelty. People high on openness to experience are imaginative, artistically sensitive, and intellectual.
 Measuring Personality Personality Is Measured by: Self-Report Surveys Observer-Rating Surveys Projective Measures Rorschach Inkblot Test Thematic Apperception Test
Measuring Personality Personality Is Measured by: Self-Report Surveys Observer-Rating Surveys Projective Measures Rorschach Inkblot Test Thematic Apperception Test
 Major Personality Attributes Influencing OB Core Self-Evaluation (Self-Esteem, Locus of Control) Machiavellianism Narcissism Self-Monitoring Risk Taking Type A vs. Type B Personality Proactive Personality
Major Personality Attributes Influencing OB Core Self-Evaluation (Self-Esteem, Locus of Control) Machiavellianism Narcissism Self-Monitoring Risk Taking Type A vs. Type B Personality Proactive Personality
 Core Self-Evaluation: Two Main Components Self-Esteem Individuals’ degree of liking or disliking themselves, degree of thinking they are worthy or unworthy as a person Locus of Control The degree to which people believe they are masters of their own fate Internals (Internal locus of control) Individuals who believe that they control what happens to them Externals (External locus of control) Individuals who believe that what happens to them is controlled by outside forces such as luck or chance
Core Self-Evaluation: Two Main Components Self-Esteem Individuals’ degree of liking or disliking themselves, degree of thinking they are worthy or unworthy as a person Locus of Control The degree to which people believe they are masters of their own fate Internals (Internal locus of control) Individuals who believe that they control what happens to them Externals (External locus of control) Individuals who believe that what happens to them is controlled by outside forces such as luck or chance
 Conditions Favouring ‘High Machs’ Face-to-face interaction with others Minimal rules and regulations Whenever lower Machs are distracted Machiavellianism Machiavellianism (Mach) Degree to which an individual is pragmatic, maintains emotional distance, and believes that ends can justify means
Conditions Favouring ‘High Machs’ Face-to-face interaction with others Minimal rules and regulations Whenever lower Machs are distracted Machiavellianism Machiavellianism (Mach) Degree to which an individual is pragmatic, maintains emotional distance, and believes that ends can justify means
 Narcissism A Narcissistic Person Has grandiose sense of self-importance Requires excessive admiration Has a sense of entitlement Is arrogant Tends to be rated as less effective
Narcissism A Narcissistic Person Has grandiose sense of self-importance Requires excessive admiration Has a sense of entitlement Is arrogant Tends to be rated as less effective
 Self-Monitoring Self-Monitoring A personality trait that measures an individual’s ability to adjust his or her behavior to external, situational factors High Self-Monitors Receive better performance ratings Likely to emerge as leaders Show less commitment to their organisations
Self-Monitoring Self-Monitoring A personality trait that measures an individual’s ability to adjust his or her behavior to external, situational factors High Self-Monitors Receive better performance ratings Likely to emerge as leaders Show less commitment to their organisations
 Risk-Taking High Risk-Taking Managers Make quicker decisions Use less information to make decisions Operate in smaller and more entrepreneurial organisations Low Risk-Taking Managers Are slower to make decisions Require more information before making decisions Exist in larger organisations with stable environments Risk Propensity Aligning managers’ risk-taking propensity to job requirements should be beneficial to organisations
Risk-Taking High Risk-Taking Managers Make quicker decisions Use less information to make decisions Operate in smaller and more entrepreneurial organisations Low Risk-Taking Managers Are slower to make decisions Require more information before making decisions Exist in larger organisations with stable environments Risk Propensity Aligning managers’ risk-taking propensity to job requirements should be beneficial to organisations
 Personality Types: Type A and B Type As Are always moving, walking, and eating rapidly Feel impatient with the rate at which most events take place Strive to think or do two or more things at once Cannot cope with leisure time Are obsessed with numbers, measuring their success in terms of how many or how much of everything they acquire Type Bs Do not suffer from a sense of time urgency with its accompanying impatience Feel no need to display or discuss either their achievements or accomplishments Play for fun and relaxation, rather than to exhibit their superiority at any cost Can relax without guilt
Personality Types: Type A and B Type As Are always moving, walking, and eating rapidly Feel impatient with the rate at which most events take place Strive to think or do two or more things at once Cannot cope with leisure time Are obsessed with numbers, measuring their success in terms of how many or how much of everything they acquire Type Bs Do not suffer from a sense of time urgency with its accompanying impatience Feel no need to display or discuss either their achievements or accomplishments Play for fun and relaxation, rather than to exhibit their superiority at any cost Can relax without guilt
 Personality Types: Proactive personality Proactive Personality Identifies opportunities, shows initiative, takes action, and perseveres until meaningful change occurs Creates positive change in the environment, regardless or even in spite of constraints or obstacles
Personality Types: Proactive personality Proactive Personality Identifies opportunities, shows initiative, takes action, and perseveres until meaningful change occurs Creates positive change in the environment, regardless or even in spite of constraints or obstacles
 Which of the following is not a typical personality trait considered to be organisationally relevant? Locus of control Self-monitoring Self-enhancing Self esteem Machiavellianism Discuss with your colleague how each of the traits above would influence a university tutor’s behavior, and where you think your tutor falls with respect to each of them. Chapter Reflection: Personality
Which of the following is not a typical personality trait considered to be organisationally relevant? Locus of control Self-monitoring Self-enhancing Self esteem Machiavellianism Discuss with your colleague how each of the traits above would influence a university tutor’s behavior, and where you think your tutor falls with respect to each of them. Chapter Reflection: Personality
 Alison arrives to class and realises that she’s forgotten to bring her assignment. She says: 'Oh no, it’s just not my lucky day today.' Alison is demonstrating ______________. Alison is demonstrating a high external locus of control. Alison believes that things outside of her control determine what happens. If Alison works on a team with you, and you have a very high internal locus of control, what kinds of discussions do you think the two of you might have? Discuss with a colleague. Chapter Reflection: Personality
Alison arrives to class and realises that she’s forgotten to bring her assignment. She says: 'Oh no, it’s just not my lucky day today.' Alison is demonstrating ______________. Alison is demonstrating a high external locus of control. Alison believes that things outside of her control determine what happens. If Alison works on a team with you, and you have a very high internal locus of control, what kinds of discussions do you think the two of you might have? Discuss with a colleague. Chapter Reflection: Personality
 Julia is known for being a go-getter. She never leaves a task incomplete, and is involved in a number of activities. Moreover, she’s at the top of her class. She’s so busy that sometimes, she forgets to stop and eat lunch. Julia can be easily characterised as someone that has/is a Type ____ Personality. A Chapter Reflection: Personality
Julia is known for being a go-getter. She never leaves a task incomplete, and is involved in a number of activities. Moreover, she’s at the top of her class. She’s so busy that sometimes, she forgets to stop and eat lunch. Julia can be easily characterised as someone that has/is a Type ____ Personality. A Chapter Reflection: Personality
 Julia is also likely to not be very: Happy? Fun? Creative? Stressed? In general, Type As are rarely creative because they generally don’t allocate the necessary time for new solution development; they usually rely on past experiences to solve problems in order to be speedy. Chapter Reflection: Personality
Julia is also likely to not be very: Happy? Fun? Creative? Stressed? In general, Type As are rarely creative because they generally don’t allocate the necessary time for new solution development; they usually rely on past experiences to solve problems in order to be speedy. Chapter Reflection: Personality

