219c50330002ce0cc3d406435f5228ca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Chapter 2 - Lesson 1 Population and Settlement Chapter 2 Patterns of Life
Chapter 2 - Lesson 1 Population and Settlement Chapter 2 Patterns of Life
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 Population distribution – the way the population is spread out over the land Environments - surroundings • • • The world’s population includes all human beings everywhere The human population is spread unevenly throughout the world Of all the continents on Antarctica does not have permanent residents
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 Population distribution – the way the population is spread out over the land Environments - surroundings • • • The world’s population includes all human beings everywhere The human population is spread unevenly throughout the world Of all the continents on Antarctica does not have permanent residents
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 • Of all the continents in the world only Antarctica does not have permanent residents!!!! • Why doesn’t Antarctica have people flocking to its land to settle down? Harsh climate, rugged land, and lack of fertile soil!!!
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 • Of all the continents in the world only Antarctica does not have permanent residents!!!! • Why doesn’t Antarctica have people flocking to its land to settle down? Harsh climate, rugged land, and lack of fertile soil!!!
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 • • • No place on Earth has a completely perfect environment for human beings Adaptations are important to human survival Humans adapt to the environment they live in, in many ways. • Can you think of some ways humans adapt to their environment? Clothes, air conditioning, heat, houses, number of windows and doors in a house, and irrigation
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 • • • No place on Earth has a completely perfect environment for human beings Adaptations are important to human survival Humans adapt to the environment they live in, in many ways. • Can you think of some ways humans adapt to their environment? Clothes, air conditioning, heat, houses, number of windows and doors in a house, and irrigation
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 Irrigation – the use of connected ditches, canals, or pipes to move water to dry areas • Irrigation is important to human survival in desert areas and areas without a direct connection to a water source • With the growing amount of desert land through the loss of fertile soil, farm land, and forests it is getting harder and harder to bring freshwater to desert areas Desertification – the change of fertile land into desert land Drought – long periods of dry weather • Droughts are also a cause of desertification
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 Irrigation – the use of connected ditches, canals, or pipes to move water to dry areas • Irrigation is important to human survival in desert areas and areas without a direct connection to a water source • With the growing amount of desert land through the loss of fertile soil, farm land, and forests it is getting harder and harder to bring freshwater to desert areas Desertification – the change of fertile land into desert land Drought – long periods of dry weather • Droughts are also a cause of desertification
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 • In the 1930’s farmers in the Mid-West over farmed their land a drought set in causing most of their fertile soil to blow away it what was called the Dust Bowl, this caused many people to move away from that region
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53 • In the 1930’s farmers in the Mid-West over farmed their land a drought set in causing most of their fertile soil to blow away it what was called the Dust Bowl, this caused many people to move away from that region
 People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53
People, Climate, and Vegetation pg 52 - 53
 • How do people adapt to climate? (pg. 53)
• How do people adapt to climate? (pg. 53)
 People, Land Water Pages 54 - 55 • The physical features of land water also affect population distribution • Landforms and bodies of water limit the number of people that can live in a specific area • Which do you think would be easier to live on?
People, Land Water Pages 54 - 55 • The physical features of land water also affect population distribution • Landforms and bodies of water limit the number of people that can live in a specific area • Which do you think would be easier to live on?
 People, Land Water Pages 54 - 55 • The greatest number of people in East Asia live in China, China has more people than any country in the world • Most of these people live along the three major river valleys: Chang Jiang, Huang He, and the Xi Jiang • India is the second most populous country in the world and most people live along the Ganges River valley • Most of the U. S. population is along the east and west coast and along the Mississippi River • Water access plays a major role in where people settle down, Why do you think that’s the case? People need access to water to drink, wash, travel, trade, water crops
People, Land Water Pages 54 - 55 • The greatest number of people in East Asia live in China, China has more people than any country in the world • Most of these people live along the three major river valleys: Chang Jiang, Huang He, and the Xi Jiang • India is the second most populous country in the world and most people live along the Ganges River valley • Most of the U. S. population is along the east and west coast and along the Mississippi River • Water access plays a major role in where people settle down, Why do you think that’s the case? People need access to water to drink, wash, travel, trade, water crops
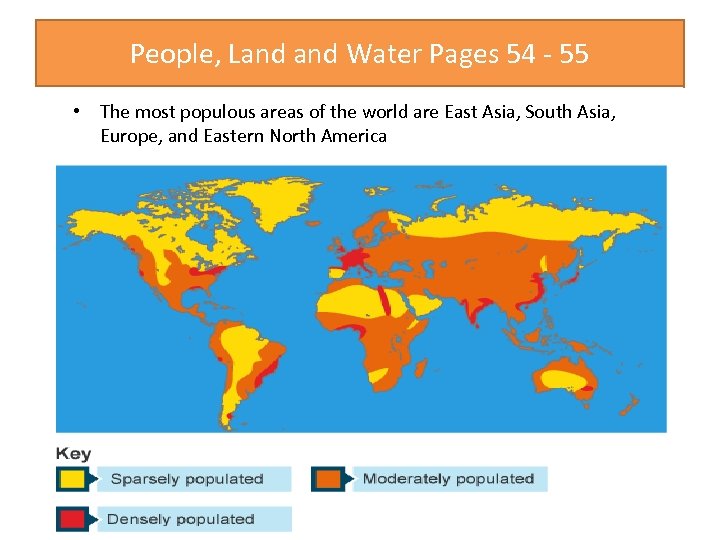 People, Land Water Pages 54 - 55 • The most populous areas of the world are East Asia, South Asia, Europe, and Eastern North America
People, Land Water Pages 54 - 55 • The most populous areas of the world are East Asia, South Asia, Europe, and Eastern North America
 • What geographic features make places easier for people to live in? (pg. 55)
• What geographic features make places easier for people to live in? (pg. 55)
 People on the Move pages 56 - 57 Migration – the movement of people from one place to another • Migration takes place for different reasons at different times • International – people migrate from country to country, they do this because there attractions of a new country that “pull” them to it or bad situations at home that “push” them out (Irish Potato Famine 1800 s) • National – push and pull factors apply only people move to a new location in the same country (Gold Rush 1849) “Pull” • Better jobs • Education • Freedom/rights • Climate “Push” • War • Poverty • Starvation/famine • Drought • unemployment
People on the Move pages 56 - 57 Migration – the movement of people from one place to another • Migration takes place for different reasons at different times • International – people migrate from country to country, they do this because there attractions of a new country that “pull” them to it or bad situations at home that “push” them out (Irish Potato Famine 1800 s) • National – push and pull factors apply only people move to a new location in the same country (Gold Rush 1849) “Pull” • Better jobs • Education • Freedom/rights • Climate “Push” • War • Poverty • Starvation/famine • Drought • unemployment
 People on the Move pages 56 - 57
People on the Move pages 56 - 57
 People on the Move pages 56 - 57 Urbanization – the movement of people from the countryside to the cities • Migration within countries also takes place from rural areas to urban areas • Some people migrate from a rural area to an urban area due to the difficulty of making a living from farming • Others are attracted to the city life and the many job opportunities cities hold • As a result of urbanization the largest concentration of people are now in metropolitan areas Metropolitan areas – big cities and the suburbs that surround them Demographers – population geographers that map out where people live and where they will live in the future
People on the Move pages 56 - 57 Urbanization – the movement of people from the countryside to the cities • Migration within countries also takes place from rural areas to urban areas • Some people migrate from a rural area to an urban area due to the difficulty of making a living from farming • Others are attracted to the city life and the many job opportunities cities hold • As a result of urbanization the largest concentration of people are now in metropolitan areas Metropolitan areas – big cities and the suburbs that surround them Demographers – population geographers that map out where people live and where they will live in the future
 People on the Move pages 56 - 57 World’s Largest Metropolitan Areas as of 2014 City 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Tokyo, Japan Seoul, South Korea Shanghai, China Guangzhou, China Delhi, India Mexico City, Mexico Beijing, China Lagos, Nigeria Sao Paulo, Brazil Mumbai, India New York, U. S. Osaka, Japan Population • 36, 923, 000 • 25, 620, 000 • 24, 750, 000 • 23, 900, 000 • 21, 750, 000 • 21, 170, 000 • 21, 150, 000 • 21, 000 • 20, 900, 000 • 20, 700, 000 • 20, 100, 000 • 20, 000
People on the Move pages 56 - 57 World’s Largest Metropolitan Areas as of 2014 City 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Tokyo, Japan Seoul, South Korea Shanghai, China Guangzhou, China Delhi, India Mexico City, Mexico Beijing, China Lagos, Nigeria Sao Paulo, Brazil Mumbai, India New York, U. S. Osaka, Japan Population • 36, 923, 000 • 25, 620, 000 • 24, 750, 000 • 23, 900, 000 • 21, 750, 000 • 21, 170, 000 • 21, 150, 000 • 21, 000 • 20, 900, 000 • 20, 700, 000 • 20, 100, 000 • 20, 000
 Terms to Know • irrigation environments. • Population density drought. • desertification migration urbanization • metropolitan areas demographers. . • What are some push and pull factors that cause migration? (pg. 57)
Terms to Know • irrigation environments. • Population density drought. • desertification migration urbanization • metropolitan areas demographers. . • What are some push and pull factors that cause migration? (pg. 57)


