21 ВАРИАНТ.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Chapter 2 Lecture Outlines Management’s Changing Landscape: Demographics, Global Economy, and Technology Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Chapter 2 Lecture Outlines Management’s Changing Landscape: Demographics, Global Economy, and Technology Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Objectives 1. Summarize the demographics of the new work force. 2. Define the term managing diversity and explain why it is particularly important today. 3. Discuss how the changing political-legal environment is affecting the practice of management. 4. Discuss why the global economy is a vital economic consideration for modern managers. 5. Describe three-step innovation process and define the term intrapreneur. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2
Chapter Objectives 1. Summarize the demographics of the new work force. 2. Define the term managing diversity and explain why it is particularly important today. 3. Discuss how the changing political-legal environment is affecting the practice of management. 4. Discuss why the global economy is a vital economic consideration for modern managers. 5. Describe three-step innovation process and define the term intrapreneur. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 2
 Dimensions of the Social Environment • Demographics – Changes in population characteristics. • The New Social Contract – Changes in the employer-employee relationship. • Inequalities – Persistent barriers encountered by women, minorities, and others in the workplace. • Managing diversity – Creating organization cultures that enable all employees to realize their potential. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 3
Dimensions of the Social Environment • Demographics – Changes in population characteristics. • The New Social Contract – Changes in the employer-employee relationship. • Inequalities – Persistent barriers encountered by women, minorities, and others in the workplace. • Managing diversity – Creating organization cultures that enable all employees to realize their potential. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 3
 Nagging Inequalities in the Workplace • Under the Glass Ceiling – Women continue to experience a significant genderwage gap and strong barriers to advancement. – Women are demanding more equitable compensation and workplace opportunities. – Women are leaving to become entrepreneurs. • Continuing Pressure for Equal Opportunity – Women, minorities, and the physically challenged are all expected to press harder for more employment opportunities. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 4
Nagging Inequalities in the Workplace • Under the Glass Ceiling – Women continue to experience a significant genderwage gap and strong barriers to advancement. – Women are demanding more equitable compensation and workplace opportunities. – Women are leaving to become entrepreneurs. • Continuing Pressure for Equal Opportunity – Women, minorities, and the physically challenged are all expected to press harder for more employment opportunities. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 4
 Managing Diversity • Managing Diversity – The process of creating an organizational culture that provides all employees, including women and minorities, with assistance and opportunities to help them realize their full potential. • More than EEO – The moral necessity and commitment in going beyond EEO and affirmative action to create flexible organizations that encompass and value diversity. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 5
Managing Diversity • Managing Diversity – The process of creating an organizational culture that provides all employees, including women and minorities, with assistance and opportunities to help them realize their full potential. • More than EEO – The moral necessity and commitment in going beyond EEO and affirmative action to create flexible organizations that encompass and value diversity. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 5
 The Political-Legal Environment • The Politicization of Management – General political responses – Defending the status quo against all comers. – Adopting a “wait and see” approach. – Proactively trying to identify and respond to issues. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 6
The Political-Legal Environment • The Politicization of Management – General political responses – Defending the status quo against all comers. – Adopting a “wait and see” approach. – Proactively trying to identify and respond to issues. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 6
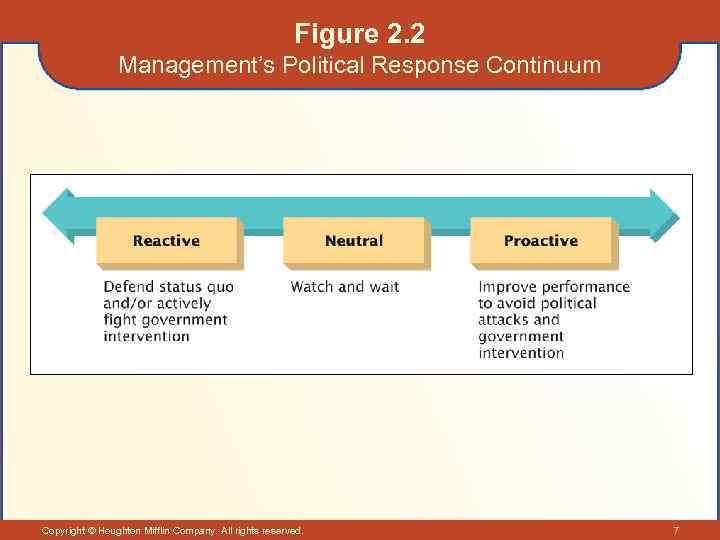 Figure 2. 2 Management’s Political Response Continuum Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7
Figure 2. 2 Management’s Political Response Continuum Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 7
 The Political-Legal Environment (cont’d) • Specific Political Strategies – Campaign financing – Lobbying – Coalition building – Indirect lobbying Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 8
The Political-Legal Environment (cont’d) • Specific Political Strategies – Campaign financing – Lobbying – Coalition building – Indirect lobbying Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 8
 Increased Personal Legal Accountability • Increases in Demands for Accountability – “Cooking the books, ” price fixing, and bid rigging are serious white-collar crimes likely to draw stiff penalties and a jail sentence. • Political and Legal Implications for Management – Increased use of legal audits – A review of all operations to pinpoint possible legal liabilities or problems. – Use of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) – Settling disputes with less costly methods, including arbitration and mediation. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9
Increased Personal Legal Accountability • Increases in Demands for Accountability – “Cooking the books, ” price fixing, and bid rigging are serious white-collar crimes likely to draw stiff penalties and a jail sentence. • Political and Legal Implications for Management – Increased use of legal audits – A review of all operations to pinpoint possible legal liabilities or problems. – Use of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) – Settling disputes with less costly methods, including arbitration and mediation. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 9
 The Economic Environment • The Job Outlook in Today’s Service Economy, Where Education Counts – Service sector job growth in high paying occupations that require at least a bachelor’s degree is twice as fast as that of all other occupations. • Benefiting from Economic Forecasts – The consensus approach uses a wide variety of economic forecasts in creating an average opinion of future economic conditions. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 10
The Economic Environment • The Job Outlook in Today’s Service Economy, Where Education Counts – Service sector job growth in high paying occupations that require at least a bachelor’s degree is twice as fast as that of all other occupations. • Benefiting from Economic Forecasts – The consensus approach uses a wide variety of economic forecasts in creating an average opinion of future economic conditions. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 10
 The Challenge of a Global Economy • A Single Global Marketplace – Global trade is causing a shift to a single economy. – The commercial world is no longer East-West, North. South. • Globalization Is Personal – Working for a foreign-owned company is a growing trend. – Meeting world standards for quality and costs (through lower wages) is necessary to be globally competitive. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11
The Challenge of a Global Economy • A Single Global Marketplace – Global trade is causing a shift to a single economy. – The commercial world is no longer East-West, North. South. • Globalization Is Personal – Working for a foreign-owned company is a growing trend. – Meeting world standards for quality and costs (through lower wages) is necessary to be globally competitive. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 11
 The Technological Environment • Technology – All the tools and ideas available for extending the natural and mental reach of humankind. – Technology is facilitating the evolution of the information age. – Information has become a valuable strategic resource for gaining competitive advantage. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 12
The Technological Environment • Technology – All the tools and ideas available for extending the natural and mental reach of humankind. – Technology is facilitating the evolution of the information age. – Information has become a valuable strategic resource for gaining competitive advantage. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 12
 The Technological Environment (cont’d) • The Innovation Process – The systematic and practical application of a new idea. • Steps in the Innovation Process – Conceptualization: when a new idea occurs to someone. – Product technology: creation of a working prototype. – Production technology: development of a profitable production process. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 13
The Technological Environment (cont’d) • The Innovation Process – The systematic and practical application of a new idea. • Steps in the Innovation Process – Conceptualization: when a new idea occurs to someone. – Product technology: creation of a working prototype. – Production technology: development of a profitable production process. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 13
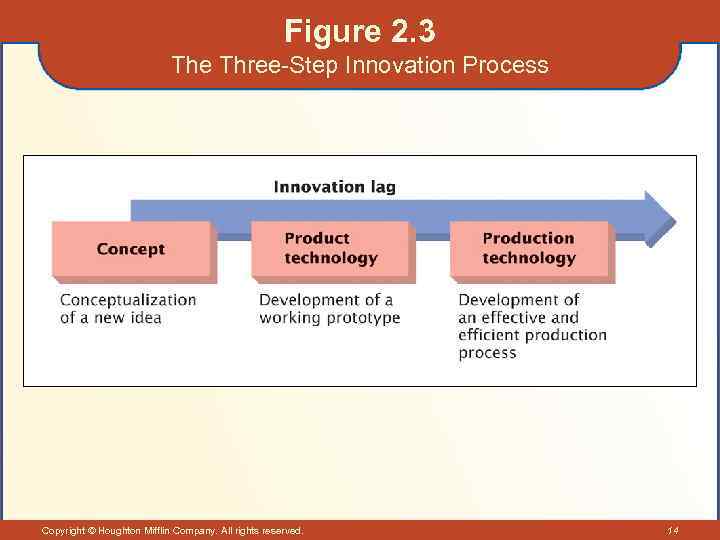 Figure 2. 3 The Three-Step Innovation Process Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 14
Figure 2. 3 The Three-Step Innovation Process Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 14
 The Technological Environment (cont’d) • Innovation Lag – The time it takes for a new product to be translated into satisfied demand. • Shortening Innovation Lag – Goal setting: creating a sense of urgency and purpose. – Empowerment: pushing decision-making authority down to the level of the decision. – Concurrent engineering: using a team approach to product design involving specialists from all functional areas including research, production, and marketing. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 15
The Technological Environment (cont’d) • Innovation Lag – The time it takes for a new product to be translated into satisfied demand. • Shortening Innovation Lag – Goal setting: creating a sense of urgency and purpose. – Empowerment: pushing decision-making authority down to the level of the decision. – Concurrent engineering: using a team approach to product design involving specialists from all functional areas including research, production, and marketing. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 15
 Promoting Innovation Through Intrapreneurship • Intrapreneur – An employee who takes personal responsibility for pushing an innovative idea through a large organization. • Fostering Intrapreneurship – Focus on results and teamwork. – Reward innovation and risk taking. – Tolerate and learn from mistakes. – Remain flexible and change-oriented. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 16
Promoting Innovation Through Intrapreneurship • Intrapreneur – An employee who takes personal responsibility for pushing an innovative idea through a large organization. • Fostering Intrapreneurship – Focus on results and teamwork. – Reward innovation and risk taking. – Tolerate and learn from mistakes. – Remain flexible and change-oriented. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. 16


