Chapter 2 Kenneth L. Bontrager John P. Lampignano


















































lagcc_chapter_2_powerpoint_image_quality_digital_technology_and_radiation_protection.ppt
- Размер: 13.8 Mегабайта
- Количество слайдов: 92
Описание презентации Chapter 2 Kenneth L. Bontrager John P. Lampignano по слайдам
 Chapter 2 Kenneth L. Bontrager John P. Lampignano Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
Chapter 2 Kenneth L. Bontrager John P. Lampignano Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
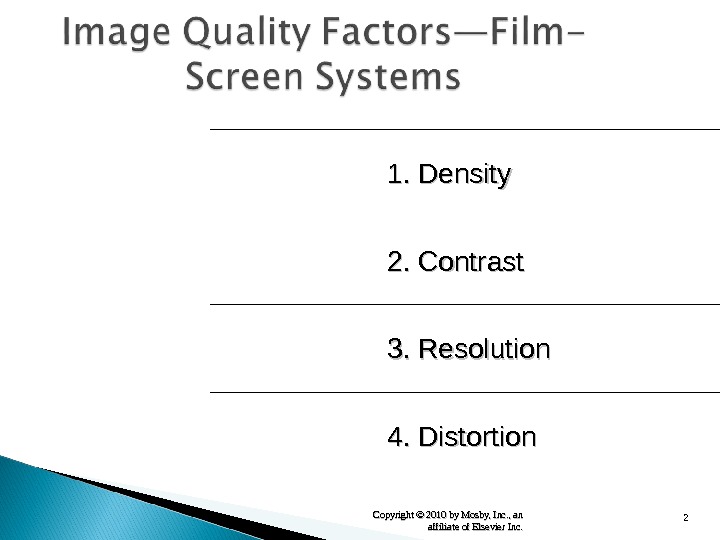
 2 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Density 2. Contrast 3. Resolution 4. Distortion
2 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Density 2. Contrast 3. Resolution 4. Distortion
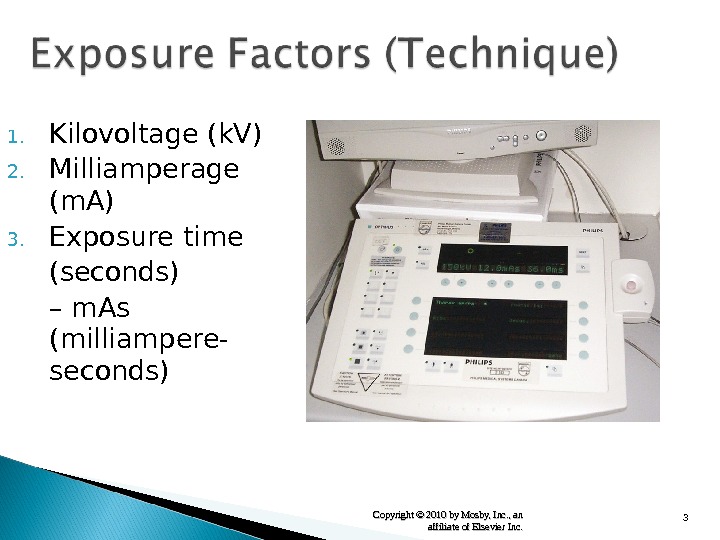
 3 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Kilovoltage (k. V) 2. Milliamperage (m. A) 3. Exposure time (seconds) – m. As (milliampere- seconds)
3 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Kilovoltage (k. V) 2. Milliamperage (m. A) 3. Exposure time (seconds) – m. As (milliampere- seconds)
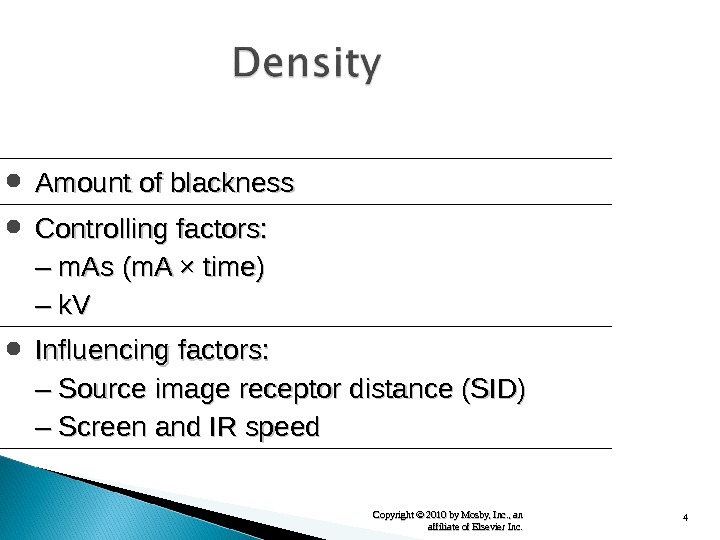
 4 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Amount of blackness Controlling factors: –– m. As (m. A × time) –– k. V Influencing factors: –– Source image receptor distance (SID) –– Screen and IR speed
4 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Amount of blackness Controlling factors: –– m. As (m. A × time) –– k. V Influencing factors: –– Source image receptor distance (SID) –– Screen and IR speed
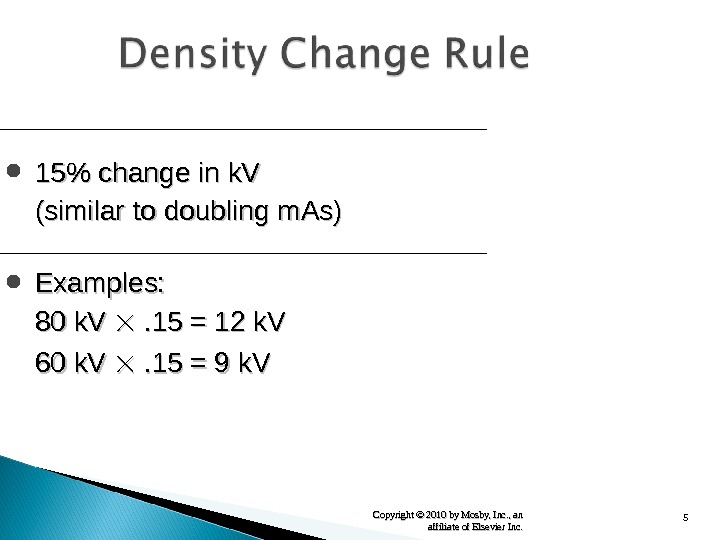
 5 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 15% change in k. V (similar to doubling m. As) Examples: 80 k. V . 15 = 12 k. V 60 k. V . 15 = 9 k. V
5 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 15% change in k. V (similar to doubling m. As) Examples: 80 k. V . 15 = 12 k. V 60 k. V . 15 = 9 k. V
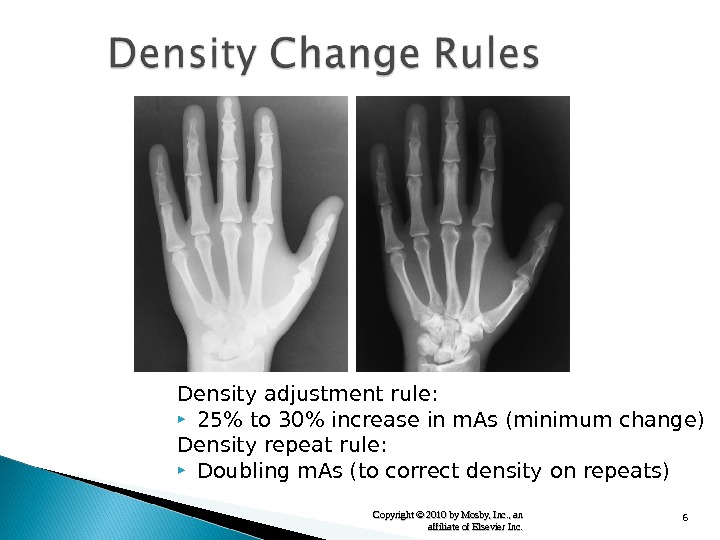
 6 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Density adjustment rule: 25% to 30% increase in m. As (minimum change) Density repeat rule: Doubling m. As (to correct density on repeats)
6 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Density adjustment rule: 25% to 30% increase in m. As (minimum change) Density repeat rule: Doubling m. As (to correct density on repeats)
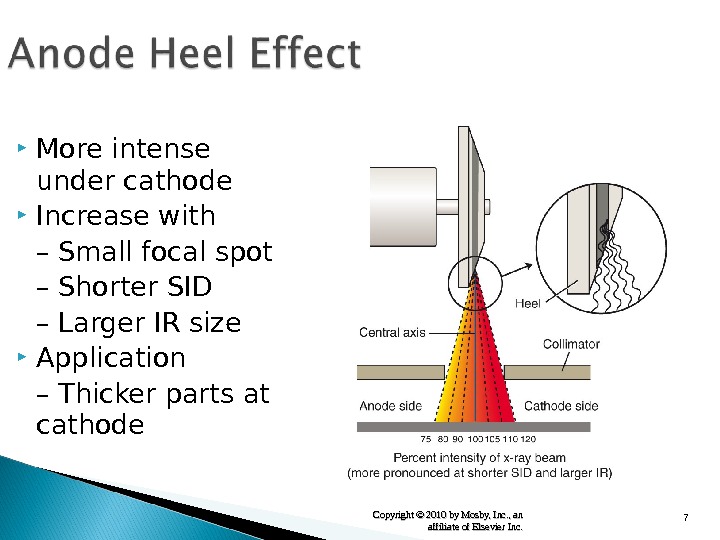
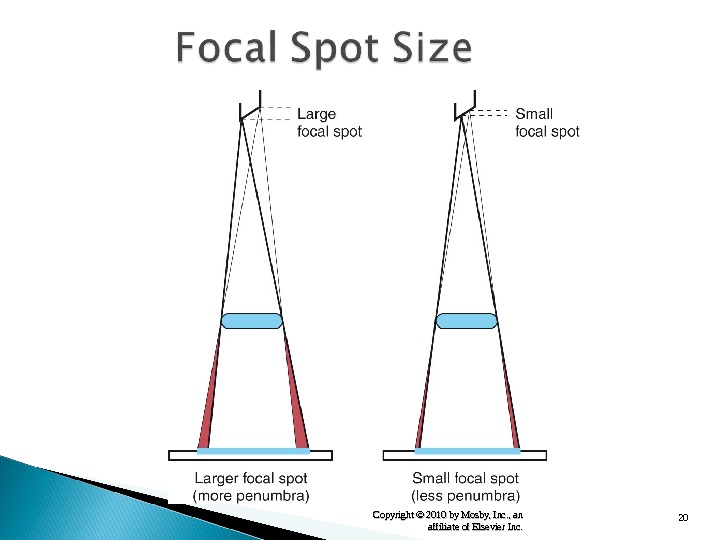
 7 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. More intense under cathode Increase with – Small focal spot – Shorter SID – Larger IR size Application – Thicker parts at cathode
7 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. More intense under cathode Increase with – Small focal spot – Shorter SID – Larger IR size Application – Thicker parts at cathode
 8 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Compensating Filters Compensating filters filter out a portion of the primary beam toward the thin or less dense part of the body that is being imaged. Types of compensating filters include the following: Wedge filter Trough Boomerang
8 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Compensating Filters Compensating filters filter out a portion of the primary beam toward the thin or less dense part of the body that is being imaged. Types of compensating filters include the following: Wedge filter Trough Boomerang
 9 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Compensating Filters Wedge filter Boomerang filter
9 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Compensating Filters Wedge filter Boomerang filter
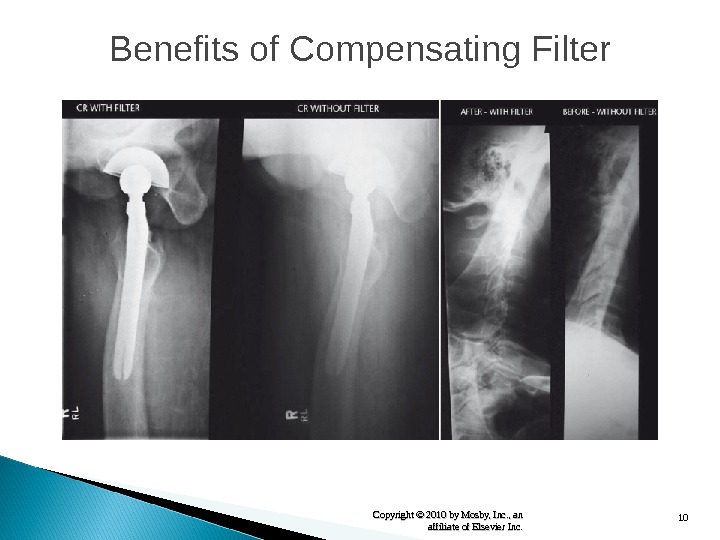
 10 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Benefits of Compensating Filter
10 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Benefits of Compensating Filter
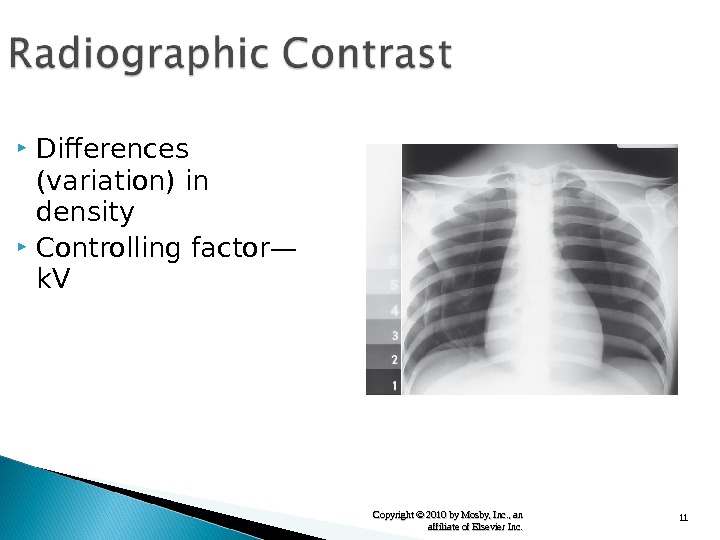
 11 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Differences (variation) in density Controlling factor — k. V
11 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Differences (variation) in density Controlling factor — k. V
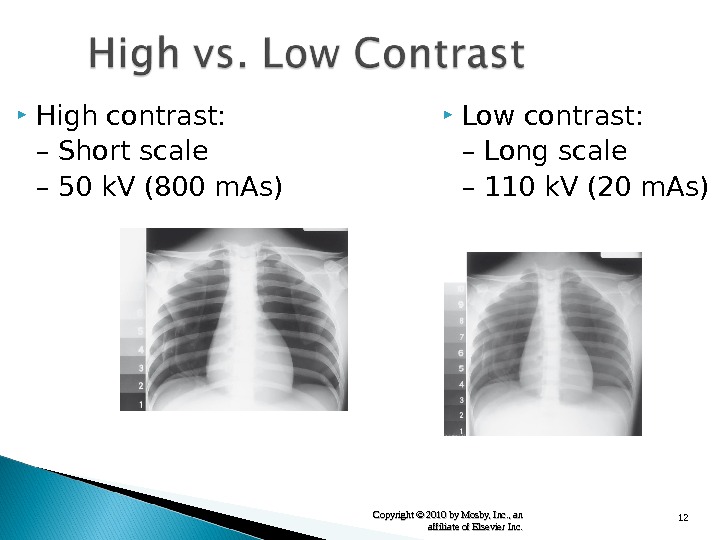
 12 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. High contrast: – Short scale – 50 k. V (800 m. As) Low contrast: – Long scale – 110 k. V (20 m. As)
12 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. High contrast: – Short scale – 50 k. V (800 m. As) Low contrast: – Long scale – 110 k. V (20 m. As)
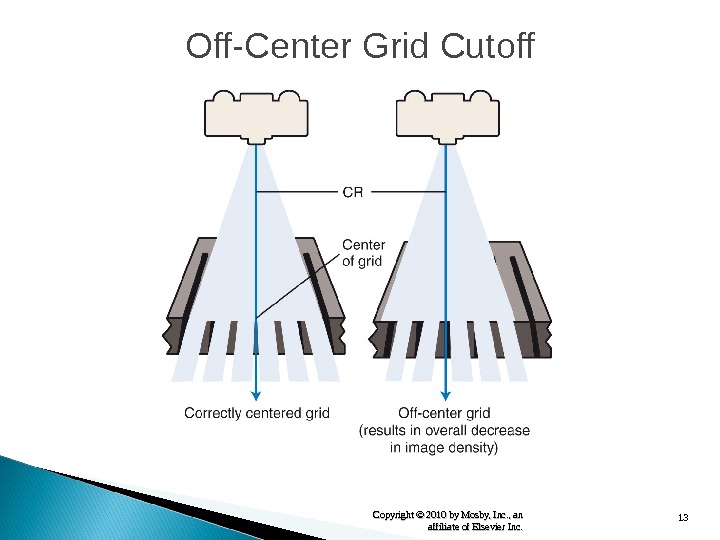
 13 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Off-Center Grid Cutoff
13 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Off-Center Grid Cutoff
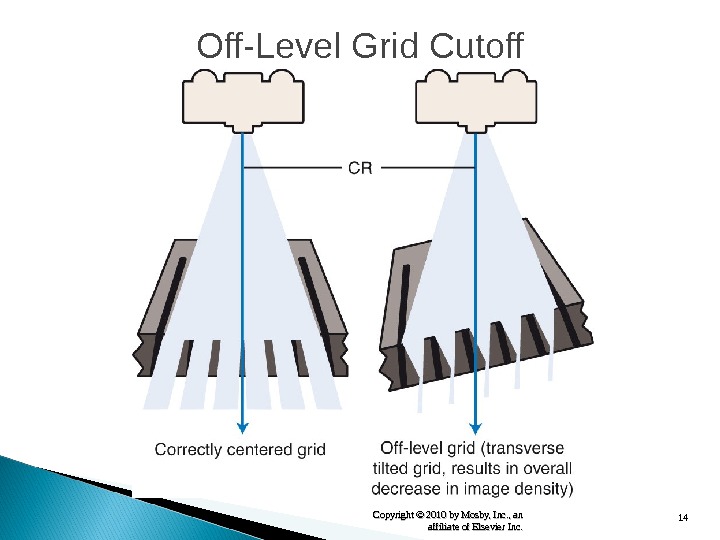
 14 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Off-Level Grid Cutoff
14 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Off-Level Grid Cutoff
 15 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Off-Focus Grid Cutoff
15 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Off-Focus Grid Cutoff
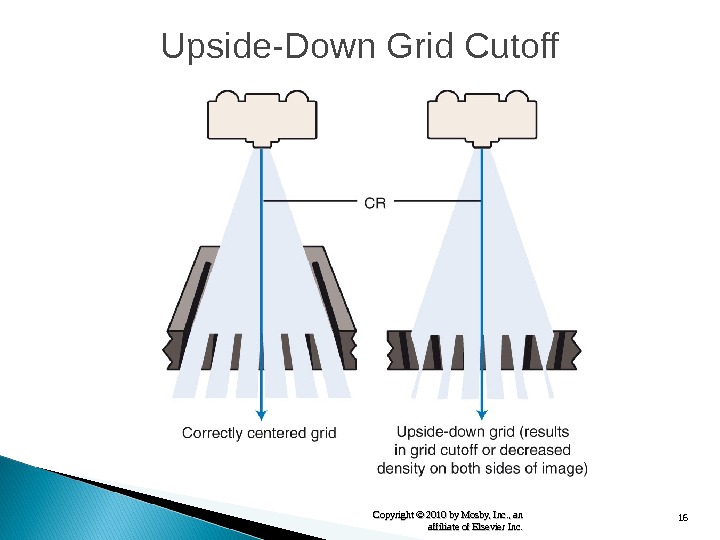
 16 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Upside-Down Grid Cutoff
16 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Upside-Down Grid Cutoff
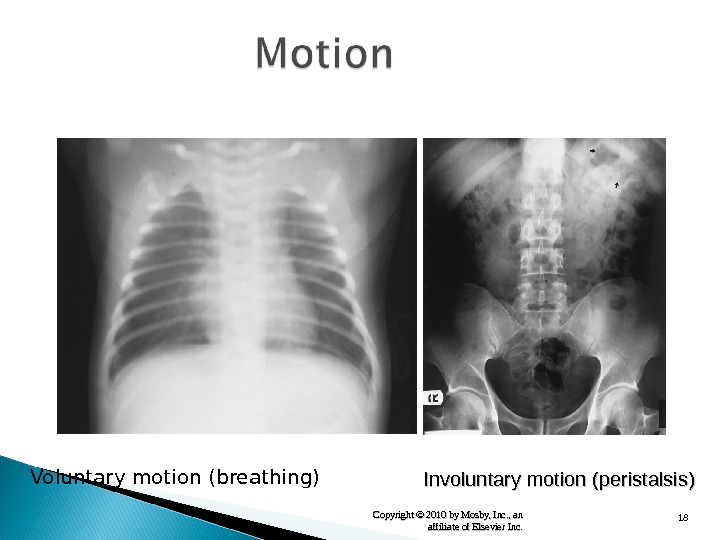
 17 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Recorded sharpness of structures Lack of definition is blur or unsharpness. Motion is greatest deterrent (two types).
17 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Recorded sharpness of structures Lack of definition is blur or unsharpness. Motion is greatest deterrent (two types).
 18 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Voluntary motion (breathing) Involuntary motion (peristalsis)
18 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Voluntary motion (breathing) Involuntary motion (peristalsis)
 19 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Small focal spot —— Use small focal spot whenever possible to improve detail. 2. Shorter exposure time —— Use shortest exposure time possible to control voluntary and involuntary motion. 3. Film-screen speed —— Use faster film-screen speed to control voluntary and involuntary motion. 4. SID —— Use longer SID to improve detail. 5. OID —— Use shorter OID to improve detail.
19 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Small focal spot —— Use small focal spot whenever possible to improve detail. 2. Shorter exposure time —— Use shortest exposure time possible to control voluntary and involuntary motion. 3. Film-screen speed —— Use faster film-screen speed to control voluntary and involuntary motion. 4. SID —— Use longer SID to improve detail. 5. OID —— Use shorter OID to improve detail.
 20 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
20 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
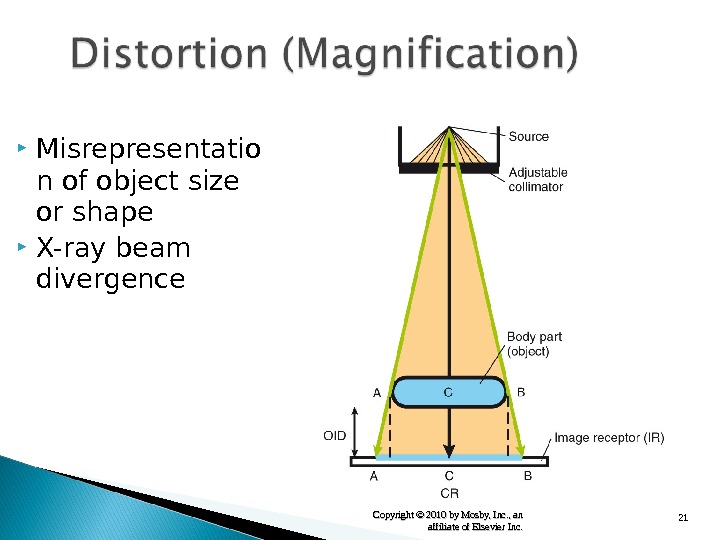
 21 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Misrepresentatio n of object size or shape X-ray beam divergence
21 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Misrepresentatio n of object size or shape X-ray beam divergence
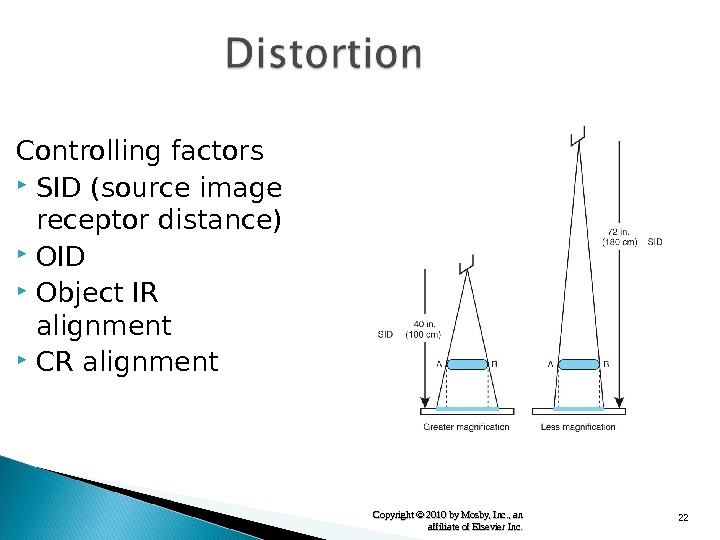
 22 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID (source image receptor distance) OID Object IR alignment CR alignment
22 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID (source image receptor distance) OID Object IR alignment CR alignment
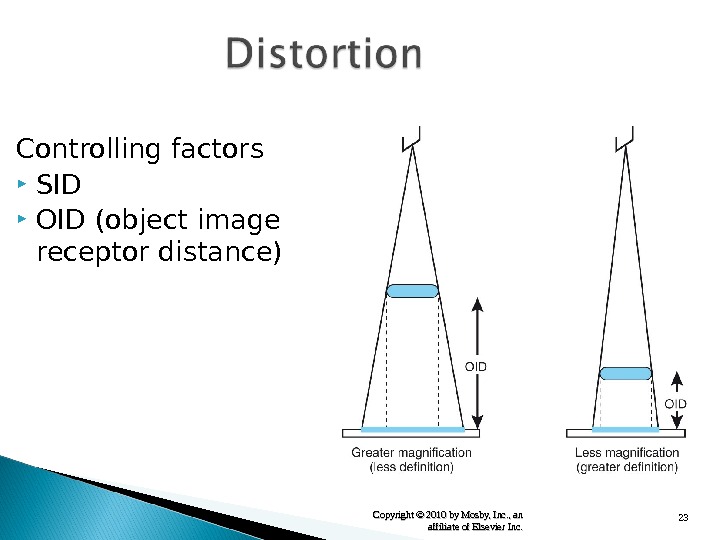
 23 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID OID (object image receptor distance)
23 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID OID (object image receptor distance)
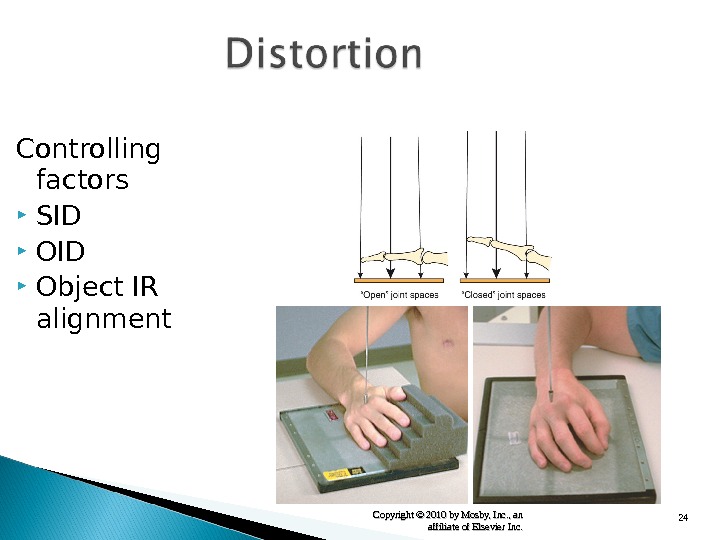
 24 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID Object IR alignment
24 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID Object IR alignment
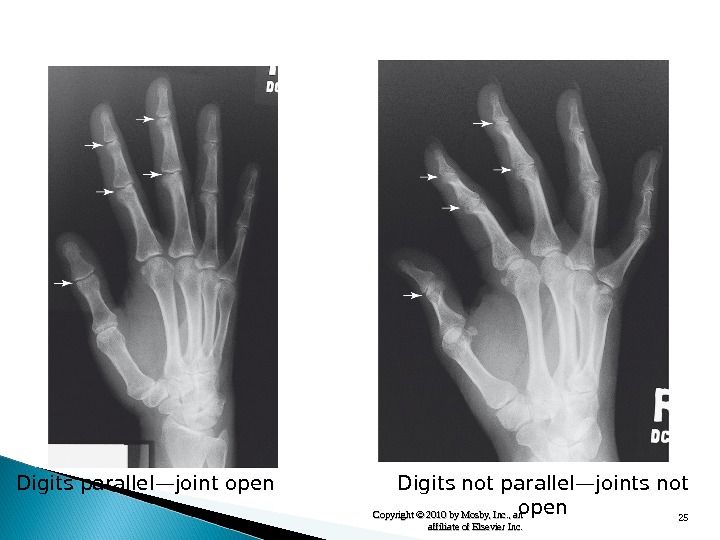
 25 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Digits parallel — joint open Digits not parallel — joints not open
25 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Digits parallel — joint open Digits not parallel — joints not open
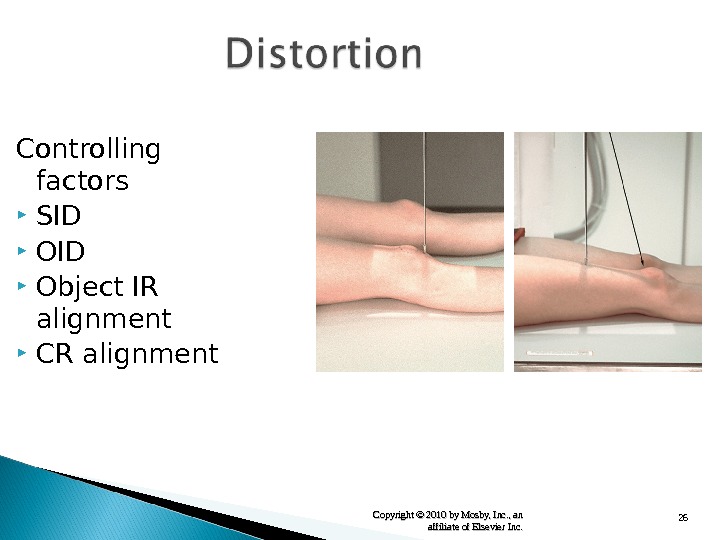
 26 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID Object IR alignment CR alignment
26 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors SID Object IR alignment CR alignment
 27 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. CR Alignment CR parallel to joint CR not parallel to joint
27 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. CR Alignment CR parallel to joint CR not parallel to joint
 28 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Which of the following is NOT a quality factor film-based radiography? A. Density B. Focal spot size C. Contrast D. Distortion E. Resolution
28 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Which of the following is NOT a quality factor film-based radiography? A. Density B. Focal spot size C. Contrast D. Distortion E. Resolution
 29 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me The primary controlling factor for density is A. m. As B. k. V C. SID D. OI
29 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me The primary controlling factor for density is A. m. As B. k. V C. SID D. OI
 30 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me When the anode heel rule is applied, the thicker aspect of the anatomy should be placed under the cathode end of the x-ray tube. A. True B. False
30 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me When the anode heel rule is applied, the thicker aspect of the anatomy should be placed under the cathode end of the x-ray tube. A. True B. False
 31 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Which of the following is not a type of compensating filter? A. Wedge B. Boomerang C. Slotted D. Trough
31 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Which of the following is not a type of compensating filter? A. Wedge B. Boomerang C. Slotted D. Trough
 32 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What is the primary controlling factor for radiographic contrast? A. m. As B. k. V C. SID D. Focal spot size
32 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What is the primary controlling factor for radiographic contrast? A. m. As B. k. V C. SID D. Focal spot size
 33 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What type of grid cutoff will occur if a shorter SID is used than what is specified for a particular grid? A. Off-center B. Off-level C. Off-focus D. Off-distance
33 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What type of grid cutoff will occur if a shorter SID is used than what is specified for a particular grid? A. Off-center B. Off-level C. Off-focus D. Off-distance
 34 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
34 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 35 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
35 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
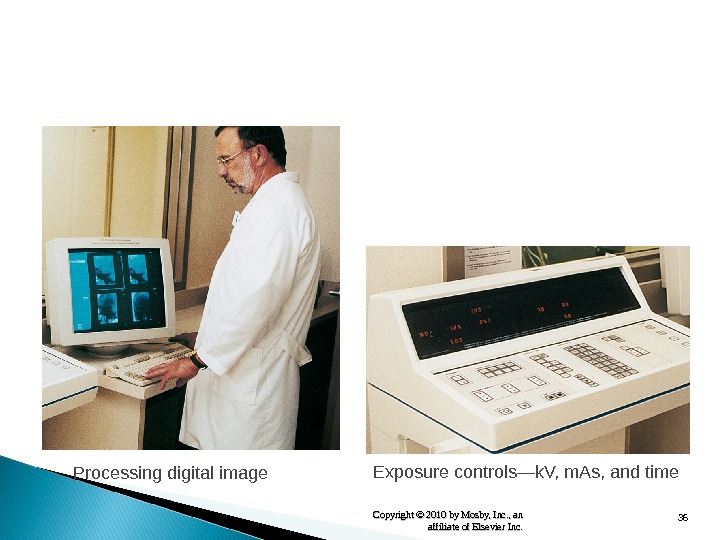
 36 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Processing digital image Exposure controls — k. V, m. As, and time
36 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Processing digital image Exposure controls — k. V, m. As, and time
 37 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Brightness Contrast Resolution Distortion Exposure index Noise
37 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Brightness Contrast Resolution Distortion Exposure index Noise
 38 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. AP shoulder — high brightness AP shoulder — less brightness. Intensity of light representing individual pixels in image
38 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. AP shoulder — high brightness AP shoulder — less brightness. Intensity of light representing individual pixels in image
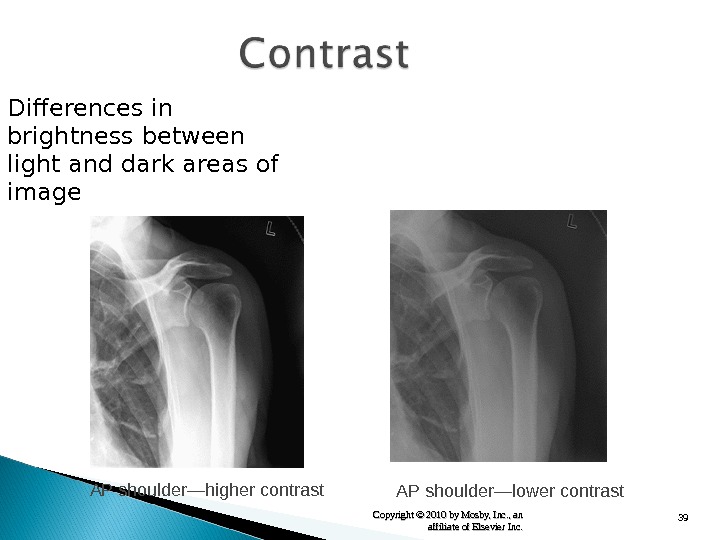
 39 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Differences in brightness between light and dark areas of image AP shoulder — higher contrast AP shoulder — lower contrast
39 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Differences in brightness between light and dark areas of image AP shoulder — higher contrast AP shoulder — lower contrast
 40 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors: Acquisition pixel size – Inherent to the digital imaging detector Display matrix – D ependent on capabilities of the display monitor Recorded Sharpness of Structures on Image
40 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors: Acquisition pixel size – Inherent to the digital imaging detector Display matrix – D ependent on capabilities of the display monitor Recorded Sharpness of Structures on Image
 41 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors: SID OID CR alignment Misrepresentation of Object Size or Shape
41 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Controlling factors: SID OID CR alignment Misrepresentation of Object Size or Shape
 42 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. A numeric value that is representative of the exposure the image receptor received May be inversely or directly proportional to radiation striking the image receptor Key in verifying optimal digital image is obtained with least dose to patient
42 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. A numeric value that is representative of the exposure the image receptor received May be inversely or directly proportional to radiation striking the image receptor Key in verifying optimal digital image is obtained with least dose to patient
 43 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Dependent on the intensity of the radiation striking the detector, which is the effect of – m. As – k. V – Total detector area irradiated – Objects exposed (air, metal implants, patient anatomy)
43 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Dependent on the intensity of the radiation striking the detector, which is the effect of – m. As – k. V – Total detector area irradiated – Objects exposed (air, metal implants, patient anatomy)
 44 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Low exposure index (high “S” number) — Underexposed Acceptable exposure index
44 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Low exposure index (high “S” number) — Underexposed Acceptable exposure index
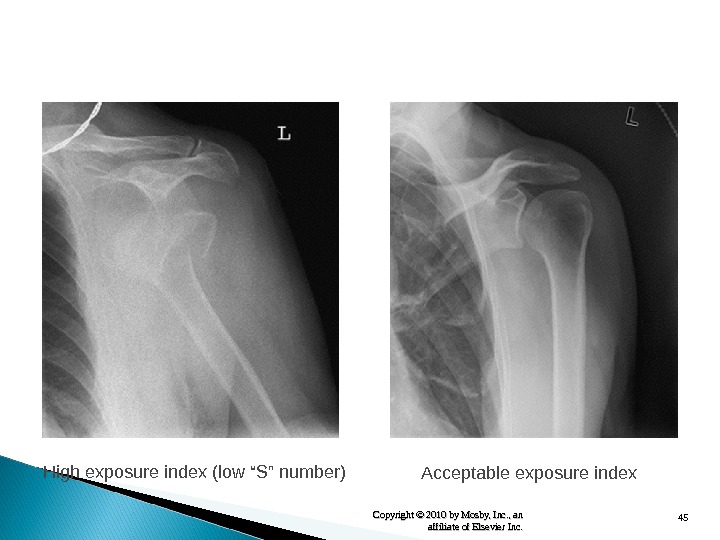
 45 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. High exposure index (low “S” number) Acceptable exposure index
45 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. High exposure index (low “S” number) Acceptable exposure index
 46 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Random disturbance that obscures image clarity High signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is desirable. Low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is undesirable.
46 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Random disturbance that obscures image clarity High signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is desirable. Low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is undesirable.
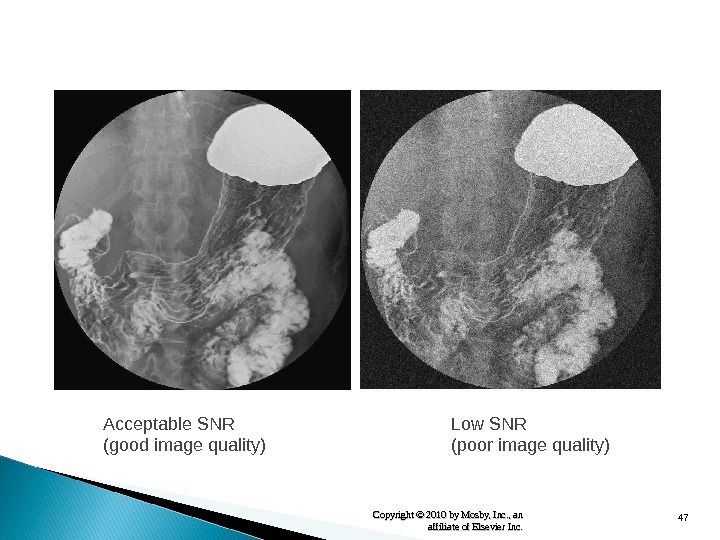
 47 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Acceptable SNR (good image quality) Low SNR (poor image quality)
47 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Acceptable SNR (good image quality) Low SNR (poor image quality)
 48 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Changing or enhancing the electronic image to improve diagnostic quality Algorithms applied to improve diagnostic quality of image Post-processing cannot improve low SNR image.
48 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Changing or enhancing the electronic image to improve diagnostic quality Algorithms applied to improve diagnostic quality of image Post-processing cannot improve low SNR image.
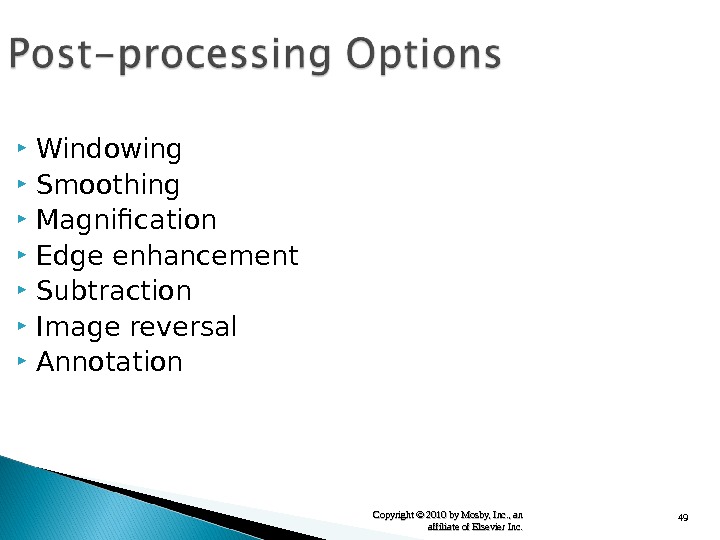
 49 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Windowing Smoothing Magnification Edge enhancement Subtraction Image reversal Annotation
49 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Windowing Smoothing Magnification Edge enhancement Subtraction Image reversal Annotation
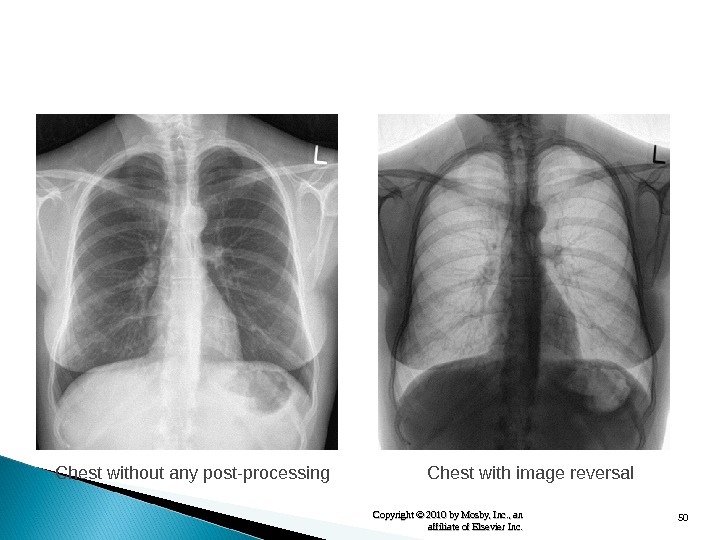
 50 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Chest without any post-processing Chest with image reversal
50 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Chest without any post-processing Chest with image reversal
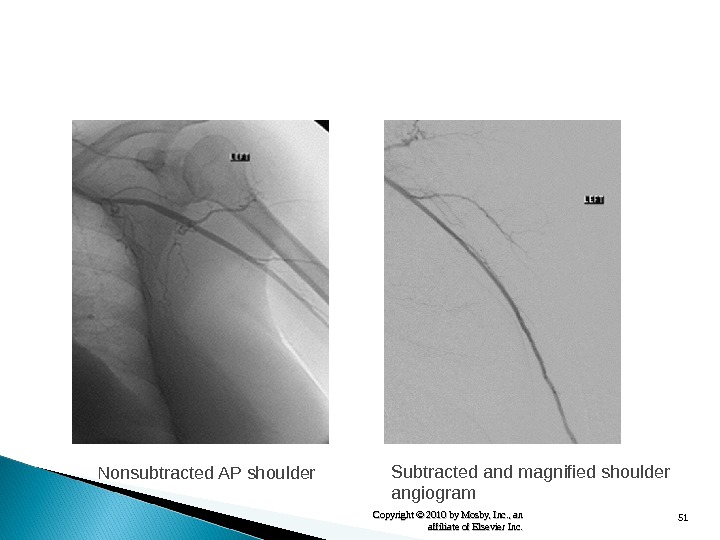
 51 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Nonsubtracted AP shoulder Subtracted and magnified shoulder angiogram
51 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Nonsubtracted AP shoulder Subtracted and magnified shoulder angiogram
 52 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Highly complex mathematical formulas are called A. Binary codes B. Exposure indices C. Equalization filters D. Algorithms
52 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Highly complex mathematical formulas are called A. Binary codes B. Exposure indices C. Equalization filters D. Algorithms
 53 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me The intensity of light that represents the individual pixels in the digital image on the monitor is the definition for A. Brightness B. Contrast C. Density D. Noise
53 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me The intensity of light that represents the individual pixels in the digital image on the monitor is the definition for A. Brightness B. Contrast C. Density D. Noise
 54 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Random disturbance that obscures or reduces clarity is the definition for A. Noise B. Resolution C. SNR D. Distortion
54 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me Random disturbance that obscures or reduces clarity is the definition for A. Noise B. Resolution C. SNR D. Distortion
 55 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me A low SNR digital image can be enhanced through post-processing techniques. A. True B. False
55 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me A low SNR digital image can be enhanced through post-processing techniques. A. True B. False
 56 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Computed tomography (CT), one of the first applications of computers in radiography
56 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Computed tomography (CT), one of the first applications of computers in radiography
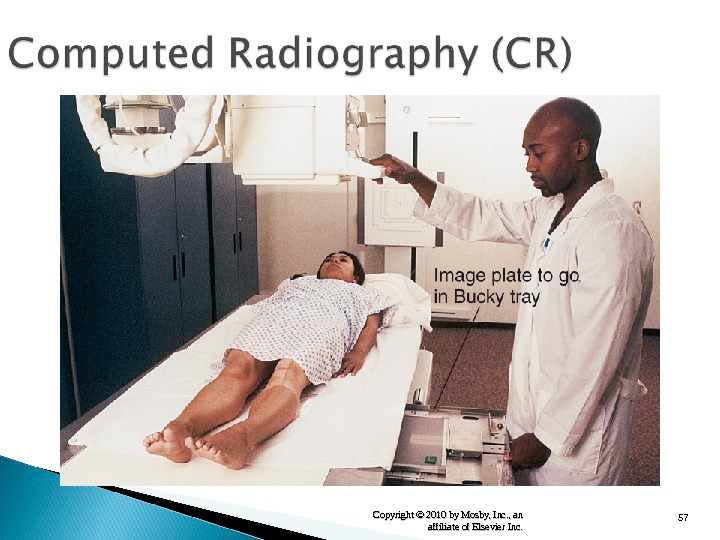
 57 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
57 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 58 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
58 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
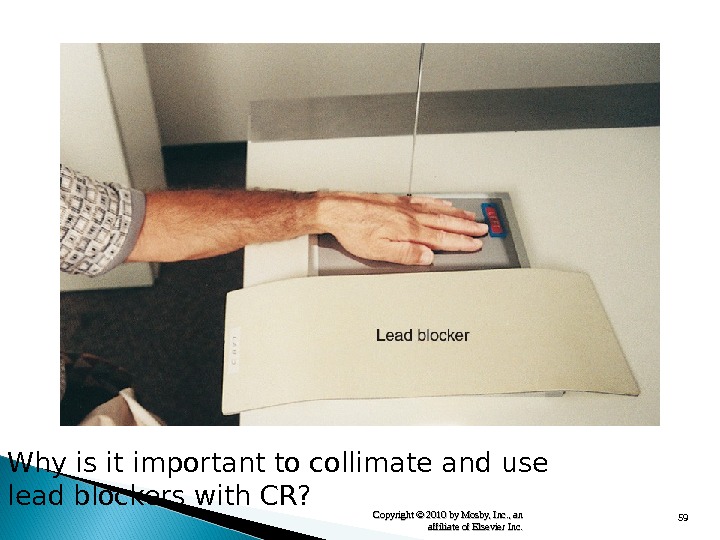
 59 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Why is it important to collimate and use lead blockers with CR?
59 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Why is it important to collimate and use lead blockers with CR?
 60 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
60 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 61 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
61 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 62 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
62 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
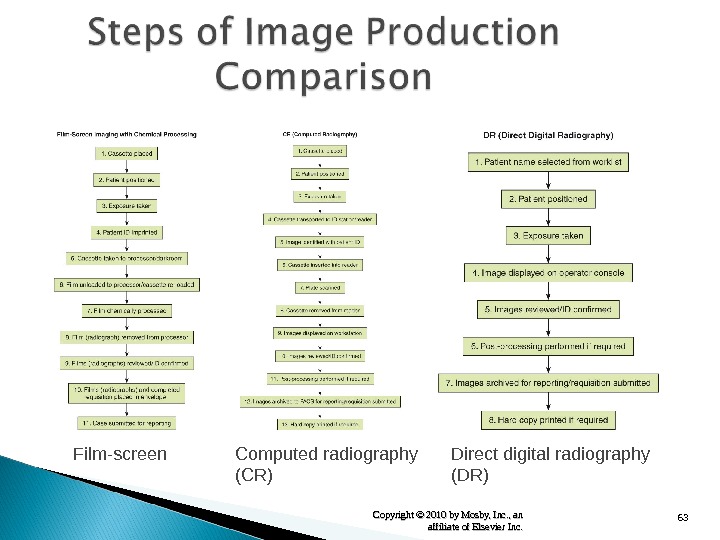
 63 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Film-screen Computed radiography (CR) Direct digital radiography (DR)
63 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Film-screen Computed radiography (CR) Direct digital radiography (DR)
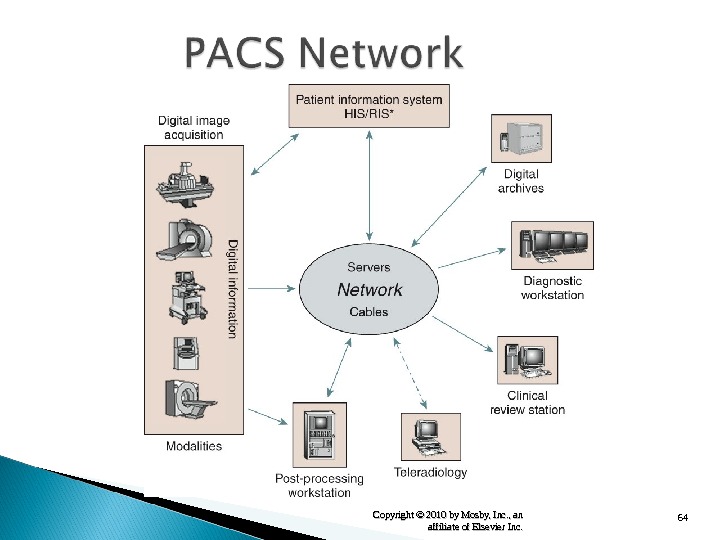
 64 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
64 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
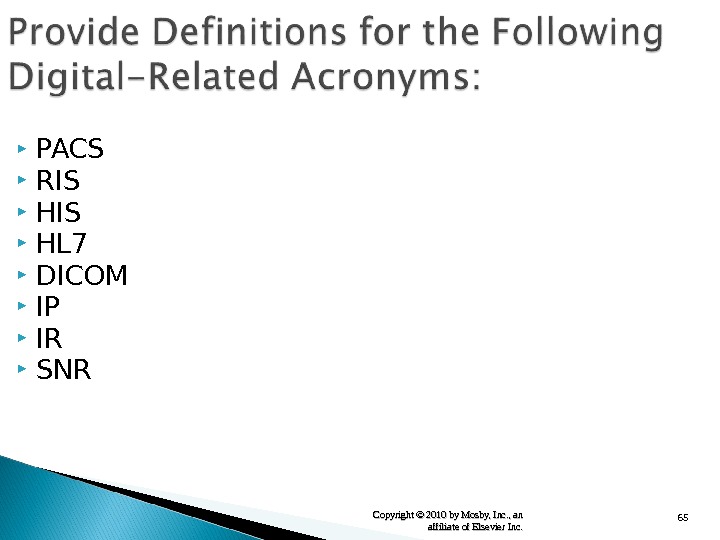
 65 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. PACS RIS HL 7 DICOM IP IR SNR
65 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. PACS RIS HL 7 DICOM IP IR SNR
 66 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. What is the difference between “window level” and “window width”? What is the difference between “density” and “brightness”? Define the term “noise. ”
66 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. What is the difference between “window level” and “window width”? What is the difference between “density” and “brightness”? Define the term “noise. ”
 67 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Patient Fellow workers Self
67 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Patient Fellow workers Self
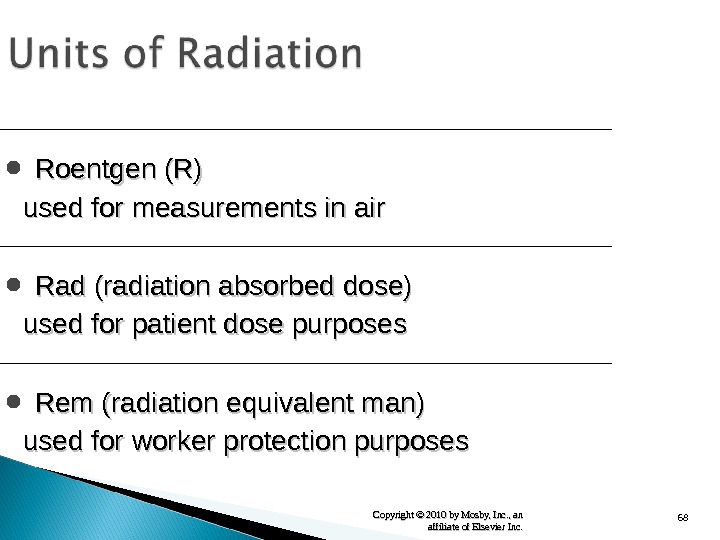
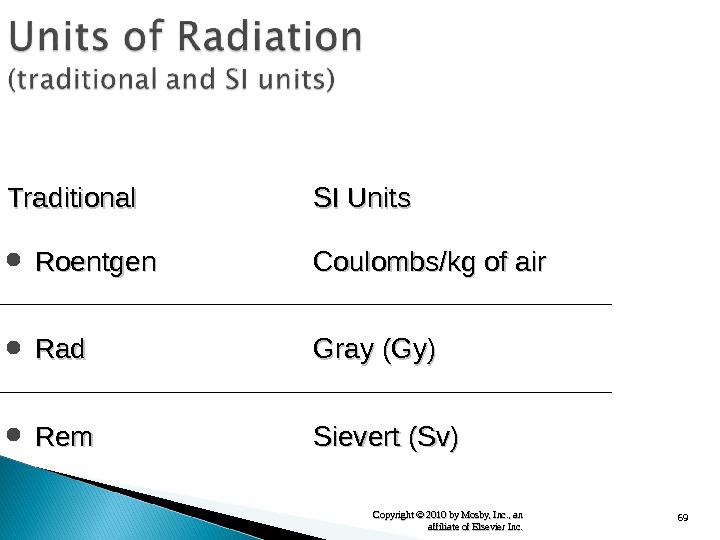
 68 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Roentgen (R) used for measurements in air Rad (radiation absorbed dose) used for patient dose purposes Rem (radiation equivalent man) used for worker protection purposes
68 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Roentgen (R) used for measurements in air Rad (radiation absorbed dose) used for patient dose purposes Rem (radiation equivalent man) used for worker protection purposes
 69 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Traditional SI Units Roentgen Coulombs/kg of air Rad Gray (Gy) Rem Sievert (Sv)
69 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Traditional SI Units Roentgen Coulombs/kg of air Rad Gray (Gy) Rem Sievert (Sv)
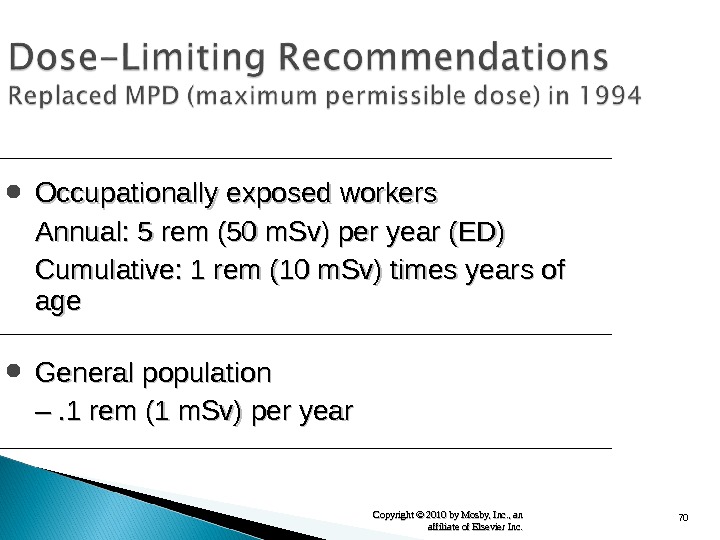
 70 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Occupationally exposed workers Annual: 5 rem (50 m. Sv) per year (ED) Cumulative: 1 rem (10 m. Sv) times years of ageage General population –– . 1 rem (1 m. Sv) per year
70 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Occupationally exposed workers Annual: 5 rem (50 m. Sv) per year (ED) Cumulative: 1 rem (10 m. Sv) times years of ageage General population –– . 1 rem (1 m. Sv) per year
 71 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. What is the dose limit for a pregnant technologist per month? What is it for the entire gestational period?
71 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. What is the dose limit for a pregnant technologist per month? What is it for the entire gestational period?
 72 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Film badge TLD (thermoluminesce nt dosimeter) OSL (optically stimulated luminescence) *Worn at waist or chest level or on collar during fluoroscopy * Consult RSO.
72 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Film badge TLD (thermoluminesce nt dosimeter) OSL (optically stimulated luminescence) *Worn at waist or chest level or on collar during fluoroscopy * Consult RSO.
 73 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Always wear a personnel monitor. 2. Radiology personnel should not restrain patients. 3. Sound radiographic exposure factors 4. Cardinal rules of radiation protection: – Time – Distance – Shielding Mobile fluoroscopy or C-arm
73 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Always wear a personnel monitor. 2. Radiology personnel should not restrain patients. 3. Sound radiographic exposure factors 4. Cardinal rules of radiation protection: – Time – Distance – Shielding Mobile fluoroscopy or C-arm
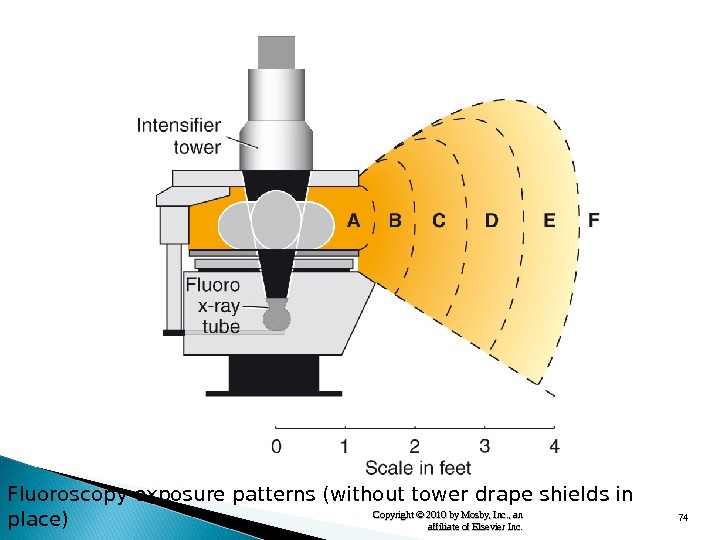
 74 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Fluoroscopy exposure patterns (without tower drape shields in place)
74 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Fluoroscopy exposure patterns (without tower drape shields in place)
 75 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Fluoroscopy exposure patterns (with tower drape shields in place)
75 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Fluoroscopy exposure patterns (with tower drape shields in place)
 76 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Bucky slot cover Lead drape . 5 mm lead apron Exposure limit: 10 R/min
76 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Bucky slot cover Lead drape . 5 mm lead apron Exposure limit: 10 R/min
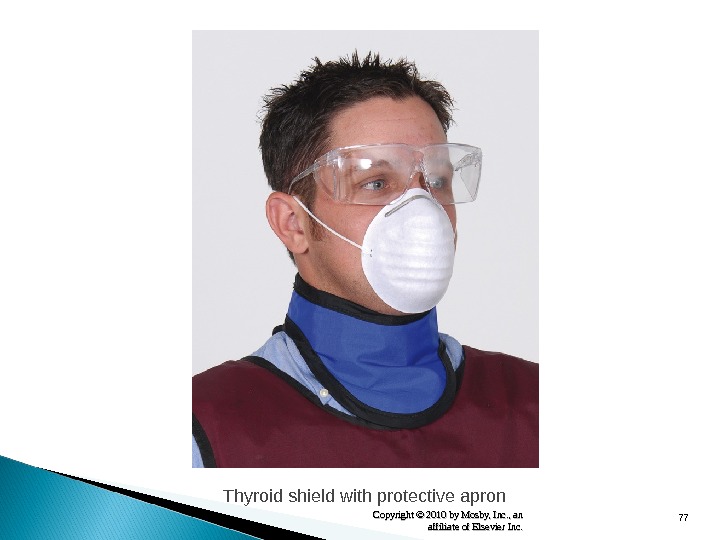
 77 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Thyroid shield with protective apron
77 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Thyroid shield with protective apron
 78 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs – Clear instructions – Positioning and exposure factors
78 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs – Clear instructions – Positioning and exposure factors
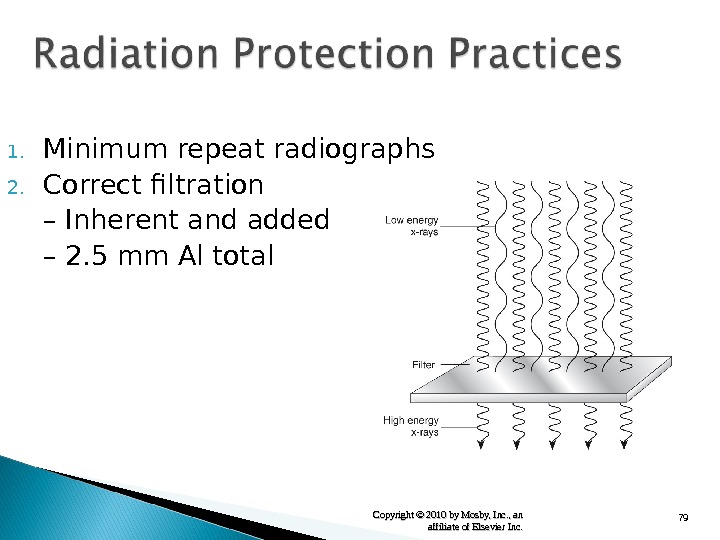
 79 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration – Inherent and added – 2. 5 mm Al total
79 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration – Inherent and added – 2. 5 mm Al total
 80 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Close four-sided collimation: One of the best ways of reducing patient exposure! (Remember divergence of x-ray beam. )
80 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Close four-sided collimation: One of the best ways of reducing patient exposure! (Remember divergence of x-ray beam. )
 81 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration 3. Accurate collimation Types of collimators – Manual type – Positive-beam limitation (PBL)
81 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration 3. Accurate collimation Types of collimators – Manual type – Positive-beam limitation (PBL)
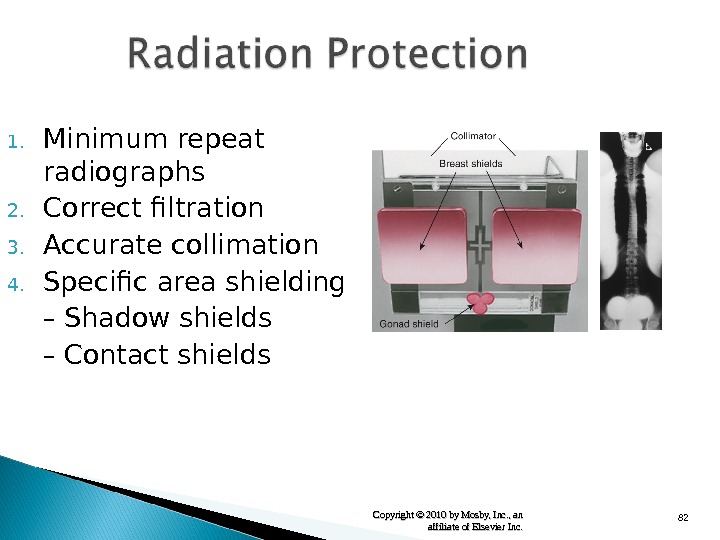
 82 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration 3. Accurate collimation 4. Specific area shielding – Shadow shields – Contact shields
82 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration 3. Accurate collimation 4. Specific area shielding – Shadow shields – Contact shields
 83 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Vinyl-covered lead shield
83 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Vinyl-covered lead shield
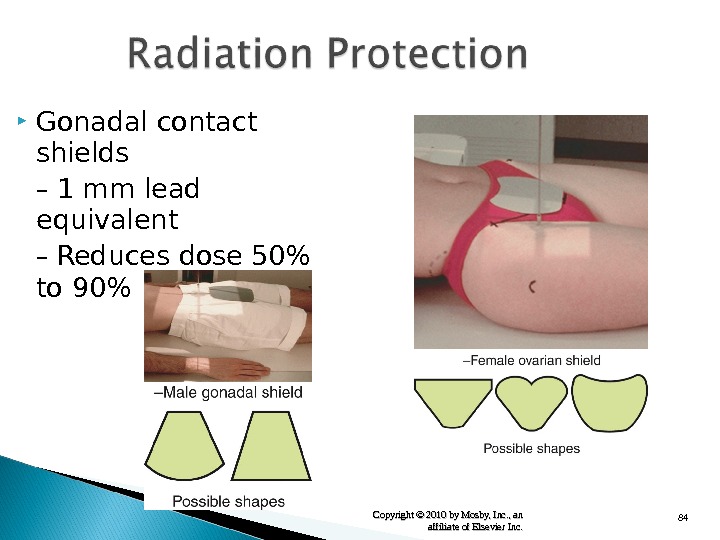
 84 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Gonadal contact shields – 1 mm lead equivalent – Reduces dose 50% to 90%
84 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Gonadal contact shields – 1 mm lead equivalent – Reduces dose 50% to 90%
 85 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration 3. Accurate collimation 4. Specific area shielding 5. Protection for pregnancies
85 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1. Minimum repeat radiographs 2. Correct filtration 3. Accurate collimation 4. Specific area shielding 5. Protection for pregnancies
 86 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me The SI unit equivalent for Rad is A. Coulombs/kg of air B. Gray C. Sievert D. Curie
86 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me The SI unit equivalent for Rad is A. Coulombs/kg of air B. Gray C. Sievert D. Curie
 87 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What is the annual dose limit for a technologist per year? A. 5 m. Sv B. 15 m. Sv C. 50 m. Sv D. 500 m. Sv
87 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What is the annual dose limit for a technologist per year? A. 5 m. Sv B. 15 m. Sv C. 50 m. Sv D. 500 m. Sv
 88 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What minimum lead thickness or equivalency must a protective apron possess when worn for a fluoroscopy procedure? A. . 5 mm Pb/Eq B. 1. 0 mm Pb/Eq C. 1. 5 mm Pb/Eq D. 2. 5 mm Pb/Eq
88 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What minimum lead thickness or equivalency must a protective apron possess when worn for a fluoroscopy procedure? A. . 5 mm Pb/Eq B. 1. 0 mm Pb/Eq C. 1. 5 mm Pb/Eq D. 2. 5 mm Pb/Eq
 89 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What is the most effective way to reduce patient dose? A. Use of high k. V B. Increase in added filtration in x-ray tube C. Use of gonadal shielding D. Close four-sided collimation
89 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. Quiz Me What is the most effective way to reduce patient dose? A. Use of high k. V B. Increase in added filtration in x-ray tube C. Use of gonadal shielding D. Close four-sided collimation
 90 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. — The End -Chapter
90 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. — The End -Chapter
 91 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. — The End -Chapter
91 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. — The End -Chapter
 92 Bontrager, K. L. , Lampignano, J. P. Textbook of Positioning and Related Anatomy, 7 th Edition, Copyright 2010 : Mosby/Elsevier Inc. , ISBN 978 -0 -323 -05410 -2 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
92 Bontrager, K. L. , Lampignano, J. P. Textbook of Positioning and Related Anatomy, 7 th Edition, Copyright 2010 : Mosby/Elsevier Inc. , ISBN 978 -0 -323 -05410 -2 Copyright © 2010 by Mosby, Inc. , an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.

