71b11e64053f74882d917f1debb79b5d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 Chapter 2: Environmental Laws, Economics, and Ethics SACCONE 2003
Chapter 2: Environmental Laws, Economics, and Ethics SACCONE 2003
 Resources • Resources are a part of the natural environment that is used to promote the welfare of people or other species. • Examples: H 2 O, air, soil, forests, minerals, & wildlife. SACCONE 2003
Resources • Resources are a part of the natural environment that is used to promote the welfare of people or other species. • Examples: H 2 O, air, soil, forests, minerals, & wildlife. SACCONE 2003
 Environmentalists • People that are concerned with the environment SACCONE 2003
Environmentalists • People that are concerned with the environment SACCONE 2003
 • Conservation: the careful management of natural resources. Conservationists feel that we can achieve a balance between progress and sustainability. SACCONE 2003
• Conservation: the careful management of natural resources. Conservationists feel that we can achieve a balance between progress and sustainability. SACCONE 2003
 Preservation • Maintaining things as they are…In a “pristine” state. • (Preservationists-Believe in nature first, humans second. ) SACCONE 2003
Preservation • Maintaining things as they are…In a “pristine” state. • (Preservationists-Believe in nature first, humans second. ) SACCONE 2003
 Resource use has rarely been conducted in a responsible manner- • Frontier Attitude: a desire to conquer and exploit nature as quickly as possible. SACCONE 2003
Resource use has rarely been conducted in a responsible manner- • Frontier Attitude: a desire to conquer and exploit nature as quickly as possible. SACCONE 2003
 Frontier Attitude SACCONE 2003
Frontier Attitude SACCONE 2003
 Wolves Among Us SACCONE 2003
Wolves Among Us SACCONE 2003
 Frontier Attitude SACCONE 2003
Frontier Attitude SACCONE 2003
 Henry David Thoreau • Walden Pond (Mass. ) • “To live deliberately” SACCONE 2003
Henry David Thoreau • Walden Pond (Mass. ) • “To live deliberately” SACCONE 2003
 Teddy Roosevelt • Set aside millions of acres • Created numerous national parks and monuments SACCONE 2003
Teddy Roosevelt • Set aside millions of acres • Created numerous national parks and monuments SACCONE 2003
 SACCONE 2003
SACCONE 2003
 John Muir • Founded the Sierra Club • Inspired “TR” • Instrumental in the creation of Yosemite and Sequoia National Parks. SACCONE 2003
John Muir • Founded the Sierra Club • Inspired “TR” • Instrumental in the creation of Yosemite and Sequoia National Parks. SACCONE 2003
 Environmentalists • Franklin Roosevelt (F. D. R): established the Civilian Conservation Corps During the great depression. Employed 175, 000 people who planted trees, made trails & roads in national parks, & built dams and other natural facilities. . SACCONE 2003
Environmentalists • Franklin Roosevelt (F. D. R): established the Civilian Conservation Corps During the great depression. Employed 175, 000 people who planted trees, made trails & roads in national parks, & built dams and other natural facilities. . SACCONE 2003
 Environmentalists • Aldo Leopold: Wildlife biologist and conservationist, who developed the concept of a “land ethic. ” Natural areas and wildlife should be managed and conserved. SACCONE 2003
Environmentalists • Aldo Leopold: Wildlife biologist and conservationist, who developed the concept of a “land ethic. ” Natural areas and wildlife should be managed and conserved. SACCONE 2003
 Environmentalists • Rachel Carson: Biologist that published Silent Spring, a book that heightened public awareness about the hazards of DDT & other pesticides to wildlife, ecosystems, and humans. SACCONE 2003
Environmentalists • Rachel Carson: Biologist that published Silent Spring, a book that heightened public awareness about the hazards of DDT & other pesticides to wildlife, ecosystems, and humans. SACCONE 2003
 Environmentalists • Gaylord Nelson: Former Wisconsin senator that organized the first official Earth day (Spring 1970), when approx. 20 million people celebrated environmentalism. By 1990, it is estimated that 200 million globally celebrated environmental awareness. • “Think globally, act locally” SACCONE 2003
Environmentalists • Gaylord Nelson: Former Wisconsin senator that organized the first official Earth day (Spring 1970), when approx. 20 million people celebrated environmentalism. By 1990, it is estimated that 200 million globally celebrated environmental awareness. • “Think globally, act locally” SACCONE 2003
 Following the Santa Barbara Oil Spill of 1969, and the 1970 Earth Day…The EPA was formed. SACCONE 2003
Following the Santa Barbara Oil Spill of 1969, and the 1970 Earth Day…The EPA was formed. SACCONE 2003
 • Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): was formed in 1970 in response to Earth day support & the 1969 Santa Barbara Oil Spill. • National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) was signed into law. This law requires Environmental Impact Statements (E. I. S’s) for federally funded construction projects. SACCONE 2003
• Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): was formed in 1970 in response to Earth day support & the 1969 Santa Barbara Oil Spill. • National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) was signed into law. This law requires Environmental Impact Statements (E. I. S’s) for federally funded construction projects. SACCONE 2003
 Environmental Impact Statements E. I. S. ’s require 1) The nature of the proposal and the reason for it. 2) The environmental impact of the proposal (short and long-term) and adverse effects. 3) Alternatives to the proposed course of action that will lessen the adverse effects. (Mitigate the impact of the project. ) Although not all environmental laws are successful, they do help to conserve our resources, and protect our citizens. SACCONE 2003
Environmental Impact Statements E. I. S. ’s require 1) The nature of the proposal and the reason for it. 2) The environmental impact of the proposal (short and long-term) and adverse effects. 3) Alternatives to the proposed course of action that will lessen the adverse effects. (Mitigate the impact of the project. ) Although not all environmental laws are successful, they do help to conserve our resources, and protect our citizens. SACCONE 2003
 Environmental legislation has been effective. • 11 National Parks • Soil erosion reduced 60% • Many endangered species are better off. • Pb levels in the air have dropped • 43% decline in air and water pollution from INDUSTRIAL sources. SACCONE 2003
Environmental legislation has been effective. • 11 National Parks • Soil erosion reduced 60% • Many endangered species are better off. • Pb levels in the air have dropped • 43% decline in air and water pollution from INDUSTRIAL sources. SACCONE 2003
 Unfunded Mandates • Are when the federal gov’t requires states to do certain things but won’t pay for them. • Unfunded Mandate Review Act of 1995. (Requires the federal government to pay for future programs that it requires states and localities to uphold. (Doesn’t cover clean air & water legislation or other previous laws. ) SACCONE 2003
Unfunded Mandates • Are when the federal gov’t requires states to do certain things but won’t pay for them. • Unfunded Mandate Review Act of 1995. (Requires the federal government to pay for future programs that it requires states and localities to uphold. (Doesn’t cover clean air & water legislation or other previous laws. ) SACCONE 2003
 Economics • The study of how people use their limited resources to try to satisfy their unlimited wants. • There always consequences associated with our actions. • Law of “supply and demand” Many products have External costs associated with them- (When people are harmed from the creation or purchase of a product. ) SACCONE 2003
Economics • The study of how people use their limited resources to try to satisfy their unlimited wants. • There always consequences associated with our actions. • Law of “supply and demand” Many products have External costs associated with them- (When people are harmed from the creation or purchase of a product. ) SACCONE 2003
 Economics • Gross Domestic Product (GDP): estimates of environmental damage should be subtracted from GDP. • Net Domestic Product (NDP): a measure of the net production of the economy after a deduction for used-up capital. SACCONE 2003
Economics • Gross Domestic Product (GDP): estimates of environmental damage should be subtracted from GDP. • Net Domestic Product (NDP): a measure of the net production of the economy after a deduction for used-up capital. SACCONE 2003
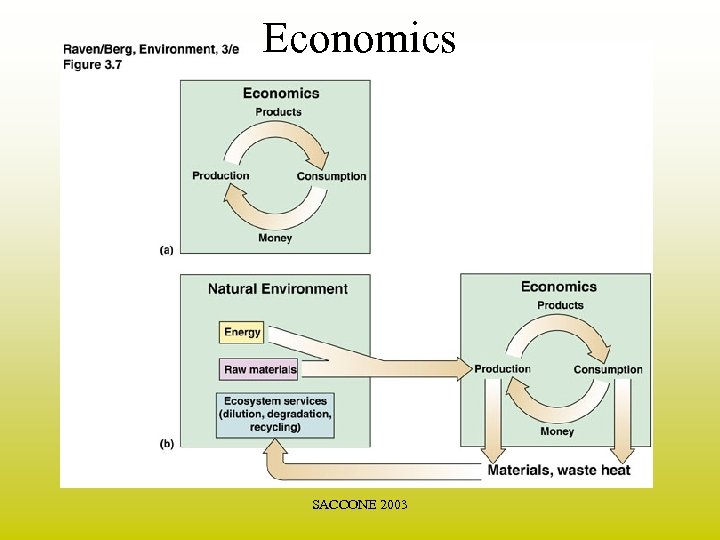 Economics SACCONE 2003
Economics SACCONE 2003
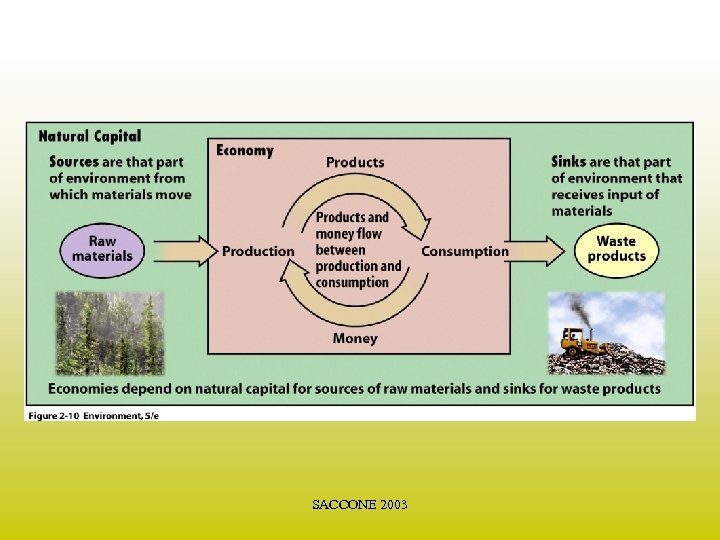 SACCONE 2003
SACCONE 2003
 How much pollution is acceptable? (Do we want wilderness or a sewer? ) • Marginal Cost: the additional cost of one more unit of something. (i. e. - The “trade-off” between more products vs. a better environment. ) • Marginal Cost of Pollution: the added cost, (in terms of damage), incurred by all present and future members of a society, for additional units of pollution. SACCONE 2003
How much pollution is acceptable? (Do we want wilderness or a sewer? ) • Marginal Cost: the additional cost of one more unit of something. (i. e. - The “trade-off” between more products vs. a better environment. ) • Marginal Cost of Pollution: the added cost, (in terms of damage), incurred by all present and future members of a society, for additional units of pollution. SACCONE 2003
 Economics continued…. • Marginal Cost of Pollution Abatement: the added cost (for all present and future members of society) of reducing a given type of pollution by one unit. • Optimum Amount of Pollution: where the marginal cost of pollution = marginal cost of abatement. SACCONE 2003
Economics continued…. • Marginal Cost of Pollution Abatement: the added cost (for all present and future members of society) of reducing a given type of pollution by one unit. • Optimum Amount of Pollution: where the marginal cost of pollution = marginal cost of abatement. SACCONE 2003
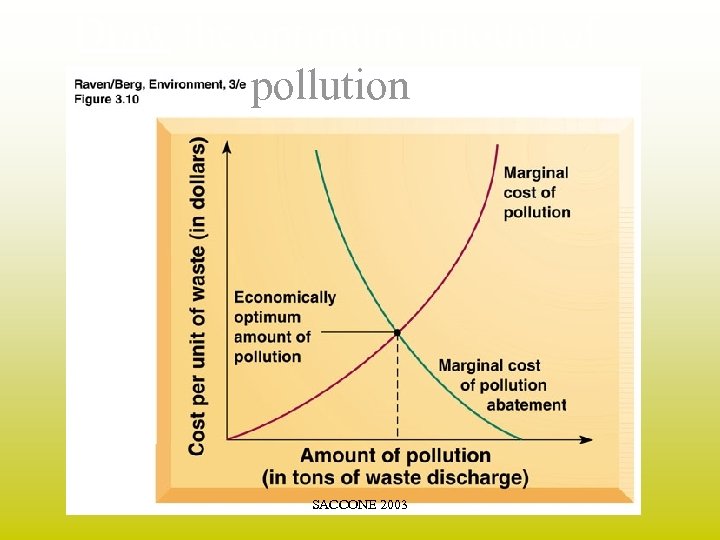 Draw the optimum amount of pollution. SACCONE 2003
Draw the optimum amount of pollution. SACCONE 2003
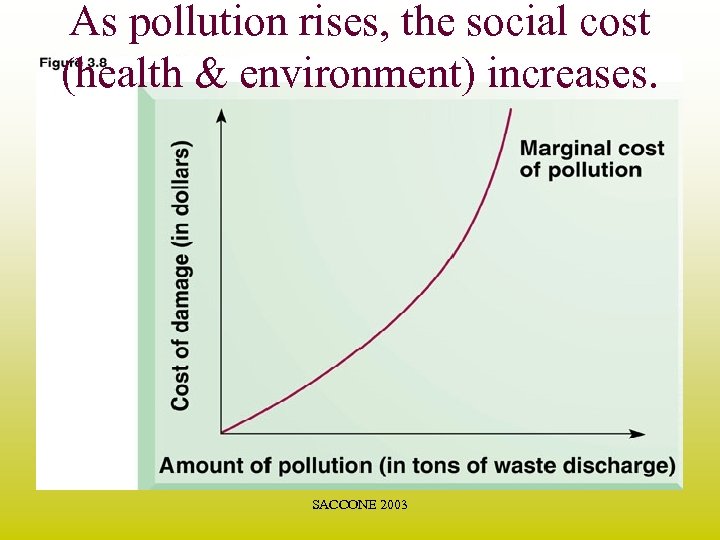 As pollution rises, the social cost (health & environment) increases. SACCONE 2003
As pollution rises, the social cost (health & environment) increases. SACCONE 2003
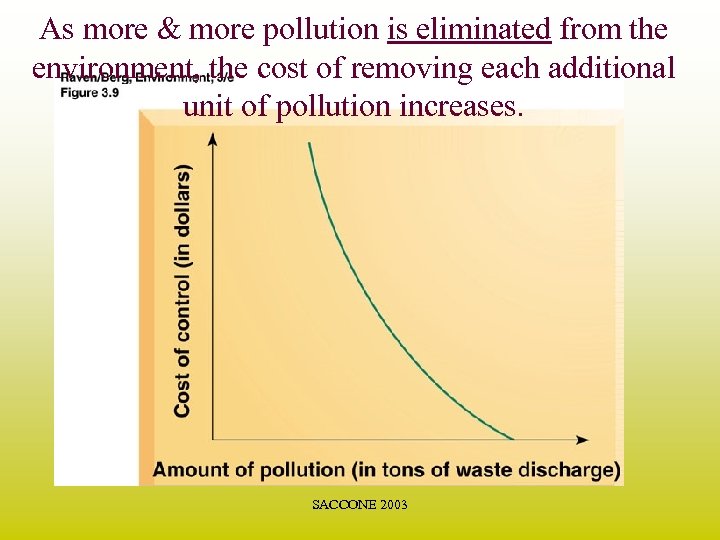 As more & more pollution is eliminated from the environment, the cost of removing each additional unit of pollution increases. SACCONE 2003
As more & more pollution is eliminated from the environment, the cost of removing each additional unit of pollution increases. SACCONE 2003
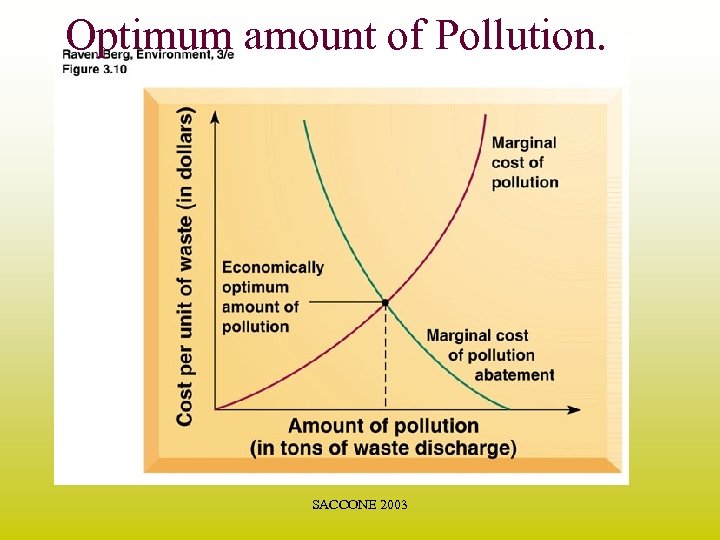 Optimum amount of Pollution. SACCONE 2003
Optimum amount of Pollution. SACCONE 2003
 Economic Solutions • Command Control Regulation Laws that set limits on pollution levels. • Incentive-based Regulation Industry is given incentives to reduce/eliminate pollution. Involves a market-based approach to pollution control. SACCONE 2003
Economic Solutions • Command Control Regulation Laws that set limits on pollution levels. • Incentive-based Regulation Industry is given incentives to reduce/eliminate pollution. Involves a market-based approach to pollution control. SACCONE 2003
 Economics Emission Charge: This is a “green tax” imposed on pollution. This includes environmental costs due to such things as: 1)cutting down a forest 2) driving a car 3) polluting streams SACCONE 2003
Economics Emission Charge: This is a “green tax” imposed on pollution. This includes environmental costs due to such things as: 1)cutting down a forest 2) driving a car 3) polluting streams SACCONE 2003
 Economic Strategies for Pollution Control Waste-discharge Permits: Allow holders to emit a specified amount of a given pollutant. Ex: Sulfur Dioxide SO 2 Emission Reduction Credits (ERC’s): a general category of permits that limit the amount of pollution. The goal is to reach the optimum amount of pollution. So far they have been very effective with SO 2. SACCONE 2003
Economic Strategies for Pollution Control Waste-discharge Permits: Allow holders to emit a specified amount of a given pollutant. Ex: Sulfur Dioxide SO 2 Emission Reduction Credits (ERC’s): a general category of permits that limit the amount of pollution. The goal is to reach the optimum amount of pollution. So far they have been very effective with SO 2. SACCONE 2003
 APES Debate Save an logger owl ban kill an owl. logging. SACCONE 2003
APES Debate Save an logger owl ban kill an owl. logging. SACCONE 2003
 Case in Point: Support for Old Growth SACCONE 2003
Case in Point: Support for Old Growth SACCONE 2003
 Environmental Battles Lost: Salvage Logging 1) 1995 Bill that allowed loggers to cut down dead & weakened trees as well as “associated trees” (those in danger of catching a disease or those in the way). SACCONE 2003
Environmental Battles Lost: Salvage Logging 1) 1995 Bill that allowed loggers to cut down dead & weakened trees as well as “associated trees” (those in danger of catching a disease or those in the way). SACCONE 2003
 Environmental Battles Lost: Salvage Logging 2) Law expired in 1996 but allowed loggers access to “off limits” forests despite the Northwest Forest Plan. SACCONE 2003
Environmental Battles Lost: Salvage Logging 2) Law expired in 1996 but allowed loggers access to “off limits” forests despite the Northwest Forest Plan. SACCONE 2003
 Environmental Battles Lost: Salvage Logging 3) Timber companies were exempt from upholding provisions of the Endangered Species Act & the Clean Air Act. SACCONE 2003
Environmental Battles Lost: Salvage Logging 3) Timber companies were exempt from upholding provisions of the Endangered Species Act & the Clean Air Act. SACCONE 2003
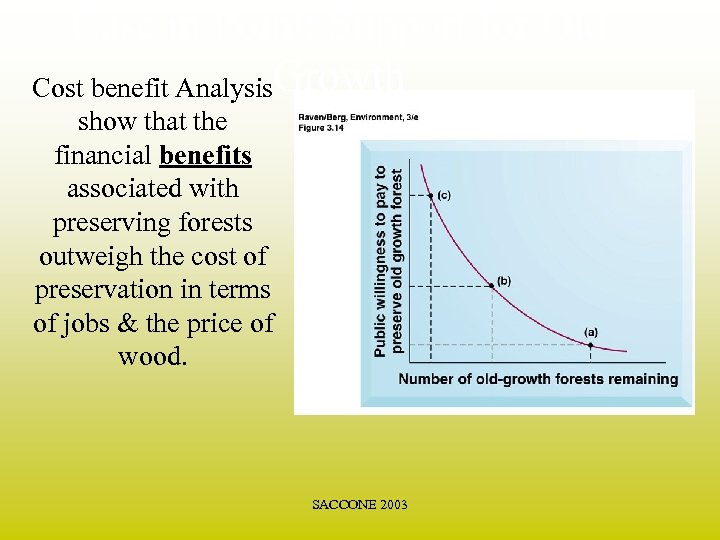 Case in Point: Support for Old Cost benefit Analysis. Growth show that the financial benefits associated with preserving forests outweigh the cost of preservation in terms of jobs & the price of wood. SACCONE 2003
Case in Point: Support for Old Cost benefit Analysis. Growth show that the financial benefits associated with preserving forests outweigh the cost of preservation in terms of jobs & the price of wood. SACCONE 2003
 Ethics, Values, &Worldviews Ethics: the branch of philosophy that deals with human values. (right or wrong) Values are principles that an individual or society considers important or worthwhile. Environmental Ethics: is a field of applied ethics that considers the moral basis of environmental responsibility & how far this responsibility extends. SACCONE 2003
Ethics, Values, &Worldviews Ethics: the branch of philosophy that deals with human values. (right or wrong) Values are principles that an individual or society considers important or worthwhile. Environmental Ethics: is a field of applied ethics that considers the moral basis of environmental responsibility & how far this responsibility extends. SACCONE 2003
 Worldviews: Two Extremes Western Worldview: human centered & utilitarian. (Frontier attitude that exploits nature). Deep Ecology: Based on the work of Arne Naess, Bill Devall, & George Sessions. This view stresses harmony with nature, respect for life, & equal worth among species. SACCONE 2003
Worldviews: Two Extremes Western Worldview: human centered & utilitarian. (Frontier attitude that exploits nature). Deep Ecology: Based on the work of Arne Naess, Bill Devall, & George Sessions. This view stresses harmony with nature, respect for life, & equal worth among species. SACCONE 2003
 Pollution in Central & Eastern Europe Late 1980’s Fall of Soviet Union & Communist Eastern European Countries. Pollution in Communist controlled Europe went unchecked. Production of goods was not for profit but environmental concerns never played a role in decision making. SACCONE 2003
Pollution in Central & Eastern Europe Late 1980’s Fall of Soviet Union & Communist Eastern European Countries. Pollution in Communist controlled Europe went unchecked. Production of goods was not for profit but environmental concerns never played a role in decision making. SACCONE 2003
 Pollution in Central & Eastern Europe The Future 1) $300 billion to clean up damage in E. Germany alone. 2) Hungary, Poland, & Czech republic are moving toward a market economy ($ available for clean up). 3) Bulgaria, Romania, & Russia are doing less to clean up the environment. SACCONE 2003
Pollution in Central & Eastern Europe The Future 1) $300 billion to clean up damage in E. Germany alone. 2) Hungary, Poland, & Czech republic are moving toward a market economy ($ available for clean up). 3) Bulgaria, Romania, & Russia are doing less to clean up the environment. SACCONE 2003
 Reasons for pollution in Central & Eastern Europe 1) No resource conservation 2) Repressive government had no accountability SACCONE 2003
Reasons for pollution in Central & Eastern Europe 1) No resource conservation 2) Repressive government had no accountability SACCONE 2003
 “How can you buy the land, or sell the sky? This idea is strange to us. If we do not own the freshness of the air & the sparkle of of the water, how can you buy them? This we know- the Earth does not belong to man, man belongs to the earth. All things are connected like the blood which unites one family. Whatever befalls the Earth befalls the sons of the Earth. Man does not weave the web of life, he is merely a strand in it. Whatever he does to the web, he does to himself. ” -Chief Sealth (Seattle) 1854 SACCONE 2003
“How can you buy the land, or sell the sky? This idea is strange to us. If we do not own the freshness of the air & the sparkle of of the water, how can you buy them? This we know- the Earth does not belong to man, man belongs to the earth. All things are connected like the blood which unites one family. Whatever befalls the Earth befalls the sons of the Earth. Man does not weave the web of life, he is merely a strand in it. Whatever he does to the web, he does to himself. ” -Chief Sealth (Seattle) 1854 SACCONE 2003
 The End!!! SACCONE 2003
The End!!! SACCONE 2003


