61c291759584cf0804e5b72bdbd040c1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 Chapter 2 Computer Numerical Control System • • § 2 -1 § 2 -2 § 2 -3 § 2 -4 CNC machine tool control basis interpolation principle tool radius compensation PLC
Chapter 2 Computer Numerical Control System • • § 2 -1 § 2 -2 § 2 -3 § 2 -4 CNC machine tool control basis interpolation principle tool radius compensation PLC
 • • • § 2 -1 CNC machine tool control basis Development of numerical control system The History of CNC System The development trend of numerical control system • Introduction to Typical Numerical Control System • The working principle of CNC system • The composition of the CNC device • • Hardware software Advantages of CNC devices The function of the CNC device
• • • § 2 -1 CNC machine tool control basis Development of numerical control system The History of CNC System The development trend of numerical control system • Introduction to Typical Numerical Control System • The working principle of CNC system • The composition of the CNC device • • Hardware software Advantages of CNC devices The function of the CNC device
 History of CNC System Development • Since the 20 th century, 50 years the world's first CNC machine tool has been introduced for more than 50 years. Development process of CNC system has two stages and six generations (common sense). The first stage is hardware NC (NC): • The first generation of 1952 Electrical tubes • 2 nd generation 1959 transistor (separation element) • 3 rd generation 1965 Small scale integrated circuit The second stage is the software CNC (CNC): • Fourth generation 1970 small computer, small and medium scale integrated circuit • 5 th generation 1974 microprocessor, large scale integrated circuit.
History of CNC System Development • Since the 20 th century, 50 years the world's first CNC machine tool has been introduced for more than 50 years. Development process of CNC system has two stages and six generations (common sense). The first stage is hardware NC (NC): • The first generation of 1952 Electrical tubes • 2 nd generation 1959 transistor (separation element) • 3 rd generation 1965 Small scale integrated circuit The second stage is the software CNC (CNC): • Fourth generation 1970 small computer, small and medium scale integrated circuit • 5 th generation 1974 microprocessor, large scale integrated circuit.
 Fig 2 -1 Electrical tubes SOT 26 TD 5 Fig 2 -2 transistor physical map TD 92
Fig 2 -1 Electrical tubes SOT 26 TD 5 Fig 2 -2 transistor physical map TD 92
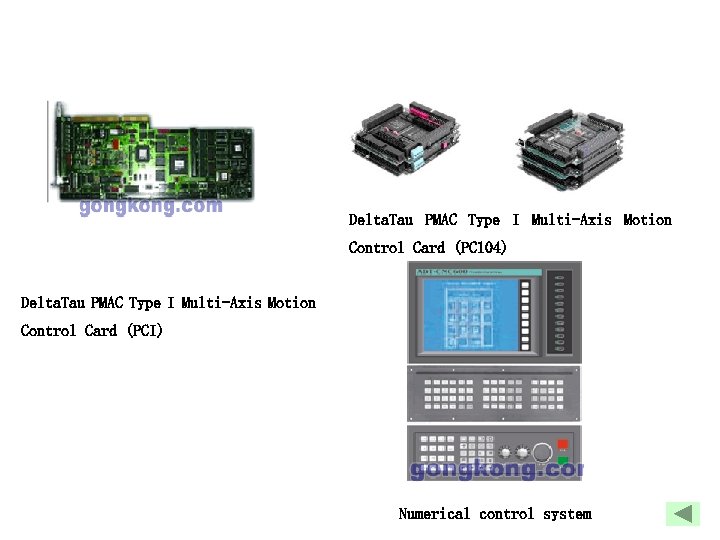 Delta. Tau PMAC Type I Multi-Axis Motion Control Card (PC 104) Delta. Tau PMAC Type I Multi-Axis Motion Control Card (PCI) Numerical control system
Delta. Tau PMAC Type I Multi-Axis Motion Control Card (PC 104) Delta. Tau PMAC Type I Multi-Axis Motion Control Card (PCI) Numerical control system
 2. the development trend of numerical control system • • High speed, high precision High reliability Openness Software numerical control system Intelligent Multi-functional Interactive network
2. the development trend of numerical control system • • High speed, high precision High reliability Openness Software numerical control system Intelligent Multi-functional Interactive network
 The development trend of CNC machine tools Since the nineties of the twentieth century, with the rapid development of international computer technology, numerical control technology continues to use computer, control theory and other fields of the latest technological achievements, so that in several directions. l Running high speed l Processing high precision l Functional compound l Intelligent control l System open l Interactive network l Driven parallelization l Control system reliability
The development trend of CNC machine tools Since the nineties of the twentieth century, with the rapid development of international computer technology, numerical control technology continues to use computer, control theory and other fields of the latest technological achievements, so that in several directions. l Running high speed l Processing high precision l Functional compound l Intelligent control l System open l Interactive network l Driven parallelization l Control system reliability
 – Running high-speed, high-precision processing Speed and precision are two important indicators of CNC equipment, CNC technology is also the eternal pursuit of the goal. Because it is directly related to the processing efficiency and product quality. A new generation of CNC equipment in the operation of high-speed, high precision processing, and so have a higher demand.
– Running high-speed, high-precision processing Speed and precision are two important indicators of CNC equipment, CNC technology is also the eternal pursuit of the goal. Because it is directly related to the processing efficiency and product quality. A new generation of CNC equipment in the operation of high-speed, high precision processing, and so have a higher demand.
 – Running high speed – So that the feed rate, spindle speed, tool exchange speed, tray exchange speed to achieve high-speed, and has a high increase (minus) rate. – High feed rate: – At a resolution of 1 μm, Fmax = 240 m / min. In the Fmax can be obtained under the complex surface of the precise processing; – Fmax = 60 m / min when the block length is 1 mm, and has an acceleration / deceleration rate of 1. 5 g;
– Running high speed – So that the feed rate, spindle speed, tool exchange speed, tray exchange speed to achieve high-speed, and has a high increase (minus) rate. – High feed rate: – At a resolution of 1 μm, Fmax = 240 m / min. In the Fmax can be obtained under the complex surface of the precise processing; – Fmax = 60 m / min when the block length is 1 mm, and has an acceleration / deceleration rate of 1. 5 g;
 • Spindle speed: the use of spindle (built-in spindle motor), that is, the spindle motor rotor shaft is the spindle components. • Spindle maximum speed of 200000 r / min. • Spindle speed of the maximum increase (minus) speed of 2 -3 g. • Tool change speed • 0. 6 seconds (knife to knife) • 2. 8 seconds (cutting to cutting) • Workbench (pallet) exchange speed of 4. 3 seconds.
• Spindle speed: the use of spindle (built-in spindle motor), that is, the spindle motor rotor shaft is the spindle components. • Spindle maximum speed of 200000 r / min. • Spindle speed of the maximum increase (minus) speed of 2 -3 g. • Tool change speed • 0. 6 seconds (knife to knife) • 2. 8 seconds (cutting to cutting) • Workbench (pallet) exchange speed of 4. 3 seconds.
 –Processing high precision – Improve the manufacture and assembly of mechanical equipment accuracy; improve the control accuracy of CNC system; the use of error compensation technology. Improve CNC system control accuracy: – Using high-speed interpolation technology to achieve a small block continuous feed, the CNC control unit refinement, – The use of high-resolution position detection device to improve the accuracy of position detection (Japan 106 servo motor has AC been equipped with pulse / turn of the built-in position detector, the position detection accuracy can reach 0. 01 mm / pulse); – Position servo system uses feedforward control and nonlinear control and other methods.
–Processing high precision – Improve the manufacture and assembly of mechanical equipment accuracy; improve the control accuracy of CNC system; the use of error compensation technology. Improve CNC system control accuracy: – Using high-speed interpolation technology to achieve a small block continuous feed, the CNC control unit refinement, – The use of high-resolution position detection device to improve the accuracy of position detection (Japan 106 servo motor has AC been equipped with pulse / turn of the built-in position detector, the position detection accuracy can reach 0. 01 mm / pulse); – Position servo system uses feedforward control and nonlinear control and other methods.
 • Using error compensation techniques: • Using reverse gap compensation, screw pitch error compensation and tool error compensation technology; • Equipment of thermal deformation error compensation and spatial error of the comprehensive compensation technology. The results show that the application of integrated error compensation technology can reduce the machining error by 60% ~ 80%. Mitsui Seiki's Jidic. H 5 D ultra-precision horizontal machining center positioning accuracy of ± 0. 1 m.
• Using error compensation techniques: • Using reverse gap compensation, screw pitch error compensation and tool error compensation technology; • Equipment of thermal deformation error compensation and spatial error of the comprehensive compensation technology. The results show that the application of integrated error compensation technology can reduce the machining error by 60% ~ 80%. Mitsui Seiki's Jidic. H 5 D ultra-precision horizontal machining center positioning accuracy of ± 0. 1 m.
 –Functional compound Composite refers to a device can achieve a variety of means of processing methods. Boring and milling drilling - Machining center (ATC), five - sided machining center (ATC, spindle vertical conversion); Turning and milling complex - turning center (ATC, power head); Milling and Boring Drill Composite - Composite Machining Center (ATC, Automatic Loading and Unloading Tool Holder); Milling and Boring Drilling Compound - Composite Machining Center (ATC, Power Grinding Head); Replaceable spindle box CNC machine tools combined processing center;
–Functional compound Composite refers to a device can achieve a variety of means of processing methods. Boring and milling drilling - Machining center (ATC), five - sided machining center (ATC, spindle vertical conversion); Turning and milling complex - turning center (ATC, power head); Milling and Boring Drill Composite - Composite Machining Center (ATC, Automatic Loading and Unloading Tool Holder); Milling and Boring Drilling Compound - Composite Machining Center (ATC, Power Grinding Head); Replaceable spindle box CNC machine tools combined processing center;
 – Intelligent control –With the continuous development of artificial intelligence technology, and to meet the manufacturing industry flexibility, manufacturing automation development needs, numerical control technology intelligent degree of continuous improvement, embodied in the following aspects:
– Intelligent control –With the continuous development of artificial intelligence technology, and to meet the manufacturing industry flexibility, manufacturing automation development needs, numerical control technology intelligent degree of continuous improvement, embodied in the following aspects:
 • Adaptive Control Technology for Processing Processes • By monitoring the machining force, cutting force, spindle and feed motor power, current, voltage and other information, the use of traditional or modern algorithm to identify the tool to identify the force, wear and damage, machine tool processing (Spindle speed, feed rate) and machining instructions, so that the equipment is in the best running state, in order to improve the machining accuracy, reduce the workpiece surface roughness and equipment operation safety.
• Adaptive Control Technology for Processing Processes • By monitoring the machining force, cutting force, spindle and feed motor power, current, voltage and other information, the use of traditional or modern algorithm to identify the tool to identify the force, wear and damage, machine tool processing (Spindle speed, feed rate) and machining instructions, so that the equipment is in the best running state, in order to improve the machining accuracy, reduce the workpiece surface roughness and equipment operation safety.
 – Mitsubishi Electric's "Miracle Fuzzy" for CNC EDM machine based on fuzzy logic adaptive controller, can automatically control and optimize the processing parameters; – Japan Makino in the spark NC system Makino_Mce 20, with the expert system instead of people for processing process monitoring. – Israel's external force adaptive controller – Programmable Power Adaptive Control of Mandelli Corporation in Italy. – Tsinghua University and other colleges of adaptive control technology research has been achieved. Commercial development is underway.
– Mitsubishi Electric's "Miracle Fuzzy" for CNC EDM machine based on fuzzy logic adaptive controller, can automatically control and optimize the processing parameters; – Japan Makino in the spark NC system Makino_Mce 20, with the expert system instead of people for processing process monitoring. – Israel's external force adaptive controller – Programmable Power Adaptive Control of Mandelli Corporation in Italy. – Tsinghua University and other colleges of adaptive control technology research has been achieved. Commercial development is underway.
 • Intelligent Optimization and Selection of Processing Parameters The experience of process experts or craftsmen, the general and special rules of part processing, the use of modern intelligent methods, based on the expert system or modelbased "intelligent optimization and selection of processing parameters", use it to obtain optimized processing parameters to achieve Improve the programming efficiency and processing technology level, shorten the purpose of production preparation time. The use of optimized processing parameters of the preparation process, the processing system can always be in a more reasonable and more economical working conditions.
• Intelligent Optimization and Selection of Processing Parameters The experience of process experts or craftsmen, the general and special rules of part processing, the use of modern intelligent methods, based on the expert system or modelbased "intelligent optimization and selection of processing parameters", use it to obtain optimized processing parameters to achieve Improve the programming efficiency and processing technology level, shorten the purpose of production preparation time. The use of optimized processing parameters of the preparation process, the processing system can always be in a more reasonable and more economical working conditions.
 – Has developed a self-learning function of the neural network EDM expert system. – Japan's Okuma company's 7000 series CNC system with artificial intelligence automatic programming function. – Tsinghua University in the processing parameters of intelligent optimization and selection and CAPP research has also made some achievements.
– Has developed a self-learning function of the neural network EDM expert system. – Japan's Okuma company's 7000 series CNC system with artificial intelligence automatic programming function. – Tsinghua University in the processing parameters of intelligent optimization and selection and CAPP research has also made some achievements.
 • Intelligent Fault Diagnosis and Self - repair Technology • Intelligent fault diagnosis technology: According to the existing fault information, the application of modern intelligent methods (AI, ES, ANN, etc. ), to achieve rapid and accurate fault positioning technology. • Intelligent fault self-repair technology: refers to the fault can be determined according to the cause and location of the fault to automatically troubleshoot or guide the troubleshooting of the technology. Intelligent self-repair technology set fault self-diagnosis, fault self-exclusion, self-recovery, self-regulation in one, and throughout the processing process throughout the life cycle. • Intelligent fault diagnosis technology in some Japan, the United States produced by the NC system has been applied, are basically application expert system to achieve.
• Intelligent Fault Diagnosis and Self - repair Technology • Intelligent fault diagnosis technology: According to the existing fault information, the application of modern intelligent methods (AI, ES, ANN, etc. ), to achieve rapid and accurate fault positioning technology. • Intelligent fault self-repair technology: refers to the fault can be determined according to the cause and location of the fault to automatically troubleshoot or guide the troubleshooting of the technology. Intelligent self-repair technology set fault self-diagnosis, fault self-exclusion, self-recovery, self-regulation in one, and throughout the processing process throughout the life cycle. • Intelligent fault diagnosis technology in some Japan, the United States produced by the NC system has been applied, are basically application expert system to achieve.
 • Intelligent AC servo drive • Has begun to study can automatically identify the load, and automatically adjust the parameters of the intelligent servo system, including intelligent spindle AC drive and intelligent feed servo device. This drive can automatically identify the motor and the load moment of inertia, and automatically control the system parameters to optimize and adjust the drive system to get the best run.
• Intelligent AC servo drive • Has begun to study can automatically identify the load, and automatically adjust the parameters of the intelligent servo system, including intelligent spindle AC drive and intelligent feed servo device. This drive can automatically identify the motor and the load moment of inertia, and automatically control the system parameters to optimize and adjust the drive system to get the best run.
 • Intelligent 4 M CNC system • In the manufacturing process, processing, testing integration is an effective way to achieve rapid manufacturing, rapid detection and rapid response, the measurement (Measurement), modeling (Modeling), manufacturing (Manufacturing), machine operation (Manipulator) four (ie 4 M) in a system, to achieve information sharing, to promote measurement, modeling, processing, clamping, operation of the integration of 4 M intelligent system.
• Intelligent 4 M CNC system • In the manufacturing process, processing, testing integration is an effective way to achieve rapid manufacturing, rapid detection and rapid response, the measurement (Measurement), modeling (Modeling), manufacturing (Manufacturing), machine operation (Manipulator) four (ie 4 M) in a system, to achieve information sharing, to promote measurement, modeling, processing, clamping, operation of the integration of 4 M intelligent system.
 –System open –Definition (IEEE) System open: a system that can implement system functions on different work platforms and interoperate with other system applications. –Open CNC system features: –System components (software and hardware) have the characteristics of Standardization and Diversification and Interchangeability –Allowing the system to increase or decrease the structure of the system to achieve the system "building blocks" of the integration. Constructs should be portable and transparent;
–System open –Definition (IEEE) System open: a system that can implement system functions on different work platforms and interoperate with other system applications. –Open CNC system features: –System components (software and hardware) have the characteristics of Standardization and Diversification and Interchangeability –Allowing the system to increase or decrease the structure of the system to achieve the system "building blocks" of the integration. Constructs should be portable and transparent;
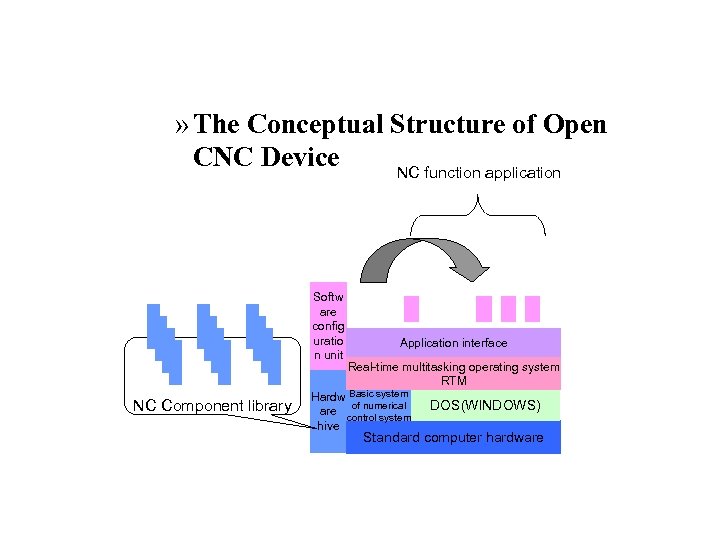 » The Conceptual Structure of Open CNC Device NC function application Softw are config uratio n unit NC Component library Application interface Real-time multitasking operating system RTM Hardw Basic system of numerical are control system hive DOS(WINDOWS) Standard computer hardware
» The Conceptual Structure of Open CNC Device NC function application Softw are config uratio n unit NC Component library Application interface Real-time multitasking operating system RTM Hardw Basic system of numerical are control system hive DOS(WINDOWS) Standard computer hardware
 • Open architecture Advantages of CNC • Open to the future technology: As the hardware and software interfaces follow a recognized standard protocol, only a small amount of redesign and adjustment, a new generation of common hardware and software resources may be adopted by existing systems, absorption and compatibility, which means that the system The development costs will be greatly reduced and the system performance and reliability will continue to improve and in a long life cycle; • Standardized man-machine interface: standardized programming language, user-friendly, reduced and operational efficiency directly related to labor consumption;
• Open architecture Advantages of CNC • Open to the future technology: As the hardware and software interfaces follow a recognized standard protocol, only a small amount of redesign and adjustment, a new generation of common hardware and software resources may be adopted by existing systems, absorption and compatibility, which means that the system The development costs will be greatly reduced and the system performance and reliability will continue to improve and in a long life cycle; • Standardized man-machine interface: standardized programming language, user-friendly, reduced and operational efficiency directly related to labor consumption;
 – Open to the user special requirements: update the product, expand the ability to provide a variety of combinations of hardware and software products to choose to meet the specific application requirements, to provide users with a method, from the low-level controller, and gradually increased until the required Performance so far. In addition the user's own technical know-how can be easily integrated to create their own brand-name products; – Can reduce product variety, easy to mass production, improve reliability and reduce costs, enhance market supply capacity and competitiveness.
– Open to the user special requirements: update the product, expand the ability to provide a variety of combinations of hardware and software products to choose to meet the specific application requirements, to provide users with a method, from the low-level controller, and gradually increased until the required Performance so far. In addition the user's own technical know-how can be easily integrated to create their own brand-name products; – Can reduce product variety, easy to mass production, improve reliability and reduce costs, enhance market supply capacity and competitiveness.
 • Research Progress of Open CNC System at Home and Abroad • US: NGC (The Next Generation Work-station / Machine Controller) and OMAC (Open Modular Architecture Controller) program • EC: OSACA (Open System Architecture for Control within Automation Systems) program • Japan: OSEC (Open System Environment for Controller) program • China: ONC (Open Numerical Control System) project • China - Type I - IPC - based Open Architecture • Space Type I CNC System - PC - based Multi - machine CNC Open Architecture
• Research Progress of Open CNC System at Home and Abroad • US: NGC (The Next Generation Work-station / Machine Controller) and OMAC (Open Modular Architecture Controller) program • EC: OSACA (Open System Architecture for Control within Automation Systems) program • Japan: OSEC (Open System Environment for Controller) program • China: ONC (Open Numerical Control System) project • China - Type I - IPC - based Open Architecture • Space Type I CNC System - PC - based Multi - machine CNC Open Architecture
 • Interactive network • Support the network communication protocol, both to meet the needs of single, but also to meet the FMC, FMS, CIMS basic equipment integration requirements of the CNC system, the system is the formation of "global manufacturing" of the basic unit. • Network resource sharing. • Remote control of CNC machine tools. • Network-based digital services (remote monitoring of CNC machine tools, fault diagnosis, remote network training and teaching, e-commerce)
• Interactive network • Support the network communication protocol, both to meet the needs of single, but also to meet the FMC, FMS, CIMS basic equipment integration requirements of the CNC system, the system is the formation of "global manufacturing" of the basic unit. • Network resource sharing. • Remote control of CNC machine tools. • Network-based digital services (remote monitoring of CNC machine tools, fault diagnosis, remote network training and teaching, e-commerce)
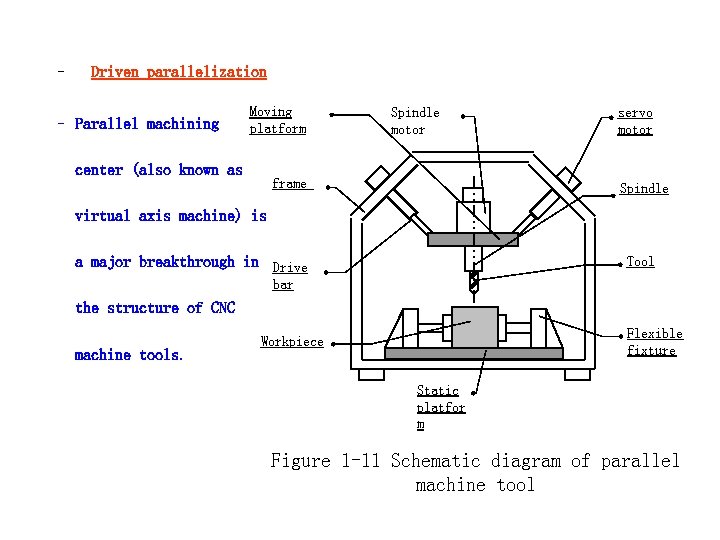 – Driven parallelization – Parallel machining Moving platform center (also known as Spindle motor frame servo motor Spindle virtual axis machine) is Tool a major breakthrough in Drive bar the structure of CNC machine tools. Flexible fixture Workpiece Static platfor m Figure 1 -11 Schematic diagram of parallel machine tool
– Driven parallelization – Parallel machining Moving platform center (also known as Spindle motor frame servo motor Spindle virtual axis machine) is Tool a major breakthrough in Drive bar the structure of CNC machine tools. Flexible fixture Workpiece Static platfor m Figure 1 -11 Schematic diagram of parallel machine tool
 Features Parallel machine tool is a combination of modern robots and traditional processing technology products; Parallel machine tools are not necessary for the traditional machine bed, columns, rails and other constraints to improve the performance of the machine structure, With a modern robot with a high degree of modularity, light weight and speed advantages. Parallel machine tools are considered "since the invention of CNC technology in the machine tool industry since the most significant progress", "the 21 st century a new generation of CNC machining equipment. "
Features Parallel machine tool is a combination of modern robots and traditional processing technology products; Parallel machine tools are not necessary for the traditional machine bed, columns, rails and other constraints to improve the performance of the machine structure, With a modern robot with a high degree of modularity, light weight and speed advantages. Parallel machine tools are considered "since the invention of CNC technology in the machine tool industry since the most significant progress", "the 21 st century a new generation of CNC machining equipment. "
 Introduction to Typical Computer Numerical Control System • • • The world's major CNC systems: FANUC (Japan) SIEMENS (Germany), Http: //www. ad. siemens. com. cn/products/ A-B (United States) FAGOR (Spain) HEIDENHAIN (HEIDENHAIN) (used to five axises machine, in normal) Mitsubishi (Japan) NUM (Switzerland) Main domestic CNC system: Huaxing NC, Central China Star, Shenyang CNC, Dalian CNC, Cage NC, DASEN, Guangzhou NC, and so on.
Introduction to Typical Computer Numerical Control System • • • The world's major CNC systems: FANUC (Japan) SIEMENS (Germany), Http: //www. ad. siemens. com. cn/products/ A-B (United States) FAGOR (Spain) HEIDENHAIN (HEIDENHAIN) (used to five axises machine, in normal) Mitsubishi (Japan) NUM (Switzerland) Main domestic CNC system: Huaxing NC, Central China Star, Shenyang CNC, Dalian CNC, Cage NC, DASEN, Guangzhou NC, and so on.
 • Siemens CNC systems are: SINUMERIK 3 / 8/810/820/850/880/805/840 series. Commonly used SINUMERIK 802 S, 802 C, 802 D, 810 D, 840 D, the instructions can go to http: //www. ad. siemens. com. cn/products/ website. These numerical control system is the same family, there is a certain inheritance.
• Siemens CNC systems are: SINUMERIK 3 / 8/810/820/850/880/805/840 series. Commonly used SINUMERIK 802 S, 802 C, 802 D, 810 D, 840 D, the instructions can go to http: //www. ad. siemens. com. cn/products/ website. These numerical control system is the same family, there is a certain inheritance.
 • The SINUMERIK 840 D is a high-performance CNC system introduced by Siemens in the late 1990 s, maintaining the three CPU architectures of the previous Siemens systems: • Man-machine communication CPU that is MMCCPU; • Digital control CPU that NC-CPU; • Programmable logic controller CPU is PLC-CPU. • Three parts in the function of mutual division of labor, but also support each other.
• The SINUMERIK 840 D is a high-performance CNC system introduced by Siemens in the late 1990 s, maintaining the three CPU architectures of the previous Siemens systems: • Man-machine communication CPU that is MMCCPU; • Digital control CPU that NC-CPU; • Programmable logic controller CPU is PLC-CPU. • Three parts in the function of mutual division of labor, but also support each other.
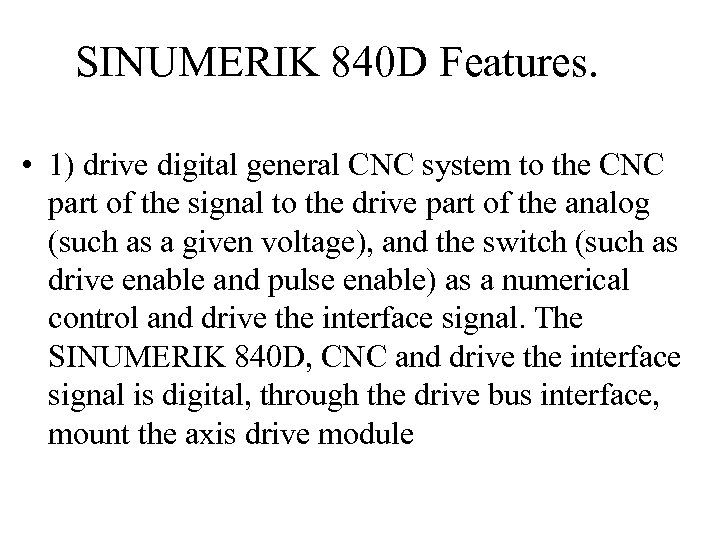 SINUMERIK 840 D Features. • 1) drive digital general CNC system to the CNC part of the signal to the drive part of the analog (such as a given voltage), and the switch (such as drive enable and pulse enable) as a numerical control and drive the interface signal. The SINUMERIK 840 D, CNC and drive the interface signal is digital, through the drive bus interface, mount the axis drive module
SINUMERIK 840 D Features. • 1) drive digital general CNC system to the CNC part of the signal to the drive part of the analog (such as a given voltage), and the switch (such as drive enable and pulse enable) as a numerical control and drive the interface signal. The SINUMERIK 840 D, CNC and drive the interface signal is digital, through the drive bus interface, mount the axis drive module
 2) Large scale can be equipped with 31 axes, which can be equipped with 10 spindle. 3) can achieve five-axis linkage Five-axis linkage control is the main indicators of the strength of CNC system, SINUMERIK 840 D can process arbitrary space surface. 4) operating system visualization of the general CNC system using a simple CNC platform or DOS platform, SINUMERIK 840 D using WINDOWS 95 as an operating platform to achieve the operating system window. So SINUMERIK 840 D system is more simple, easy to use, easy to master and other important features. 5) software content is rich, powerful, including MS-DOS, WINDOWS 95, SERVICE SOFTWARE, MMC SYSTEM SOFTWARE, MANUFACTURE SOFTWARE, USER SOFTWARE, OEM SOFTWARE. Which OEM SOFTWARE in accordance with the wishes of users, to achieve the development of open CNC system. 6) with remote diagnostic functions such as the scene with the PC adapter, MODEM card, through the telephone line to achieve communication with the exotic PC, complete the modification of PLC programs and monitoring machine status and other remote diagnostic functions.
2) Large scale can be equipped with 31 axes, which can be equipped with 10 spindle. 3) can achieve five-axis linkage Five-axis linkage control is the main indicators of the strength of CNC system, SINUMERIK 840 D can process arbitrary space surface. 4) operating system visualization of the general CNC system using a simple CNC platform or DOS platform, SINUMERIK 840 D using WINDOWS 95 as an operating platform to achieve the operating system window. So SINUMERIK 840 D system is more simple, easy to use, easy to master and other important features. 5) software content is rich, powerful, including MS-DOS, WINDOWS 95, SERVICE SOFTWARE, MMC SYSTEM SOFTWARE, MANUFACTURE SOFTWARE, USER SOFTWARE, OEM SOFTWARE. Which OEM SOFTWARE in accordance with the wishes of users, to achieve the development of open CNC system. 6) with remote diagnostic functions such as the scene with the PC adapter, MODEM card, through the telephone line to achieve communication with the exotic PC, complete the modification of PLC programs and monitoring machine status and other remote diagnostic functions.
 • 7) Safeguard function In order to protect the CNC system, the SINUMERIK 840 D system software is divided into seven software protection grades such as Siemens service level, machine tool manufacturer and end user level, making the SINUMERIK 840 D CNC system more secure and reliable. • 8) Hardware is highly integrated • Modular design • 10) built a large capacity PLC system • 11) PC is in line with the current development trend of numerical control system.
• 7) Safeguard function In order to protect the CNC system, the SINUMERIK 840 D system software is divided into seven software protection grades such as Siemens service level, machine tool manufacturer and end user level, making the SINUMERIK 840 D CNC system more secure and reliable. • 8) Hardware is highly integrated • Modular design • 10) built a large capacity PLC system • 11) PC is in line with the current development trend of numerical control system.
 • The most prominent product SINUMERIK 840 D, it is in the complex system platform, through the system settings and suitable for a variety of control technology. The 840 D, together with the SINUMERIK_611 digital drive system and the SIMATICS 7 programmable controller, forms an all-digital control system that is suitable for control of complex machining tasks with superior dynamic quality and control accuracy over other systems. The standard control system has a lot of special features. Such as drilling, turning, milling, grinding and manual machining. The system is also suitable for other special techniques such as cutting, stamping and laser processing.
• The most prominent product SINUMERIK 840 D, it is in the complex system platform, through the system settings and suitable for a variety of control technology. The 840 D, together with the SINUMERIK_611 digital drive system and the SIMATICS 7 programmable controller, forms an all-digital control system that is suitable for control of complex machining tasks with superior dynamic quality and control accuracy over other systems. The standard control system has a lot of special features. Such as drilling, turning, milling, grinding and manual machining. The system is also suitable for other special techniques such as cutting, stamping and laser processing.
 SINUMERIK appearance drawing 802 S SINUMERIK appearance 840 Di
SINUMERIK appearance drawing 802 S SINUMERIK appearance 840 Di
 • issue: • 1, open CNC system (definition, characteristics, domestic • Outside the development of the status quo) • 2, find Fanuc numerical control system series, and the series • Features.
• issue: • 1, open CNC system (definition, characteristics, domestic • Outside the development of the status quo) • 2, find Fanuc numerical control system series, and the series • Features.
 Definition of CNC system • According to the definition of the American Electronics Industry Association (EIA) CNC Standardization Committee, the CNC system is equipped with an interface circuit, a dedicated servo drive device by means of a computer that performs part or all of its functions by executing a program in its memory.
Definition of CNC system • According to the definition of the American Electronics Industry Association (EIA) CNC Standardization Committee, the CNC system is equipped with an interface circuit, a dedicated servo drive device by means of a computer that performs part or all of its functions by executing a program in its memory.
 CNC system components: • program, • Input and output devices, • A computer numerical control device (a CNC device, or a computer part) • Programmable logic controller (PLC), • Spindle drive and servo drive.
CNC system components: • program, • Input and output devices, • A computer numerical control device (a CNC device, or a computer part) • Programmable logic controller (PLC), • Spindle drive and servo drive.
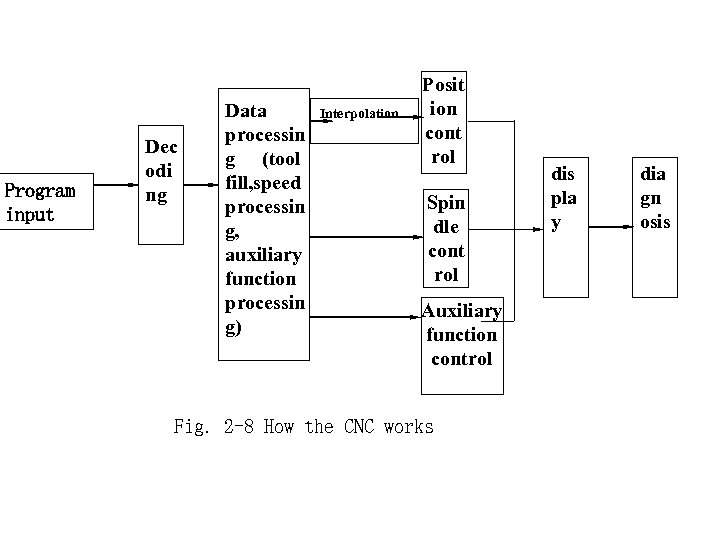 Program input Dec odi ng Data processin g (tool fill, peed s processin g, auxiliary function processin g) Interpolation Posit ion cont rol Spin dle cont rol Auxiliary function control Fig. 2 -8 How the CNC works dis pla y dia gn osis
Program input Dec odi ng Data processin g (tool fill, peed s processin g, auxiliary function processin g) Interpolation Posit ion cont rol Spin dle cont rol Auxiliary function control Fig. 2 -8 How the CNC works dis pla y dia gn osis
 • First, the program input • input devices are: tape reader input, keyboard input, disk input, communication interface input and connected to a computer DNC (Direct Numerical Control) interface input device to input of all the information into the CNC device's internal memory.
• First, the program input • input devices are: tape reader input, keyboard input, disk input, communication interface input and connected to a computer DNC (Direct Numerical Control) interface input device to input of all the information into the CNC device's internal memory.
 Second, decoding (F code) and other auxiliary functions (M, S, T) information are included in the input workpiece processing program, and the decoding program is programmed with a program (starting point, end point, straight line, arc, etc. ) Paragraph as a unit, according to certain rules will be translated into the information inside the computer can identify the form of data, and in the agreed format stored in the specified memory interval.
Second, decoding (F code) and other auxiliary functions (M, S, T) information are included in the input workpiece processing program, and the decoding program is programmed with a program (starting point, end point, straight line, arc, etc. ) Paragraph as a unit, according to certain rules will be translated into the information inside the computer can identify the form of data, and in the agreed format stored in the specified memory interval.
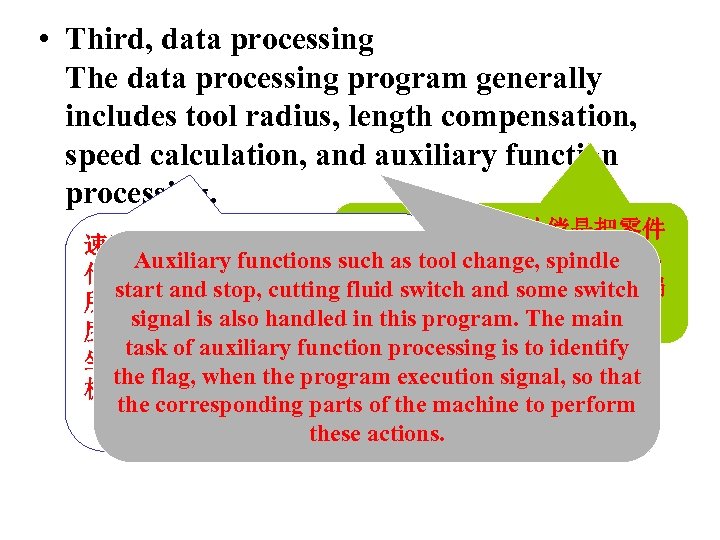 • Third, data processing The data processing program generally includes tool radius, length compensation, speed calculation, and auxiliary function processing. 刀具半径、长度补偿是把零件 速度计算是解决该加 程序段以 轮廓轨迹转化成刀具中心轨迹, Auxiliary functions such as tool change, spindle 什么样的速度运动的问题。编程 编程员只需按零件轮廓轨迹编 start and stop, cutting fluid switch and some switch 所给的进给速度是合成速度,速 程,减轻了 作量。 signal is also handled in this program. The main 度计算是根据合成速度来计算各 task of auxiliary function processing is to identify 坐标运动方向的分速度。另外对 the flag, when the program execution signal, so that 机床允许的最低速度和最高速度 the corresponding parts of the machine to perform 的限制进行判断并处理。 these actions.
• Third, data processing The data processing program generally includes tool radius, length compensation, speed calculation, and auxiliary function processing. 刀具半径、长度补偿是把零件 速度计算是解决该加 程序段以 轮廓轨迹转化成刀具中心轨迹, Auxiliary functions such as tool change, spindle 什么样的速度运动的问题。编程 编程员只需按零件轮廓轨迹编 start and stop, cutting fluid switch and some switch 所给的进给速度是合成速度,速 程,减轻了 作量。 signal is also handled in this program. The main 度计算是根据合成速度来计算各 task of auxiliary function processing is to identify 坐标运动方向的分速度。另外对 the flag, when the program execution signal, so that 机床允许的最低速度和最高速度 the corresponding parts of the machine to perform 的限制进行判断并处理。 these actions.
 Fourth, interpolation In CNC machining, the starting point coordinates, the end point coordinates and the curve equation and the feed rate of the motion trajectory are generally known. How can the cutting movement move along the predetermined trajectory? The task of interpolation is to interpolate the program by "data point densification" on the basis of the known information, that is, inserting some intermediate points between the start and end points.
Fourth, interpolation In CNC machining, the starting point coordinates, the end point coordinates and the curve equation and the feed rate of the motion trajectory are generally known. How can the cutting movement move along the predetermined trajectory? The task of interpolation is to interpolate the program by "data point densification" on the basis of the known information, that is, inserting some intermediate points between the start and end points.
 CNC system display is mainly for the convenience of the operator, usually: parts program display, parameter settings, tool position display, machine status display, alarm display, tool processing track dynamic simulation display and online programming, such as graphical display
CNC system display is mainly for the convenience of the operator, usually: parts program display, parameter settings, tool position display, machine status display, alarm display, tool processing track dynamic simulation display and online programming, such as graphical display
 Eight, diagnosis Mainly refers to the CNC system using built-in diagnostic procedures for self-diagnosis, mainly off-line diagnosis and online diagnosis. Offline diagnosis refers to the CNC system every time from the power into the normal operation of the preparation of the state, the corresponding system within the diagnostic process automatically check the system hardware, software and related peripherals are normal. Only when the inspection of each project are confirmed correctly, the entire system can enter the normal state of preparation. Otherwise, the CNC system will indicate the fault information through the alarm mode. At this time, the offline diagnosis process can not be completed and the system can not be put into operation. Online diagnosis is in the system is in normal operation, by the system corresponding to the built-in diagnostic procedures, through the periodic interrupt cycle scan to check the CNC system itself and the peripherals. As long as the system is not power, online diagnostics will not stop.
Eight, diagnosis Mainly refers to the CNC system using built-in diagnostic procedures for self-diagnosis, mainly off-line diagnosis and online diagnosis. Offline diagnosis refers to the CNC system every time from the power into the normal operation of the preparation of the state, the corresponding system within the diagnostic process automatically check the system hardware, software and related peripherals are normal. Only when the inspection of each project are confirmed correctly, the entire system can enter the normal state of preparation. Otherwise, the CNC system will indicate the fault information through the alarm mode. At this time, the offline diagnosis process can not be completed and the system can not be put into operation. Online diagnosis is in the system is in normal operation, by the system corresponding to the built-in diagnostic procedures, through the periodic interrupt cycle scan to check the CNC system itself and the peripherals. As long as the system is not power, online diagnostics will not stop.
 The hardware of the CNC device • • Single microprocessor Multi-microprocessor. CNC device basic hardware CPU; BUS; Memory; HMI; I / O interface.
The hardware of the CNC device • • Single microprocessor Multi-microprocessor. CNC device basic hardware CPU; BUS; Memory; HMI; I / O interface.
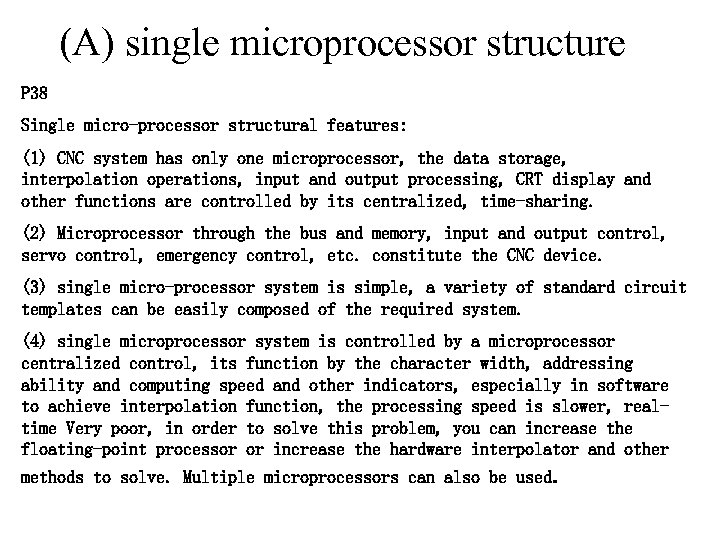 (A) single microprocessor structure P 38 Single micro-processor structural features: (1) CNC system has only one microprocessor, the data storage, interpolation operations, input and output processing, CRT display and other functions are controlled by its centralized, time-sharing. (2) Microprocessor through the bus and memory, input and output control, servo control, emergency control, etc. constitute the CNC device. (3) single micro-processor system is simple, a variety of standard circuit templates can be easily composed of the required system. (4) single microprocessor system is controlled by a microprocessor centralized control, its function by the character width, addressing ability and computing speed and other indicators, especially in software to achieve interpolation function, the processing speed is slower, realtime Very poor, in order to solve this problem, you can increase the floating-point processor or increase the hardware interpolator and other methods to solve. Multiple microprocessors can also be used.
(A) single microprocessor structure P 38 Single micro-processor structural features: (1) CNC system has only one microprocessor, the data storage, interpolation operations, input and output processing, CRT display and other functions are controlled by its centralized, time-sharing. (2) Microprocessor through the bus and memory, input and output control, servo control, emergency control, etc. constitute the CNC device. (3) single micro-processor system is simple, a variety of standard circuit templates can be easily composed of the required system. (4) single microprocessor system is controlled by a microprocessor centralized control, its function by the character width, addressing ability and computing speed and other indicators, especially in software to achieve interpolation function, the processing speed is slower, realtime Very poor, in order to solve this problem, you can increase the floating-point processor or increase the hardware interpolator and other methods to solve. Multiple microprocessors can also be used.
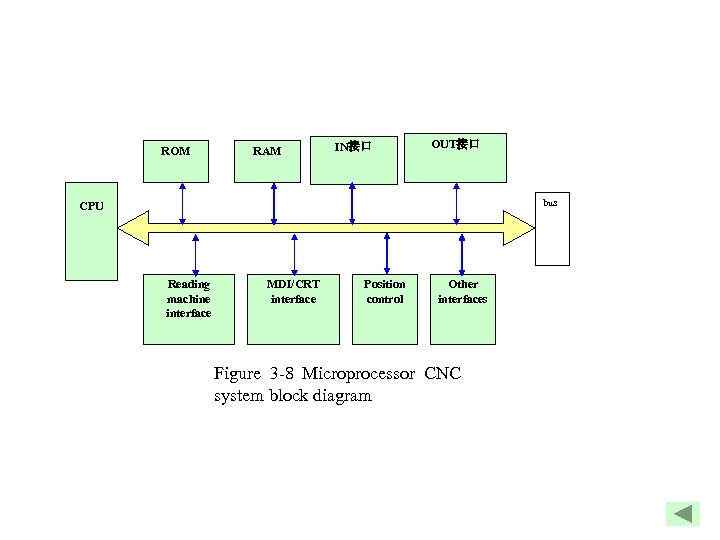 ROM RAM IN接口 OUT接口 bus CPU Reading machine interface MDI/CRT interface Position control Other interfaces Figure 3 -8 Microprocessor CNC system block diagram
ROM RAM IN接口 OUT接口 bus CPU Reading machine interface MDI/CRT interface Position control Other interfaces Figure 3 -8 Microprocessor CNC system block diagram
 (B) multi-microprocessor structure 1, multi-microprocessor structure is composed of two or more microprocessors to form processing components. Each microprocessor is connected by a set of common addresses and data buses, each microprocessor sharing system common memory or I / O interface, each microprocessor sharing part of the work of the system, which will be in a single microprocessor CNC devices in the order to complete the work to multimicroprocessor parallel, while the completion of the work, thus greatly improving the overall system processing speed. Divided into shared memory, shared bus type two. • P 40
(B) multi-microprocessor structure 1, multi-microprocessor structure is composed of two or more microprocessors to form processing components. Each microprocessor is connected by a set of common addresses and data buses, each microprocessor sharing system common memory or I / O interface, each microprocessor sharing part of the work of the system, which will be in a single microprocessor CNC devices in the order to complete the work to multimicroprocessor parallel, while the completion of the work, thus greatly improving the overall system processing speed. Divided into shared memory, shared bus type two. • P 40
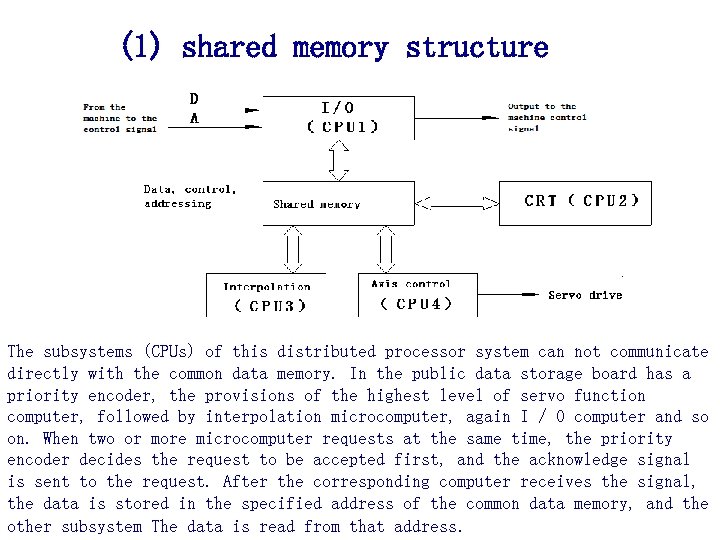 (1) shared memory structure The subsystems (CPUs) of this distributed processor system can not communicate directly with the common data memory. In the public data storage board has a priority encoder, the provisions of the highest level of servo function computer, followed by interpolation microcomputer, again I / O computer and so on. When two or more microcomputer requests at the same time, the priority encoder decides the request to be accepted first, and the acknowledge signal is sent to the request. After the corresponding computer receives the signal, the data is stored in the specified address of the common data memory, and the other subsystem The data is read from that address.
(1) shared memory structure The subsystems (CPUs) of this distributed processor system can not communicate directly with the common data memory. In the public data storage board has a priority encoder, the provisions of the highest level of servo function computer, followed by interpolation microcomputer, again I / O computer and so on. When two or more microcomputer requests at the same time, the priority encoder decides the request to be accepted first, and the acknowledge signal is sent to the request. After the corresponding computer receives the signal, the data is stored in the specified address of the common data memory, and the other subsystem The data is read from that address.
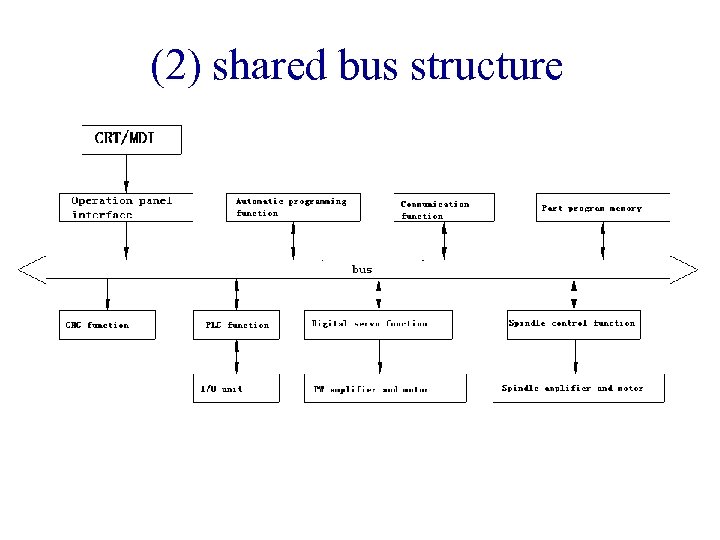 (2) shared bus structure
(2) shared bus structure
 (2) shared bus structure • The system bus as the center of the multi-microprocessor structure, said multi-microprocessor shared bus structure. • Each function module in the CNC unit is divided into two main categories: CPU main module and CPU (RAM / ROM, I / O) slave module. All master and slave modules are plugged into a cabinet with a bus socket to share the standard system bus. • The role of the system bus is to effectively connect the various modules together, according to the exchange of data and control information, constitute a complete system to achieve a variety of predetermined functions. • Only the master module has the right to control the use of the bus. Since a main module can only be occupied by a primary module at a time, there must be a quorum circuit to determine that multiple master modules simultaneously request the use of a system bus. The purpose of arbitration is to determine the level of priority of each module, and the priority of each master module has been pre-arranged according to the importance of the task. Support for multi-computer system bus arbitration agencies, there are usually two ways to decide, that is, serial and parallel mode.
(2) shared bus structure • The system bus as the center of the multi-microprocessor structure, said multi-microprocessor shared bus structure. • Each function module in the CNC unit is divided into two main categories: CPU main module and CPU (RAM / ROM, I / O) slave module. All master and slave modules are plugged into a cabinet with a bus socket to share the standard system bus. • The role of the system bus is to effectively connect the various modules together, according to the exchange of data and control information, constitute a complete system to achieve a variety of predetermined functions. • Only the master module has the right to control the use of the bus. Since a main module can only be occupied by a primary module at a time, there must be a quorum circuit to determine that multiple master modules simultaneously request the use of a system bus. The purpose of arbitration is to determine the level of priority of each module, and the priority of each master module has been pre-arranged according to the importance of the task. Support for multi-computer system bus arbitration agencies, there are usually two ways to decide, that is, serial and parallel mode.
 2. The structural characteristics of microprocessors • (1) high cost performance. • (2) the use of modular structure, with a good adaptation • Sex and scalability. • (3) hardware is easy to organize the scale of production. • (4) have a high reliability.
2. The structural characteristics of microprocessors • (1) high cost performance. • (2) the use of modular structure, with a good adaptation • Sex and scalability. • (3) hardware is easy to organize the scale of production. • (4) have a high reliability.
 CPU • • • Is the core of the CNC system and the "mind", the main function: Can be arithmetic, logic operations; Can save a small amount of data; Can decode the instruction and perform the specified action; Can exchange data with memory and peripherals; Provide the timing and control required for the entire system; Can respond to other parts of the pulse request; Included parts: Arithmetic, logic, accumulators and general purpose registers, program counters, instruction registers, decoders, timing and control components
CPU • • • Is the core of the CNC system and the "mind", the main function: Can be arithmetic, logic operations; Can save a small amount of data; Can decode the instruction and perform the specified action; Can exchange data with memory and peripherals; Provide the timing and control required for the entire system; Can respond to other parts of the pulse request; Included parts: Arithmetic, logic, accumulators and general purpose registers, program counters, instruction registers, decoders, timing and control components
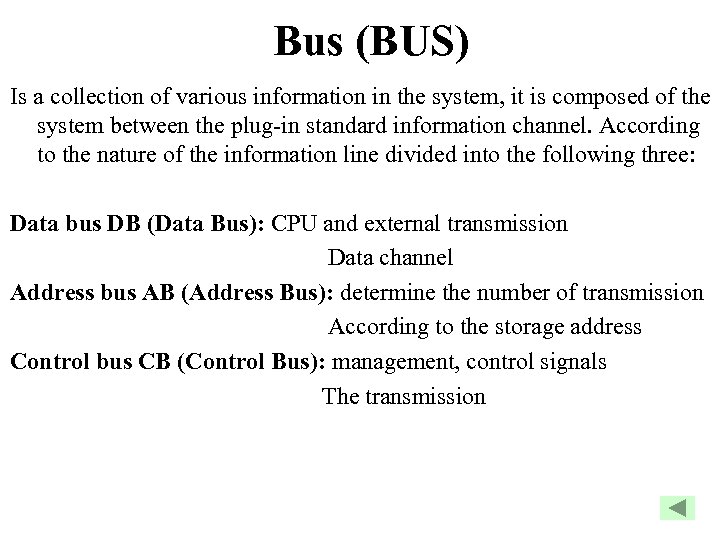 Bus (BUS) Is a collection of various information in the system, it is composed of the system between the plug-in standard information channel. According to the nature of the information line divided into the following three: Data bus DB (Data Bus): CPU and external transmission Data channel Address bus AB (Address Bus): determine the number of transmission According to the storage address Control bus CB (Control Bus): management, control signals The transmission
Bus (BUS) Is a collection of various information in the system, it is composed of the system between the plug-in standard information channel. According to the nature of the information line divided into the following three: Data bus DB (Data Bus): CPU and external transmission Data channel Address bus AB (Address Bus): determine the number of transmission According to the storage address Control bus CB (Control Bus): management, control signals The transmission
 ROM、RAM • Devices and devices that store CNC system control software, part programs, raw data, parameters, intermediate results, and processed results. • ROM system control software for curing CNC system. • RAM stores information that may be overwritten.
ROM、RAM • Devices and devices that store CNC system control software, part programs, raw data, parameters, intermediate results, and processed results. • ROM system control software for curing CNC system. • RAM stores information that may be overwritten.
 HMI • • • Tape reader (rarely seen); Tape perforation machine (rare); keyboard; Operation control panel; monitor; External storage device.
HMI • • • Tape reader (rarely seen); Tape perforation machine (rare); keyboard; Operation control panel; monitor; External storage device.
 I / O interface • There are three types of information to be exchanged between the CNC and the controlled device: • Switch signal, analog signal, pulse signal, • However, these signals are generally not directly associated with the CNC device, the need for an interface (that is, equipment auxiliary control interface) to exchange these signals, the purpose is: • 1) the corresponding conversion of the signal, the input must be controlled by the state of the device information into digital form to meet the computer input and output signal requirements; output, should meet the various input elements of the input requirements. The signal conversion mainly includes level conversion, digital quantity and analog quantity conversion, digital quantity and pulse quantity conversion and power matching. • 2) to block the external interference signal into the computer, the electrical device will be isolated with the external signal to improve the reliability of CNC device operation. • In short: level conversion, power amplification, electrical isolation.
I / O interface • There are three types of information to be exchanged between the CNC and the controlled device: • Switch signal, analog signal, pulse signal, • However, these signals are generally not directly associated with the CNC device, the need for an interface (that is, equipment auxiliary control interface) to exchange these signals, the purpose is: • 1) the corresponding conversion of the signal, the input must be controlled by the state of the device information into digital form to meet the computer input and output signal requirements; output, should meet the various input elements of the input requirements. The signal conversion mainly includes level conversion, digital quantity and analog quantity conversion, digital quantity and pulse quantity conversion and power matching. • 2) to block the external interference signal into the computer, the electrical device will be isolated with the external signal to improve the reliability of CNC device operation. • In short: level conversion, power amplification, electrical isolation.
 I / O interface • Including man-machine interface, communication interface, feed axis position control interface, spindle control interface, • Auxiliary function control interface, etc. , the interface includes: • 1) man-machine interface • Keyboard (MDl, that is, Manual Data input) • Display (CRT) • Operation panel (OPERATOR PANEL) • Hand pulse generator (MPG) • 2) communication interface • Usually CNC system has a standard RS 232 serial communication interface • High-end CNC system also has RS 485, MAP and other network interfaces • 3) Position control interface for the axis • Feed rate control • Interpolation operation (reference pulse method, sampling data method) • Position closed loop control
I / O interface • Including man-machine interface, communication interface, feed axis position control interface, spindle control interface, • Auxiliary function control interface, etc. , the interface includes: • 1) man-machine interface • Keyboard (MDl, that is, Manual Data input) • Display (CRT) • Operation panel (OPERATOR PANEL) • Hand pulse generator (MPG) • 2) communication interface • Usually CNC system has a standard RS 232 serial communication interface • High-end CNC system also has RS 485, MAP and other network interfaces • 3) Position control interface for the axis • Feed rate control • Interpolation operation (reference pulse method, sampling data method) • Position closed loop control
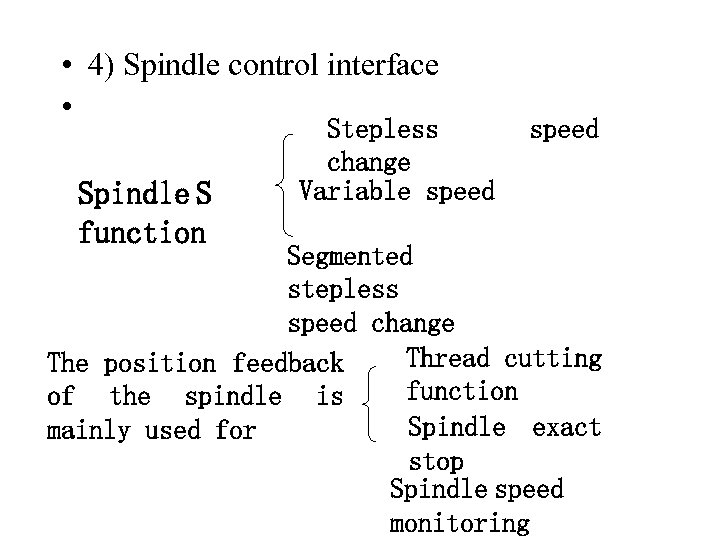 • 4) Spindle control interface • Spindle S function Stepless change Variable speed Segmented stepless speed change Thread cutting The position feedback function of the spindle is Spindle exact mainly used for stop Spindle speed monitoring
• 4) Spindle control interface • Spindle S function Stepless change Variable speed Segmented stepless speed change Thread cutting The position feedback function of the spindle is Spindle exact mainly used for stop Spindle speed monitoring
 • 5) Auxiliary function control interface • CNC device control of the device is divided into two categories: • One is the "trajectory control" for the speed and position of each axis; • One is the "sequential control" of the device action. • "Sequential control" refers to the NC machine tool running, the CNC and the machine inside the trip switch, sensors, buttons, relays and other switch signal status conditions, and in accordance with the pre-specified logic order such as the spindle start and stop, change To the replacement of the tool, the workpiece clamping, release, hydraulic, cooling, lubrication system operation to control. • The auxiliary control interface module mainly receives the signals from the operation panel, the travel switches on the machine, the sensors, the buttons, the relay in the strong electric cabinet and the control of the spindle control and the magazine control, and the output is processed to control the operation of the corresponding devices.
• 5) Auxiliary function control interface • CNC device control of the device is divided into two categories: • One is the "trajectory control" for the speed and position of each axis; • One is the "sequential control" of the device action. • "Sequential control" refers to the NC machine tool running, the CNC and the machine inside the trip switch, sensors, buttons, relays and other switch signal status conditions, and in accordance with the pre-specified logic order such as the spindle start and stop, change To the replacement of the tool, the workpiece clamping, release, hydraulic, cooling, lubrication system operation to control. • The auxiliary control interface module mainly receives the signals from the operation panel, the travel switches on the machine, the sensors, the buttons, the relay in the strong electric cabinet and the control of the spindle control and the magazine control, and the output is processed to control the operation of the corresponding devices.
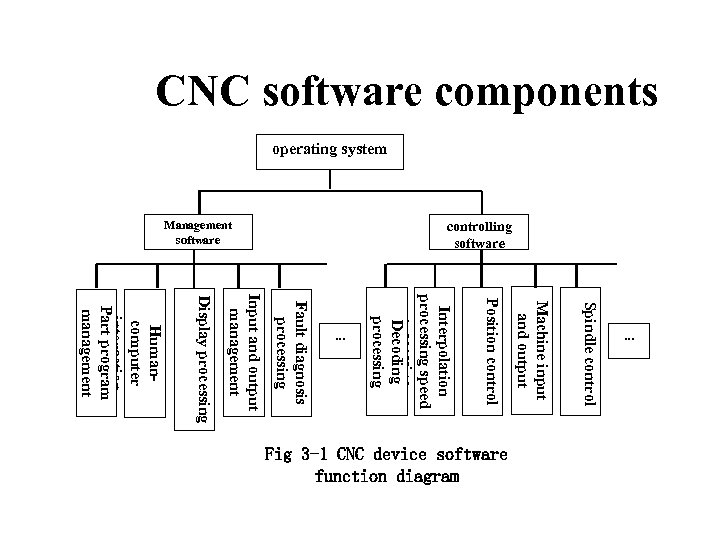 CNC software components operating system controlling software Management software Spindle control Machine input and output Position control Interpolation processing speed processing Decoding processing Fault diagnosis processing Input and output management Display processing Humancomputer interaction Part program management Fig 3 -1 CNC device software function diagram . . .
CNC software components operating system controlling software Management software Spindle control Machine input and output Position control Interpolation processing speed processing Decoding processing Fault diagnosis processing Input and output management Display processing Humancomputer interaction Part program management Fig 3 -1 CNC device software function diagram . . .
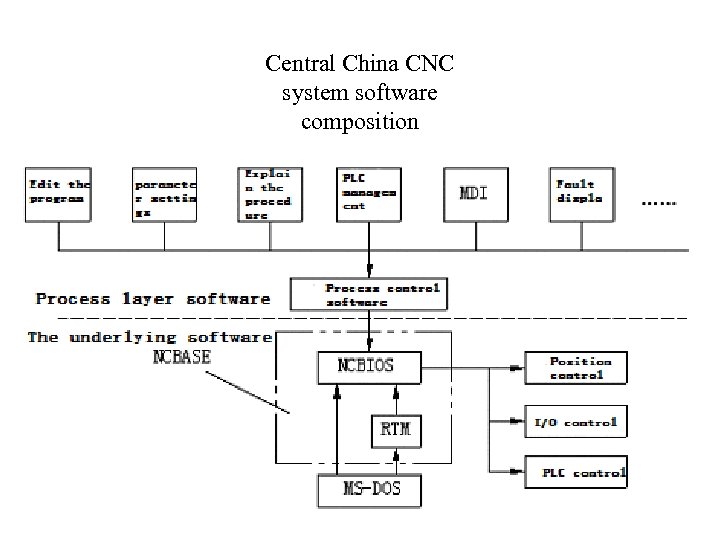 Central China CNC system software composition
Central China CNC system software composition
 Structure of CNC device software • At present, CNC device software structure of the following models: • (A) front and rear or super-loop system (Super. Loops). Front and rear refers to no operating system support, • (B) interrupted structure model using C language programming, • (C) based on real-time operating system The front desk to complete the interpolation structure model operation, location control, fault diagnosis and other real • Parallel operating mode refers to a highly time strong task; integrated operating system, such as μC / OS-II (Such as background program) running display, system. editing management of parts processing program, input and output of system, interpolation preprocessing (decoding, knife compensation, speed preprocessing) and other weak real-time tasks. Application is an infinite loop program, in the foreground and background programs without priority
Structure of CNC device software • At present, CNC device software structure of the following models: • (A) front and rear or super-loop system (Super. Loops). Front and rear refers to no operating system support, • (B) interrupted structure model using C language programming, • (C) based on real-time operating system The front desk to complete the interpolation structure model operation, location control, fault diagnosis and other real • Parallel operating mode refers to a highly time strong task; integrated operating system, such as μC / OS-II (Such as background program) running display, system. editing management of parts processing program, input and output of system, interpolation preprocessing (decoding, knife compensation, speed preprocessing) and other weak real-time tasks. Application is an infinite loop program, in the foreground and background programs without priority
 The function of the CNC device • Basic functions and additional functions • Basic functions: the basic functions of CNC system configuration, that is, the necessary functions. Interpolation function, control function, preparation function (G), feed function (F), tool function (T), spindle function (S), auxiliary function (M), character display function. • Additional features: The user can select the function according to the actual requirements. Compensation function, fixed cycle function, graphic display function, communication function, man-machine dialogue programming function.
The function of the CNC device • Basic functions and additional functions • Basic functions: the basic functions of CNC system configuration, that is, the necessary functions. Interpolation function, control function, preparation function (G), feed function (F), tool function (T), spindle function (S), auxiliary function (M), character display function. • Additional features: The user can select the function according to the actual requirements. Compensation function, fixed cycle function, graphic display function, communication function, man-machine dialogue programming function.
 • • • (1) control function (2) to prepare the function (3) interpolation function and fixed cycle function (4) Feed function (5) Spindle function (6) auxiliary function (7) tool management functions (8) compensation function (9) man-machine dialogue function (10) self-diagnostic function (11) communication function
• • • (1) control function (2) to prepare the function (3) interpolation function and fixed cycle function (4) Feed function (5) Spindle function (6) auxiliary function (7) tool management functions (8) compensation function (9) man-machine dialogue function (10) self-diagnostic function (11) communication function
 Advantages of CNC devices • • • With flexibility and versatility NC function is rich High reliability Easy to use and maintain Easy to achieve mechanical and electrical integration
Advantages of CNC devices • • • With flexibility and versatility NC function is rich High reliability Easy to use and maintain Easy to achieve mechanical and electrical integration


