c2006b6058df5ddcf806463c22d9239b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Chapter 2 Communicating in Groups and Teams Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Copyright © 2003
Chapter 2 Communicating in Groups and Teams Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Copyright © 2003
 Why form groups and teams? • • Better decisions Faster response Increased productivity Greater “buy-in” Less resistance to change Improved employee morale Reduced risks Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 2
Why form groups and teams? • • Better decisions Faster response Increased productivity Greater “buy-in” Less resistance to change Improved employee morale Reduced risks Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 2
 Four Phases of Team Development Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 3
Four Phases of Team Development Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 3
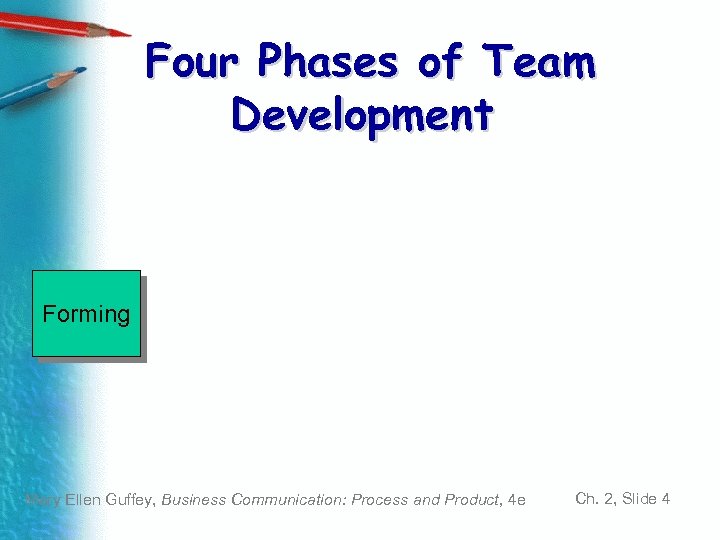 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 4
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 4
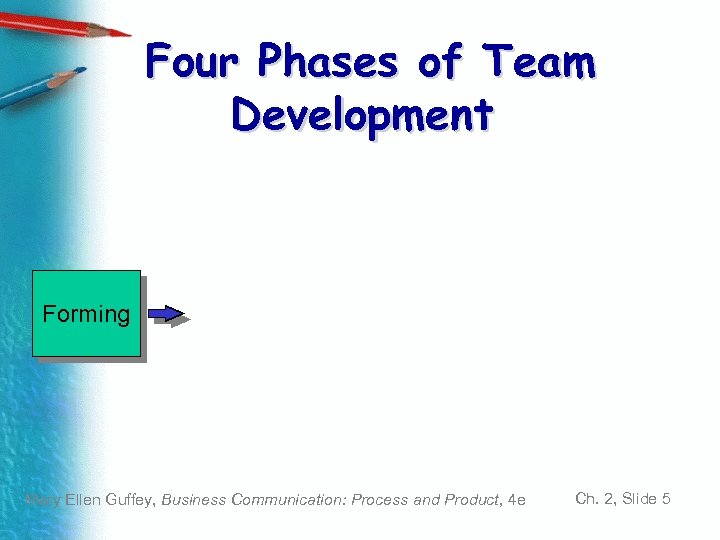 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 5
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 5
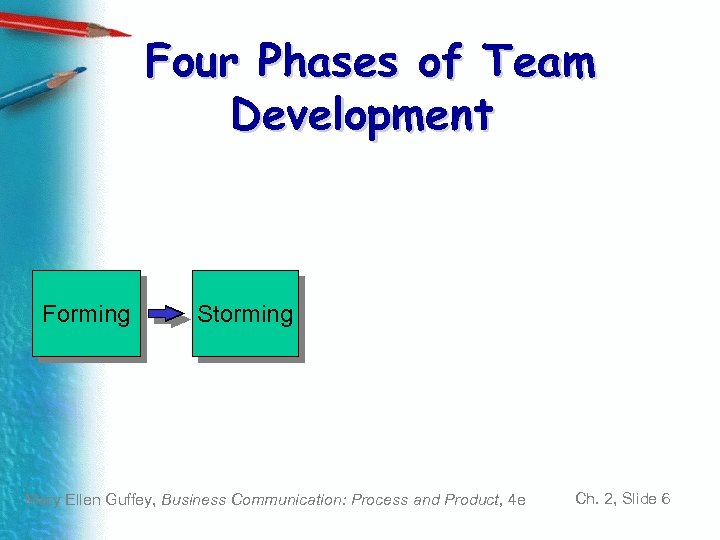 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 6
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 6
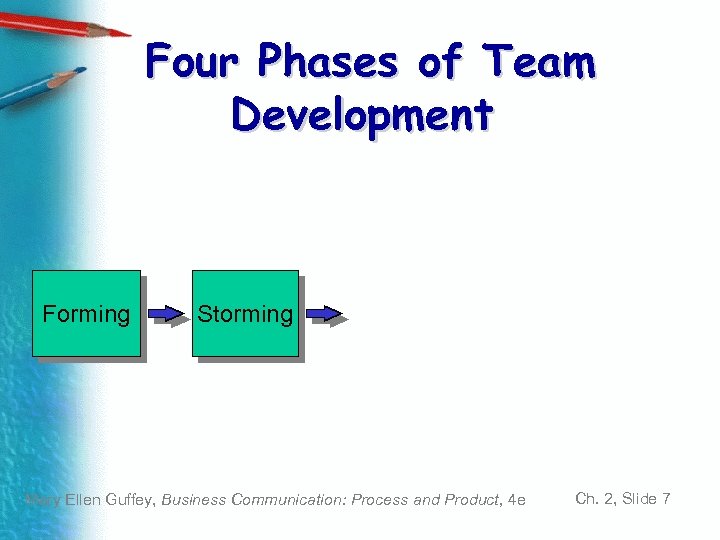 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 7
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 7
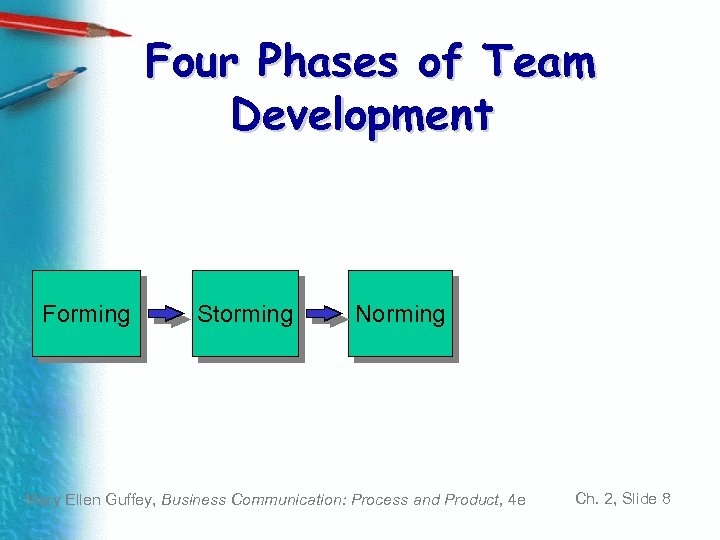 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 8
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 8
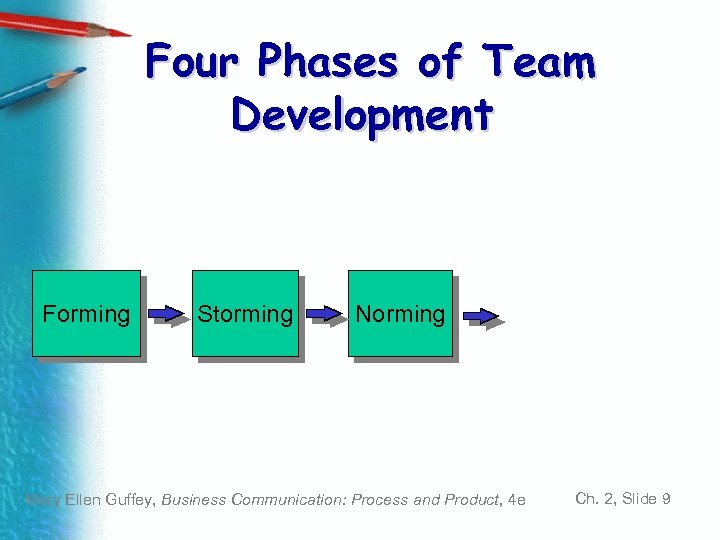 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 9
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 9
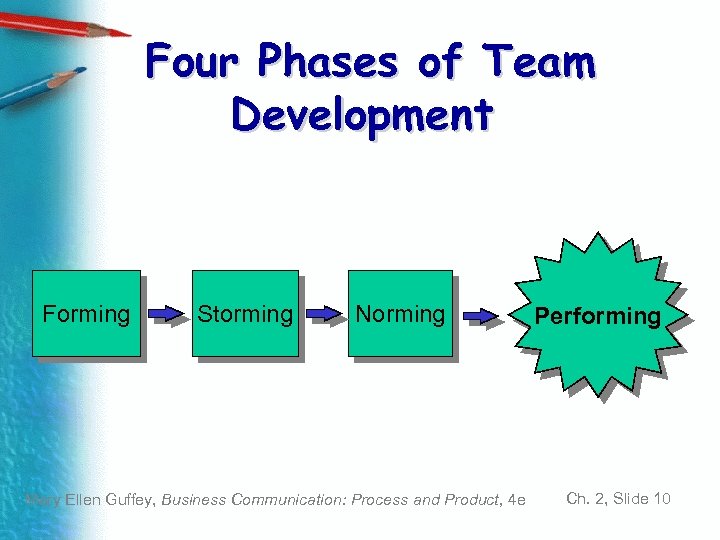 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Performing Ch. 2, Slide 10
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Performing Ch. 2, Slide 10
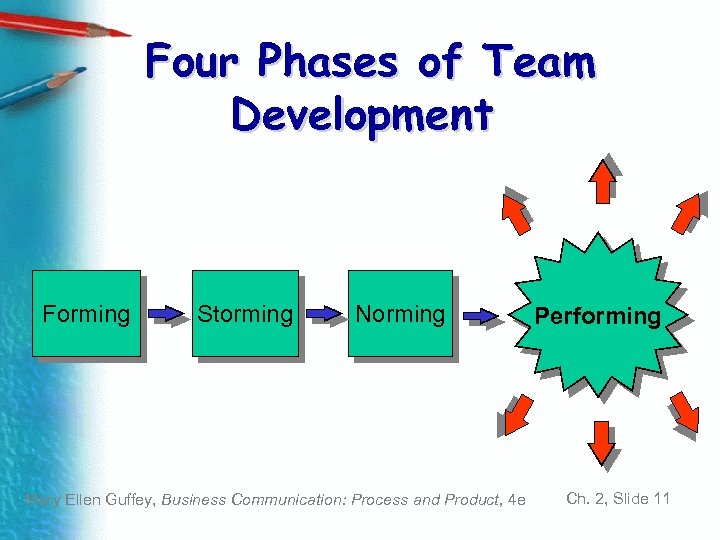 Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Performing Ch. 2, Slide 11
Four Phases of Team Development Forming Storming Norming Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Performing Ch. 2, Slide 11
 Characteristics of Successful Teams • • • Small size, diverse makeup Agreement on purpose Agreement on procedures Ability to deal with conflict Use of good communication techniques • Ability to collaborate rather than compete • Shared leadership Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 12
Characteristics of Successful Teams • • • Small size, diverse makeup Agreement on purpose Agreement on procedures Ability to deal with conflict Use of good communication techniques • Ability to collaborate rather than compete • Shared leadership Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 12
 Roles Played by Team Members Task Roles • Initiator • Information seeker/giver • Opinion seeker/giver • Direction giver • Summarizer • Energizer Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 13
Roles Played by Team Members Task Roles • Initiator • Information seeker/giver • Opinion seeker/giver • Direction giver • Summarizer • Energizer Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 13
 Roles Played by Team Members • Gatekeeper • Reality tester What kinds of statements might be made by these role players? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 14
Roles Played by Team Members • Gatekeeper • Reality tester What kinds of statements might be made by these role players? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 14
 Roles Played by Team Members Relationship Roles • • • Participation encourager Harmonizer/tension reliever Evaluator of emotional climate Praise giver Empathic listener What kinds of statements might be made by these role players? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 15
Roles Played by Team Members Relationship Roles • • • Participation encourager Harmonizer/tension reliever Evaluator of emotional climate Praise giver Empathic listener What kinds of statements might be made by these role players? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 15
 Roles Played by Team Members Dysfunctional Roles • • • Blocker Attacker Recognition-seeker Joker Withdrawer What kinds of statements might be made by these role players? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 16
Roles Played by Team Members Dysfunctional Roles • • • Blocker Attacker Recognition-seeker Joker Withdrawer What kinds of statements might be made by these role players? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 16
 Skills for Team Leaders Task Relationships • Goal setting • Agenda making • Clarifying • Summarizing • Verbalizing consensus • Establishing work patterns • Following procedures Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 17
Skills for Team Leaders Task Relationships • Goal setting • Agenda making • Clarifying • Summarizing • Verbalizing consensus • Establishing work patterns • Following procedures Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 17
 Skills for Team Leaders Interpersonal Relationships • Regulating participation • Maintaining positive climate • Maintaining mutual respect • Instigating group self-analysis • Resolving conflict • Instigating conflict Based on Cragan and Wright, Communication in Small Groups, 5 e, Wadsworth, 1999. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 18
Skills for Team Leaders Interpersonal Relationships • Regulating participation • Maintaining positive climate • Maintaining mutual respect • Instigating group self-analysis • Resolving conflict • Instigating conflict Based on Cragan and Wright, Communication in Small Groups, 5 e, Wadsworth, 1999. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 18
 Methods for Reaching Group Decisions • • • Majority Consensus Minority Averaging Authority rule with discussion What are the advantages and disadvantages of each method? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 19
Methods for Reaching Group Decisions • • • Majority Consensus Minority Averaging Authority rule with discussion What are the advantages and disadvantages of each method? Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 19
 Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 1. When attacked, negotiate rather than escalate. • • Separate the issue from the person. Act as if the other side does not want to harm you personally. 2. Use third person. • Avoid “you” and “I” statements. Not: You never come prepared, and I’m sick of it. But: It’s hard to discuss this without all the facts. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 20
Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 1. When attacked, negotiate rather than escalate. • • Separate the issue from the person. Act as if the other side does not want to harm you personally. 2. Use third person. • Avoid “you” and “I” statements. Not: You never come prepared, and I’m sick of it. But: It’s hard to discuss this without all the facts. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 20
 Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 3. Work to maintain a calm tone of voice. • Stay away from provocative verbal emphasis. Not: It’s HARD to discuss this without ALL the facts. 4. Practice compassionate, helpful feedback. • Focus on behaviors, not attitudes. • Talk about things that can be changed. Not: Stop being aggressive! But: It would be easier to respond if you lowered your voice. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 21
Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 3. Work to maintain a calm tone of voice. • Stay away from provocative verbal emphasis. Not: It’s HARD to discuss this without ALL the facts. 4. Practice compassionate, helpful feedback. • Focus on behaviors, not attitudes. • Talk about things that can be changed. Not: Stop being aggressive! But: It would be easier to respond if you lowered your voice. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 21
 Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 5. Avoid sending threatening signals. • Don’t engage in sustained eye contact. • Keep hand gestures to a minimum. 6. Don’t use “First Strike” language. You always. . . or If you really. . . or Try to understand. . . 7. When provoked, try a listening check. Calmly and respectfully restate both sides of the argument. Take time to walk around the topic–and cool off. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 22
Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 5. Avoid sending threatening signals. • Don’t engage in sustained eye contact. • Keep hand gestures to a minimum. 6. Don’t use “First Strike” language. You always. . . or If you really. . . or Try to understand. . . 7. When provoked, try a listening check. Calmly and respectfully restate both sides of the argument. Take time to walk around the topic–and cool off. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 22
 Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 8. Clear the air. • If you’re on a team with someone who seems consistently irritated with you, ask for a private meeting. • Solicit feedback; listen without interrupting and with an open mind. • Request permission to respond with equal openness. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 23
Strategies for Effective Conflict Resolution 8. Clear the air. • If you’re on a team with someone who seems consistently irritated with you, ask for a private meeting. • Solicit feedback; listen without interrupting and with an open mind. • Request permission to respond with equal openness. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 23
 Planning and Participating in Meetings Before the meeting • Consider alternatives. Is a meeting necessary? • Invite the right people. Include. . . those who have information. those who can make decisions. those who must implement decisions. • Distribute an agenda. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 24
Planning and Participating in Meetings Before the meeting • Consider alternatives. Is a meeting necessary? • Invite the right people. Include. . . those who have information. those who can make decisions. those who must implement decisions. • Distribute an agenda. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 24
 Planning and Participating in Meetings During the Meeting • • • Start on time and introduce the agenda. Appoint a secretary and a recorder. Encourage balanced participation. Confront conflict frankly. Summarize points of consensus along the way. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 25
Planning and Participating in Meetings During the Meeting • • • Start on time and introduce the agenda. Appoint a secretary and a recorder. Encourage balanced participation. Confront conflict frankly. Summarize points of consensus along the way. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 25
 Planning and Participating in Meetings Ending the Meeting and Following Up • Review meeting decisions. • Distribute minutes of meeting. • Remind people of action items. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 26
Planning and Participating in Meetings Ending the Meeting and Following Up • Review meeting decisions. • Distribute minutes of meeting. • Remind people of action items. Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 26
 End Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 27
End Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 27
 So True! • One of the best ways to persuade others is with your ears – by listening to them. --- Dean Rusk • The reason why we have two ears and one mouth is that we may listen the more and talk the less. ---Zeno of Citium Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 28
So True! • One of the best ways to persuade others is with your ears – by listening to them. --- Dean Rusk • The reason why we have two ears and one mouth is that we may listen the more and talk the less. ---Zeno of Citium Mary Ellen Guffey, Business Communication: Process and Product, 4 e Ch. 2, Slide 28


