ebdcf4ab79cdd9ccf387e0f48504492a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Chapter 2 Ancient Middle East and Egypt
Chapter 2 Ancient Middle East and Egypt
 Chapter 2, Section 1 City – States of Ancient Sumer
Chapter 2, Section 1 City – States of Ancient Sumer
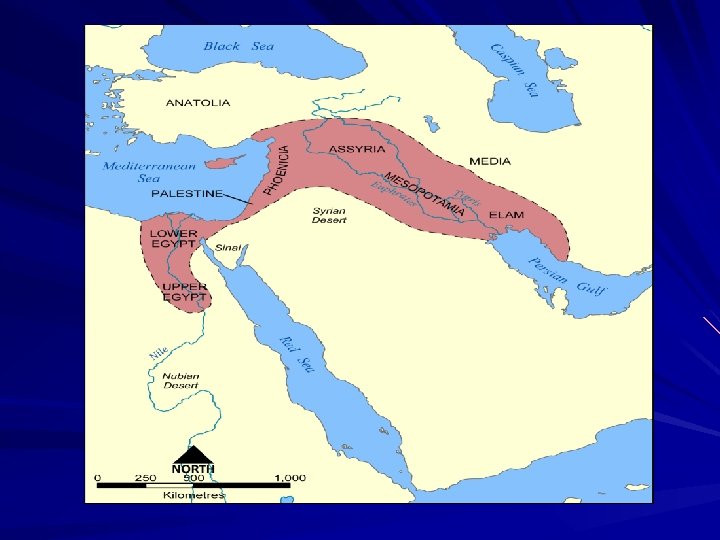
 Geography Influences Fertile Crescent land between Persian Gulf and Mediterranean Sea Within the Fertile Crescent lies a region named “Mesopotamia” – Area of land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers – Flows from highlands of modern day Turkey through Iraq into the Persian Gulf
Geography Influences Fertile Crescent land between Persian Gulf and Mediterranean Sea Within the Fertile Crescent lies a region named “Mesopotamia” – Area of land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers – Flows from highlands of modern day Turkey through Iraq into the Persian Gulf
 Floods and Irrigation Tigris and Euphrates rivers frequently rose in terrifying floods that washed away topsoil and destroyed mud – brick villages – These floods occurred regularly during the ancient days of the Fertile Crescent Villagers who lived along the river worked together building irrigation ditches – These efforts were organized by priests and royal officials
Floods and Irrigation Tigris and Euphrates rivers frequently rose in terrifying floods that washed away topsoil and destroyed mud – brick villages – These floods occurred regularly during the ancient days of the Fertile Crescent Villagers who lived along the river worked together building irrigation ditches – These efforts were organized by priests and royal officials
 Sumerians Thriving Cities Sumerians lacked resources such as timber and stone They built with clay and water Clay would make bricks and they would dry in the sun Traders took great risk of traveling in deserts to carry goods to Sumer – Evidence that the first wheel was created by Sumerians
Sumerians Thriving Cities Sumerians lacked resources such as timber and stone They built with clay and water Clay would make bricks and they would dry in the sun Traders took great risk of traveling in deserts to carry goods to Sumer – Evidence that the first wheel was created by Sumerians
 Sumerian Civilization Complex Government – Each city state had a ruler who was responsible for maintaining city walls and irrigation systems as well as collecting taxes and keeping records Structure of Society – Distinct social hierarchy system of ranking groups – Highest class: ruling family, leading officials, high priests – Middle class: lesser priests, scribes, merchants and artisans – Lower class: majority of people peasant farmers
Sumerian Civilization Complex Government – Each city state had a ruler who was responsible for maintaining city walls and irrigation systems as well as collecting taxes and keeping records Structure of Society – Distinct social hierarchy system of ranking groups – Highest class: ruling family, leading officials, high priests – Middle class: lesser priests, scribes, merchants and artisans – Lower class: majority of people peasant farmers
 Sumerian Civilization Role of Women – Sumerian women never held legal rights – Some rulers’ wives had supervisory powers – Rarely would women inherit land Religion – Polytheistic – Many gods controlled all aspects of life – It was believed that gods controlled violence and suffering as well as justice
Sumerian Civilization Role of Women – Sumerian women never held legal rights – Some rulers’ wives had supervisory powers – Rarely would women inherit land Religion – Polytheistic – Many gods controlled all aspects of life – It was believed that gods controlled violence and suffering as well as justice
 Sumerian Civilization Religion (cont) – Each city built a ziggurat large stepped platform built to show dedication to the city’s god or goddess – Also believed in an afterlife Writing – Invented earliest known writing called cuneiform (grew out of a system of pictographs) – Symbols would represent complicated thoughts – Recorded economic exchanges as well as myths, prayers, laws, business contracts, etc.
Sumerian Civilization Religion (cont) – Each city built a ziggurat large stepped platform built to show dedication to the city’s god or goddess – Also believed in an afterlife Writing – Invented earliest known writing called cuneiform (grew out of a system of pictographs) – Symbols would represent complicated thoughts – Recorded economic exchanges as well as myths, prayers, laws, business contracts, etc.
 Ziggurat
Ziggurat
 Legacy of Sumerian people left a lasting legacy Newcomers to their region adopted many new ideas and innovations – Cuneiform adopted by Assyrians – Sumerian scholars began developing astronomy and mathematics – Babylonians built upon the Sumerian mathematics to develop algebra and geometry
Legacy of Sumerian people left a lasting legacy Newcomers to their region adopted many new ideas and innovations – Cuneiform adopted by Assyrians – Sumerian scholars began developing astronomy and mathematics – Babylonians built upon the Sumerian mathematics to develop algebra and geometry
 Review 1) The area of land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers is known as what? • • 2) A B C D Fertile Crescent Wetlands Dryland Mesopotamia Which of the following was the name of the writing system invented by the Sumerians? – – A B C D English Cuneiform Spanish Sumerian Language
Review 1) The area of land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers is known as what? • • 2) A B C D Fertile Crescent Wetlands Dryland Mesopotamia Which of the following was the name of the writing system invented by the Sumerians? – – A B C D English Cuneiform Spanish Sumerian Language
 Chapter 2, Section 2 Invaders, Traders, and Empire Builders
Chapter 2, Section 2 Invaders, Traders, and Empire Builders
 First Empires in Mesopotamia Sargon – 2300 B. C. Akkad (ruler of Sargon) invaded and conquered Sumer – He continued to take over surrounding areas – He built the first empire known in history Hammurabi brings Babylonian to Power – Sumerian city states revived and rebuilt power – However, new leaders of Sargon followed Akkad’s footsteps – Hammurabi, King of Babylon, took over much of Mesopotamia
First Empires in Mesopotamia Sargon – 2300 B. C. Akkad (ruler of Sargon) invaded and conquered Sumer – He continued to take over surrounding areas – He built the first empire known in history Hammurabi brings Babylonian to Power – Sumerian city states revived and rebuilt power – However, new leaders of Sargon followed Akkad’s footsteps – Hammurabi, King of Babylon, took over much of Mesopotamia
 First Empires in Mesopotamia Hammurabi’s Code – Published set of laws known as “Hammurabi’s Code” – First important attempt by a ruler to codify arrange and set laws in writing – Much of Hammurabi’s code was established to benefit the powerless (slaves, women) Ex: One law allowed women to own land pass it on to her children
First Empires in Mesopotamia Hammurabi’s Code – Published set of laws known as “Hammurabi’s Code” – First important attempt by a ruler to codify arrange and set laws in writing – Much of Hammurabi’s code was established to benefit the powerless (slaves, women) Ex: One law allowed women to own land pass it on to her children
 First Empires in Mesopotamia Hammurabi (cont) – Improved system of irrigation – Organized a well trained army – Ordered several temples to be repaired – Addressed Criminal Law in his code Dealt with offenses against others Robbery Assault Murder
First Empires in Mesopotamia Hammurabi (cont) – Improved system of irrigation – Organized a well trained army – Ordered several temples to be repaired – Addressed Criminal Law in his code Dealt with offenses against others Robbery Assault Murder
 New Empires and Ideas Hittites Secret of Iron – Hittites were pushed out of Asia Minor and into Mesopotamia in 1400 B. C. – Brought the knowledge of creating tools and weapons from iron – Were able to arm more people at a cheap cost Assyrian Warriors – Established an Empire in Mesopotamia by 1350 B. C. and by 1100 B. C. they expanded across all of Mesopotamia – Earned a reputation for being among the most feared warriors in history
New Empires and Ideas Hittites Secret of Iron – Hittites were pushed out of Asia Minor and into Mesopotamia in 1400 B. C. – Brought the knowledge of creating tools and weapons from iron – Were able to arm more people at a cheap cost Assyrian Warriors – Established an Empire in Mesopotamia by 1350 B. C. and by 1100 B. C. they expanded across all of Mesopotamia – Earned a reputation for being among the most feared warriors in history
 New Empires and Ideas Nebuchadnezzar revives Babylon – By 625 B. C. Babylon reestablished power under their aggressive leader Nebuchadnezzar – The new empire stretched from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea He surrounded Babylon with a defensive moat He built the most famous hanging gardens – known as the seven wonders of the ancient world
New Empires and Ideas Nebuchadnezzar revives Babylon – By 625 B. C. Babylon reestablished power under their aggressive leader Nebuchadnezzar – The new empire stretched from the Persian Gulf to the Mediterranean Sea He surrounded Babylon with a defensive moat He built the most famous hanging gardens – known as the seven wonders of the ancient world
 Persians Establish Huge Empire In 539 B. C. Babylon fell to the Persian armies of Cyrus the Great Cyrus and his successors built the largest empire yet – Persian kings pursued a policy of tolerance or acceptance toward people they conquered Respected their customs of the diverse groups within their empire
Persians Establish Huge Empire In 539 B. C. Babylon fell to the Persian armies of Cyrus the Great Cyrus and his successors built the largest empire yet – Persian kings pursued a policy of tolerance or acceptance toward people they conquered Respected their customs of the diverse groups within their empire
 Persians Establish Huge Empire Darius Unites Many Peoples – Ruled from 522 B. C. to 486 B. C. real unification of Persia took place – Set up a bureaucracy who followed set rules – Darius divided the empire into provinces – He adapted laws from conquered people and made his own code to rule the empire Improving Economic Life – Darius set up a common set of weights and measures – Encouraged use of coins (first money economy)
Persians Establish Huge Empire Darius Unites Many Peoples – Ruled from 522 B. C. to 486 B. C. real unification of Persia took place – Set up a bureaucracy who followed set rules – Darius divided the empire into provinces – He adapted laws from conquered people and made his own code to rule the empire Improving Economic Life – Darius set up a common set of weights and measures – Encouraged use of coins (first money economy)
 Persians Establish Huge Empire New Religion – Religious beliefs by Zoroaster helped unite the empire – Rejected the old Persian gods and taught one single god (Ahura Mazda) ruled the world – However, Ahura Mazda was in battle with Ahriman (prince of lies and evil) – People had to choose which side to support – Zoroaster taught that Ahura Mazda would prevail over Ahriman
Persians Establish Huge Empire New Religion – Religious beliefs by Zoroaster helped unite the empire – Rejected the old Persian gods and taught one single god (Ahura Mazda) ruled the world – However, Ahura Mazda was in battle with Ahriman (prince of lies and evil) – People had to choose which side to support – Zoroaster taught that Ahura Mazda would prevail over Ahriman
 Phoenician Sea Traders Expanding Manufacturing and Trade – Phoenicians made glass from coastal sand – They traded with people around Mediterranean Sea To promote trade they set up colonies around North Africa Establishing Alphabet – Writing system in which each symbol represents a single basic sound – Most significant Phoenician contribution
Phoenician Sea Traders Expanding Manufacturing and Trade – Phoenicians made glass from coastal sand – They traded with people around Mediterranean Sea To promote trade they set up colonies around North Africa Establishing Alphabet – Writing system in which each symbol represents a single basic sound – Most significant Phoenician contribution
 Review 1) Hammurabi’s Code of laws was established to benefit which of the following groups of people? A B C D 2) Powerful Power seeking Powerless Power dominated The ruler, Darius, accomplished all of the following except? A B C D Set up a bureaucracy who followed set rules Divided the empire into provinces Encouraged use of coins Created the first football game
Review 1) Hammurabi’s Code of laws was established to benefit which of the following groups of people? A B C D 2) Powerful Power seeking Powerless Power dominated The ruler, Darius, accomplished all of the following except? A B C D Set up a bureaucracy who followed set rules Divided the empire into provinces Encouraged use of coins Created the first football game
 Chapter 2, Section 3 Kingdom of the Nile
Chapter 2, Section 3 Kingdom of the Nile
 Geography Shapes Egypt “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile. ” – Herodotus (Greek Historian) People settled and established farming villages along the Nile Egyptians depended on annual floods to soak the land deposit a layer of silt, or rich soil – People had to build dikes, reservoirs, and irrigation ditches to store water for dry season
Geography Shapes Egypt “Egypt is wholly the gift of the Nile. ” – Herodotus (Greek Historian) People settled and established farming villages along the Nile Egyptians depended on annual floods to soak the land deposit a layer of silt, or rich soil – People had to build dikes, reservoirs, and irrigation ditches to store water for dry season
 Uniting Two Regions Ancient Egypt had two distinct regions. . . Upper and Lower – Upper stretched from the first cataract (waterfall), north to within 100 miles of the Mediterranean Sea – Lower covered the delta region of the Nile The two areas were united about 3100 B. C. – Traffic moved along the Nile via barges, sailboats etc. . . – The Nile helped make Egypt one of the world’s first unified states – Later saw trade with the Middle East
Uniting Two Regions Ancient Egypt had two distinct regions. . . Upper and Lower – Upper stretched from the first cataract (waterfall), north to within 100 miles of the Mediterranean Sea – Lower covered the delta region of the Nile The two areas were united about 3100 B. C. – Traffic moved along the Nile via barges, sailboats etc. . . – The Nile helped make Egypt one of the world’s first unified states – Later saw trade with the Middle East
 Three Kingdoms We can describe the history of Ancient Egypt using three main periods: – The Old Kingdom (2700 -2200 B. C. ) – The Middle Kingdom (2050 -1800 B. C. ) – The New Kingdom (1550 -1100 B. C. )
Three Kingdoms We can describe the history of Ancient Egypt using three main periods: – The Old Kingdom (2700 -2200 B. C. ) – The Middle Kingdom (2050 -1800 B. C. ) – The New Kingdom (1550 -1100 B. C. )
 The Old Kingdom Pharaohs organized a strong central state, were absolute rulers, and were considered gods – Used vizier (chief minister) to supervise governments – Various departments under vizier (tax collection, farming, irrigation system) People expected Pharaohs to act morally and judged them for their deeds Great Pyramids were built to preserve the bodies of the deceased – Power struggles, crop failures, and cost of pyramids contributed to the collapse of the Old Kingdom
The Old Kingdom Pharaohs organized a strong central state, were absolute rulers, and were considered gods – Used vizier (chief minister) to supervise governments – Various departments under vizier (tax collection, farming, irrigation system) People expected Pharaohs to act morally and judged them for their deeds Great Pyramids were built to preserve the bodies of the deceased – Power struggles, crop failures, and cost of pyramids contributed to the collapse of the Old Kingdom
 The Middle Kingdom The Nile did not rise regularly as it had before Large drainage project created arable farmland Traders had contacts with Middle East and Crete Corruption and rebellions were common Hyksos invaded and occupied the delta region – Used chariots. . . eventually used by Egyptians Chariots are horse drawn war vehicles – Hyksos were impressed by Egyptian civilization and later adopted customs and beliefs The_Nile__Where_Egypt_Began. asf
The Middle Kingdom The Nile did not rise regularly as it had before Large drainage project created arable farmland Traders had contacts with Middle East and Crete Corruption and rebellions were common Hyksos invaded and occupied the delta region – Used chariots. . . eventually used by Egyptians Chariots are horse drawn war vehicles – Hyksos were impressed by Egyptian civilization and later adopted customs and beliefs The_Nile__Where_Egypt_Began. asf
 The New Kingdom Egypt reaches its greatest power at this time – Reached the Euphrates River Hatshepsut. . . First female pharaoh – Encouraged trade with the Middle East and the Mediterranean lands Thutmose III… Hatshepsut’s step son took power once he reached adulthood – Stretched Egypt’s borders to greatest extent Ramses II…expanded Egypt north and battled the Hittites – Signed a peace treaty with Hittites. . . first such document
The New Kingdom Egypt reaches its greatest power at this time – Reached the Euphrates River Hatshepsut. . . First female pharaoh – Encouraged trade with the Middle East and the Mediterranean lands Thutmose III… Hatshepsut’s step son took power once he reached adulthood – Stretched Egypt’s borders to greatest extent Ramses II…expanded Egypt north and battled the Hittites – Signed a peace treaty with Hittites. . . first such document
 Chapter 2, Section 4 Egyptian Civilization
Chapter 2, Section 4 Egyptian Civilization
 Religion Shapes Life in Ancient Egypt Chief Gods and Goddesses – Chief God in Egypt was the Sun God – Re Sun God worshipped during Old Kingdom – Amon – Re Great lord of the gods (worshipped during Middle Kingdom) – Pharaohs received right to rule from Amon – Re
Religion Shapes Life in Ancient Egypt Chief Gods and Goddesses – Chief God in Egypt was the Sun God – Re Sun God worshipped during Old Kingdom – Amon – Re Great lord of the gods (worshipped during Middle Kingdom) – Pharaohs received right to rule from Amon – Re
 Osiris and Isis Most Egyptians related to the God Osiris and the Goddesses Isis (story of these two gods touched human emotions such as love and jealousy) Osiris ruled the underworld and was also known as the god of the Nile – he controlled the annual flooding Isis appealed to women – It was said she first taught women to care for children – She promised the faithful they would have life after death
Osiris and Isis Most Egyptians related to the God Osiris and the Goddesses Isis (story of these two gods touched human emotions such as love and jealousy) Osiris ruled the underworld and was also known as the god of the Nile – he controlled the annual flooding Isis appealed to women – It was said she first taught women to care for children – She promised the faithful they would have life after death
 The Afterlife Affected the highest noble and lowest peasant People buried their dead with everything they would need for eternity (afterlife was supposed to similar to life on earth) – Mummification: process of wrapping the dead in cloth in order to preserve the bodies – All Egyptians used this process (even their pets were mummified)
The Afterlife Affected the highest noble and lowest peasant People buried their dead with everything they would need for eternity (afterlife was supposed to similar to life on earth) – Mummification: process of wrapping the dead in cloth in order to preserve the bodies – All Egyptians used this process (even their pets were mummified)
 Tomb of “King Tut” In 1922, British archaeologist Howard Carter discovered the tomb of Tutankhamen (son in law of Akhenaton) The tomb had remained untouched for 3, 000 years Buried in the tomb was weapons, chariots, furniture, jewelry, toys, games, etc. This gave historians a wealth of knowledge
Tomb of “King Tut” In 1922, British archaeologist Howard Carter discovered the tomb of Tutankhamen (son in law of Akhenaton) The tomb had remained untouched for 3, 000 years Buried in the tomb was weapons, chariots, furniture, jewelry, toys, games, etc. This gave historians a wealth of knowledge
 Egyptians Organize Society Most people were farmers during the Old and Middle Kingdoms During the New Kingdom social classes became more and more prevalent Trade and warfare were increasing – Trade offered opportunities for people to gain wealth – Foreign conquests brought more riches to Egypt (What else could happen? )
Egyptians Organize Society Most people were farmers during the Old and Middle Kingdoms During the New Kingdom social classes became more and more prevalent Trade and warfare were increasing – Trade offered opportunities for people to gain wealth – Foreign conquests brought more riches to Egypt (What else could happen? )
 Egyptians Organize Society Women enjoy higher status – Inherit property – Enter into business deals – Buy and sell goods – Go to court – Obtain a divorce Despite these opportunities, few women learned to read and write
Egyptians Organize Society Women enjoy higher status – Inherit property – Enter into business deals – Buy and sell goods – Go to court – Obtain a divorce Despite these opportunities, few women learned to read and write
 Advances in Learning Egyptians developed multiple writing systems Hieroglyphics was the first system invented – Symbols to represent ideas or themes Hieratic was also developed by scribes for everyday use – Form of writing which simplified the objects used in hieroglyphics
Advances in Learning Egyptians developed multiple writing systems Hieroglyphics was the first system invented – Symbols to represent ideas or themes Hieratic was also developed by scribes for everyday use – Form of writing which simplified the objects used in hieroglyphics
 Math and Science Advances Doctors learned a great deal about the human body from mummification – They could observe symptoms – Diagnose illnesses – Find cures Math was developed to solve everyday problems – Boundaries were re - drawn because of floods – Geometry used to build pyramids and temples
Math and Science Advances Doctors learned a great deal about the human body from mummification – They could observe symptoms – Diagnose illnesses – Find cures Math was developed to solve everyday problems – Boundaries were re - drawn because of floods – Geometry used to build pyramids and temples
 Arts and Literature Egyptian Arts – Showed everyday scenes of farming, trade, etc. – Painting and sculpture styles remained unchanged for thousands of years – Carvings in temples, wall paintings in tombs were both common forms of art Egyptian Literature – Oldest literatures includes hymns, prayers to gods, love poems – Folk tales were told The Tale of Sinuhe
Arts and Literature Egyptian Arts – Showed everyday scenes of farming, trade, etc. – Painting and sculpture styles remained unchanged for thousands of years – Carvings in temples, wall paintings in tombs were both common forms of art Egyptian Literature – Oldest literatures includes hymns, prayers to gods, love poems – Folk tales were told The Tale of Sinuhe
 Review 1) Egyptian women could do all of the following except? – – A B C D Go to court Inherit property Buy goods Hold government jobs 2) Because of mummification doctors could now do all of the following except? – – A B C D Diagnose illness Find cures Operate in the ER Observe patient symptoms
Review 1) Egyptian women could do all of the following except? – – A B C D Go to court Inherit property Buy goods Hold government jobs 2) Because of mummification doctors could now do all of the following except? – – A B C D Diagnose illness Find cures Operate in the ER Observe patient symptoms
 Chapter 2, Section 5 Roots of Judaism
Chapter 2, Section 5 Roots of Judaism
 Ancient Israelites (also called Hebrews) were monotheistic belief in only one god At this time, all other peoples worshipped many gods Israelites believed in all – powerful God who had plans for each person – Each event that took place was part of God’s plan
Ancient Israelites (also called Hebrews) were monotheistic belief in only one god At this time, all other peoples worshipped many gods Israelites believed in all – powerful God who had plans for each person – Each event that took place was part of God’s plan
 Ancient Israelites Torah most sacred text of the Israelites – Text of recorded events and laws Includes the first five (of 24 total) books of the Hebrew Bible 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Genesis Exodus Leviticus Numbers Deuteronomy
Ancient Israelites Torah most sacred text of the Israelites – Text of recorded events and laws Includes the first five (of 24 total) books of the Hebrew Bible 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Genesis Exodus Leviticus Numbers Deuteronomy
 God’s Covenant Israelites believed God made a covenant, or promise and agreement with Abraham (the father of Israelite people) – God declared he would have a special relationship with Abraham and his descendants – God declared Canaan (promise land) would one day belong to the Israelites – Moses later renewed God’s covenant with the Israelites
God’s Covenant Israelites believed God made a covenant, or promise and agreement with Abraham (the father of Israelite people) – God declared he would have a special relationship with Abraham and his descendants – God declared Canaan (promise land) would one day belong to the Israelites – Moses later renewed God’s covenant with the Israelites
 Kingdom of Israelites had set up the Kingdom of Israel by 1000 B. C. David, who was a strong ruler united 12 separate Israel tribes into one nation Solomon, David’s son, followed his father as king and began turning Jerusalem into a capital city – Solomon tried to increase Israel’s influence around the region by negotiating with empires in Egypt and Mesopotamia
Kingdom of Israelites had set up the Kingdom of Israel by 1000 B. C. David, who was a strong ruler united 12 separate Israel tribes into one nation Solomon, David’s son, followed his father as king and began turning Jerusalem into a capital city – Solomon tried to increase Israel’s influence around the region by negotiating with empires in Egypt and Mesopotamia
 Division and Conquest Solomon’s building projects required tremendous amounts of taxes and labor – People began to revolt after he died (922 B. C) – Kingdom was then split in two – Israel in the North – Judah in the South – Israel would remain independent for about 200 years and then fall to more powerful people
Division and Conquest Solomon’s building projects required tremendous amounts of taxes and labor – People began to revolt after he died (922 B. C) – Kingdom was then split in two – Israel in the North – Judah in the South – Israel would remain independent for about 200 years and then fall to more powerful people
 Division and Conquest Israel is conquered by Assyrians in 722 B. C. 586 B. C. Babylonians captured Judah – Nebuchadnezzar forced many people he conquered into exile in Babylon – This time period was called Babylonian Captivity (lasted for 50 years) 539 B. C. Cyrus the Great conquers Babylon and frees the Israelites
Division and Conquest Israel is conquered by Assyrians in 722 B. C. 586 B. C. Babylonians captured Judah – Nebuchadnezzar forced many people he conquered into exile in Babylon – This time period was called Babylonian Captivity (lasted for 50 years) 539 B. C. Cyrus the Great conquers Babylon and frees the Israelites
 Law and Morality Israelite society was patriarchal: men held the greatest legal and moral authority The oldest male relative in a family was the head of the household and arranged marriages for his daughters – In the patriarchal society, women had fewer legal rights than men
Law and Morality Israelite society was patriarchal: men held the greatest legal and moral authority The oldest male relative in a family was the head of the household and arranged marriages for his daughters – In the patriarchal society, women had fewer legal rights than men
 Law and Morality The Jews used the Ten Commandments as a guide for their lives First four commandments stress religious duties toward God – Example: Keeping the Sabbath: holy day for rest and worship – The rest of the commandments stress conduct toward others
Law and Morality The Jews used the Ten Commandments as a guide for their lives First four commandments stress religious duties toward God – Example: Keeping the Sabbath: holy day for rest and worship – The rest of the commandments stress conduct toward others
 Law and Morality Prophets: spiritual leaders that interpret God’s will emerged throughout Jewish history to remind people of their duties The prophets taught a strong code of ethics they urged personal morality and social justice (rich and powerful must protect the poor and weak) – Two important prophets are Isaiah and Jeremiah
Law and Morality Prophets: spiritual leaders that interpret God’s will emerged throughout Jewish history to remind people of their duties The prophets taught a strong code of ethics they urged personal morality and social justice (rich and powerful must protect the poor and weak) – Two important prophets are Isaiah and Jeremiah
 Maintaining Beliefs Over Time Throughout their history, Jews have been exiled and persecuted, yet they still maintain their beliefs today Judaism is considered a major world religion Judaism has contributed to Christianity and Islam
Maintaining Beliefs Over Time Throughout their history, Jews have been exiled and persecuted, yet they still maintain their beliefs today Judaism is considered a major world religion Judaism has contributed to Christianity and Islam
 Review 1) Belief in only one god is known as what? – – A B C D Polytheism Monotheism One god system Mesopotamia 2) People began revolting after Solomon’s death because… – – A B C D His building projects required high taxes and labor He was a terrible leader He gave away too much money He never asked anyone for help
Review 1) Belief in only one god is known as what? – – A B C D Polytheism Monotheism One god system Mesopotamia 2) People began revolting after Solomon’s death because… – – A B C D His building projects required high taxes and labor He was a terrible leader He gave away too much money He never asked anyone for help


