9ae5f5b8aa79e877487fcdaeb206a494.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Chapter 19 Weather Detection
Chapter 19 Weather Detection
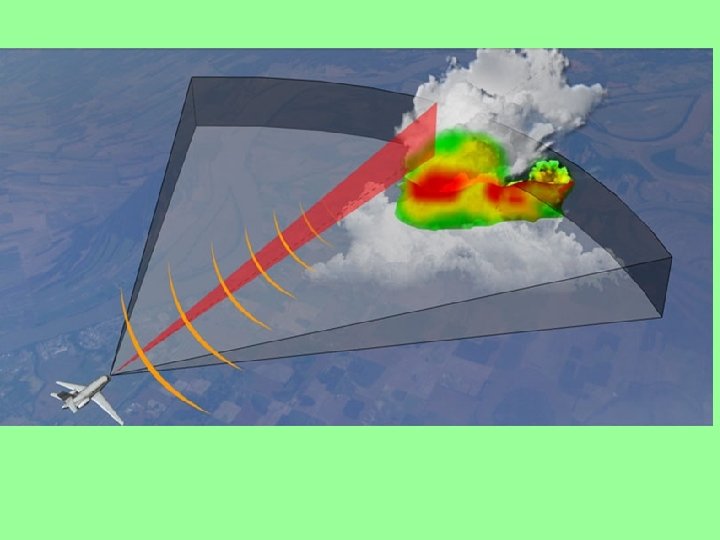
 Weather Radar Weather radar helps pilots avoid dangerous weather by creating a picture on the radar screen of storms and where they are most intense. Weather radar works by transmitting a pulse and that pulse hits rain droplets and reflects back. New weather radar displays are color which can also express intensity of the storm and rain moving horizontally which indicates turbulence. In the new “glass cockpits” weather radar is displayed on a multifunction display along with, for example a compass card.
Weather Radar Weather radar helps pilots avoid dangerous weather by creating a picture on the radar screen of storms and where they are most intense. Weather radar works by transmitting a pulse and that pulse hits rain droplets and reflects back. New weather radar displays are color which can also express intensity of the storm and rain moving horizontally which indicates turbulence. In the new “glass cockpits” weather radar is displayed on a multifunction display along with, for example a compass card.
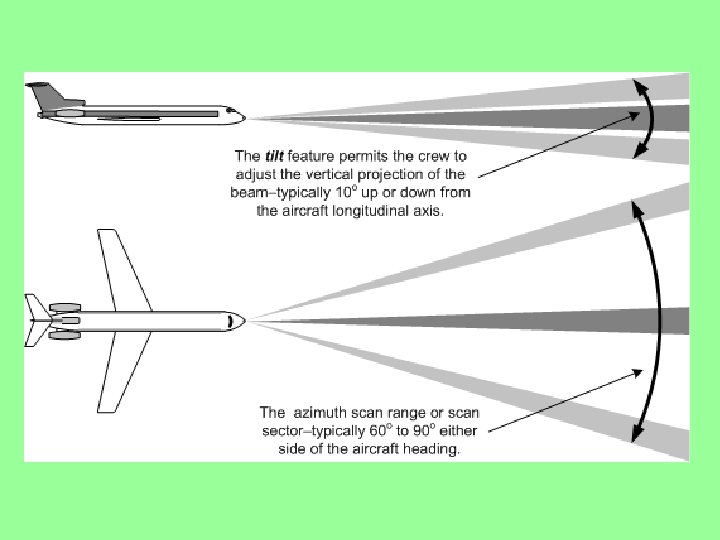
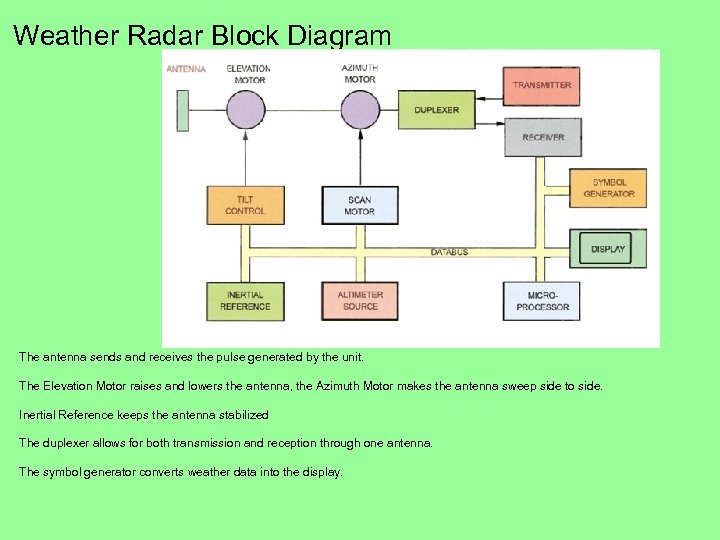 Weather Radar Block Diagram The antenna sends and receives the pulse generated by the unit. The Elevation Motor raises and lowers the antenna, the Azimuth Motor makes the antenna sweep side to side. Inertial Reference keeps the antenna stabilized The duplexer allows for both transmission and reception through one antenna. The symbol generator converts weather data into the display.
Weather Radar Block Diagram The antenna sends and receives the pulse generated by the unit. The Elevation Motor raises and lowers the antenna, the Azimuth Motor makes the antenna sweep side to side. Inertial Reference keeps the antenna stabilized The duplexer allows for both transmission and reception through one antenna. The symbol generator converts weather data into the display.
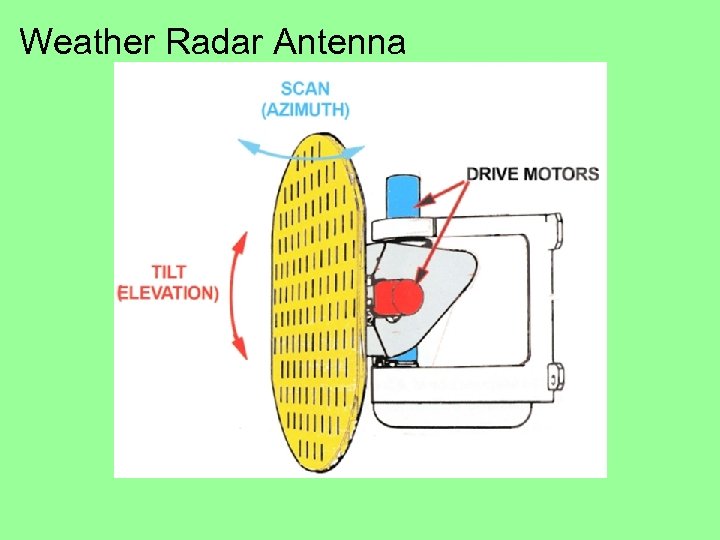 Weather Radar Antenna
Weather Radar Antenna
 Weather Radar Antenna
Weather Radar Antenna
 WX Radar Radome
WX Radar Radome
 WX Radar Radome
WX Radar Radome
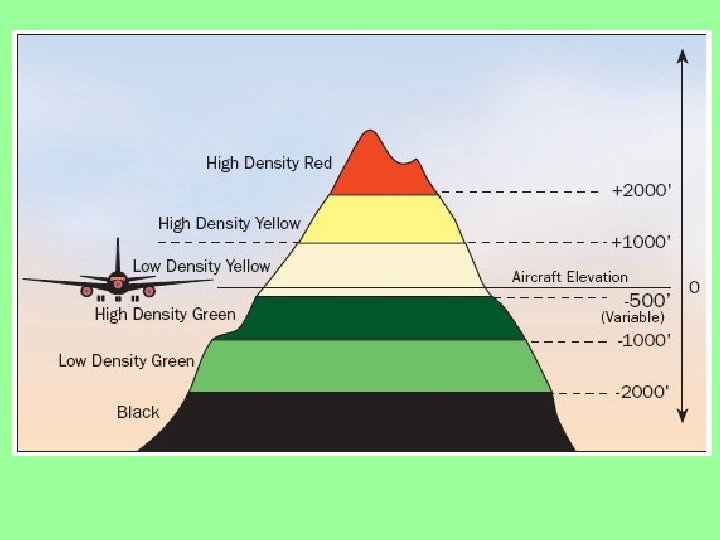
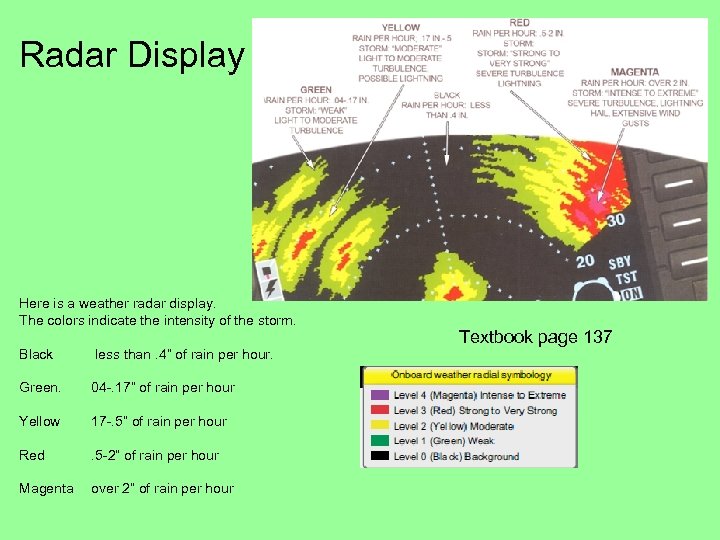 Radar Display Here is a weather radar display. The colors indicate the intensity of the storm. Black less than. 4” of rain per hour. Green. 04 -. 17” of rain per hour Yellow 17 -. 5” of rain per hour Red . 5 -2” of rain per hour Magenta over 2” of rain per hour Textbook page 137
Radar Display Here is a weather radar display. The colors indicate the intensity of the storm. Black less than. 4” of rain per hour. Green. 04 -. 17” of rain per hour Yellow 17 -. 5” of rain per hour Red . 5 -2” of rain per hour Magenta over 2” of rain per hour Textbook page 137
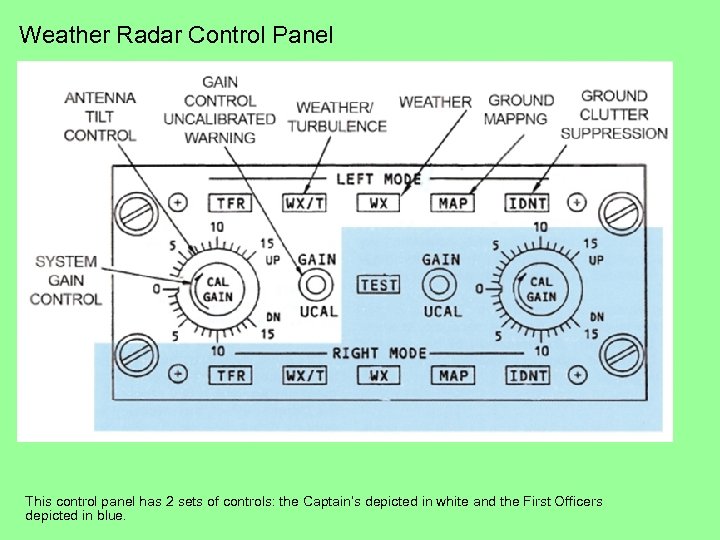 Weather Radar Control Panel This control panel has 2 sets of controls: the Captain’s depicted in white and the First Officers depicted in blue.
Weather Radar Control Panel This control panel has 2 sets of controls: the Captain’s depicted in white and the First Officers depicted in blue.
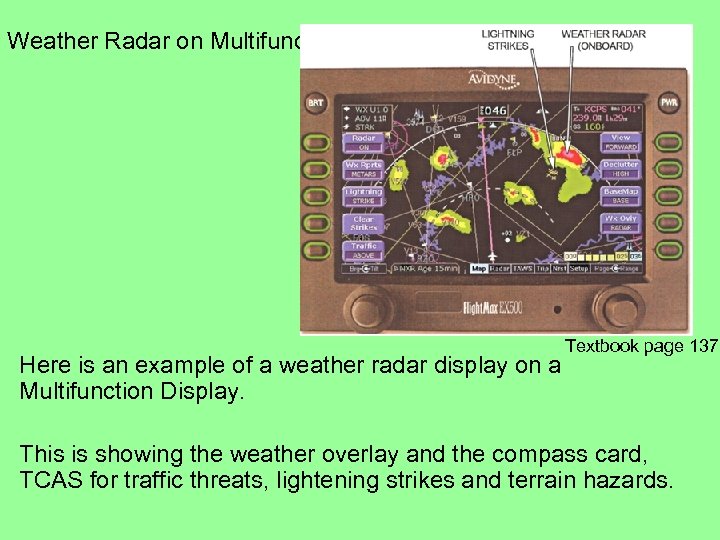 Weather Radar on Multifunction Display Here is an example of a weather radar display on a Multifunction Display. Textbook page 137 This is showing the weather overlay and the compass card, TCAS for traffic threats, lightening strikes and terrain hazards.
Weather Radar on Multifunction Display Here is an example of a weather radar display on a Multifunction Display. Textbook page 137 This is showing the weather overlay and the compass card, TCAS for traffic threats, lightening strikes and terrain hazards.
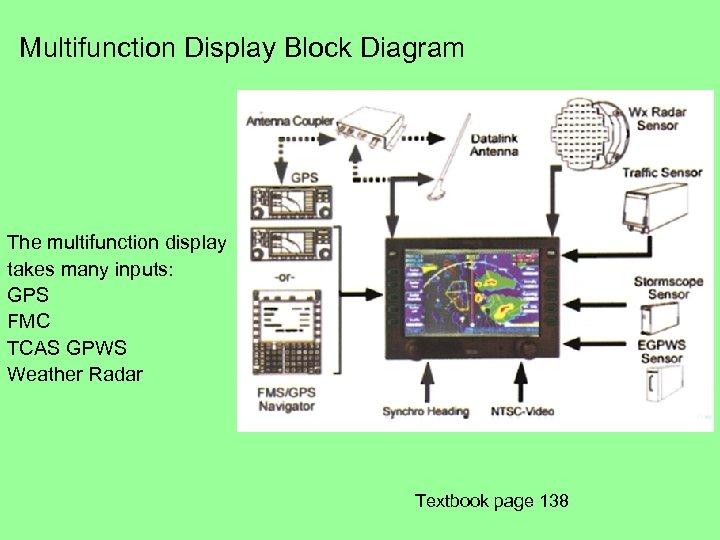 Multifunction Display Block Diagram The multifunction display takes many inputs: GPS FMC TCAS GPWS Weather Radar Textbook page 138
Multifunction Display Block Diagram The multifunction display takes many inputs: GPS FMC TCAS GPWS Weather Radar Textbook page 138



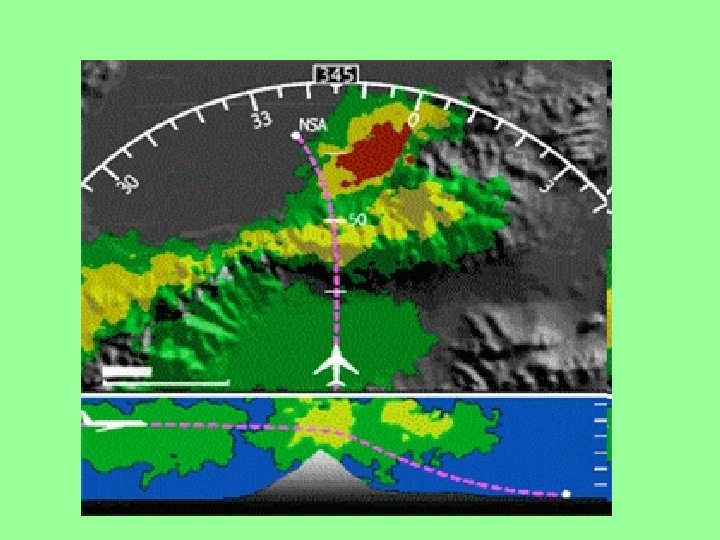
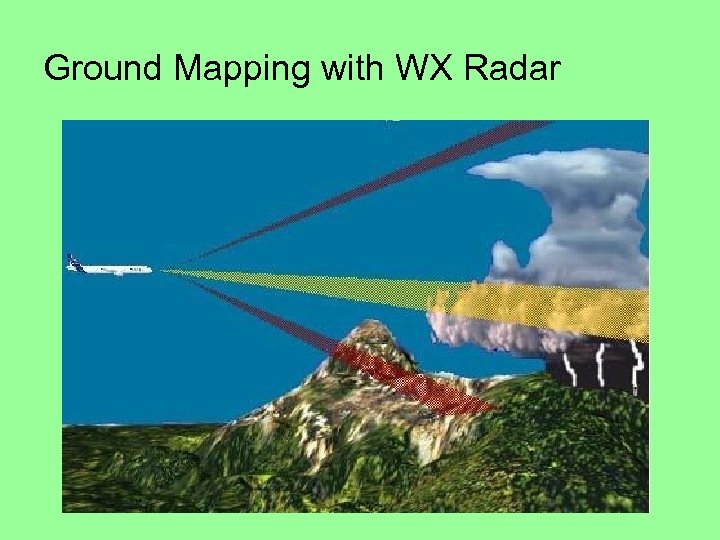 Ground Mapping with WX Radar
Ground Mapping with WX Radar

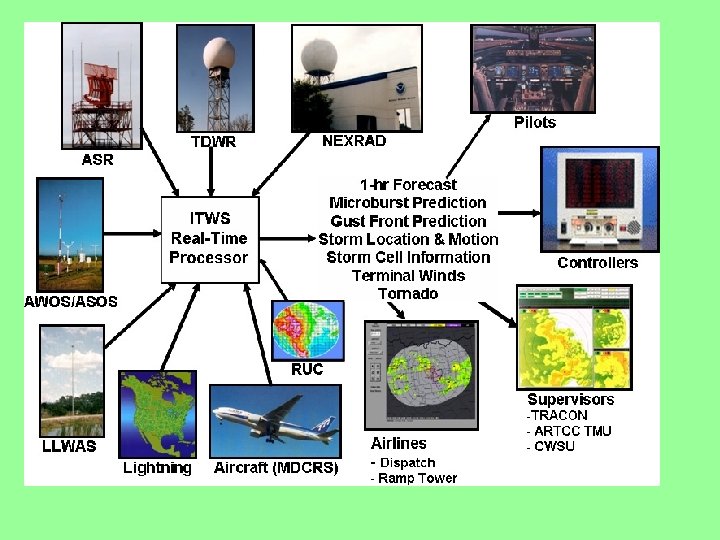
 DATALINK Datalink sends images and text via satellite from the National Weather Service. Nextrad, is a system of high-power ground radar stations that sweeps the sky for five minutes, mapping precipitation horizontally and sampling 14 different elevations up to 140 miles away. The horizontal sweep give a conventional weather radar view while the elevation sampling provides a storm profile.
DATALINK Datalink sends images and text via satellite from the National Weather Service. Nextrad, is a system of high-power ground radar stations that sweeps the sky for five minutes, mapping precipitation horizontally and sampling 14 different elevations up to 140 miles away. The horizontal sweep give a conventional weather radar view while the elevation sampling provides a storm profile.
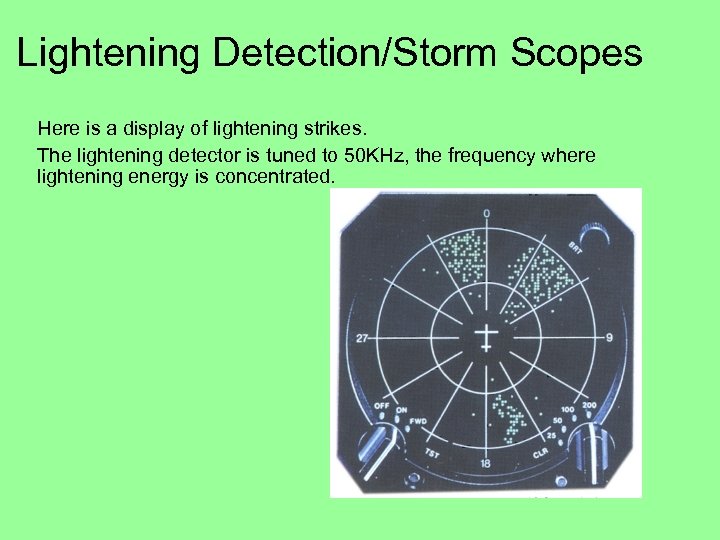 Lightening Detection/Storm Scopes Here is a display of lightening strikes. The lightening detector is tuned to 50 KHz, the frequency where lightening energy is concentrated.
Lightening Detection/Storm Scopes Here is a display of lightening strikes. The lightening detector is tuned to 50 KHz, the frequency where lightening energy is concentrated.
 Windshear
Windshear
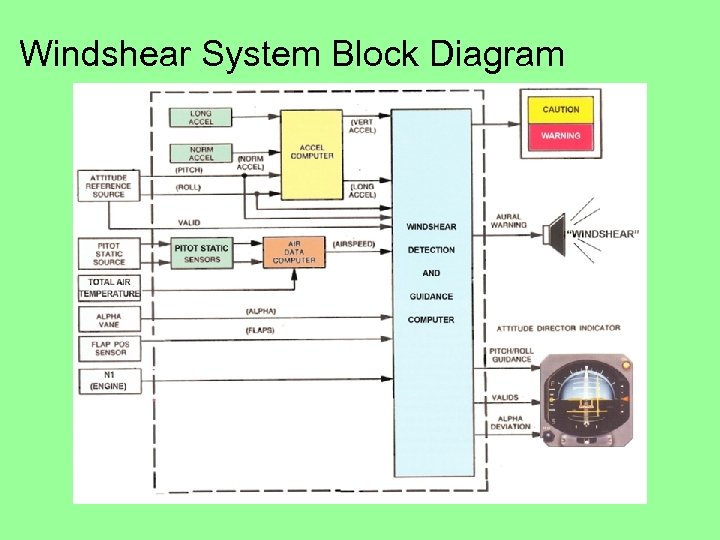 Windshear System Block Diagram
Windshear System Block Diagram
 AWOS Automated Weather Observing System ASOS Automated Surface Observing System http: //www. coastalenvironmental. com/awos. shtml#
AWOS Automated Weather Observing System ASOS Automated Surface Observing System http: //www. coastalenvironmental. com/awos. shtml#


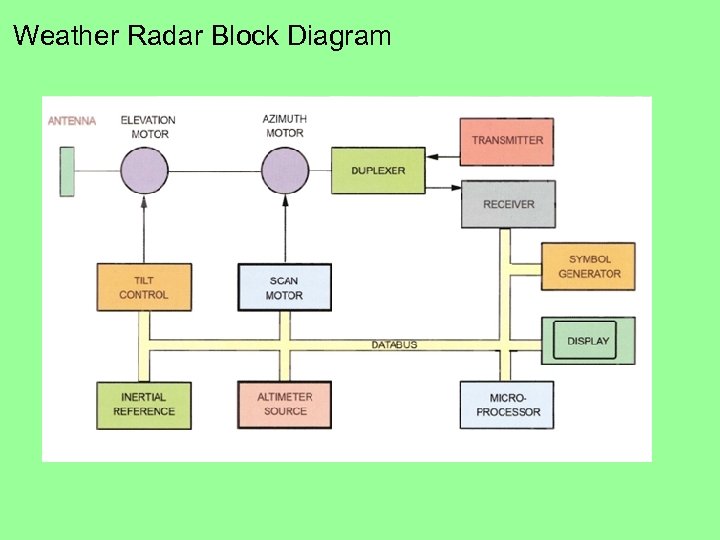 Weather Radar Block Diagram
Weather Radar Block Diagram
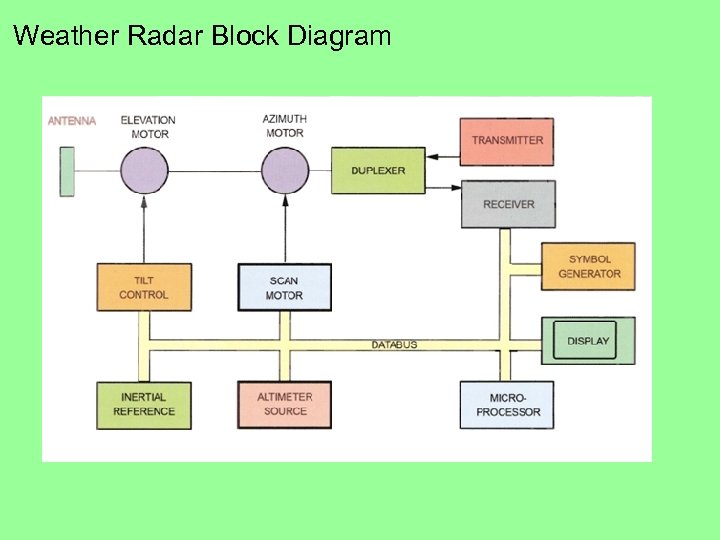 Weather Radar Block Diagram
Weather Radar Block Diagram
 Review Q&A Chapter 19 Weather Detection 19. 1 What is the greatest threat of a thunderstorm to an aircraft? Answer: Turbulence 19. 2 On a weather radar display, what color indicates maximum hazard to aircraft? Answer: Magenta 19. 3 Weather radar detects storms by transmitting ____ of radio energy and measuring their echoes from water droplets. Answer: Pulses 19. 4 Detecting turbulence in a storm is done by measuring echoes from the ____movement of water droplets. Answer: Horizontal. 19. 5 What is the normal use of the tilt control? Answer: Ground Mapping. 19. 6 What raises and lowers the radar antenna in a vertical direction for tilt control? Answer: Elevation Motor 19. 7 What causes the radar antenna to scan left and right (horizontal motion)? Answer: Azimuth Motor 19. 8 How is the radar antenna stabilized as the airplane maneuvers through pitch and roll? Answer: Inertial Reference. 19. 9 What is a typical frequency for an airborne weather radar? Answer: 9, 333. 8 MHz 19. 10 Lightening detection systems are usually tuned to a frequency of ____. Answer: 50 KHz 19. 11 What is the most recent method for delivering weather images to the cockpit? Answer: Datalink. 19. 12 What is the purpose of a radome? Answer: To provide an aerodynamic cover for the antenna. 19. 13 Radomes must reduce radar power by no more than ____. Answer: 10%. 19. 14 Wind shear is a sudden change in wind ___ and is most dangerous near the ____. Answer: Direction, Ground 19. 15 A dangerous form of windshear, which occurs over a small area, is known as a ____. Answer: Microburst 1916 Windshear detection systems warn the pilot and also provide____. Answer: Guidance
Review Q&A Chapter 19 Weather Detection 19. 1 What is the greatest threat of a thunderstorm to an aircraft? Answer: Turbulence 19. 2 On a weather radar display, what color indicates maximum hazard to aircraft? Answer: Magenta 19. 3 Weather radar detects storms by transmitting ____ of radio energy and measuring their echoes from water droplets. Answer: Pulses 19. 4 Detecting turbulence in a storm is done by measuring echoes from the ____movement of water droplets. Answer: Horizontal. 19. 5 What is the normal use of the tilt control? Answer: Ground Mapping. 19. 6 What raises and lowers the radar antenna in a vertical direction for tilt control? Answer: Elevation Motor 19. 7 What causes the radar antenna to scan left and right (horizontal motion)? Answer: Azimuth Motor 19. 8 How is the radar antenna stabilized as the airplane maneuvers through pitch and roll? Answer: Inertial Reference. 19. 9 What is a typical frequency for an airborne weather radar? Answer: 9, 333. 8 MHz 19. 10 Lightening detection systems are usually tuned to a frequency of ____. Answer: 50 KHz 19. 11 What is the most recent method for delivering weather images to the cockpit? Answer: Datalink. 19. 12 What is the purpose of a radome? Answer: To provide an aerodynamic cover for the antenna. 19. 13 Radomes must reduce radar power by no more than ____. Answer: 10%. 19. 14 Wind shear is a sudden change in wind ___ and is most dangerous near the ____. Answer: Direction, Ground 19. 15 A dangerous form of windshear, which occurs over a small area, is known as a ____. Answer: Microburst 1916 Windshear detection systems warn the pilot and also provide____. Answer: Guidance


