2fd937290504691577fab48addbb62fd.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

Chapter 19 TOWARD AN URBAN SOCIETY, 1877– 1900 America Past and Present

The Lure of the City u City becomes a symbol of the new America between 1870– 1900 u Explosive urban growth – Sources included immigration, movement from countryside – Six cities over 500 k by 1900 u Three: NYC, Chicago, & Philadelphia had >1 M p. 540

Skyscrapers & Suburbs u Steel permits construction of skyscrapers – Made possible by the Bessemer process – Louis H. Sullivan, architect who studied at MIT & in Paris, invented the skyscrapper u Streetcars allow growth of suburbs u Streetcar cities allow more fragmented and stratified city – Middle-class residential rings surrounding business & working-class core p. 540 -541

Tenements and the Problems of Overcrowding u Tenements house working class u James Ware and dumbbell design u Tenement problems – Overcrowding – Inadequate sanitation – Poor ventilation – Polluted water u Urban – – problems Poor public health Juvenile crime p. 541 -543

Strangers in a New Land u 1890: 15% of U. S. population was foreign- born u Most immigrants moved for economic reasons & entered through Ellis Island (next slide) – Cong sought to keep immigration under control (i. e. , keep out undesirables) u By 1900, most urban dwellers foreign-born or children of immigrants u 1880 s: Eastern, southern European immigrants prompt resurgent Nativism u Nativist organizations try to limit immigration p. 543 -547

Ellis Island p. 544 -545
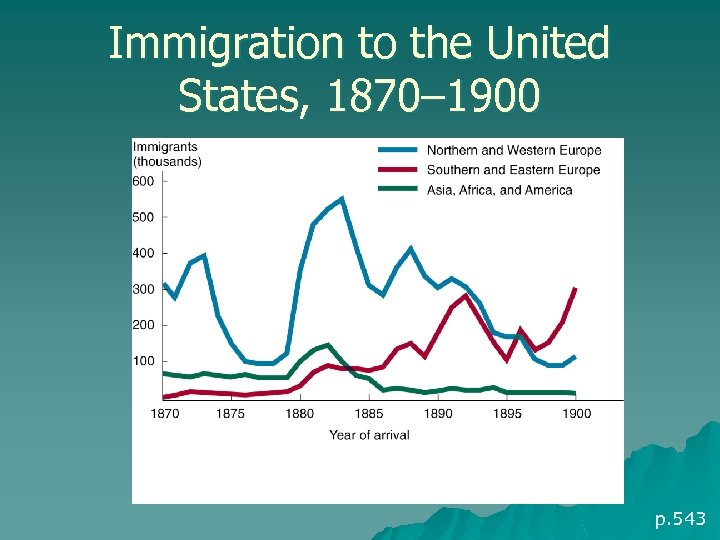
Immigration to the United States, 1870– 1900 p. 543
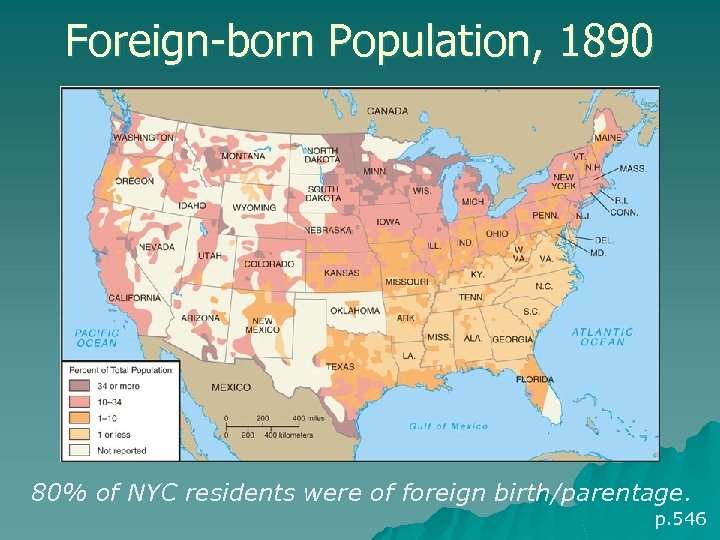
Foreign-born Population, 1890 80% of NYC residents were of foreign birth/parentage. p. 546

Immigrants and the City: Families and Ethnic Identity u Immigrants marry within own ethnic groups & have more children than native-born Americans u Immigrant associations – – u Preserve old country language & customs, aid adjustment Irish Benevolent Society, “We visit our sick & bury our dead” Deutsch-Amerikanischer Nationalbund, 2 M members in several cities Polish National Alliance As new immigrants entered American society they clung to the customs of their native countries p. 547 -548

The House That Tweed Built u Urban party machines headed by “bosses” Most famous of the urban political bosses in the late 19 th century was William Tweed of NYC – Most trade services for votes – Why bosses stayed in power – Good organizational skill – Helped immigrants – u Most bosses improve conditions u Role of bosses can be over emphasized p. 548 -550

Social & Cultural Change 1877 – 1900 u End of Reconstruction marks shift of attention to new concerns u Population growth – 1877: 47 million – 1900: 76 million & more diverse u Urbanization, industrialization changing all aspects of American life p. 550 -551
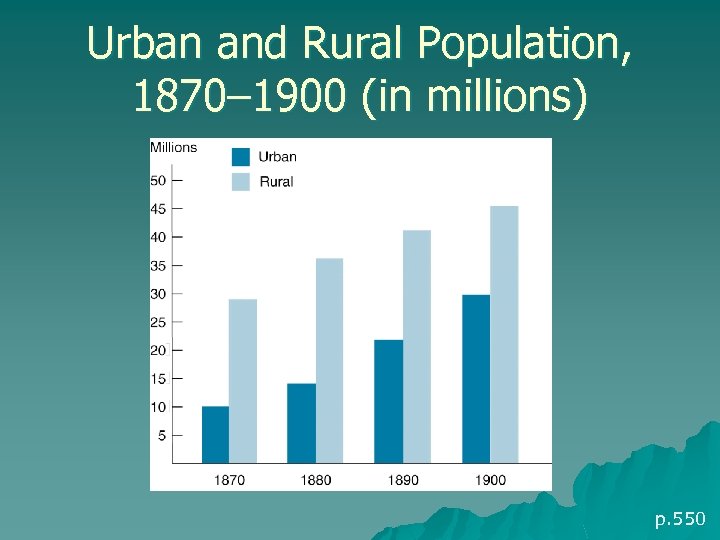
Urban and Rural Population, 1870– 1900 (in millions) p. 550

Manners & Mores u Victorian morality prescribed strict standards of dress, manners, & sexual behavior – Children were to be seen but not heard – Older children were often chaperoned u Religious values strong – 80% were church attending Protestants – Most of the rest were Roman Catholic u With slavery abolished, reformers turned to to new issues – Women’s Christian Temperance Union u Frances E. Willard p. 551 -552

Leisure & Entertainment u Domestic leisure: card, parlor, yard games u Sentimental ballads, ragtime popular u Entertainment outside home – – Circus immensely popular Street lights, streetcars make evening a time for entertainment and pleasure u Most popular spectator sport was baseball – Increase in spectator sports indicated the increased amount of leisure time p. 552 -553
Changes in Family Life u Urbanization, industrialization alter family u Family life virtually disappears among poorly paid working class u Suburban commute takes fathers from middle-class homes u Domesticity encouraged, women housebound, child-oriented consumers u White middle-class birth rates decline – 1800 = 7, 1880 = 4, 1900 = 3 p. 554

Changing Views: A Growing Assertiveness among Women u "New women”: Self-supporting careers u Demand an end to gender discrimination u 1890: Many states were beginning to allow women to control their earnings & inherit property u Speak openly about once-forbidden topics – New interest in psychology & medicine made it “possible” to discuss sexual issues, childbirth which were formerly held as “taboo” p. 554 -555

Educating the Masses u Trend is toward universal education: By 1900, 31 states & territories had compulsory education u Purpose of public education was to train people for life & work in industrial society u Teaching unimaginative, learning passive, Webster’s Spellers and Mc. Guffey’s Readers Wm H. Mc. Guffey (since 1836) u 1896: Plessy v. Ferguson allows "separate p. 555 -557 but equal" schools
Higher Education u Nearly 150 colleges & universities founded between 1880 & 1900 – Many by govt grants – Some by private philanthropy u Leland Stanford = Stanford U in California ~ $24 M u J. D. Rockefeller = U of Chicago ~ $34 M u Greater emphasis on professions & research & away from training ministers – 1876: Johns Hopkins University: First separate graduate school u Increasing # of women admitted to college p. 557 -558

Higher Education: African Americans usually confined to all black institutions u Booker T. Washington ~ Tuskegee Institute – Concentrated on practical/trades education u W. E. B. Du Bois ~ Had attended Harvard – Advocated professional degrees in medicine, dentistry, & law – Believed educational advancement was the key to success p. 558 -559

The Stirrings of Reform u Social Darwinists see attempts at social reform as useless & harmful – Things are the way they are ~ Just wait for evolution – The laws of nature apply to sociology – Herbert Spencer, “Survival of the fittest” u Reformers begin to seek changes in U. S. living, working conditions p. 560

New Currents in Social Thought Clarence Darrow rejected Social Darwinism, argued poverty at crime’s root ~ 40 yr career ~ Lawyer u Richard T. Ely’s “Younger Economics” urged govt intervention in economic affairs u Thorstein Veblen’s Theory of the Leisure Class asserted that classic economic “laws” were masks for human greed u Liberal Protestants preach "Social Gospel" u – – Purpose: Reform industrial society Means: Introduce Christian standards into the economic sphere p. 560 -561

The Settlement Houses u Famous – – Houses 1886: Stanton Coit’s Neighborhood Guild, New York 1889: Jane Addams' Hull House, Chicago 1892: Robert A. Woods’ South End House, Boston 1893: Lillian Wald’s Henry Street Settlement, New York u Characteristics – – – Many workers women Classical, practical education for poor Study social composition of neighborhood p. 562 -563

A Crisis in Social Welfare u Depression of 1893 reveals insufficiency of private charity u New professionalism in social work u New efforts to understand poverty’s sources u Increasing calls for government intervention u Social tensions engender sense of crisis p. 564 -565

The Pluralistic Society u Immigration & urban growth reshaped American politics & culture u By 1920, most Americans lived in cities & almost half of them were descendants of people who arrived after the Revolution u Society experienced a crisis between 1870 & 1900 u Reformers turned to state & federal government for remedies to social ills p. 564

Chapter 19 TOWARD AN URBAN SOCIETY, 1877– 1900 America Past and Present End
2fd937290504691577fab48addbb62fd.ppt